No One Definitive Cause Of Parkinsons
There are no biomarkers or objective screening tests that indicate one has Parkinsons. That said, medical experts have shown that a constellation of factors are linked to it.
Parkinsons causes are likely a blend of genetics and environmental or other unknown factors. About 10 to 20 percent of Parkinsons disease cases are linked to a genetic cause, says Ted Dawson, M.D., Ph.D., director of the Institute for Cell Engineering at Johns Hopkins. The types are either autosomal dominant or autosomal recessive .
But that leaves the majority of Parkinsons cases as idiopathic, which means unknown. We think its probably a combination of environmental exposure to toxins or pesticides and your genetic makeup, says Dawson.
Age. The biggest risk factor for developing Parkinsons is advancing age. The average age of onset is 60.
Gender. Men are more likely to develop Parkinsons disease than women.
Genetics. Individuals with a parent or sibling who is affected have approximately two times the chance of developing Parkinsons. Theres been an enormous amount of new information about genetics and new genes identified over the past 10 or 15 years that have opened up a greater understanding of the disease, says Dawson.
Pathogenic Protein Function In Autoimmunity
As discussed above, molecular mimicry and cross immunoreactions are two of the primary mechanisms through which autoimmunity is triggered. Molecular mimicry between herpes simplex virus 1 and human -syn was detected in PD patients in 2016. HSV1 infection could enhance the development of autoimmunity because autoreactive antibodies induced by HSV1 have the same response to the human -syn homologous peptide bound to the membrane of DNs and lead to DN destruction . These results also support the assumption that -syn participates in autoimmunity involved in the pathological progression of PD.
First Direct Evidence That Abnormal Protein In Parkinsons Disease Triggers Immune Response
New York, NY Researchers have found the first direct evidence that autoimmunityin which the immune system attacks the bodys own tissuesplays a role in Parkinsons disease, the neurodegenerative movement disorder. The findings raise the possibility that the death of neurons in Parkinsons could be prevented by therapies that dampen the immune response.
The study, led by scientists at Columbia University Irving Medical Center and the La Jolla Institute for Allergy and Immunology, was published today in Nature.
The idea that a malfunctioning immune system contributes to Parkinsons dates back almost 100 years, said study co-leader David Sulzer, PhD, professor of neurobiology . But until now, no one has been able to connect the dots. Our findings show that two fragments of alpha-synuclein, a protein that accumulates in the brain cells of people with Parkinsons, can activate the T cells involved in autoimmune attacks.
It remains to be seen whether the immune response to alpha-synuclein is an initial cause of Parkinsons or if it contributes to neuronal death and worsening symptoms after the onset of the disease, said study co-leader Alessandro Sette, Dr. Biol. Sci., professor in the Center for Infectious Disease at La Jolla Institute for Allergy and Immunology in La Jolla, Calif. These findings, however, could provide a much-needed diagnostic test for Parkinsons disease and could help us to identify individuals at risk or in the early stages of the disease.
Recommended Reading: Diseases Similar To Parkinson’s
Best Evidence Yet That Parkinson’s Could Be Autoimmune Disease
Parkinsons begins with abnormal clumping of a protein called synuclein in the brain
R. Bick, B. Poindexter, UT Medical School/SPL
EVIDENCE that Parkinsons disease may be an autoimmune disorder could lead to new ways to treat the illness.
Parkinsons begins with abnormal clumping of a protein called synuclein in the brain. Neighbouring dopamine-producing neurons then die, causing tremors and difficulty moving.
The prevailing wisdom has been that these neurons die from a toxic reaction to synuclein deposits. However, Parkinsons has been linked to some gene variants that affect how the immune system works, leading to an alternative theory that synuclein causes Parkinsons by triggering the immune system to attack the brain.
An argument against this theory has been that brain cells are safe from immune system attack, because most neurons dont have antigens the markers immune cells use to recognise a target. But by studying postmortem brain tissue samples, David Sulzer at Columbia University and his team have discovered that dopamine-producing neurons do display antigens. The team has now conducted blood tests to reveal that people with Parkinsons show an immune response to these antigens, while people who dont have the condition do not .
This article appeared in print under the headline Parkinsons may be the result of immune attack
More on these topics:
Thanks For Signing Up
We are proud to have you as a part of our community. To ensure you receive the latest Parkinsons news, research updates and more, please check your email for a message from us. If you do not see our email, it may be in your spam folder. Just mark as not spam and you should receive our emails as expected.
