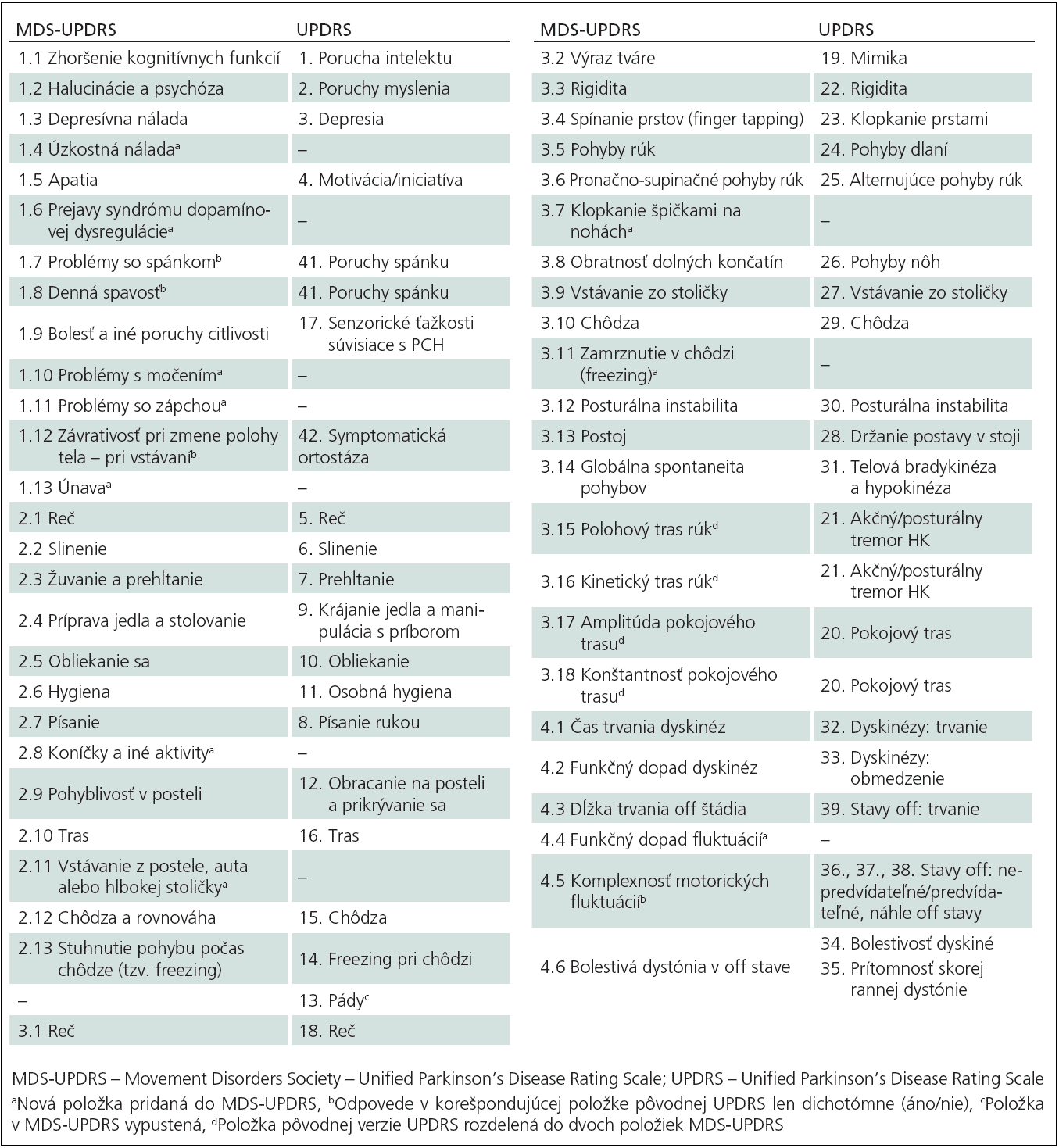
Unified Parkinsons Disease Rating Scale
The Unified Parkinsons Disease Rating Scale has four parts. Each part has multiple points that are individually scored, using zero for normal or no problems, 1 for minimal problems, 2 for mild problems, 3 for moderate problems, and 4 for severe problems.
