Fluid Tissue And Genetic Markers
Altered -synuclein metabolism in the central nervous system has a central role in the pathogenesis of PD and several studies have focused on determining -synuclein species in different fluids and tissues. The -synuclein is mainly expressed by neuronal cells as a cytoplasmic protein in its native form or in the oligomeric, phosphorylated form. However, because of its access to the extracellular space, it can be detected in cerebrospinal fluid . Longitudinal changes in CSF -synuclein and other biomarkers in PD have been examined in different cohorts with different results . In a recent study by Mollenhauser et al. CSF–synuclein in drug-naïve PD, healthy controls, and prodromal PD in the Parkinson’s Progression Markers Initiative up to 36-month follow-up was analyzed. According to the results, CSF -synuclein decreases early in the disease, preceding motor PD. However, CSF- -synuclein does not correlate with progression and therefore does not reflect ongoing dopaminergic neurodegeneration. Blood has been a disappointing target to-date because red cells contain large quantities of -synuclein, obscuring any theoretical difference in levels between patients and controls .
Table 2. Fluid, tissue, and genetic markers of prodromal Parkinson’s disease.
Genetic Cohorts
Starting Treatment In Early Parkinson’s Disease
The optimal time to start treatment in PD has been the source of much debate. In an open-label study of 198 patients with untreated PD, quality of life as measured by the Parkinson’s Disease Questionnaire-39 worsened in those left untreated, but was stable or improved in patients receiving dopaminergic treatment. In an observational study comparing Italian patients with PD who started levodopa early with those in Ghana where therapy was delayed, motor fluctuations and dyskinesia occurred at similar disease duration. This showed that duration of disease rather than treatment is a key determinant of motor complications. Therefore, delaying dopaminergic therapy does not avoid the development of motor complications and may be associated with poorer QoL. The recent delayed-start LEAP study showed no disease-modifying effect of levodopa in patients diagnosed < 2 years prior, but PDQ-39 score was improved in the blinded phase in those receiving early vs delayed treatment.
Software Analyzes Facial Expressions Hand Movements
Smiles are not the only behaviors that Hoque and his lab can analyze for early symptoms of Parkinsons disease or related disorders.
In collaboration with Ray Dorseya leading expert in Parkinsons disease and the David M. Levy Professor of Neurology at Rochesterand the Universitys Morris K. Udall Parkinson Disease Research Center, the researchers have developed a five-pronged test that neurologists could administer to patients sitting in front of their computer webcams hundreds of miles away.
This could be transformative for patients who are quarantined, immobile, or living in underdeveloped areas where access to a neurologist is limited, Hoque says.
In addition to making the biggest smile, and alternating it with a neutral expression three times, patients taking the test are also asked to:
- Read aloud a complex written sentence
- Touch their index finger to their thumb 10 times as quickly as possible
- Make the most disgusted look possible, alternating with a neutral expression, three times
- Raise their eyebrows as high as possible, then lower them as far as they can, three times slowly
Using machine learning algorithms, the computer program showswithin minutesa percentage likelihood from each of the tests whether the patient is showing symptoms of Parkinsons disease or related disorders.
Hence the importance of testing other expressions and movements, according to Ali, a former postdoctoral associate in Hoques lab who now is an associate data scientist at Sysco.
You May Like: Heart Failure And Parkinson’s Disease
When Should I See My Healthcare Provider Or When Should I Seek Care
You should see your healthcare provider as recommended, or if you notice changes in your symptoms or the effectiveness of your medication. Adjustments to medications and dosages can make a huge difference in how Parkinsons affects your life.
When should I go to ER?
Your healthcare provider can give you guidance and information on signs or symptoms that mean you should go to the hospital or seek medical care. In general, you should seek care if you fall, especially when you lose consciousness or might have an injury to your head, neck, chest, back or abdomen.
Anatomy Morphology And Functional Organization Of The Midbrain Da System
The complexity of the dopaminergic system seems to coincide with evolutionary development given that the number, size, and distribution, as well as receptor subtypes of dopaminergic neurons in the brain, increases alongside phylogenetic complexity . For example, dopaminergic terminal fields arising from midbrain clusters are more prominent and less segregated in the neocortex of primates than in rodents .
Dopaminergic neurons in the midbrain are mainly located in the SNc and VTA, although some smaller clusters have been found elsewhere, for instance, the dorsal and median raphe nuclei . In a classic article by Dahlstroem and Fuxe , SNc and VTA DA neurons were characterized based on their organization and projection patterns, which, in rat, can be found discrete clusters . SNc neurons innervate the dorsal and lateral striatum, thus forming a nigrostriatal pathway , and are necessary for the initiation and control of motor movements. Accordingly, the degeneration of this pathway is considered to be responsible for much of the motor dysfunction associated with PD. The VTA innervates the ventral striatum, nucleus accumbens, and limbic and cortical areas, and this way forms the mesolimbic and mesocortical pathways .