You May Like: What Drugs Can Cause Parkinson’s Disease
Autoimmunity In Neurodegenerative Diseases And Its Relevance To Pd
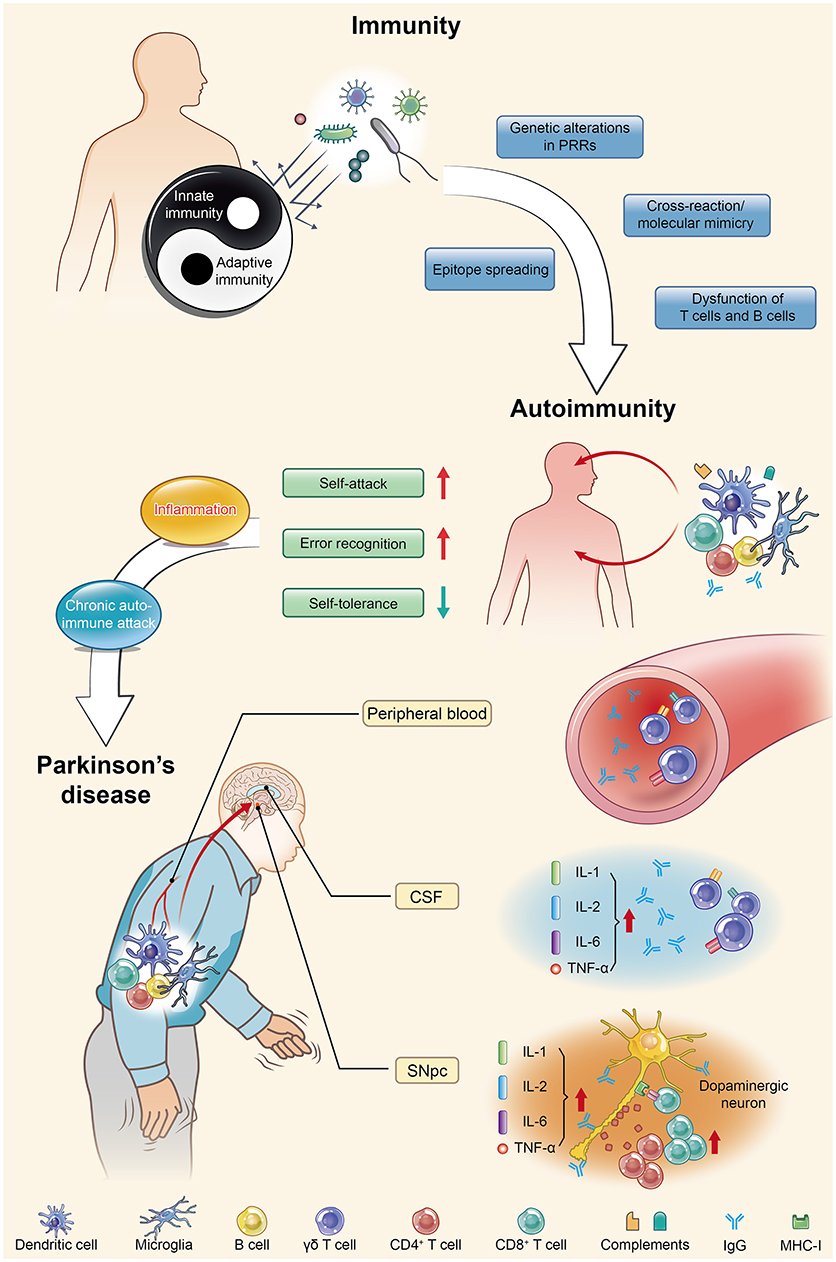
Parkinson’s disease is actually an autoimmune disease. Autoimmunity occurs when immune homeostasis is broken by several main mechanisms shown in this figure, which directly result in an increase in error recognition and self-attack and a decrease in self-tolerance to autoantigens. Regarding PD, chronic autoimmune attack is not only its pathogenesis but also always involved throughout the entire disease process. Inflammation is the first step of this attack, with the subsequent participation of various immune cells and immunoglobulins they produce, ultimately leading to the death of dopaminergic neurons. PRRs, pattern recognition receptors CSF, cerebrospinal fluid SNpc, substantia nigra pars compacta IL, interleukin TNF, tumor necrosis factor.
