Medicines For Parkinsons Disease
Medicines can help treat the symptoms of Parkinsons by:
- Increasing the level of dopamine in the brain
- Having an effect on other brain chemicals, such as neurotransmitters, which transfer information between brain cells
- Helping control non-movement symptoms
The main therapy for Parkinsons is levodopa. Nerve cells use levodopa to make dopamine to replenish the brains dwindling supply. Usually, people take levodopa along with another medication called carbidopa. Carbidopa prevents or reduces some of the side effects of levodopa therapy such as nausea, vomiting, low blood pressure, and restlessness and reduces the amount of levodopa needed to improve symptoms.
People living with Parkinsons disease should never stop taking levodopa without telling their doctor. Suddenly stopping the drug may have serious side effects, like being unable to move or having difficulty breathing.
The doctor may prescribe other medicines to treat Parkinsons symptoms, including:
- Dopamine agonists to stimulate the production of dopamine in the brain
- Enzyme inhibitors to increase the amount of dopamine by slowing down the enzymes that break down dopamine in the brain
- Amantadine to help reduce involuntary movements
- Anticholinergic drugs to reduce tremors and muscle rigidity
Parkinsons Disease Medication: What To Know
Over the years, the production of new drugs for Parkinsons disease and proper Sensitization on how to use them and older drugs have helped manage the progression of the condition. Parkinsons disease and drugs Experts have made Many significant changes over the past few years in managing Parkinsons disease …
How Is Parkinson Disease Treated
Parkinson disease can’t be cured. But there are different therapies that can help control symptoms. Many of the medicines used to treat Parkinson disease help to offset the loss of the chemical dopamine in the brain. Most of these medicines help manage symptoms quite successfully.
A procedure called deep brain stimulation may also be used to treat Parkinson disease. It sends electrical impulses into the brain to help control tremors and twitching movements. Some people may need surgery to manage Parkinson disease symptoms. Surgery may involve destroying small areas of brain tissue responsible for the symptoms. However, these surgeries are rarely done since deep brain stimulation is now available.
Don’t Miss: Voice Exercises For Parkinson’s Patients
Support For People Living With Parkinsons Disease
While the progression of Parkinsons is usually slow, eventually a persons daily routines may be affected. Activities such as working, taking care of a home, and participating in social activities with friends may become challenging. Experiencing these changes can be difficult, but support groups can help people cope. These groups can provide information, advice, and connections to resources for those living with Parkinsons disease, their families, and caregivers. The organizations listed below can help people find local support groups and other resources in their communities.
So What Relationship Do The Health Effects Of Parkinsons Have With Death
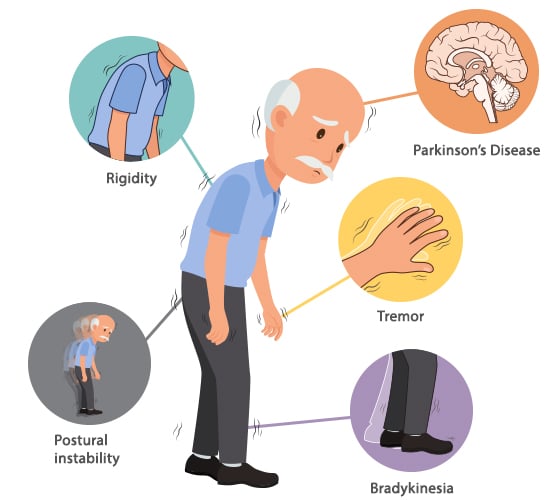
The adverse health effects of Parkinsons are serious, and you should work with your doctor to explore the many ways to manage your Parkinsons symptoms. However, Parkinsonian symptoms do not directly cause death, but they do increase your risk for other factors that can lead to death. For instance, one of the symptoms of Parkinsons is postural instability which leads to an increased risk of falls. Postural instability by itself will not cause death but falls can lead to serious injuries that can result in death. So, Parkinsons symptoms can increase the risk for death but will not cause death in and of itself.
This is an important distinction to make because instead of seeing Parkinsons as a death sentence we should look at it as a manageable risk factor the same way we look at dieting. A poor diet will not kill you, but it will increase your risk for developing diseases that can. We should think of Parkinsons in the same way, that if we manage our symptoms of Parkinsons through exercise, medication, etc. we decrease the likelihood of risk factors that lead to death.
