If I Go Into Hospital What Happens About My Medication
It is vital to get the right medication at the right time every time, not just at the set times scheduled for hospital medication rounds, in order for your symptoms to continue to be well managed and to speed up recovery. If admission is as an emergency, this can be more difficult as staff may not have a clear picture of your needs and may be very busy, so it is a good idea to discuss this scenario with those close to you so that they can liaise with staff on your behalf.
For any admission it is essential that staff have clear notes regarding your medication. A medication diary can be very helpful with this, specifying:
- dosage and timing of each medication you have to take, including complementary, trial, non-Parkinsons medications and over the counter medications
- clear instructions on how each medication should be taken, e.g. with food, with water, avoiding protein etc.
Some hospitals will allow you to self-medicate but this is not always the case.
Make sure that you take plenty of each medication with you into hospital as they might not have ready supplies, and ensure that the dosage on the label is what you have indicated on any medications list you provide. If not, staff can sometimes only be authorised to dispense what is written on the label, which could be incorrect.
What If I Forget To Take It
If you forget to take a tablet, take it as soon as you remember, unless it’s nearly time for your next dose. In this case, leave out the missed dose and take your next dose as usual.
Never take 2 doses at the same time. Never take an extra dose to make up for a forgotten dose.
If you often forget doses, it may help to set an alarm to remind you. You could also ask a pharmacist for other ways to help you remember to take your medicine.
What Is Levodopa + Carbidopa
Levodopa + carbidopa in combination is used to treat the symptoms of Parkinson’s disease, or Parkinson-like symptoms such as tremor, shakiness, stiffness, and difficulty moving. Levodopa changes into dopamine, a chemical in the brain that helps control movement. Carbidopa prevents levodopa changing to dopamine in the bloodstream. This means that more levodopa can enter the brain, and it helps to lessen some of the side effects such as nausea and vomiting . Levodopa becomes less effective over time. This is because it treats the symptoms of Parkinson’s but cannot stop the dopamine-producing cells from being lost. This means that as they are lost you will continue to get symptoms and need more frequent doses over time. Your brain cant become resistant to levodopa. People with Parkinsons will benefit from medications containing levodopa throughout their lifetime.
Don’t Miss: Michael J Fox Living With Parkinson’s
Dosage For Parkinsons Disease And Parkinsonism
Sinemet is approved to treat Parkinsons disease and certain cases of parkinsonism, which is a condition thats similar to PD.
For these uses, the recommended starting dosage of Sinemet is typically one tablet of 25 mg carbidopa / 100 mg levodopa, taken three times per day.
In some cases, your doctor may have you start taking one tablet of 10 mg carbidopa / 100 mg levodopa, three to four times per day. But this dose may not contain enough carbidopa to reduce your symptoms.
If your starting dosage of Sinemet doesnt reduce your symptoms, your doctor may have you add a tablet to one or more of your doses. For example, your doctor may recommend that you add a 25 mg carbidopa / 100 mg levodopa tablet or a 10 mg carbidopa / 100 mg levodopa tablet, either every day or every other day.
The maximum recommended daily dose of Sinemet is eight tablets of either:
- Sinemet 10 mg/ 100 mg, or
- Sinemet 25 mg / 100 mg
Regular dosing interval
Sinemet should be taken at a regular dosing interval. A dosing interval is how often you should take a medication so that its most effective. Your dosing interval depends on how many times per day youre taking the drug. Spacing out your doses with an even dosing interval helps keep the amount of Sinemet in your body consistent over time. This consistency can help reduce your symptoms.
Dosage when switching from levodopa
You May Like: Signs Of Early Onset Parkinsons
How Can I Remember To Take My Parkinsons Medication On Time
There are lots of things you can do to help you get your medication on time.
For example, you could:
-
set an alarm on your phone or smart watch
-
get a family member to call you at the right time or arrange care visits around when you need to take your medication
-
use a pill box with sections for each day and time. You pharmacist can advise on the different ones available and we also sell them on the Parkinsons UK shop
Talk to your Parkinsons nurse if you are struggling to remember to take your medication. They can work with you to reschedule your treatment regime so that it fits around you.