T Cells In The Midbrain Of Pd Patients
Perhaps as a result of peripheral inflammation, changes in lymphocyte subtype populations, and BBB breakdown, T cells can infiltrate the affected brain regions of PD patients. First reported by the McGeers in 1988, CD3+ cells, a marker for T cells, were detected within the CNS of PD brains . Brochard et al. showed that both CD4+ and CD8+ T cells, but not B and natural killer cells, infiltrated the SN of PD patients and were present at much far greater levels than in healthy controls. These T cells were located near blood vessels and neuromelanin-containing dopaminergic neurons . The presence of T cells in the region affected in the disease suggests a targeted extravasation, rather than a random consequence of increased BBB permeability by peripheral inflammation. If T cells that had escaped self-tolerance circulate in the blood of PD patients, it is plausible that they could infiltrate into the brain permitted by a leaky BBB. The causal role of infiltrating T cells is further elucidated in studies from mouse models of PD.
Also Check: Does Weed Help With Parkinson’s
What Causes Parkinsons Disease
Parkinsons disease is a chronic, progressive neurological disease that currently affects about 1 million Americans. Parkinsons disease involves a small, dark-tinged portion of the brain called the substantia nigra. This is where you produce most of the dopamine your brain uses. Dopamine is the chemical messenger that transmits messages between nerves that control muscle movements as well as those involved in the brains pleasure and reward centers. As we age, its normal for cells in the substantia nigra to die. This process happens in most people at a very slow rate.
But for some people, the loss happens rapidly, which is the start of Parkinsons disease. When 50 to 60 percent of the cells are gone, you begin to see the symptoms of Parkinsons.
Autoimmunity As A Trigger Of Axonal Dying
The death of the brain cells that produce dopamine, the chemical messenger that signals other cells involved in motor control, triggers the symptoms of Parkinsons disease. But researchers still dont know exactly what causes those dopamine-producing cells to die.
At the University of Montreal, Professor Louis-Eric Trudeau, a neuroscientist, investigates the possibility that an autoimmune attack on those dopamine cells is the culprit.
Trudeau and his immunologist colleague, Michel Desjardins, are studying the role of the portion of cells called axon terminals. These terminalsthe root-like extremities of cellsrelease the chemical messengers that send communication signals. Trudeau believes the death of these terminals, before the death of the dopamine cells themselves, is where the trouble starts.
Using dopamine-producing brain cells from genetically modified mice, Trudeau and his team are exposing dopamine cells directly to immune cells. Then they closely study the axon terminals of those dopamine cells to see what happens in an immune attack.
This project is focused on trying to develop a better understanding of why the terminals are affected, Trudeau says. This is a relatively new field in Parkinsons disease looking at the possibility that this disease is at least in part an autoimmune disease, in some ways like Multiple Sclerosis .
The immune system can be relatively easily targeted for treatment, Trudeau says.
Search
Read Also: Rbd And Parkinson’s Disease
Potential New Treatment Strategies For Parkinson’s
This new finding provides additional knowledge and understanding of the disease processes that are present in PD and opens the door for using immunotherapies, drugs that suppress the abnormal immune response seen in autoimmune disorders. Additional research is needed to understand the molecular steps that occur in PD and the immune response, but researchers are hopeful that an immunotherapy strategy could help to prevent or lessen worsening symptoms in people with PD.1,2
Scientists Link Immune Cells To Parkinson’s Disease Onset
- Date:
- La Jolla Institute for Immunology
- Summary:
- A new study adds increasing evidence that Parkinson’s disease is partly an autoimmune disease. In fact, the researchers report that signs of autoimmunity can appear in Parkinson’s disease patients years before their official diagnosis.
A new study co-led by scientists at the La Jolla Institute for Immunology adds increasing evidence that Parkinson’s disease is partly an autoimmune disease. In fact, the researchers report that signs of autoimmunity can appear in Parkinson’s disease patients years before their official diagnosis.
The research could make it possible to someday detect Parkinson’s disease before the onset of debilitating motor symptoms — and potentially intervene with therapies to slow the disease progression.
The study, published in the April 20, 2020, issue of Nature Communications, was co-led by LJI professor Alessandro Sette, Dr. Biol. Sci, and Professor David Sulzer, Ph.D., of the Columbia University Medical Center.
Scientists have long known that clumps of a damaged protein called alpha-synuclein build up in the dopamine-producing brain cells of patients with Parkinson’s disease. These clumps eventually lead to cell death, causing motor symptoms and cognitive decline.
The researchers hope to study more Parkinson’s patients and follow them over longer time periods to better understand how T cell reactivity changes as the disease progresses.
Story Source:
Don’t Miss: Apps For Parkinson’s Disease
Other Causes Of Parkinsonism
“Parkinsonism” is the umbrella term used to describe the symptoms of tremors, muscle rigidity and slowness of movement.
