Brainstem Ventilatory Dysfunction: A Plausible Mechanism For Dyspnea In Parkinson’s Disease
Perron Institute for Neurological and Translational Sciences, Nedlands, Perth, Western Australia, Australia
Correspondence to:
West Australian Sleep Disorders Research Institute, Sir Charles Gairdner Hospital, Nedlands, Perth, Western Australia, Australia
School of Human Sciences, University of Western Australia, Crawley, Western Australia, Australia
Frank L Mastaglia MD, FRACP, FRCP
Perron Institute for Neurological and Translational Sciences, Nedlands, Perth, Western Australia, Australia
Perron Institute for Neurological and Translational Sciences, Nedlands, Perth, Western Australia, Australia
Correspondence to:
West Australian Sleep Disorders Research Institute, Sir Charles Gairdner Hospital, Nedlands, Perth, Western Australia, Australia
School of Human Sciences, University of Western Australia, Crawley, Western Australia, Australia
Frank L Mastaglia MD, FRACP, FRCP
Perron Institute for Neurological and Translational Sciences, Nedlands, Perth, Western Australia, Australia
Relevant conflicts of interest/financial disclosures:Funding agencies:
Effect Of Antiparkinsonian Drugs On Lungs Volumes
Regarding the dopasensitivity, some researchers consider that the effect of L-DOPA in the restrictive syndrome is only partial although others did not highlight any signification variation due to treatment .Yet, even on on drug condition, FVC remained below the norm . Some researchers suggest that acute and chronic administrationL-DOPA can improve the flow-volume curve . These results must be interpreted with caution, since some of the studies included patients with asthma or obstructive bronchopulmonary disease . Furthermore, it has been suggested that obstructive pulmonary syndrome is due to bronchoconstriction caused by sympathetic hyperactivation .
Apda In Your Community
APDAParkinson’s Disease SymptomsCould this be due to Parkinsons Disease? Uncommon non-motor symptoms of Parkinsons Disease
It is common for a person with Parkinsons disease to attribute every new symptom that develops to PD. That is largely because the list of non-motor symptoms commonly associated with PD is so varied, it can seem that almost anything is a symptom of PD! But if you take a closer look, there are some symptoms that are very commonly associated with PD, others that are virtually never associated with PD, and some in between.
Lets divide up non-motor symptoms into the following categories:
Also Check: Fitflop Shoes For Parkinson’s
Symptoms That Are Commonly Associated With Pd
These symptoms include sleep disorders, abnormalities in blood pressure, urinary problems, constipation, depression, and anxiety. Even though these symptoms are so commonly seen in PD, they are also commonly associated with other issues that have nothing to do with PD, so it is vital to keep an open mind about their cause. If any symptom is new or worsening, it could be an indication of a new medical problem. For example, urinary problems are extremely common in PD, but may be a sign of an enlarged prostate, which can be treated in an entirely different way.
Respiratory Disorders Of Parkinsons Disease

Parkinsons disease is characterized by the progressive loss of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra, mainly affecting people over 60 yr of age. Patients develop both classic symptoms and nonclassical symptoms . Thus, patients with PD can have a significantly impaired quality of life, especially when they do not have multimodality therapeutic follow-up. The respiratory alterations associated with this syndrome are the main cause of mortality in PD. They can be classified as peripheral when caused by disorders of the upper airways or muscles involved in breathing and as central when triggered by functional deficits of important neurons located in the brainstem involved in respiratory control. Currently, there is little research describing these disorders, and therefore, there is no well-established knowledge about the subject, making the treatment of patients with respiratory symptoms difficult. In this review, the history of the pathology and data about the respiratory changes in PD obtained thus far will be addressed.
Also Check: Parkinson Silverware
Data Synthesis And Analysis
The heterogeneity of the interventions, training protocols as well as the wide variety of primary outcome measures made it impossible to pool the results in meta-analyses. Instead, we present a narrative synthesis organized by intervention and training protocols and outcome measures. The Grading of Recommendation Assessment, Development and Evaluation approach was used to rate level of evidence into high, moderate, low, or very low . Detailed GRADE guidance was used to evaluate the risk of bias, imprecision, inconsistency, indirectness, and publication bias. These were all reasons to downgrade the level of evidence . Upgrading the level of evidence was possible in case of a large effect size, evidence of dose-response gradient, or all plausible confounding factors reducing an apparent effect.
Tips For Coping With Breathing Difficulties
- Work with your doctor to identify and treat any non-PD causes of shortness of breath, such as lung disease, heart disease or lack of physical conditioning and endurance.
- Exercise as much as possible. Shortness of breath may lead a person to move less. Less physical activity reduces the ability to take deep breaths. Staying active improves pulmonary function.
- Take steps to cope with anxiety. Talk with your doctor to figure out what sets off anxiety and find treatments and techniques that work for you.
- Speak to your doctor about getting an evaluation performed by a speech-language pathologist who can help you address issues related to swallowing.
- Give up smoking.
Page reviewed by Dr. Chauncey Spears, Movement Disorders Fellow at the University of Florida, a Parkinsons Foundation Center of Excellence.
