What Happens Before Surgery
In the doctor’s office you will sign consent forms and complete paperwork to inform the surgeon about your medical history, including allergies, medicines, anesthesia reactions, and previous surgeries. Presurgical tests may need to be done several days before surgery. Consult your primary care physician about stopping certain medications and ensure you are cleared for surgery.You may also need clearance from your cardiologist if you have a history of heart conditions.
Stop taking all non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medicines and blood thinners 7 days before surgery. Stop using nicotine and drinking alcohol 1 week before and 2 weeks after surgery to avoid bleeding and healing problems.
You may be asked to wash your skin and hair with Hibiclens or Dial soap before surgery. It kills bacteria and reduces surgical site infections.
No food or drink, including your Parkinson’s medication, is permitted after midnight the night before surgery.
Try to get a good night’s sleep. The DBS surgery involves multiple steps and lasts most of the day, during which you may be awake and off medication.
Morning of surgery
Arrive at the hospital 2 hours before your scheduled surgery time to complete the necessary paperwork and pre-procedure work-ups. An anesthesiologist will talk with you and explain the effects of anesthesia and its risks.
What Happens During Surgery
For stage 1, implanting the electrodes in the brain, the entire process lasts 4 to 6 hours. The surgery generally lasts 3 to 4 hours.
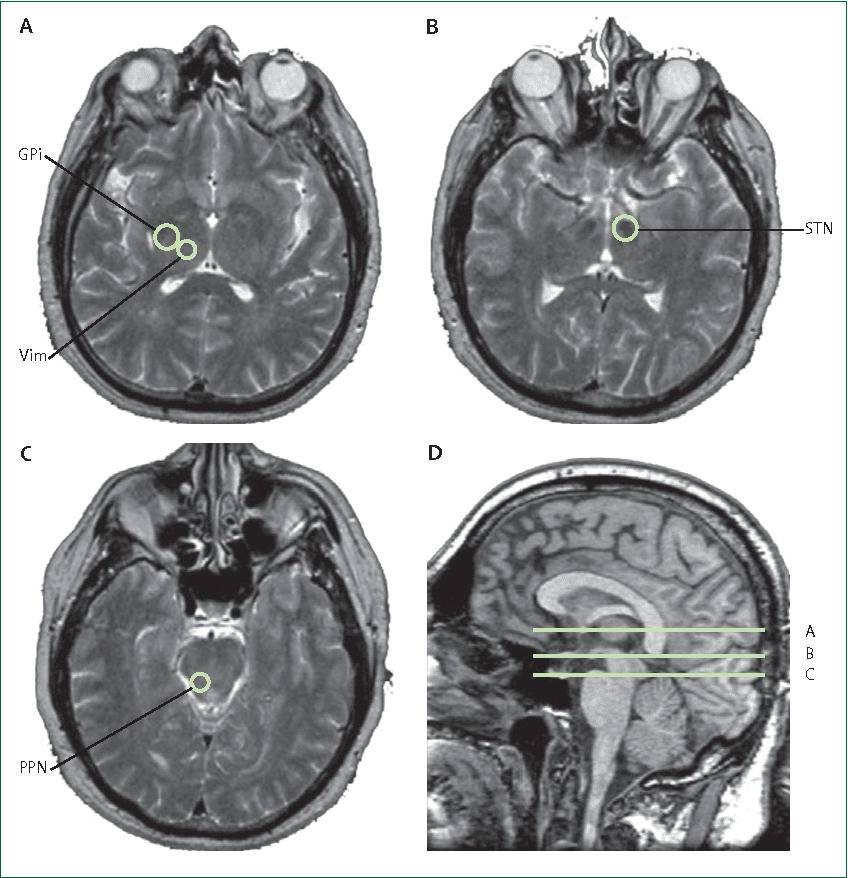
Step 1: attach stereotactic frameThe procedure is performed stereotactically, which requires attaching a frame to your head. While you are seated, the frame is temporarily positioned on your head with Velcro straps. The four pin sites are injected with local anesthesia to minimize discomfort. You will feel some pressure as the pins are tightened .