Don’t Miss: How Do You Know If Someone Has Parkinson’s Disease
Medicines For Parkinsons Disease
Medicines can help treat the symptoms of Parkinsons by:
- Increasing the level of dopamine in the brain
- Having an effect on other brain chemicals, such as neurotransmitters, which transfer information between brain cells
- Helping control non-movement symptoms
The main therapy for Parkinsons is levodopa. Nerve cells use levodopa to make dopamine to replenish the brains dwindling supply. Usually, people take levodopa along with another medication called carbidopa. Carbidopa prevents or reduces some of the side effects of levodopa therapy such as nausea, vomiting, low blood pressure, and restlessness and reduces the amount of levodopa needed to improve symptoms.
People living with Parkinsons disease should never stop taking levodopa without telling their doctor. Suddenly stopping the drug may have serious side effects, like being unable to move or having difficulty breathing.
The doctor may prescribe other medicines to treat Parkinsons symptoms, including:
- Dopamine agonists to stimulate the production of dopamine in the brain
- Enzyme inhibitors to increase the amount of dopamine by slowing down the enzymes that break down dopamine in the brain
- Amantadine to help reduce involuntary movements
- Anticholinergic drugs to reduce tremors and muscle rigidity
Causes Of Parkinson’s Disease
Parkinson’s disease is caused by a loss of nerve cells in part of the brain called the substantia nigra. This leads to a reduction in a chemical called dopamine in the brain.
Dopamine plays a vital role in regulating the movement of the body. A reduction in dopamine is responsible for many of the symptoms of Parkinson’s disease.
Exactly what causes the loss of nerve cells is unclear. Most experts think that a combination of genetic and environmental factors is responsible.
Read Also: Parkinson’s And Kidney Problems
The Role Of Aggregation Of Misfolded Proteins In Pd
Tau. Hyper-phosphorylation of tau can cause an accumulation of paired helical filaments of tau, known as neurofibrillary tangles , a hallmark pathology of different neurodegenerative diseases, including AD, frontotemporal dementia with parkinsonism , and progressive supra-nuclear palsy . The FTDP is linked to chromosome 17 , with p-tau accumulation occurring in cortex and SNpc areas . The p-tau can also be co-localized with LB, which is often associated with the development of sporadic PD . Similarly, in the case of FTDP, a mutation of gene coding for microtubule associated protein causes an increase in the accumulation of p-tau . The p-tau also has been linked to the LRRK2 gene mutations . Although NFTs are associated most closely with AD, they can co-localize with SNCA in LB and play an important role in destabilization of DA-neuronal architecture, which ultimately leads to rapid degeneration and death of DA neurons .
Fig. 4
Schematic diagram showing the steps that cause an accumulation of SNCA. Natural SNCA becomes misfolded under stress and is deposited as oligomers, small aggregates, or fibrils, which play a significant role in DA-neuronal loss in PD
What Are The Important Points Regarding Duodopa At The End Of Life
Duodopa is a continuous infusion of dopaminergic medication administered as a gel into the gut, pumped via a percutaneously inserted gastrostomy tube . There is a requirement for care of the stoma and PEG tube together with functioning of the pump by the patient or carer.41 It reduces the time in motor off periods in advanced PD and quality of life.42 There is evidence of effective treatment up until death from within a case series.43
Read Also: Sam Waterston Parkinsons
Also Check: Parkinson’s Disease Herbs Vitamins Supplements
The Evolution Of Critical Symptoms Involved In Diagnostic Procedures Of Pd
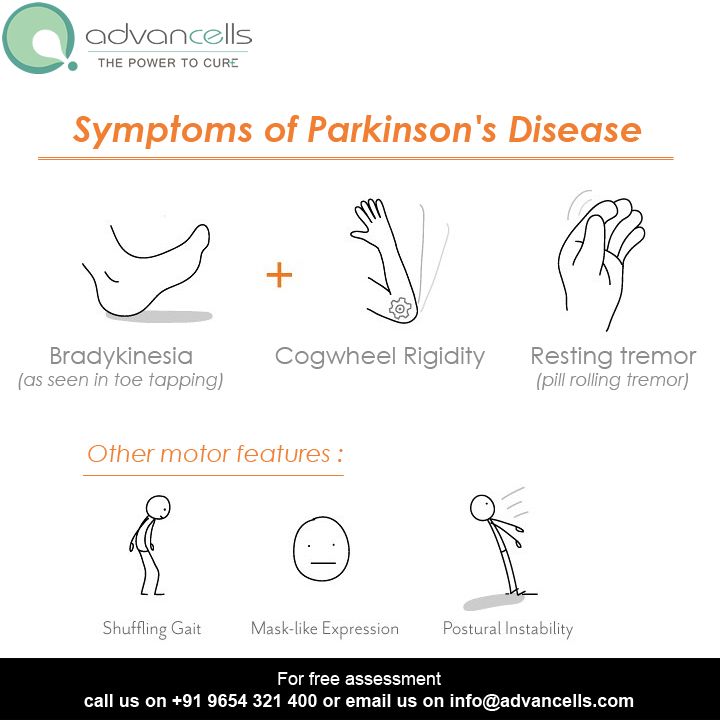
- Diagnostic criteria: presence of bradykinesia and at least one of the following symptoms: muscular rigidity, 46 Hz rest tremor and postural instability
- Exclusion criteria: history of repeated strokes or head injury, encephalitis, early severe autonomic involvement or dementia, Babinski sign, negative response to levodopa treatment and MPTP exposure