These scores are tallied to indicate the severity of the disease, with 199 points being the worst and total disability and 0 meaning no disability.3
In 2001, the Movement Disorder Society updated the rating scale with involvement from patients and caregivers. The updated scale is referred to as the UPDRS-MDS, and it was published in 2008. It now includes the following sections:3
Iv Complications Of Therapy
A. DYSKINESIAS
32. Duration: What proportion of the waking day are dyskinesias present?
0 = None.
33. Disability: How disabling are the dyskinesias?
0 = Not disabling.
34. Painful Dyskinesias: How painful are the dyskinesias?
0 = No painful dyskinesias.
35. Presence of Early Morning Dystonia
0 = No
36. Are off periods predictable?
0 = No
37. Are off periods unpredictable?
0 = No
38. Do off periods come on suddenly, within a few seconds?
0 = No
39. What proportion of the waking day is the patient off on average?
0 = None
40. Does the patient have anorexia, nausea, or vomiting?
0 = No
41. Any sleep disturbances, such as insomnia or hypersomnolence?
0 = No 1 = Yes
42. Does the patient have symptomatic orthostasis?
0 = No
The Advantage Of Deep Learning
The dual-channel LSTM developed in our preliminary work provides only slightly higher performance than Gradient Tree Boosting with a 0.62 correlation vs. 0.61. However, transfer learning from the activity recognition dataset improves performance by providing a 10% higher correlation and 13% lower MAE when compared to Gradient Tree Boosting. This behavior indicates that temporal dependencies captured by the first two LSTM layers using hand-crafted features extracted from healthy subjects are beneficial to UPDRS-III estimation.
Another observation is that both the 1D and 2D CNN-LSTM networks outperform Gradient Tree with 0.70 and 0.67 correlation, respectively with greater than 10% increase in correlation, and 6.93 and 7.11 MAE, respectively, with a decrease of greater than 9% in MAE. These networks achieve comparable performance to the dual-channel LSTM with hand-crafted features, which means CNN could extract relevant data-driven features.
We also observe that the ensemble of the models based on hand-crafted and data-driven features improves the performance. The ensemble of multiple models is known to improve the regression results if the models solve different aspects of the given problem . Hence, we can conclude that the trained deep models are diverse and learn different views of the motion signals , and therefore, are necessary for successful UPDRS-III estimation.
Recommended Reading: Most Effective Treatment For Parkinson’s
Is Theracycle Safe To Use
The Theracycle is designed specifically for users with movement disorders and has many safety features. Its motion can be stopped instantly using either a push of a button or a pull of the safety cord. The structural steel frame can support up to 350lbs and cast iron parts are extremely durable and built to last. The seat is extra large for added comfort, safety and stability.
Parkinsons Disease With Mild Cognitive Impairment May Has A Lower Risk Of Cognitive Decline After Subthalamic Nucleus Deep Brain Stimulation: A Retrospective Cohort Study
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Beijing Tiantan Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing, China
- 2Beijing Key Laboratory of Neurostimulation, Beijing, China
- 3Department of Functional Neurosurgery, Beijing Neurosurgical Institute, Capital Medical University, Beijing, China
Background: The cognitive outcomes induced by subthalamic nucleus deep brain stimulation remain unclear, especially in PD patients with mild cognitive impairment . This study explored the cognitive effects of STN-DBS in PD patients with MCI.
Methods: This was a retrospective cohort study that included 126 PD patients who underwent STN-DBS all patients completed cognitive and motor assessments before and at least 6 months after surgery. Cognitive changes were mainly evaluated by the Montreal cognitive assessment scale and the seven specific MoCA domains, including visuospatial/executive function, naming, attention, language, abstract, delayed recall, and orientation. Motor improvement was evaluated by the UPDRS-III. Cognitive changes and motor improvements were compared between PD-MCI and normal cognitive patients. Logistic regression analyses were performed to explore predictors of post-operative cognitive change.
PD-MCI patients are at a lower risk of cognitive decline after STN-DBS compared with PD-NC patients.
Also Check: How Long Can A Person Live With Parkinson’s
Limitations And Future Work
Our algorithm provides overall high performance for UPDRS-III estimation using patients free body movement data. However, we notice that the model underestimates high UPDRS-scores, as shown in Fig. . This is because of the imbalanced data distribution as there are only nine rounds of ADL with the UPDRS III score of higher than 40, and only one is above 50 . Parisi et al. reported a similar limitation due to the imbalance distribution of their training data toward the mean score of UPDRS III. Collecting more data in a home setting with a uniform data distribution is expected to improve our algorithms performance further and consists of the main aspect of our future work.