Step 2: MRI or CT scanYou will then have an imaging scan, using either CT or MRI. A box-shaped localizing device is placed over the top of the frame. Markers in the box show up on the scan and help pinpoint the exact three-dimensional coordinates of the target area within the brain. The surgeon uses the MRI / CT scans and special computer software to plan the trajectory of the electrode.
Step 3: skin and skull incisionYou will be taken to the operating room. You will lie on the table and the stereotactic head frame will be secured. This prevents any small movements of your head while inserting the electrodes. You will remain awake during surgery. Light sedation is given to make you more comfortable during the initial skin incision, but then stopped so that you can talk to the doctors and perform tasks.
Living With A Stimulator
Once the DBS has been programmed, you are sent home with instructions for adjusting your own stimulation. The handheld controller allows you turn the stimulator on and off, select programs, and adjust the strength of the stimulation. Most patients keep their DBS system turned on 24 hours day and night. Some patients with essential tremor can use it during the day and turn off the system before bedtime. Your doctor may alter the settings on follow-up visits if necessary.
If your DBS has a rechargeable battery, you will need to use a charging unit. On average charging time is 1 to 2 hours per week. You will have a choice of either a primary cell battery or a rechargeable unit and you should discuss this with you surgeon prior to surgery.
Just like a cardiac pacemaker, other devices such as cellular phones, pagers, microwaves, security doors, and anti theft sensors will not affect your stimulator. Be sure to carry your Implanted Device Identification card when flying, since the device is detected at airport security gates.
Recommended Reading: Unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale Updrs
When Should I Call My Healthcare Provider Or Go To The Hospital
Because DBS involves surgery especially the procedure on your brain there are some warning signs you shouldn’t ignore. You should call your healthcare provider immediately or go to the hospital outside of business hours if you have the following symptoms:
- Severe headache that happens suddenly or wont go away.
- Bleeding from your incisions.
- Redness, swelling or unusual warmth which are signs of infection around your incisions.
- Sudden changes in your vision, such as seeing double, blurred vision or loss of vision.
- Fever of 101 degrees F or higher.
Who Is A Candidate
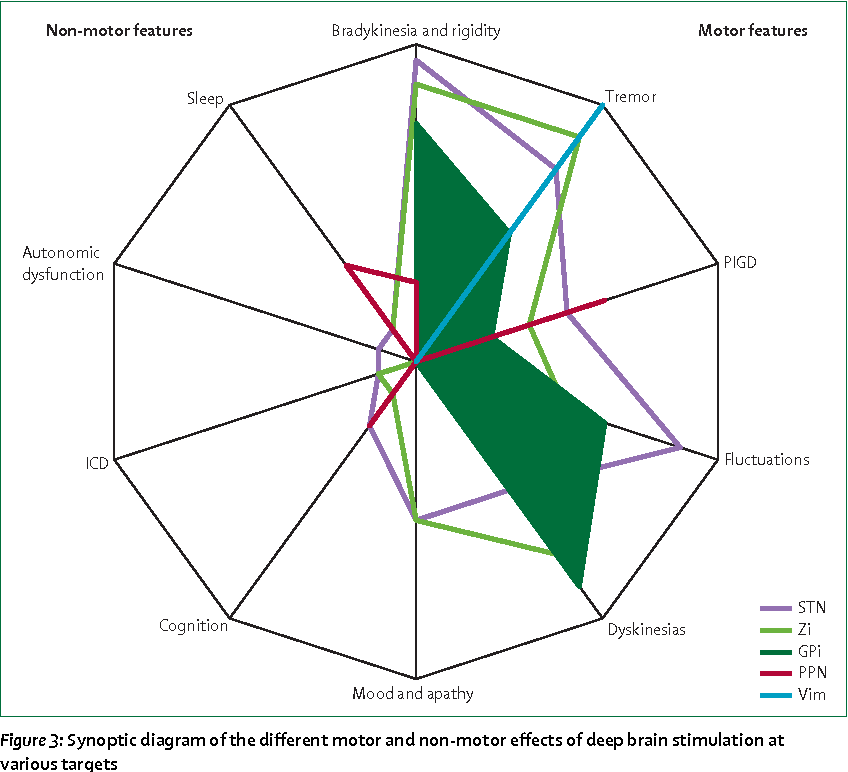
You may be a candidate for DBS if you have:
- a movement disorder with worsening symptoms and your medications have begun to lose effectiveness.