- Supportive criteria : unilateral onset, rest tremor, progressive course, persistent asymmetry, excellent response to dopaminergic therapy, levodopa-induced dyskinesia, positive levodopa response five years or more and clinical course of ten years or more
Stooping Or Hunching Over
Are you not standing up as straight as you used to? If you or your family or friends notice that you seem to be stooping, leaning or slouching when you stand, it could be a sign of Parkinson’s disease.What is normal? If you have pain from an injury or if you are sick, it might cause you to stand crookedly. Also, a problem with your bones can make you hunch over.
Recommended Reading: Infrared Helmet For Parkinson’s Disease
What Is Parkinson’s Disease
Parkinsons disease occurs when brain cells that make dopamine, a chemical that coordinates movement, stop working or die. Because PD can cause tremor, slowness, stiffness, and walking and balance problems, it is called a movement disorder. But constipation, depression, memory problems and other non-movement symptoms also can be part of Parkinsons. PD is a lifelong and progressive disease, which means that symptoms slowly worsen over time.
The experience of living with Parkinson’s over the course of a lifetime is unique to each person. As symptoms and progression vary from person to person, neither you nor your doctor can predict which symptoms you will get, when you will get them or how severe they will be. Even though broad paths of similarity are observed among individuals with PD as the disease progresses, there is no guarantee you will experience what you see in others.
Estimates suggest that Parkinsons affects nearly 1 million people in the United States and more than 6 million people worldwide.
For an in-depth guide to navigating Parkinsons disease and living well as the disease progresses, check out our Parkinsons 360 toolkit.
What Is Parkinson’s Disease?
Dr. Rachel Dolhun, a movement disorder specialist and vice president of medical communications at The Michael J. Fox Foundation, breaks down the basics of Parkinson’s.
Is Parkinsons Disease Fatal
Parkinsons disease itself doesnt cause death. However, symptoms related to Parkinsons can be fatal. For example, injuries that occur because of a fall or problems associated with dementia can be fatal.
Some people with Parkinsons experience difficulty swallowing. This can lead to aspiration pneumonia. This condition is caused when foods, or other foreign objects, are inhaled into the lungs.
- depression and anxiety
- mild cognitive impairment slight memory problems and problems with activities that require planning and organisation
- dementia a group of symptoms, including more severe memory problems, personality changes, seeing things that are not there and believing things that are not true
You May Like: What Causes Parkinson’s Syndrome
What Tests Will Be Done To Diagnose This Condition
When healthcare providers suspect Parkinsons disease or need to rule out other conditions, various imaging and diagnostic tests are possible. These include:
New lab tests are possible
Researchers have found possible ways to test for possible indicators or Parkinsons disease. Both of these new tests involve the alpha-synuclein protein but test for it in new, unusual ways. While these tests cant tell you what conditions you have because of misfolded alpha-synuclein proteins, that information can still help your provider make a diagnosis.
The two tests use the following methods.
- Spinal tap. One of these tests looks for misfolded alpha-synuclein proteins in cerebrospinal fluid, which is the fluid that surrounds your brain and spinal cord. This test involves a spinal tap , where a healthcare provider inserts a needle into your spinal canal to collect some cerebrospinal fluid for testing.
- Skin biopsy. Another possible test involves a biopsy of surface nerve tissue. A biopsy includes collecting a small sample of your skin, including the nerves in the skin. The samples come from a spot on your back and two spots on your leg. Analyzing the samples can help determine if your alpha-synuclein has a certain kind of malfunction that could increase the risk of developing Parkinsons disease.