Read Also: Idiopathic Parkinson’s Disease Symptoms
Parkinsons Disease: Causes Symptoms And Treatments
Parkinsons disease is a brain disorder that causes unintended or uncontrollable movements, such as shaking, stiffness, and difficulty with balance and coordination.
Symptoms usually begin gradually and worsen over time. As the disease progresses, people may have difficulty walking and talking. They may also have mental and behavioral changes, sleep problems, depression, memory difficulties, and fatigue.
While virtually anyone could be at risk for developing Parkinsons, some research studies suggest this disease affects more men than women. Its unclear why, but studies are underway to understand factors that may increase a persons risk. One clear risk is age: Although most people with Parkinsons first develop the disease after age 60, about 5% to 10% experience onset before the age of 50. Early-onset forms of Parkinsons are often, but not always, inherited, and some forms have been linked to specific gene mutations.
Prevention Of Motor Complications
Strategies to delay or prevent the development of motor complications represent an unmet need in the treatment of PD. As yet, no therapies exist which have been proven to slow the progression of disease. Such disease-modifying therapies would clearly represent the most impactful interventions to prevent the development of motor complications, and the state of work on these efforts is described elsewhere. Other strategies that have been considered in an attempt to delay motor complications include utilizing existing symptomatic therapies as part of levodopa-sparing regimens and efforts to achieve continuous dopaminergic stimulation .
Choice of Initial Therapy: Levodopa-Sparing Therapies
Based on these observations, most experts introduce levodopa when the patient requires it for symptomatic and functional benefit as evidence is lacking to indicate that it should be started immediately upon diagnosis or that it should be delayed as long as possible. However, there is general consensus, with good supportive evidence, that levodopa doses above those required for adequate control of symptoms should be avoided as higher doses may unnecessarily increase the risk for motor fluctuations and dyskinesia.
Continuous Dopaminergic Stimulation
Also Check: History Of Parkinson’s Disease
Does Parkinsons Affect Your Lifespan
Parkinsons research and treatments have come a long way, so much so that the average life span of a person with Parkinsons is the same or near the same as someone without Parkinsons disease. However, the lifespan of a person can vary widely based upon that persons health choices, such as their diet, exercise routine, if they have a history of smoking and many other factors. So, for most people with Parkinsons, as long as you focus on managing your Parkinsons disease and make healthy choices your lifespan should not be shortened.
Illustrative Case Of Acute Psychosis
An 80-year-old woman with Parkinsons disease was brought by her caregiver to the hospital emergency room because of marked agitation and paranoid ideation. She had physically attacked a staff member at the nursing home where she had been recently placed. One year earlier she developed visual hallucinations, initially well controlled with quetiapine . In the last 6 months she had developed frequent delusions with loss of insight. On admission to the Neurology ward she was taking 300mg per day of levodopa and quetiapine . Her cognitive state was normal. Other medical conditions known to cause acute psychosis were ruled out. Several treatment changes were tried. First, levodopa dose was halved without any significant motor worsening or improvement in hallucinations or delusions. In consequence, quetiapine was switched to clozapine , prompting improvement in psychiatric symptoms. In the end, levodopa was raised back to 300mg a day and clozapine was maintained. A few months later she had developed cognitive decline and rivastigmine was added.
-
Learning points: Psychosis exacerbation after nursing home placement loss of insight and delusions as severity markers before adding antipsychotic therapy for psychosis consider dopaminergic drug reduction, especially in advanced disease stages after acute episode resolution check cognitive status.
Read Also: Parkinson’s And Dry Cough
What Are The Symptoms
The best-known symptoms of Parkinson’s disease involve loss of muscle control. However, experts now know that muscle control-related issues aren’t the only possible symptoms of Parkinson’s disease.
Motor-related symptoms
Motor symptoms which means movement-related symptoms of Parkinsons disease include the following:
Additional motor symptoms can include:
- Blinking less often than usual. This is also a symptom of reduced control of facial muscles.
- Cramped or small handwriting. Known as micrographia, this happens because of muscle control problems.
- Drooling. Another symptom that happens because of loss of facial muscle control.
- Mask-like facial expression. Known as hypomimia, this means facial expressions change very little or not at all.