Also Check: Can Stem Cells Help Parkinson’s Disease
What Form Does This Medication Come In
100 mg/10 mg Each blue, oval tablet, with one side scored and engraved “100 10” on one side and engraved “APO” on the other, contains levodopa 100 mg and carbidopa 10 mg. Nonmedicinal ingredients: FD& C Blue No. 1 Aluminum Lake, croscarmellose sodium, FD& C Blue No. 2 Aluminum Lake, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, and sorbitol.
100 mg/25 mg Each yellow, oval tablet, with one side scored and engraved “100 25” on one side and engraved “APO” on the other, contains levodopa 100 mg and carbidopa 25 mg. Nonmedicinal ingredients: croscarmellose sodium, D& C Yellow No. 10 Aluminum Lake, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, and sorbitol.
250 mg/25 mg Each blue, oval tablet, with one side scored and engraved “250 25” on one side and engraved “APO” on the other, contains levodopa 250 mg and carbidopa 25 mg. Nonmedicinal ingredients: FD& C Blue No. 1 Aluminum Lake, croscarmellose sodium, FD& C Blue No. 2 Aluminum Lake, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, and sorbitol.
What Other Drugs Could Interact With This Medication
There may be an interaction between levodopa – carbidopa and any of the following:
- aldesleukin
- alpha-blockers
- angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors
- angiotensin receptor blockers
- antipsychotics
- apomorphine
- beta-adrenergic blockers
- bortezomib
- calcium channel blockers
- clofarabine
- diuretics
- duloxetine
- iron salts
- isoniazid
- MAO inhibitors
- methylphenidate
- multivitamins with minerals
- nabilone
- nitrates
- obinutuzumab
- phosphodiesterase 5 inhibitors
- pyridoxine
- tretinoin
- tricyclic antidepressants
If you are taking any of these medications, speak with your doctor or pharmacist. Depending on your specific circumstances, your doctor may want you to:
- stop taking one of the medications,
- change one of the medications to another,
- change how you are taking one or both of the medications, or
- leave everything as is.
An interaction between two medications does not always mean that you must stop taking one of them. Speak to your doctor about how any drug interactions are being managed or should be managed.
Medications other than those listed above may interact with this medication. Tell your doctor or prescriber about all prescription, over-the-counter , and herbal medications you are taking. Also tell them about any supplements you take. Since caffeine, alcohol, the nicotine from cigarettes, or street drugs can affect the action of many medications, you should let your prescriber know if you use them.
You May Like: Ten Steps To Identify Atypical Parkinsonism
How Should This Medicine Be Used
The combination of levodopa and carbidopa comes as a regular tablet, an orally disintegrating tablet, an extended-release tablet, and an extended-release capsule to take by mouth. The combination of levodopa and carbidopa also comes as a suspension to be given into your stomach through a PEG-J tube or sometimes through a naso-jejunal tube using a special infusion pump. The regular and orally disintegrating tablets are usually taken three or four times a day. The extended-release tablet is usually taken two to four times a day. The extended-release capsule is usually taken three to five times a day. The suspension is usually given as a morning dose and then as a continuous dose , with extra doses given no more than once every 2 hours as needed to control your symptoms. Take levodopa and carbidopa at around the same times every day. Follow the directions on your prescription label carefully, and ask your doctor or pharmacist to explain any part you do not understand. Take levodopa and carbidopa exactly as directed. Do not take more or less of it or take it more often than prescribed by your doctor.
Swallow the extended-release tablets whole do not chew or crush them.
To take the orally disintegrating tablet, remove the tablet from the bottle using dry hands and immediately place it in your mouth. The tablet will quickly dissolve and can be swallowed with saliva. No water is needed to swallow disintegrating tablets.
Discontinuation Of Amantadine Therapy Dosing:
If amantadine treatment is to be discontinued the dose reduction should be done at a slow taper. Gocovri: when discontinuing Gocovri the dose should be reduced by half for the last week of therapy.
Osmolex ER: when discontinuing Osmolex ER the dose should gradually be reduced down from a higher dose to 129mg daily. You should remain on 129 mg daily for 1 to 2 weeks before stopping Osmolex ER.