Parkinson’s disease is the most common type of parkinsonism, but there are also some rarer types where a specific cause can be identified.
These include parkinsonism caused by:
- medication where symptoms develop after taking certain medications, such as some types of antipsychotic medication, and usually improve once the medication is stopped
- other progressive brain conditions such as progressive supranuclear palsy, multiple systems atrophy and corticobasal degeneration
- cerebrovascular disease where a series of small strokes cause several parts of the brain to die
You can read more about parkinsonism on the Parkinson’s UK website.
Page last reviewed: 30 April 2019 Next review due: 30 April 2022
New Research Gives Further Evidence That Autoimmunity Plays A Role In Parkinsons Disease
Member for
ScienMag
A new study co-led by scientists at the La Jolla Institute for Immunology adds increasing evidence that Parkinsons disease is partly an autoimmune disease. In fact, the researchers report that signs of autoimmunity can appear in Parkinsons disease patients years before their official diagnosis. The research could make it possible to someday detect Parkinsons disease before the onset of debilitating motor symptomsand potentially intervene with therapies to slow the disease progression. The Parkinsons Foundation supports this research.
Also Check: If My Parent Has Parkinson’s Will I Get It
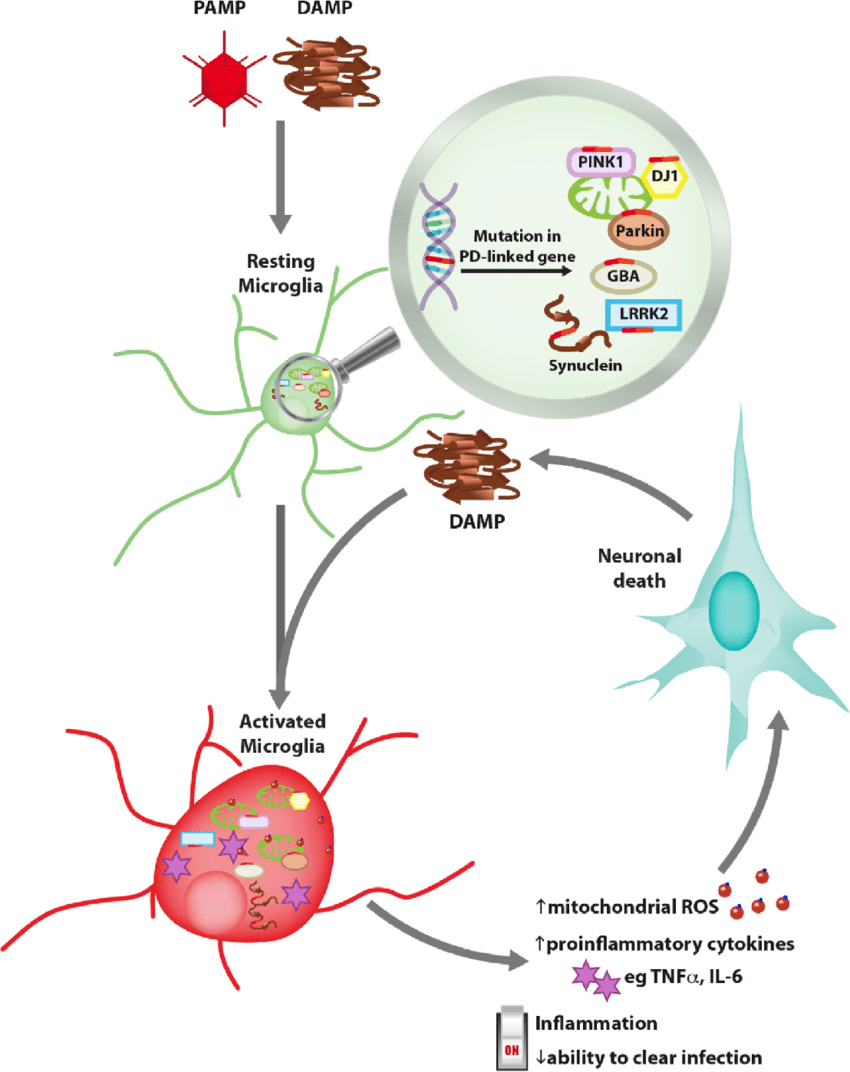
Validation In Mouse Models
The new findings of Dr Michel Desjardins from the University of Montreal and Dr Heidi McBride of MNI, linking Parkinsons disease to autoimmune mechanisms, have been validated in a mouse model of Parkinsons disease where PINK1 or Parkin are absent.