- troubling “off” periods when your medication wears off before the next dose can be taken.
- troubling “on” periods when you develop medication-induced dyskinesias .
DBS may not be an option if you have severe untreated depression, advanced dementia, or if you have symptoms that are not typical for Parkinson’s.
DBS can help treat symptoms caused by:
- Parkinson’s disease: tremor, rigidity, and slowness of movement caused by the death of dopamine-producing nerve cells responsible for relaying messages that control body movement.
- Essential tremor: involuntary rhythmic tremors of the hands and arms, occurring both at rest and during purposeful movement. Also may affect the head in a “no-no” motion.
- Dystonia: involuntary movements and prolonged muscle contraction, resulting in twisting or writhing body motions, tremor, and abnormal posture. May involve the entire body, or only an isolated area. Spasms can often be suppressed by “sensory tricks,” such as touching the face, eyebrows, or hands.
After your evaluation and videotaping is complete, your case will be discussed at a conference with multiple physicians, nurses, and surgeons. The team discusses the best treatment plan for each patient. If the team agrees that you are a good candidate for DBS, you will be contacted to schedule an appointment with a neurosurgeon.
You May Like: What Are The Complications Of Parkinson Disease
How Can Parkinsons New Zealand Help
Parkinson’s New Zealand offers information and professional support to people living with Parkinsons. Our team of Parkinsons Community Educators can provide home visits for personalised sessions.
Community Educators work closely with the person with Parkinsons and their carers to develop a medical plan that upholds their health and lifestyle. Community Educators liaise with health professionals that treat Parkinsons in the community, including speech-language therapists, occupational therapists, and physiotherapists.
Parkinsons New Zealand also has support groups for members for sharing their coping strategies, experiences, and is a chance to establish social networks. Programs for people with Parkinsons include exercise, physiotherapy, hydrotherapy, and art or music therapy sessions.
The Case For Doing Dbs Sooner Rather Than Later
In many cases, movement disorder patients only turn to DBS after their medications are no longer working as well as in the past. However, at Neurology Solutions, our position is that movement disorder patients who qualify for DBS should consider getting the procedure done sooner rather than later.
There are a few good reasons why doing DBS earlier might be beneficial, including:
- The brain stimulation inherent to DBS is potentially beneficial to the patient .
- A successful DBS procedure may allow the patient to substantially reduce their medications thus reducing potential long-term toxicity.
- Studies have shown that performing DBS earlier helps the patient have a better long-term outcome.
Also Check: Does Parkinson Disease Affect The Immune System
What Are The Risks Or Complications Of Dbs
Because DBS does involve surgery, there are some possible complications and risks. Your healthcare provider is the best person to tell you about the possible risks and complications. They’re the best source of information because they can consider your medical history, circumstances and more.
The possible complications of surgery include:
How Does Deep Brain Stimulation Work
Movement-related symptoms of Parkinsons disease and other neurological conditions are caused by disorganized electrical signals in the areas of the brain that control movement. When successful, DBS interrupts the irregular signals that cause tremors and other movement symptoms.
After a series of tests that determines the optimal placement, neurosurgeons implant one or more wires, called leads, inside the brain. The leads are connected with an insulated wire extension to a very small neurostimulator implanted under the persons collarbone, similar to a heart pacemaker. Continuous pulses of electric current from the neurostimulator pass through the leads and into the brain.
A few weeks after the neurostimulator has been in place, the doctor programs it to deliver an electrical signal. This programming process may take more than one visit over a period of weeks or months to ensure the current is properly adjusted and providing effective results. In adjusting the device, the doctor seeks an optimal balance between improving symptom control and limiting side effects.