Also Check: Does Weed Help With Parkinsons
You May Like: When To Start Medication For Parkinson’s
Assessing The Importance Of A Missed Dose
The severity of the patient’s condition, whether clinically significant breakthrough effects are likely to be observed, and the characteristics of the medication should be considered when deciding the most appropriate strategy following a missed dose. Vulnerable patients are easily recognisable in any practice and include those on medications of low therapeutic index,bor suffering from conditions which require constant maintenance of therapeutic concentrations . On the other hand, for most people with hypertension or hypercholesterolaemia a single missed dose will be of little consequence.
The patients should be informed at the time of prescribing and dispensing, of strategies to minimise missed doses and to redeem the situation when a dose is missed. Highlighting the strategy as it appears on the CMI or writing out an action plan as a reminder to the patient may prove very useful.
While a pre-emptive approach is ideal it is recognised that requests for information about missed doses are common. Knowledge of a drug’s half-life, a major determinant of the fluctuation in interdose concentrations at steady state, is useful for making recommendations on what to do if a dose is missed. Upon cessation of therapy, it takes four to five half-lives for the drug to be completely eliminated.
Changes In Sleeping Patterns
As Parkinsons progresses, you can also develop problems with sleep patterns. These may not happen in the early stages, but can be noticeable later. You might wake up often in the middle of the night or sleep more during the day than you do at night.
Another common sleep disturbance for people with Parkinsons is rapid eye movement sleep behavior disorder. This is when you start acting out your dreams in your sleep, such as verbally and physically, which can get uncomfortable if someone is sharing your bed. Dr. Rundle-Gonzalez says many times a bed partner will be the one to notice sleep problems.
REM sleep behavior disorder can also happen in people who dont have Parkinsons. However, if this isnt something youve dealt with before, its likely related to your disease. There are medications your doctor can prescribe to help you sleep comfortably through the night.
Don’t Miss: Keto Diet And Parkinson’s
How Should I Take Rytary
Take Rytary exactly as prescribed by your doctor. Follow all directions on your prescription label and read all medication guides or instruction sheets. Your doctor may occasionally change your dose.
If you already take levodopa, you must stop taking it at least 12 hours before you start taking Rytary.
Rytary can be taken with or without food. Take your doses at regular intervals to keep a steady amount of the drug in your body at all times.
Swallow the capsule whole and do not crush, chew, break, or open it.
It may take up to several weeks of using Rytary before your symptoms improve. For best results, keep using the medication as directed. Talk with your doctor if your symptoms do not improve after a few weeks of treatment. Also tell your doctor if the effects of this medication seem to wear off quickly in between doses.
If you use Rytary long-term, you may need frequent medical tests.
This medicine can affect the results of certain medical tests. Tell any doctor who treats you that you are using Rytary.
Do not stop using Rytary suddenly, or you could have unpleasant withdrawal symptoms. Ask your doctor how to safely stop using this medicine.
Store at room temperature away from moisture, heat, and light.
Are There Clinical Trials For Parkinsons

A clinical trial is a research program done with patients to evaluate a new medical treatment, drug, or device. The goal is to find new and improved ways to treat diseases and conditions.
During a clinical trial, doctors use the best available treatment as a standard to evaluate new treatments. The new treatments are hoped to be at least as effective as — or possibly more effective than — the standard.
New treatment options are first carefully researched in the laboratory — in the test tube and in animals. Treatments most likely to work are further evaluated in a small group of humans. Then, they may be moved to a larger clinical trial.
When a new medical treatment is studied for the first time in humans, scientists don’t know exactly how itâll work. Any new treatment has possible risks and benefits. Clinical trials help doctors find out:
- If the treatment is safe and effective
- If the treatment could be better than treatments currently available
- The side effects of the treatment
- Possible risks of the treatment
Some advantages of taking part in a clinical trial are:
Some disadvantages of participating in a clinical trial are:
If you take part in a clinical trial, you may notice some changes in your care:
If you think you might want to take part in a clinical trial, find out as much as possible about the study before you decide. You can ask:
For information about ongoing Parkinson’s disease studies, contact the National Institutes of Health.