Clinicians have shown that the immune system is activated in the brain of Parkinsons disease patients, said Dr Diana Matheoud, a postdoctoral fellow from the University of Montreal. Our study explains how an attack by the immune system may be responsible for the destruction of dopaminergic neurons during the disease. We are currently testing whether autoimmune mechanisms lead to the loss of dopaminergic neurons in mice, and developing systems to extend our study to human neurons.
Antigen presentation was not believed to play a direct role in Parkinsons disease, added McBride. While most laboratories are following the trail of the toxic mitochondria model, our path led us to observe Parkinsons disease from a different point of view. Our approach, centred on the immune system, led us down a different road where we were able to observe that autoimmunity is likely to play an important role in the progression of the disease.
Is Parkinsons An Autoimmune Disease
Parkinsons disease is a neurological condition resulting from an imbalance of dopamine and acetylcholine, two chemical messengers in the brain that help control movement. Too little dopamine leads to problems with gross and fine motor coordination. It is thought to be caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors, in conjunction with increasing age. More recently an immunological cause has been under investigation. Below we examine the possibility of a connection between Parkinsons and autoimmune disease.
What are the signs and symptoms of Parkinsons disease?
Aside from those above, Parkinsons patients may present with a fairly wide range of other signs and symptoms, which are alternately present or absent depending on the individual. They may experience psychological issues such as depression or anxiety, which is likely the result of biochemical changes within the brain, coupled with the considerable burden of living with Parkinsons. And some patients will exhibit varying degrees of autonomic dysfunction, where the automatic/involuntary functions of the body, such as urination or sweating, are disrupted. Still others have trouble maintaining their balance during normal activities.
Have there been studies linking Parkinsons to an autoimmune trigger?
Does the research indicate that, similar to hypothyroidism, Parkinsons has an autoimmune and non-autoimmune root cause?
Questions for your doctor:
You May Like: Beginning Signs Of Parkinson’s
Is There A Cure For Parkinsons
Theres currently no cure for Parkinsons, a disease that is chronic and worsens over time. More than 50,000 new cases are reported in the United States each year. But there may be even more, since Parkinsons is often misdiagnosed.
Its reported that Parkinsons complications was the
Complications from Parkinsons can greatly reduce quality of life and prognosis. For example, individuals with Parkinsons can experience dangerous falls, as well as blood clots in the lungs and legs. These complications can be fatal.
Proper treatment improves your prognosis, and it increases life expectancy.
It may not be possible to slow the progression of Parkinsons, but you can work to overcome the obstacles and complications to have a better quality of life for as long as possible.
Parkinsons disease is not fatal. However, Parkinsons-related complications can shorten the lifespan of people diagnosed with the disease.
Having Parkinsons increases a persons risk for potentially life threatening complications, like experiencing:
- falls
Parkinsons often causes problems with daily activities. But very simple exercises and stretches may help you move around and walk more safely.
Matching Cases With Controls
All PD patients were labeled with a matching type constructed from a combination of three study-related variables and eight technical variables. The three study-related variables were: birth year, sex, birth location. The remaining technical variables were not related to our research question but were used to ensure that the cohort used did not interfere nor bias the study results . In total there were 8404 unique matching types.
For each matching type, the following procedure was done:
-
1) PD case individuals of this type were extracted and ordered randomly, forming a pool of cases, named A. PD control individuals of this type were extracted and ordered randomly, forming a much larger pool of controls, named B.
-
2) To find matches for individuals in the pool A, a sub-pool b was formed by selecting individuals from pool B using the following procedure. For each individual in sub-pool b, their personal follow-up end date must supersede the date of PD diagnosis for each individual in pool A. Individual b1, who is the first person in sub-pool b, is assigned to the first person in pool A . Individual b1 is permanently eliminated from pools b and B.
-
3) The step 2) is repeated sequentially with all individuals in A.
-
4) The step 3) is repeated maximum 200 times, or until the pool B is depleted, or until none of the individuals in A is assigned a new match.
Don’t Miss: Parkinson’s Big Movement Exercises
Advances To Prevent The Symptoms Of Parkinsons
These findings suggest a possible treatment. In this case, immunotherapy could be used to increase the tolerance of the immune system to this protein. This could help improve or prevent the worsening of symptoms in patients with Parkinsons. It could also provide a diagnostic test to identify the individuals most at risk. And those who are in the early stages of the disease.
This research, together with other work, such as that being carried out at the Karolinska Institute in Stockholm, which has found that the disease could originate in the bowels and spread to the brain through the vagus nerve, shows that progress is gradually being made in improving knowledge about a disease that affects more than six million people around the world.