You May Like: Antipsychotics In Parkinson’s Disease
Who May Benefit From Deep Brain Stimulation
A number of criteria can help identify people who are good candidates for deep brain stimulation. This includes people who:
- Have been living with Parkinsons disease for at least five years, though the procedure was approved for early symptoms in 2016 and is now being evaluated to see if it offers benefits for people earlier in the disease
- Have symptoms that are not well controlled on medications
- Are responding to Parkinsons medications : The procedure should only be done for people who are responding to this treatment, but the medication effects fluctuate during the day and the effectiveness of the medication is getting shorter.
- Find that the uncontrolled symptoms are lowering their quality of life
- Are doing relatively well cognitively
At the current time, there is no set age limit for DBS, but the effectiveness may be lower in older people.
How Long Does The Battery Last What Is Involved If You Must Replace The Battery
It depends on the type of battery. Rechargeable IPGs last 9-15 years, as long as they are not allowed to run too low on their charge. Non-rechargeable IPG battery life will depend upon the settings programmed by the neurologist, but patients should expect the IPG to last 2-5 years.
Replacement of the IPG is a 20-minute surgical procedure performed as an outpatient. The chest incision over the IPG is opened. The wires are disconnected from the old IPG and connected to a new IPG. Usually it is done with local anesthesia with sedation.
Recommended Reading: Parkinson’s Age Of Onset
Does Dbs Stop Parkinson’s Progression
Deep brain stimulation does not stop the progression of Parkinsons disease. It is not a cure for Parkinsons and does not stop the disease from getting worse. However, DBS surgery can help to lessen Parkinson’s disease symptoms like tremors, dyskinesias, slowness, stiffness, and problems with walking. Deep brain stimulation can also help to lower the doses of PD medications. However, symptoms like speech impairments, poor posture, freezing, and balance problems may be persistent even after DBS surgery.
Deep Brain Stimulation For Parkinson’s May Help Long Term
HealthDay Reporter
THURSDAY, June 3, 2021 — Parkinson’s disease patients can get symptom relief with deep brain stimulation therapy that lasts over the long term, a new study shows.
Over 15 years, patients who received DBS, which requires surgical implantation, had significant improvement in motor symptoms and less need for medication, researchers found.
“Our study, for the first time, supports the efficacy of deep brain stimulation in the very long term — 15 years after surgery and 25 years since Parkinson’s diagnosis,” said senior researcher Dr. Elena Moro, director of the Movement Disorders Unit at Grenoble Alpes University in France.
“Indeed, after an average of 15 years after surgery, patients could experience improvement, compared to before surgery,” she said. “Moreover, we could still observe a marked reduction of anti-Parkinson’s medication and improvement of quality of life, compared with before the intervention.”
Patients with Parkinson’s disease no longer make dopamine, which affects their speech, walking and balance. Symptoms can be partially relieved by the drug levodopa, which temporarily restores dopamine.
But as levels of dopamine fluctuate during the day, patients can suffer from dyskinesia, a side effect of levodopa that can cause twisting, swaying or head bobbing.
For the study, Moro’s team collected data on 51 patients being treated with DBS. On average, they had the device for 17 years.
More information
Show Sources
Recommended Reading: Parkinson’s Medication For Restless Leg
What Happens After Surgery
After surgery, you may take your regular dose of Parkinson’s medication immediately. You are kept overnight for monitoring and observation. Most patients are discharged home the next day.
During the recovery time after implanting the electrodes, you may feel better than normal. Brain swelling around the electrode tip causes a lesion effect that lasts a couple days to weeks. This temporary effect is a good predictor of your outcome once the stimulator is implanted and programmed.
About a week later, you will return to the hospital for outpatient surgery to implant the stimulator in the chest/abdomen. This surgery is performed under general anesthesia and takes about an hour. Patients go home the same day.
Step 7: implant the stimulator You will be taken to the OR and put to sleep with general anesthesia. A portion of the scalp incision is reopened to access the leads. A small incision is made near the collarbone and the neurostimulator is implanted under the skin. The lead is attached to an extension wire that is passed under the skin of the scalp, down the neck, to the stimulator/battery in the chest or abdomen. The device will be visible as a small bulge under the skin, but it is usually not seen under clothes.