Read Also: First Line Treatment For Parkinson’s
How To Take Rasagiline
- Before you start this treatment, read the manufacturer’s printed information leaflet from inside your pack. The leaflet will give you more information about rasagiline and a full list of side-effects which you may experience from taking it.
- Take rasagiline tablets exactly as your doctor has told you. Take one tablet a day. Try to take the tablets at the same time of day each day, as this will help you to remember to take them.
- You can take the tablets before or after meals.
- If you forget to take a dose, take it as soon as you remember. If you do not remember until the following day, skip the missed dose. Do not take two doses together to make up for a forgotten dose.
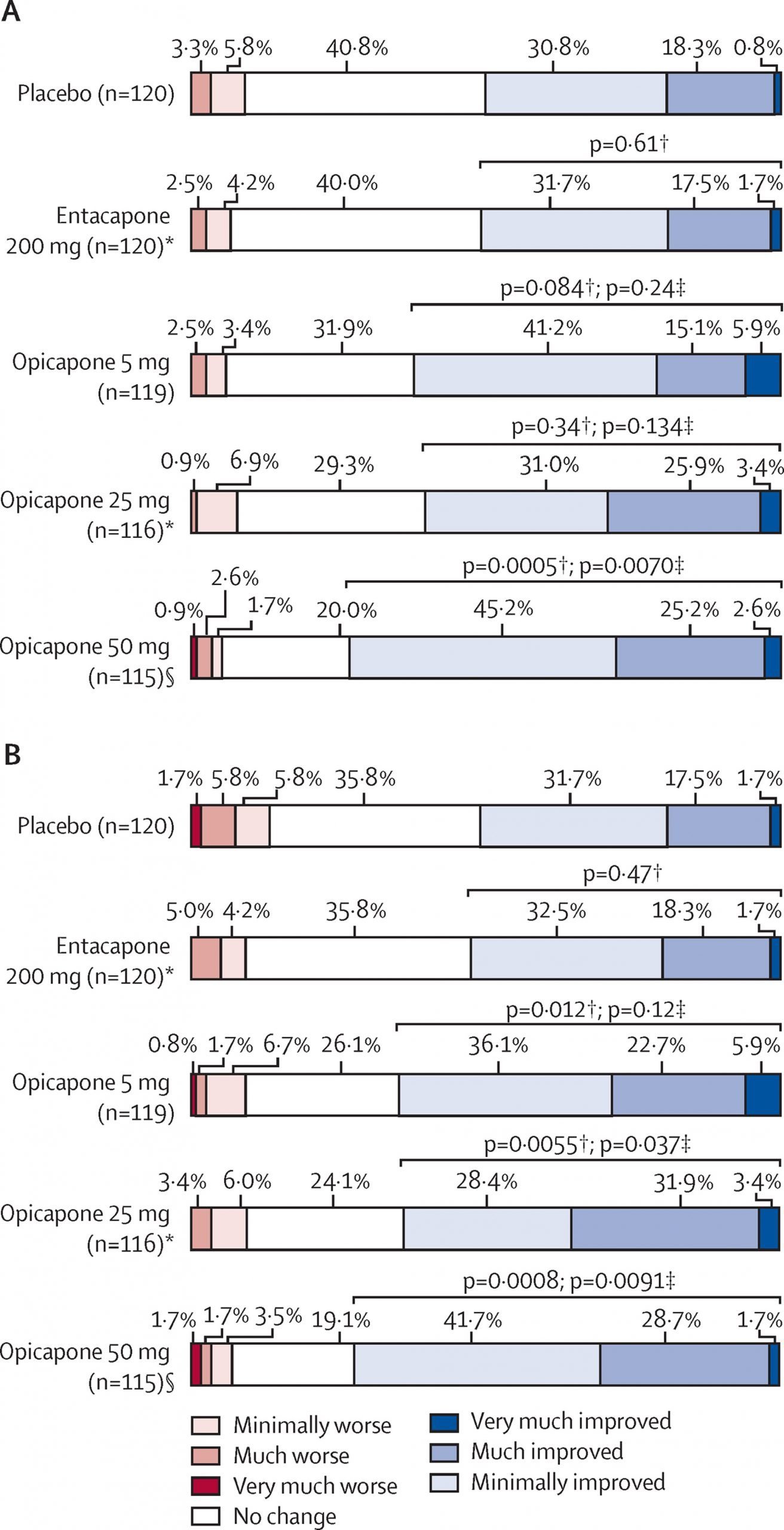
Advantages Of Comt Inhibitors
When used with levodopa, COMT inhibitors can reduce the daily off time and increase the on time.