Episode : Staging Pd Updrs: What It Measures And What Your Score Means
Disease rating scales give clinicians a snapshot in time of the severity of a disease, how it may be affecting a patient, and areas where therapies may be applied. Put together over time, rating scale results can indicate the progression of a disease and possibly help with long term planning. In the case of Parkinsons disease , the Hoehn and Yahr scale, published in 1967, describes the progression of PD according to five stages from earliest to most advanced, based on severity of symptoms and level of disability. The Unified Parkinsons Disease Rating Scale consists of four parts, each of which encompasses several subparts to give an overall total score reflecting the severity of a persons disease. In 2001, the Movement Disorder Society took input from patients and care partners to incorporate into the UPDRS what was important to them and in 2008 published the revised MDS-UPDRS rating scale. Besides evaluating any one persons disease, rating scales provide criteria for enrollment in clinical trials and help to compare trials and outcomes.
Released: June 16, 2020
You May Like: The Progression Of Parkinson’s
Using Cognitive Pretesting In Scale Development For Parkinson’s Disease: The Movement Disorder Society Unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale Example
Article type: Research Article
Authors: Tilley, Barbara C. | LaPelle, Nancy R. | Goetz, Christopher G. | Stebbins, Glenn T. | on behalf of the MDS-UPDRS Task Force
Affiliations: Division of Biostatistics, University of Texas School of Public Health at Houston, Houston, TX, USA | Division of Preventive and Behavioral Medicine, University of Massachusetts, Worcester, Massachusetts, USA | Department of Neurological Sciences, Rush University Medical Center, Chicago, Illinois, USA
Note: Correspondence to: Barbara C. Tilley, Ph.D., Division of Biostatistics, University of Texas School of Public Health at Houston, 1200 Pressler Drive, RAS 833E, Houston, TX 77030, USA. Tel.: +1 713 500 9564 Fax: +1 713 500 9525 E-mail:
Keywords: Cognitive pretesting, Parkinson’s disease, scale development, Modified Unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale
DOI: 10.3233/JPD-130310
Journal: Journal of Parkinson’s Disease, vol. 4, no. 3, pp. 395-404, 2014
I Mentation Behavior And Mood
1. Intellectual Impairment
0 = None. 1 = Mild. Consistent forgetfulness with partial recollection of events and no other difficulties. 2 = Moderate memory loss, with disorientation and moderate difficulty handling complex problems. Mild but definite impairment of function at home with need of occasional prompting. 3 = Severe memory loss with disorientation for time and often to place. Severe impairment in handling problems. 4 = Severe memory loss with orientation preserved to person only. Unable to make judgements or solve problems. Requires much help with personal care. Cannot be left alone at all.
2. Thought Disorder
0 = None. 2 = Benign hallucinations with insight retained. 3 = Occasional to frequent hallucinations or delusions without insight could interfere with daily activities. 4 = Persistent hallucinations, delusions, or florrid psychosis. Not able to care for self.
3. Depression
1 = Periods of sadness or guilt greater than normal, never sustained for days or weeks. 2 = Sustained depression . 3 = Sustained depression with vegetative symptoms . 4 = Sustained depression with vegetative symptoms and suicidal thoughts or intent.
4. Motivation/Initiative
1 = Less assertive than usual more passive. 2 = Loss of initiative or disinterest in elective activities. 3 = Loss of initiative or disinterest in day to day activities. 4 = Withdrawn, complete loss of motivation.
Read Also: Parkinson’s And Loss Of Taste
Assessments For Geriatric Symptom Complaints
Demographic characteristics , cardiometabolic conditions , the history of smoking/alcohol consumption, drug prescriptions for DLB/PDD were recorded. A battery of standardized instruments, including the Chinese version of the MMSE , Montreal Cognitive Assessment , activities of daily living and NPI, was used to evaluate cognitive function status, activities of daily living and neuropsychiatric symptoms respectively. The scores of C-MMSE and MoCA range 0 to 30 . The NPI comprises 12 items and provided by their caregivers. Each subscale ranges between 0 and 12 and the total composite score between 0 and 144. The Chinese version of ADL consists of 20 items to evaluate the function of physical self-maintenance and instrumental activities , with the total scores between 20 and 80 .
