So What’s The Difference Between Als And Parkinson’s Disease
Clockwise from top left: Robin Williams had been diagnosed with Parkinsons before his death Stephen Hawking has been living with ALS for 50 years Lou Gehrig brought ALS, now also know as Lou Gehrigs disease, to the publics attention and Michael J. Fox received his Parkinsons diagnosis in 1992.
News that Robin Williams had been grappling with a diagnosis of Parkinsons disease before ending his life has sparked increased interest in the disorder this week. And thats coincided with a fast-rising awareness of a similar disease amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, or ALS due to the Ice Bucket Challenge, a fundraising campaign thats swept social media recently, prompting everyone from Ethel Kennedy to Justin Timberlake to dump freezing water over their heads in the name of research. So how closely linked to Parkinsons is ALS? Both are progressive neurodegenerative diseases, and neither has a cure. But beyond that, the differences are vast.
Both occur because some cells in the brain degenerate, and both are diseases of the motor system, meaning they affect how someone moves, Dr. U. Shivraj Sohur, a movement disorder specialist with the MassGeneral Institute for Neurodegenerative Disease, told Yahoo Health. From there, the separation happens quickly, both from a neurology point of view and from a patients experience.
Related:Robin Williams: Is Parkinsons Disease Linked to Suicide?
Related:#IceBucketChallenge Goes Big on Social Media
Parkinsons disease
Whats The Difference Between Lewy Body Dementia Parkinsons Disease And Alzheimers Disease
Lewy body dementia is an umbrella term for two related clinical diagnoses: dementia with Lewy bodies and Parkinsons disease dementia. These disorders share the same underlying changes in the brain and very similar symptoms, but the symptoms appear in a different order depending on where the Lewy bodies first form.
Dementia with Lewy bodies is a type of dementia that causes problems with memory and thinking abilities that are severe enough to interfere with everyday activities. It specifically affects a persons ability to plan and solve problems, called executive function, and their ability to understand visual information. Dementia always appears first in DLB. The motor symptoms of Parkinsons such as tremor, slowness, stiffness and walking/balance/gait problems usually become more evident as the disease progresses. Visual hallucinations, REM sleep behavior disorder, fluctuating levels of alertness and attention, mood changes and autonomic dysfunction are also characteristic of DLB.
Finally, Alzheimers is characterized by different abnormal clumps called amyloid plaques, and jumbled fiber bundles called tau tangles. These microscopic structural changes in the brain were discovered by Dr. Alois Alzheimer in 1906. These plaques and tangles, together with loss of connections between nerve cells, contribute to loss of coherence and memory, as well as a progressive impairment in conducting normal activities of daily living.
What Is Lewy Body Dementia
Lewy body dementia is not a single disorder but rather a spectrum of closely-related disorders involving disturbances of cognition, behavior, sleep, movement and autonomic function.
In these progressive disorders, Lewy bodies build up in the brain. Lewy bodies in the brain stem cause a disruption in the production of chemical messengers called dopamine. Too little dopamine can cause parkinsonism, a clinical syndrome thats characterized by tremor, bradykinesia , rigidity and postural instability. Parkinsonism can be caused by Parkinsons disease itself as well as by other underlying neurological conditions such as LBD. These Lewy bodies are also found throughout other areas of the brain, including the cerebral cortex. The neurotransmitter acetylcholine is also depleted, causing disruption of perception, thinking and behavior.
A German neurologist, Friederich H. Lewy, first discovered the abnormal protein deposits in the early 1900s as he was conducting research on Parkinsons disease.
You May Like: Judy Woodruff Parkinson’s
They Are About The Same
Parkinsons Disease and Huntingtons Disease are about the same as far as the impact they have on quality of life. They both begin gradually starting with simple coordination problems. Then that leads on to loss of motor control. Then later they both lead to deterioration of a persons mental capacity. I do not see how one could be any worse than the other. They are both horrible.
Serotonergic Degeneration In Pd And Als
Staging of brain pathology in PD demonstrated an early involvement of Lewy body depositions within the RN. In more detail, Halliday et al. firstly described a 56% loss of serotonergic neurons in the median RN of PD compared to control brain. Afterwards, Braak et al. determined six stages in the evolution of PD-related pathology, with lesions being present in the median RN in the caudal brainstem already from stage two onwards. Furthermore, 5-HT depletion was observed in various target areas of the RN, such as in the basal ganglia, hypothalamus, hippocampus, and prefrontal cortex . This was later confirmed by in vivo imaging studies, revealing new insights. For instance, Politis et al. applied 11C-DASB-PET to early-stage PD patients, and demonstrated reduced SERT binding in the caudate nucleus, thalamus, and anterior cingulate cortex, whereas PD subjects with established disease showed additional 11C-DASB binding reductions in the putamen, insula, posterior cingulate cortex, and, prefrontal cortex. Further binding reductions were noticed in the ventral striatum, RN, and amygdala of advanced PD patients. Interestingly, the loss of SERT binding in the RN occurred in later stages, pointing to an earlier loss of serotonergic projections instead of the neurons themselves.