- Trouble swallowing . This happens with reduced throat muscle control. It increases the risk of problems like pneumonia or choking.
- Unusually soft speaking voice . This happens because of reduced muscle control in the throat and chest.
Non-motor symptoms
Several symptoms are possible that aren’t connected to movement and muscle control. In years past, experts believed non-motor symptoms were risk factors for this disease when seen before motor symptoms. However, theres a growing amount of evidence that these symptoms can appear in the earliest stages of the disease. That means these symptoms might be warning signs that start years or even decades before motor symptoms.
Non-motor symptoms include:
Stages of Parkinsons disease
Drastic Changes In Blood Pressure
PD can cause drastic changes in blood pressure because it affects the autonomic nervous system, which controls blood flow and blood pressure. Unlike other parts of the body, we do not have control over our nervous system. When PD occurs, it takes over the nervous system creating changes in blood pressure throughout the day, says Medical News Today.
These drastic changes in blood pressure can lead to orthostatic hypertension, a drop in blood pressure that causes a person to feel dizzy or faint when they stand up, writes the source. It can also lead to falls and fainting. Another common problem is low blood pressure, also known as hypotension. High blood pressure can also be a problem for some people. Any type of wild fluctuation between the two can lead to heart problems. To help treat this complication and avoid any drastic changes, doctors can sometimes prescribe medications that will help stabilize blood pressure. Patients can also invest in a pair of compression stockings which may also be helpful.
Also Check: Can Medication Cause Parkinson’s
Temperature Sensitivity In Multiple Sclerosis Causes Symptoms And Precautions
Overview MS, which stands for multiple sclerosis , is a central nervous system disease, including the brain and spinal cord. It is a condition in which the immune system attacks the protective sheath that covers nerve fibers, resulting in a problem in communication between the brain and other parts of …
Clinical Management Of Motor Complications
In early PD, treatment with CD-LD IR 25100 mg administered TID typically provides relatively sustained relief of motor symptoms through the day with benefit lasting from dose to dose. Once the duration of symptomatic benefit shortens and patients begin to experience OFF episodes, treatment strategies are available to mitigate the impact of these motor fluctuations.
If a patient is experiencing wearing off motor fluctuations on CD-LD IR, a common strategy is to increase the frequency of administration. Many patients will experience resolution of mild wearing off when going from CD-LD IR TID to QID . If wearing off fluctuations are still present on a QID regimen, further shortening of the interdose interval can be attempted, but such regimens are a challenge for patients and adherence decreases . Therefore, to reduce motor fluctuations in patients who are on CD-LD IR QID, adding an adjunctive medication or switching to CD-LD ER may be advantageous. In our practice, we commonly add one or possibly two adjunctive therapies first, and if that is insufficient, we then favor converting the levodopa regimen to CD-LD ER.
Available adjunctive medications include MAO-B inhibitors , mixed selective MAO-B inhibitors and ion channel inhibitors , COMT inhibitors , an adenosine 2A receptor antagonist , and dopamine agonists . The choice of adjunctive medication typically depends on a combination of patient factors and medication characteristics .
Also Check: Cleveland Clinic Parkinson’s Center Of Excellence
How Is Parkinson Disease Diagnosed
Parkinson disease can be hard to diagnose. No single test can identify it. Parkinson can be easily mistaken for another health condition. A healthcare provider will usually take a medical history, including a family history to find out if anyone else in your family has Parkinsons disease. He or she will also do a neurological exam. Sometimes, an MRI or CT scan, or some other imaging scan of the brain can identify other problems or rule out other diseases.
Dont Miss: On And Off Phenomenon
Prevalence Incidence And Risk Factors For Motor Complications
Nearly all patients develop motor fluctuations and LID by 15 to 20 years from time of diagnosis . However, prevalence and incidence figures through the course of PD vary depending on the study methodology employed and by the predominant treatment strategies of the time. Early literature suggested that approximately 10% of patients per year following initiation of treatment with levodopa develop motor fluctuations, with 40% of patients developing these complications within 46 years of treatment . A large cross-sectional study of 617 patients with PD found an overall prevalence of wearing off of 57% as assessed by neurologists and 67% as assessed by a patient-completed questionnaire . Of patients with disease duration < 2.5 years, wearing off was identified in 41.8% by the WOQ-19 and in 21.8% by neurologists, indicating that motor fluctuations can emerge as early as several months to a few years after the initiation of levodopa, as has also been observed in other studies . A retrospective analysis of an incident cohort of PD found estimated rates of dyskinesia of 30% by 5 treatment years and 59% by 10 treatment years .