Patients were routinely evaluated the geriatric symptoms and conditions in our clinic, including OH, constipation, urinary symptoms, hyperhidrosis , falls, FoF, delusion, depression, anxiety, apathy, loss of appetite, insomnia, and excessive daytime sleepiness . The measurement instruments were described as below:
Why Does The Theracycle Cost More Than A Basic Exercise Bike
The Theracycle is not a simple or traditional exercise bike. The biggest difference is the unique motorized technology and the 15-speed variable gearbox, which allows you to attain and maintain a significantly faster cadence for a longer period than you can achieve using a traditional stationary or road bike. A Theracycle has been proven to reduce neurological symptoms and improve motor function and mobility.
Additionally, the bike is custom engineered for the specific needs of people with movement disorders, not only in its open walk-though design, but also when it comes to durability and, most importantly, stability. The Theracycle is built on a very sturdy, heavy structural steel frame. It has a low center of gravity by design, which is ideal for those with balance, dexterity or gait issues providing a safe and secure exercise option in the comfort of your own home. Also important is the motor-assisted handlebar which provides both core and upper body exercise with a repetitive rowing motion for a full-body workout. A Theracycle provides a meditative and relaxing option for both mental and physical therapy that is low impact to your joints and muscles.
Recommended Reading: How To Prevent Parkinson’s Dementia
What Are The Theracycle Specifications
Theracycle 100
20 W x 44 L x 57 H 240 lbs. Boxed for shipping 240 lbs
The electrical cord on all models is 9-feet long.
The Theracycle is a custom product, made in the USA by hand in Franklin, MA.
We first speak with every potential customer to assess their needs. This allows us to recommend with confidence the model that will immediately bring you the best result. During this conversation, we can also determine if customization is necessary. Our sales specialists do not work on commission. They are well informed about your condition and truly want to help you live the best life.
To speak to a sales specialist, please call us at , MondayFriday from 8:305:00 EST.
During this call you will be asked for information on where to ship, the riders height and weight for fitting, along with a credit card, which will be held securely until your unit is produced. Lead times vary, your sales specialist will let you know the expected ship window.
After your order has been placed, you will receive a sales order confirming your sale and your Theracycle will be placed into production.
Once packed and ready for shipment, your credit card will be charged. You will then receive an email with a copy of the paid invoice, tracking information and a link to an informational page on our website with details on what to expect next.