Don’t Miss: Judy Woodruff Health Problems
Possible Link To Alzheimers
Though Alzheimers, Huntingtons, and Parkinsons are distinctly different diseases, some evidence has emerged that shows a common link between the three.
All three diseases have proteins within the cells that do not assemble properly. Though the molecular and cellular changes that occur in each disease vary greatly, this protein degradation has been shown to precede early clinical signs in each disease. This is promising news, as more studies are being done to determine whether this can either predict or prevent these neurodegenerative diseases.
Dont Miss: Can Parkinsons Psychosis Be Reversed
Progressive Supranuclear Palsy And Multiple Systems Atrophy
Progressive supranuclear palsy and multiple systems atrophy are rare variants of NDD. PSP is characterized by degeneration of neurons in the basal ganglia and brainstem, including the substantia nigra. Clinically, patients present with vertical ophthalmoplegia, postural instability, pseudobulbar palsy, mild dementia and parkinsonism unresponsive to levodopa however, there is wide variation in presentation and significant overlap amongst this sub-group of NDDs, making the diagnosis difficult.
MSA is a sporadic NDD characterized by various degrees of autonomic dysfunction, cerebellar abnormalities, parkinsonism, and corticospinal degeneration. MSA can be further classified into two sub-types, one involving degeneration of nigrostriatal pathways with parkinsonian features. The second primarily involves olivopontocerebellar atrophy and presents with more prominent cerebellar ataxia. Given the diverse clinical features of MSA and significant overlap with PD and PSP, early diagnosis of MSA can be challenging. As in other NDDs, a diagnosis of MSA is presumed until confirmed by post-mortem autopsy with tissue samples showing -synuclein inclusions in glial cells.
Recently, spectral domain optical coherence tomography has been employed to evaluate retinal thickness in PSP both individually and compared to PD patients. Significant differences were found both compared to age-matched controls and PD patients, so SD-OCT has shown promise as a future diagnostic aid for PSP .
Recommended Reading: Sam Waterston Parkinson’s
Living With Huntingtons Disease
Huntingtons disease is progressive. That means it gets worse over time. Living with the disorder means preparing for the symptoms to worsen. Eventually you will need help with everyday activities. These include getting around your home, hygiene, eating, and decision-making. A trusted advisor can help with important decisions and in monitoring changes in your behavior.
People with Huntingtons disease usually die within 15 to 20 years of their diagnosis. The most common causes of death are infections and injuries related to falls.
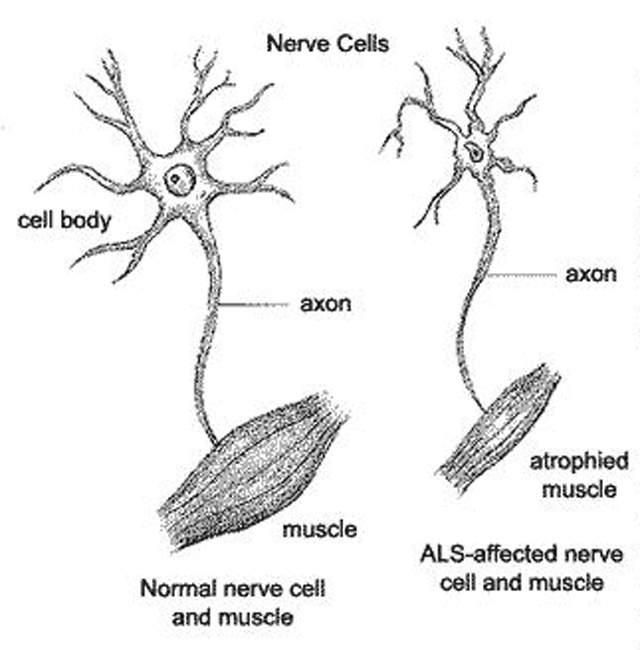
Classical Als Pls And Pma
ALS can be classified by the types of motor neurons that are affected. Typical or “classical” ALS involves upper motor neurons in the brain and lower motor neurons in the spinal cord.Primary lateral sclerosis involves only upper motor neurons, and progressive muscular atrophy involves only lower motor neurons. There is debate over whether PLS and PMA are separate diseases or simply variants of ALS.
Primary lateral sclerosis accounts for about 5% of all cases of ALS and affects upper motor neurons in the arms and legs. However, more than 75% of people with apparent PLS develop lower motor neuron signs within four years of symptom onset, meaning that a definite diagnosis of PLS cannot be made until then. PLS has a better prognosis than classic ALS, as it progresses slower, results in less functional decline, does not affect the ability to breathe, and causes less severe weight loss.