Also Check: Speech Therapy For Parkinson’s Disease
Parkinsons Disease And The Gut
Parkinsons disease is primarily a neurological condition however, symptoms also manifest outside of the brain itself, including within the gut . This article aims to provide a simple background to Parkinsons disease, and some insights into how these GI symptoms may arise and how we can treat them. Increased awareness of these often-overlooked GI issues in Parkinsons might lead to better understanding of the condition by researchers, as well as improved treatment and quality of life for patients.
What Tests Will Be Done To Diagnose This Condition
When healthcare providers suspect Parkinsons disease or need to rule out other conditions, various imaging and diagnostic tests are possible. These include:
New lab tests are possible
Researchers have found possible ways to test for possible indicators or Parkinsons disease. Both of these new tests involve the alpha-synuclein protein but test for it in new, unusual ways. While these tests cant tell you what conditions you have because of misfolded alpha-synuclein proteins, that information can still help your provider make a diagnosis.
The two tests use the following methods.
- Spinal tap. One of these tests looks for misfolded alpha-synuclein proteins in cerebrospinal fluid, which is the fluid that surrounds your brain and spinal cord. This test involves a spinal tap , where a healthcare provider inserts a needle into your spinal canal to collect some cerebrospinal fluid for testing.
- Skin biopsy. Another possible test involves a biopsy of surface nerve tissue. A biopsy includes collecting a small sample of your skin, including the nerves in the skin. The samples come from a spot on your back and two spots on your leg. Analyzing the samples can help determine if your alpha-synuclein has a certain kind of malfunction that could increase the risk of developing Parkinsons disease.
Don’t Miss: Cold Hands Parkinson’s Disease
Who Does It Affect
The risk of developing Parkinsons disease naturally increases with age, and the average age at which it starts is 60 years old. Its slightly more common in men or people designated male at birth than in women or people designated female at birth .
While Parkinsons disease is usually age-related, it can happen in adults as young as 20 .
Living With Parkinson Disease
These measures can help you live well with Parkinson disease:
- An exercise routine can help keep muscles flexible and mobile. Exercise also releases natural brain chemicals that can improve emotional well-being.
- High protein meals can benefit your brain chemistry
- Physical, occupational, and speech therapy can help your ability to care for yourself and communicate with others
- If you or your family has questions about Parkinson disease, want information about treatment, or need to find support, you can contact the American Parkinson Disease Association.
Recommended Reading: Diseases Similar To Parkinsons
Also Check: Parkinson’s Disease Charity Donations
What Tests Are Used To Diagnose Narcolepsy
Overview Narcolepsy is a rare condition. According to the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke , it affects between 135,000 and 200,000 in the United States. Narcolepsy is a condition that causes one to feel sleepy during the day, thereby affecting your sleep-wake cycle. Proper diagnosis is required for
What Causes Parkinsons Disease
The most prominent signs and symptoms of Parkinsons disease occur when nerve cells in the basal ganglia, an area of the brain that controls movement, become impaired and/or die. Normally, these nerve cells, or neurons, produce an important brain chemical known as dopamine. When the neurons die or become impaired, they produce less dopamine, which causes the movement problems associated with the disease. Scientists still do not know what causes the neurons to die.
People with Parkinsons disease also lose the nerve endings that produce norepinephrine, the main chemical messenger of the sympathetic nervous system, which controls many functions of the body, such as heart rate and blood pressure. The loss of norepinephrine might help explain some of the non-movement features of Parkinsons, such as fatigue, irregular blood pressure, decreased movement of food through the digestive tract, and sudden drop in blood pressure when a person stands up from a sitting or lying position.
Many brain cells of people with Parkinsons disease contain Lewy bodies, unusual clumps of the protein alpha-synuclein. Scientists are trying to better understand the normal and abnormal functions of alpha-synuclein and its relationship to genetic mutations that impact Parkinsons andLewy body dementia.
Recommended Reading: Parkinson’s Best Treatment Centers