Progress In The Treatment Of Parkinsons Disease
Despite the fact that 200 years passed since the discovery of PD, it was not until later in the 20th century that progress in the treatment of PD was achieved, predominantly due to the limited understanding of PD pathophysiology. Given Carlssons discoveries of DAs involvement in the 1950s, it became clear that PD development involved dopaminergic cell death and a decrease of DA in the striatum and other structures of the forebrain. The first steps towards treatment were made by Carlsson , who proposed targeting this DA deficiency to facilitate symptom reduction.
Also Check: Parkinson’s Treatment 10 Secrets To A Happier Life
Diagnosis Of Parkinson’s Disease
The diagnosis of PD is clinical and requires bradykinesia, defined as slowness of movement and decrement in amplitude or speed, usually assessed using finger tapping, foot tapping or pronationsupination hand movements. In addition, rest tremor or rigidity is required to confirm a parkinsonian syndrome. Tremor was absent at presentation in 30% in one series of pathologically proven PD. Patients with suspected PD should be referred quickly and untreated to a specialist in movement disorders for evaluation. Key points for discussion at diagnosis include the need to inform vehicle licensing agencies and insurers, signposting to written or web-based information on newly diagnosed PD, and provision of contact details for the local PD nurse specialist .
Current International Parkinson and Movement Disorder Society diagnostic criteria for Parkinson’s disease adapted from Postuma RB, Berg D, Stern M et al. MDS clinical diagnostic criteria for Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 2015 30:1591601. At least two supportive criteria and no red flags required for a diagnosis of clinically established Parkinson’s disease. Conditions in italics should be considered if the corresponding exclusion criteria or red flags are present.
How Soon After Treatment Will I Feel Better And How Long Will It Take To Recover
The time it takes to recover and see the effects of Parkinson’s disease treatments depends strongly on the type of treatments, the severity of the condition and other factors. Your healthcare provider is the best person to offer more information about what you can expect from treatment. The information they give you can consider any unique factors that might affect what you experience.
You May Like: Parkinson And Movement Disorder Alliance
What Are The Different Stages Of Parkinsons Disease
Each person with Parkinsons disease experiences symptoms in in their own unique way. Not everyone experiences all symptoms of Parkinsons disease. You may not experience symptoms in the same order as others. Some people may have mild symptoms others may have intense symptoms. How quickly symptoms worsen also varies from individual to individual and is difficult to impossible to predict at the outset.
In general, the disease progresses from early stage to mid-stage to mid-late-stage to advanced stage. This is what typically occurs during each of these stages:
Early stage
Early symptoms of Parkinsons disease are usually mild and typically occur slowly and do not interfere with daily activities. Sometimes early symptoms are not easy to detect or you may think early symptoms are simply normal signs of aging. You may have fatigue or a general sense of uneasiness. You may feel a slight tremor or have difficulty standing.
Often, a family member or friend notices some of the subtle signs before you do. They may notice things like body stiffness or lack of normal movement slow or small handwriting, lack of expression in your face, or difficulty getting out of a chair.
Mid stage
Mid-late stage
Standing and walking are becoming more difficult and may require assistance with a walker. You may need full time help to continue to live at home.
Advanced stage
Caregiver Burden And Questionnaire Assessment
The mean ZBI score shows a tendency to be lower in LCIG group compared to CSAI or CU group, even if no statistically significant difference was found among groups . The boxplot of the ZBI Score showed that LCIG and CU populations have a very similar distribution . The CSAI ZBI boxplot distribution is slightly wider but not statistically different . The aggregated results on ZBI scores never/rarely vs. sometimes/quite frequently/nearly always did not show a significant difference between groups for each question, except for the question number 6, regarding the negative influence of the assistance on the relationship with other relatives or friends in this case, a difference was found between LCIG and CSAI . The following variables were correlated with the ZBI score: caregivers change in capability to perform family duties and leisure activities,caregivers change in work,need of professional assistance,patients judgment on QoL, and caregivers judgment on QoL.18 The analysis of the distribution of these significant associations is described in Figure 2A and B. The UPDRS-IV item 39 and the H& Y stage did not show any association with the ZBI score .
|
Figure 1 Frequency of symptoms reported by caregivers and kind of mood change in each group. |
|
Table 3 Aggregated Results for ZBI Scores in the Three Groups of Treatment. The Total Percentage in Each Group Were Computed Excluding the Missing Data |
Dont Miss: Parkinson Bicycle Cleveland Clinic
Also Check: Stage 3 Parkinson’s Disease