You will have lifting and activity restrictions for 6-8 weeks while the incisions heal. Follow all discharge instructions and the neck exercises provided. Incision pain can be managed with medication.
What Is The Success Rate Of Deep Brain Stimulation
In general, deep brain stimulation is usually successful. The success rate depends on the condition involved. For conditions like epilepsy and Parkinson’s disease, DBS is very effective. More research is necessary for conditions where DBS is experimental before experts know if DBS is likely to help.
Read Also: Does Parkinson’s Cause Tinnitus
What Happens After Deep Brain Stimulation
Your healthcare provider will schedule a follow-up appointment that will take place within a few weeks of the pulse generator implantation procedure. At this appointment, they’ll start programming the pulse generator.
All pulse generators now in use have a wireless antenna built-in. That allows your healthcare provider to access and program the device from outside your body. Finding the right settings for the pulse generator may take some time and additional visits for adjustments.
Most pulse generators have special batteries that have long lifespans. Standard batteries for these devices last about three to five years. Some devices use rechargeable batteries, which can last about nine years. Replacing the battery also takes a surgery procedure, but this is usually shorter and quicker than the original surgery to implant the pulse generator. You’ll still go home the same day for battery replacements.
Testing Before Deep Brain Stimulation
For patients with Parkinsons disease, the doctor must confirm that the PD is levodopa-responsive and determine which symptoms are most likely to respond to DBS and discuss these with the patient.
To accomplish these two objectives, the movement disorders neurologist will examine the patient in the absence of his or her PD medications, then again after having taken them. Seeing the effect of PD medications on the movement and non-motor symptoms helps the physician and patient identify good target symptoms for DBS.
A cognitive assessment can help determine a persons ability to participate in the procedure, which involves providing feedback to the doctor during surgery and throughout the neurostimulator adjustment process. This assessment also informs the team of the risk of having worsened confusion or cognitive problems following the procedure.
Some hospitals also perform an occupational therapy review or speech, language and swallowing assessment. A psychiatrist may examine the person to determine if a condition such as depression or anxiety requires treatment before the DBS procedure.
Read Also: Adaptive Silverware For Parkinsons
Recommended Reading: Toothbrush For Parkinson’s Patients
How Does Deep Brain Stimulation For Parkinsons Work
Deep brain stimulation works by modifying abnormal electrical activity in the brain. It was first approved for Parkinsons tremors in 1997 and has become an established treatment to control additional motor symptoms of Parkinsons disease.
DBS involves three main components:
- Leads: Leads are implanted in the brain in a region responsible for motor activity.
- Implantable pulse generator : A separate procedure is performed to implant a battery-operated device in the chest or in the abdomen. An IPG is similar to a pacemaker for the heart and has been coined by some as a pacemaker for the brain.
- Extension: A thin, insulated wire is passed beneath the skin between the leads and implantable pulse generator to deliver the electrical stimulation from the pulse generator to the leads.
The target area in the brain is first identified by magnetic resonance imaging or computed tomography . Then, the leads are placed via small holes that a surgeon drills in the skull.
This is considered a minimally invasive surgery that is done in the operating room with local anesthesia. It usually requires an overnight stay.
The IPG is inserted in a separate surgical procedure in the operating room roughly a week later.
After a few weeks, a neurologist begins to program the unit. This process can take several additional weeks to months. When this is completed, people are able to manage the device with a handheld remote control.
Surgical Relief For Neurological Disorders
When medication isnt enough to control symptoms of certain neurological disorders, deep brain stimulation can be a viable option for symptom relief. For those who experience tremors, stiffness, slowness and involuntary movements, performance of daily tasks can be difficult or frustrating.
While DBS doesnt provide a cure, it can be used to significantly control symptoms for a number of conditions for many years. For example, DBS is the most commonly performed surgical treatment for Parkinsons disease and can help reduce symptoms such as tremor, stiffness and slowed movement while allowing a reduction in medication. Often, the reduction in medication improves many side effects.
Also Check: Breathing Exercises For Parkinson’s