In many cases, the dose and frequency of levodopa can also be reduced.
The terms on/off or motor fluctuations refer to the period when people can no longer rely on the smooth and even symptom control that their drugs once gave them.
Dont Miss: Can Medication Cause Parkinsons
Also Check: Parkinson’s Disease Dementia Prognosis
Alternative Treatments For Parkinson’s Disease
Alternative therapy may also be used to treat Parkinson’s disease. The most touted in recent years has been the effect of Vitamin E on reversing the progression of the disease although, this effect is still being debated by the scientific community.
Relaxation and guided imagery have also been suggested to help with stress, depression, and anxiety. Medical studies have shown that relaxation and guided imagery may help slow the progression of symptoms as well as quicken healing time after surgeries or injuries.
Show Sources
What Side Effects Are Possible With This Medication
Many medications can cause side effects. A side effect is an unwanted response to a medication when it is taken in normal doses. Side effects can be mild or severe, temporary or permanent.
The side effects listed below are not experienced by everyone who takes this medication. If you are concerned about side effects, discuss the risks and benefits of this medication with your doctor.
The following side effects have been reported by at least 1% of people taking this medication. Many of these side effects can be managed, and some may go away on their own over time.
Contact your doctor if you experience these side effects and they are severe or bothersome. Your pharmacist may be able to advise you on managing side effects.
- burning sensation on the tongue
- change in colour of urine, saliva, or sweat
- changed sense of taste
- mood or mental changes
- patches of discolouration on the skin
- signs of bleeding in the stomach
- signs of depression
- signs of infection
- skin changes
- spasms that move the eye into a fixed position
- sudden onset of sleep
- symptoms of a urinary tract infection
- unusual and uncontrolled movements of the body, including face, tongue, arms, hands, head, and upper body
Stop taking the medication and seek immediate medical attention if any of the following occur:
- long-lasting and painful erection
- seizures
- signs of neuroleptic malignant syndrome
- signs of a heart attack
- signs of a serious allergic reaction
- thoughts of self harm or suicide
Read Also: Foot Pain And Parkinson’s
What Are The Most Common Medicines Used To Treat Pd
Sinemet®
Levodopa is the most commonly prescribed and most effective medicine for controlling the symptoms of PD, particularly bradykinesia and rigidity.
Levodopa is a chemical found naturally in our brains. When given as a medicine, it is transported to the nerve cells in the brain that produce dopamine. It is then converted into dopamine for the nerve cells to use as a neurotransmitter.
Sinemet is made up of levodopa and another drug called carbidopa. Levodopa enters the brain and is converted to dopamine while carbidopa prevents or lessens many of the side effects of levodopa, such as nausea, vomiting, and occasional heart rhythm disturbances. It is generally recommended that patients take Sinemet on an empty stomach, at least ½ hour before or one hour after meals.
There are two forms of Sinemet: controlled-release or immediate-release Sinemet. Controlled-release Sinemet and immediate-release Sinemet are equally effective in treating the symptoms of PD, but some people prefer the controlled release version. Ask your doctor which approach is best for you.
Dopamine agonists
Dopamine agonists are medicines that activate the dopamine receptor. They mimic or copy the function of dopamine in the brain.
Parlodel®, Requip®, and Mirapex® are all dopamine agonists. These medicines might be taken alone or in combination with Sinemet. Generally, dopamine agonists are prescribed first and levodopa is added if the patient’s symptoms cannot be controlled sufficiently.
Symmetrel®