Progressive muscular atrophy accounts for about 5% of all cases of ALS and affects lower motor neurons in the arms and legs. While PMA is associated with longer survival on average than classic ALS, it still progresses to other spinal cord regions over time, eventually leading to respiratory failure and death. Upper motor neuron signs can develop late in the course of PMA, in which case the diagnosis might be changed to classic ALS.
Recommended Reading: Yopd Life Expectancy
Parkinsons Disease Dementiawhen The Disease Takes Its Full Course
We remember their love when they can no longer remember.
One million people in the US have Parkinsons, and that number is expected to rise. Its most famous patient? Michael J. Fox.
But there have been many more: Alan Alda, George H. W. Bush, Billy Graham, Muhammad Ali, Jesse Jackson
When Do Parkinsons Dementia Symptoms Start?
Although Michael J. Fox was diagnosed early , most Parkinsons Disease diagnoses come around sixty or older. Some research suggests that age is dropping down into the fifties range.
Either way, from disease diagnosis, Parkinsons Dementia symptoms may not start for another ten years, but definitely wont start for a year or more.
If they do? Its not called Parkinsons Dementia. Its Lewy Body Dementia .
Hence the importance of keeping track of symptoms when you notice them.
Its a chicken/egg-first situation. Both dementias are characterized by Lewy bodies in the brain. But they start in different regions.
- DLB is dementia that affects the mind. As it attacks mental abilities, movement will become affected. Youll see it as one of three patterns.
- Dementia shows up first.
- Dementia shows up at the same time as the physical symptoms.
- Dementia shows up within one year of a Parkinsons diagnosis .
In fact, Parkinsons doesnt always make that jump. 20-50% wont. But 50-80% will.
You might see ,
Nilotinib Regulates Mirnas Associated With Ubiquitination
Changes of miRNAs associated with the ubiquitination pathways were detected only in nilotinib, 300 vs 150 mg and placebo . We observed disinhibition of SQSTM1, SMURF2, FBXW7, BTRC , and SKP1 , which mediate substrate recognition and recruitment for lysosomal degradation. These specific gene targets show that while initiation of lysosomal-autophagy is functioning, nilotinib, 300 mg, is able to facilitate the completion of these biological waste-control mechanisms. Nilotinib, 300 mg, significantly altered a number of ubiquitination genes and ubiquitin ligases, including NEDD4 , UBEs , MDM , and PSMDs as well as deubiquitination genes and ubiquitin-specific proteases , suggesting regulation of the ubiquitination/deubiquitination cycle, in agreement with previous reports., Alterations of autophagy-ubiquitination genes are also concurrent with significant changes of several heat shock proteins and vesicular transport genes , suggesting facilitation of cellular transport and protein clearance.
You May Like: Parkinson’s Double Vision
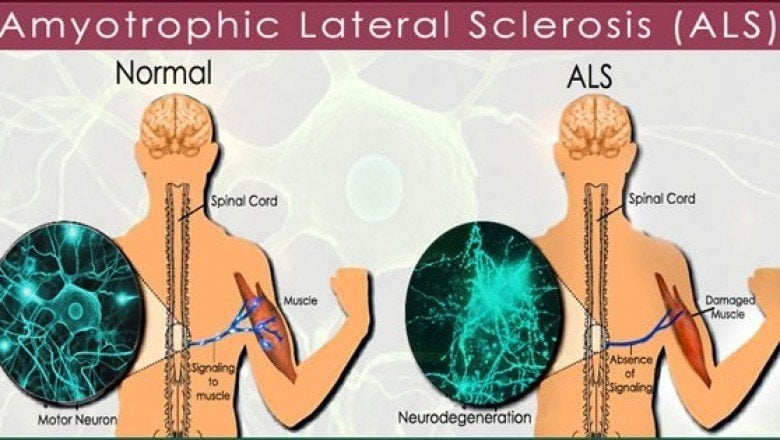
Diseases Similar To Als
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, also called ALS or Lou Gehrig’s disease, is a neurodegenerative disorder characterized by a loss of muscle function as a result of nerve deterioration.ALS affects a subset of cells known as motor neurons. These cells connect the muscles to the central nervous system and allow for muscle movement and locomotion. In ALS, the motor neurons become progressively more damaged, leading to muscle weakness, followed by paralysis and eventually death. A number of other conditions also affect motor neurons and result in symptoms similar to ALS.
If you are experiencing serious medical symptoms, seek emergency treatment immediately.
Protein Degradation Pathway Key
The findings add to the evidence that a defect in a process known as the protein degradation pathway contributes to ALS and possibly other degenerative disorders, such as Parkinsonâs disease and even Alzheimerâs, the researchers conclude.