Theracycle Therapy Products are made in the USA and shipped from Franklin, MA.
Comparison To Related Work
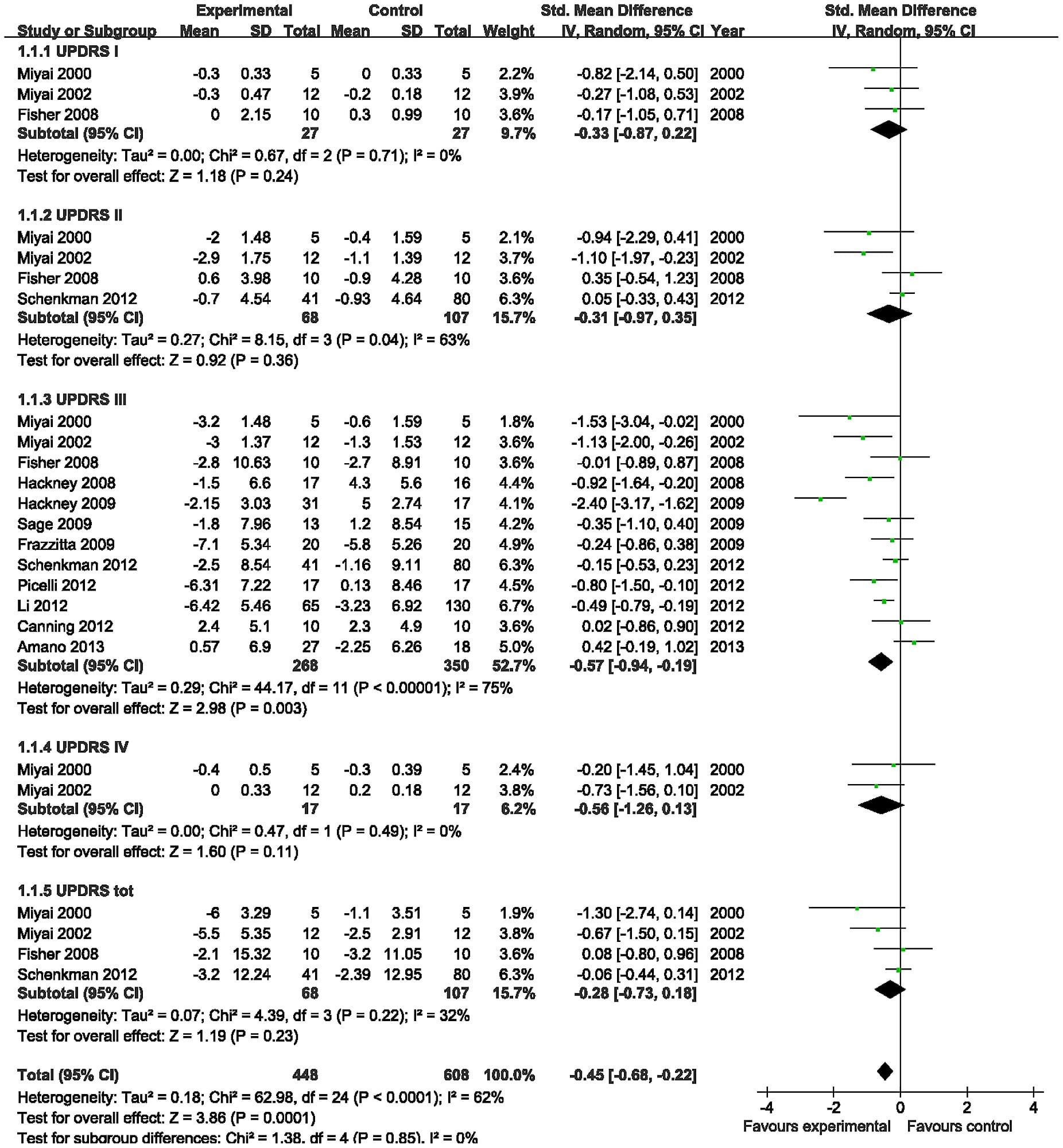
A review of the methods proposed for estimating the severity of PD is shown in Table . Comparing our algorithm to task-dependent approaches indicates that our method provides comparable performance with the advantage of not constraining PwPs activities. For example, it has a better correlation than Ref. with -0.56, equal or slightly lower than Refs. and lower than Ref. with 0.88. However, it is worth mentioning that the work in Ref. is based on performing a series of tasks using a smartphone application, while ours is solely based on movement data patterns.
Table 2 Proposed methods in the literature for estimating the severity of PD represented by UPDRS III
Recommended Reading: Can Lead Poisoning Cause Parkinson’s
Unobtrusive Estimation Of Updrs Iii
We hypothesized that advanced machine-learning algorithms could estimate UPDRS III from patients free body movements as collected using two wearable sensors placed on the upper and lower extremities. Our analysis indicated such a possibility with a high correlation of \\) and low MAE = 5.95 when using an ensemble of three deep-learning models. Most of the existing work for UPDRS III estimation requires PwPs active engagement to perform the specific tasks used in the UPDRS-III procedure . Unlike these approaches, our algorithm could estimate UPDRS III as the patients performed a variety of ADL without the need for performing constrained tasks. As a result, our system has the potential to be translated into unobtrusive home-based monitoring for continuous assessments of UPDRS III. It can track changes in motor fluctuations due to the medication wearing-off effect, as shown in Fig. , and tracking the response to medication, as shown in Fig. .
Unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale
| Unified Parkinson’s disease rating scale | |
|---|---|
| Purpose | used to follow the longitudinal course of Parkinson’s disease |
The unified Parkinson’s disease rating scale is used to follow the longitudinal course of Parkinson’s disease. The UPD rating scale is the most commonly used scale in the clinical study of Parkinson’s disease.
The UPDRS is made up of these sections:
- Part I: evaluation of mentation, behavior, and mood
- Part II: self-evaluation of the activities of daily life including speech, swallowing, handwriting, dressing, hygiene, falling, salivating, turning in bed, walking, and cutting food
- Part III: clinician-scored monitored motor evaluation
- Part IV: complications of therapy
- Part V: Hoehn and Yahr staging of severity of Parkinson’s disease
- Part VI: Schwab and England ADL scale
These are evaluated by interview and clinical observation. Some sections require multiple grades assigned to each extremity.