âAbnormality in protein degradation has been suspected, but there was little direct evidence before this study,â study co-author Han-Xiang Deng, MD, notes in a written statement.
Raymond Roos, MD, the Marjorie and Robert Straus Professor of Neurological Science at the University of Chicago Medical Center, says the discovery appears to represent an important step forward in the understanding of ALS.
He adds that it remains unclear why ubiquilin2 does not function properly in some patients without a family history of ALS.
âThis moves the field forward in an impressive way, but like many breakthroughs, many questions remain to be answered,â he says.
There is only one drug approved for the treatment of ALS. It is used to slow disease progression but is not a cure. ALS Association President and CEO Jane H. Gilbert says effective therapies for ALS are long overdue.
âThis is very exciting research that has huge promise for the discovery of new treatments,â she tells WebMD.
Lucie Bruijn, PhD, scientific director of the ALS Association, says she is optimistic that better drugs or drug combinations will emerge to slow disease progression.
Show Sources
Recommended Reading: Prayer For Parkinson’s Disease
Onset Of Als And Parkinsons
There are several different variants of ALS but it generally affects people between the age of 40 and 70. Juvenile onset ALS, however, can start in childhood or typically before the age of 25, although this form of ALS is particularly rare. The onset of ALS is estimated to be 20% more common in men compared with women and in 10% of cases there is likely to be a genetic component.
Parkinsons disease is usually diagnosed in people over the age of 60, though a small percentage exhibit the symptoms before the age of 50.
Once again, men are more likely to develop Parkinsons than women.
Difference In Parkinsons Disease And Als Diagnosis And Treatment
There is currently no specific test that can be performed to directly diagnose Parkinsons disease, but an array of different tests can help narrow down on a diagnosis. If Parkinsons disease is suspected, a patient will be referred to a neurologist and geriatrician. Diagnosis is commonly confirmed with the presence of at least two of the three most common symptoms: Shaking or tremor that occurs at rest, slowness of movement, and muscle stiffness. A doctor will also perform brain scans to diagnose Parkinsons disease and to check for other conditions that could be causing similar symptoms.
There is also no cure for Parkinsons disease, but treatments are available to manage the symptoms and slow down the disease progression. Alongside traditional treatments, supportive therapies are used to improve different aspects of a persons health.
Common medications prescribed in Parkinsons disease include dopamine replacement therapy, dopamine agonists, anticholinergics, amantadine, monomine oxidase type B inhibitors, and catechol-o-methyl transferase inhibitors.
Surgery is also a treatment option for Parkinsons disease and is best suited for those who had a good response to levodopa, but still have difficulties with movement or who experience large fluctuations in their levodopa levels.
You May Like: On And Off Phenomenon
Muscle Cramps And Stiffness
Medications, such as botulinum toxin , can help. Botox injections can block the signals from the brain to the stiff muscles for about 3 months at a time.
Baclofen , a muscle relaxer, may help ease muscle stiffness, spasms, and yawning. A doctor can surgically implant a small pump to deliver regular doses to the space around the spinal cord. From there, the drug reaches the nervous system.
Some people may also find that physical therapy helps alleviate cramps and stiffness.
How Are Als And Ms Diagnosed
To make a diagnosis, your doctor will ask for detailed information about your symptoms and your health history. There are also tests they can perform to help make a diagnosis.
If ALS is suspected, your doctor may order electrodiagnostic tests, such as an electromyography or a nerve conduction study.
These tests provide information on the transmission of nerve signals to your muscles and can show certain patterns that are consistent with a diagnosis of ALS.
A muscle or nerve biopsy may also be recommended for evaluation of ALS.
Your doctor may also order blood and urine samples, or perform a lumbar puncture to examine your spinal fluid.
MRI scans or X-rays may be ordered as well. If you have an MRI scan, you may have special images ordered to increase visualization of demyelinating areas in the brain and spine.
Doctors can use MRI results to distinguish between MS and ALS. MS targets and attacks myelin in a process called demyelination.
Demyelination prevents the nerves from performing as well as they once did, and it can be detected by an MRI scan.
On the other hand, ALS attacks the motor neurons, which doesnt appear on brain or spine MRIs.
Theres no cure for either condition, but treatments are available.
You May Like: On-off Phenomenon
Whats The Difference Between Multiple System Atrophy And Parkinsons
Parkinsons and MSA both affect the movement control system and the involuntary autonomic control system and early symptoms can make a differential diagnosis a challenge. MSA, however, tends to progress faster than Parkinsons balance problems and a stooped posture happen earlier and get worse more quickly with MSA and autonomic functions such as blood pressure, heart rate, breathing, sweating, bladder function, and sexual problems are more severe in people with MSA.
For more information on multiple symptom atrophy, read this fact sheet.