Clinicians and researchers alike use the UPDRS and the motor section in particular to follow the progression of a person’s Parkinson’s disease. Scientific researchers use it to measure benefits from a given therapy in a more unified and accepted rating system. Neurologists also use it in clinical practice to follow the progression of their patients’ symptoms in a more objective manner.
Read Also: Parkinson’s Non Motor Symptoms
Assessments For Core Clinical Features
Fluctuating cognition
The Mayo Fluctuations Composite Scale was used to confirm the presence of cognitive fluctuations, with three or more yes responses required for structured questions from caregivers .
Visual hallucinations
Specifically formed and detailed VH and illusions, that were complained about by the patient and/or caregiver were determined by confirmation and quantification according to the hallucinations item of the NPI . The chief complaint of seeing people, children or animals that were not present was recorded as visual hallucination.
Parkinsonism
One or more spontaneous cardinal features of parkinsonism included bradykinesia , rest tremor or rigidity, diagnosed by the motor section of the Movement Disorders Society Unified Parkinsons Disease Rating Scale .
Rapid eye movement sleep behavior disorder : This was confirmed by caregivers who mentioned five or more behaviors that are mentioned in the RBD screening questionnaire or someone who was diagnosed using an overnight video polysomnography . Totally, 37 patients with DLB and 45 patients with PDD underwent polysomnography and 83 patients with DLB and 81 patients with PDD underwent RBD-SQ to confirm RBD.
Therapeutic Role Of Rtms In Parkinson Disease
Early studies suggested an improvement in pointing performance and on the Unified Parkinson Disease Rating Scale after rTMS to the motor cortex.101 Subthreshold rTMS applied to the motor cortex at both 0.5 Hz and 10 Hz improved motor performance.102 However, such changes lasted only for minutes. A long-lasting effect of rTMS may be obtained with repeated application over a period of days. In a randomized study, patients receiving 5-Hz rTMS to the motor cortex experienced improvements in the UPDRS motor scores, walking speed, and a self-assessment scale that persisted for over 1 month.103 In a double-blind, placebo-controlled study, rTMS over 4 weeks using four cortical targets in each session showed a therapeutic effect that lasted for at least 1 month after treatment ended.104
Low-frequency rTMS studies, by contrast, showed no significant reduction in motor UPDRS but may be a potential treatment for levodopa-induced dyskinesias.106 A single session of rTMS at 1 Hz to the supplementary motor area bilaterally lowered the severity of dyskinesias for 30 minutes after stimulation.108 Repeated administration of 1-Hz rTMS of the motor cortex109,110 and cTBS to the cerebellum111 have shown promise also as potential treatment for levodopa-induced dyskinesias.
Don’t Miss: Most Common Symptoms Of Parkinson’s Disease
Parkinsons Disease Research Education And Clinical Centers
UNIFIED PARKINSON’S DISEASE RATING SCALE
Fahn S, Elton R, Members of the UPDRS Development Committee.In: Fahn S, Marsden CD, Calne DB, Goldstein M, eds.Recent Developments in Parkinson’s Disease, Vol 2. Florham Park, NJ. Macmillan Health Care Information 1987, pp 15 3-163, 293-304
I. MENTATION, BEHAVIOR AND MOOD
1. Intellectual Impairment
1 = Mild. Consistent forgetfulness with partial recollection of events and no other difficulties.2 = Moderate memory loss, with disorientation and moderate difficulty handling complex problems. Mild but definiteimpairment of function at home with need of occasional prompting.3 = Severe memory loss with disorientation for time and often to place. Severe impairment in handling problems.4 = Severe memory loss with orientation preserved to person only. Unable to make judgements or solve problems.Requires much help with personal care. Cannot be left alone at all.
2. Thought Disorder
0 = None.2 = “Benign” hallucinations with insight retained.3 = Occasional to frequent hallucinations or delusions without insight could interfere with daily activities.4 = Persistent hallucinations, delusions, or florrid psychosis. Not able to care for self.
3. Depression
1 = Periods of sadness or guilt greater than normal, never sustained for days or weeks.2 = Sustained depression .3 = Sustained depression with vegetative symptoms .4 = Sustained depression with vegetative symptoms and suicidal thoughts or intent.
4. Motivation/Initiative
5. Speech
6. Salivation