Also Check: Cleveland Clinic Parkinson’s Bicycle Study 2017
Involvement In The Neurodegenerative Process
Neurodegeneration of the substantia nigra pars compacta is accompanied by extensive loss of neurons in extranigral sites, including the brainstem nuclei involved in sleep physiology and respiratory control . This localized neurodegeneration in some parts of the brainstem may account for the occurrence of ventilatory disorders in PD. However, a number of questions have yet to be resolved.
Inspiratory And Expiratory Muscles Weakness
Several studies have evidenced weakness of both inspiratory and expiratory muscles in PD . The maximal inspiratory mouth pressures seems to be more affected than the maximal expiratory mouth pressure according to several researchers . Besides, in this latter paper, inspiratory muscles weakness is very severe . The correlation with respiratory symptoms remains unclear, since some of the studies included patients with severe PD and limitations in their activities of daily living. There are few studies of the pathophysiology of this respiratory muscle weakness. Tremor may be involved or jerky movements of the diaphragm . Accessory muscles seem to be affected in PD, although data on diaphragm function in PD are scarce. Vercueil et al. observed a differential impact of the disease on inspiratory muscles . A link between respiratory muscles disturbance and impaired lung volumes has been suggested . Spirometry results would be the consequence of a reduced efficiencyduring repetitive motor tasks. Furthermore, respiratory muscles strength seems to decrease with the course of the disease since a negative correlation was highlighted between MIP, MEP and the motor section of UPDRS .
Recommended Reading: What Foods Should Be Avoided When Taking Levodopa
Effects Of Dopaminergic Therapy: Risk Or Protection
Studies have provided controversial results about the therapeutic effects of dopaminergic stimulation, and the role of drugs commonly used in the treatment of PD is still debated, strictly depending both on disease stage and administration modality.
Most papers strengthen the role of anti-Parkinsonian drugs as a protective factor against the development of respiratory failure. Levodopa increases inspiratory muscle function in anaesthetised dogs , and dopamine improves diaphragm function during acute respiratory failure in patients with COPD . In early stages, the levodopa equivalent daily dose does not correlate with pulmonary functional testing as the disease progresses, anti-Parkinsonian medications may be responsible for the maintenance of the maximal inspiratory mouth pressure and sniff nasal inspiratory pressure . Accordingly, bedtime controlled-release levodopa is associated with less severe obstructive sleep apnoea in PD . Because dopamine is not known to increase muscle strength, it may ameliorate respiratory function by improving muscle coordination by a central activity .
Many authors have investigated the effect of dopaminergic therapy on aforementioned respiratory dysfunction, especially on obstructive and restrictive patterns .
Main findings of major studies we considered about the effects of dopaminergic drugs on respiratory parameters and respiratory dysfunctions
Impact Of Treatments On Dyspnea
However, dopamine does not seem to be the only neurotransmitter involved in dyspnea. Although there is still a doubt about the role of serotonin , anti-inflammatory drugs like steroids may interfere in dyspnea sensation . After the administration of L-DOPA, improvements in lung function were not correlated with the reduction in the symptoms reported by the patients . Paradoxically, antiparkinsonian medications can trigger dyspnea. Thus, L-DOPA-induced dyskinesia has been reported as a possible cause of dysregulated breathing , perhaps as a result of the loss of muscle control. Likewise, a longitudinal study has shown that dyspnea can be a side effect of subthalamic nucleus deep brain stimulation . The authors mentioned the following mechanisms underlying this phenomenon: An alteration of dyspnea perception, a bronchoconstriction, a disturbance in upper airway control or a disturbed respiratory muscle control. Surprisingly, a fixed epiglottis has been observed in subthalamic nucleus deep brain stimulation patients .
Therefore, the precise mechanisms of dyspnea and the effect of treatments remain unknown.
You May Like: Voice Amplifiers For Parkinson’s
What Are The Causes
People with Parkinsons may experience varied respiratory symptoms, ranging from shortness of breath without exertion to acute stridor, the sudden onset of high-pitched breathing sounds when taking a breath.1,3
Dysfunction can be caused by a variety of factors including physiological restrictive changes in the lungs, upper airway obstruction, and response to medications.1,3
Breathing Problems In Parkinsons Disease: A Common Problem Rarely Diagnosed
Parkinsons disease is the second most common neurodegenerative disorder after Alzheimers disease. It is characterized by bradykinesia tremor, rigidity, and postural instability. Potential non-motor manifestations of PD include depression, anxiety, constipation, overactive bladder symptoms, dementia, and sleep disturbances.
Although James Parkinson, in 1817, described breathing abnormalities in his Essay on the shaking palsy, there has been limited research on this important non-motor symptom.
People living with Parkinsons may present with a wide variety of respiratory symptoms, ranging from shortness of breath at rest to acute stridor. Shortness of breath can be very distressing for patients and clinicians alike. Multiple investigations may be undertaken, looking for infection, blood clots and heart problems. Although these potential causes of breathing abnormalities need to be excluded, clinicians must remember that PD itself and its medications can cause SOB and that normal investigations should not automatically lead to a diagnosis of anxiety, depression or lead to inappropriate treatment plans.
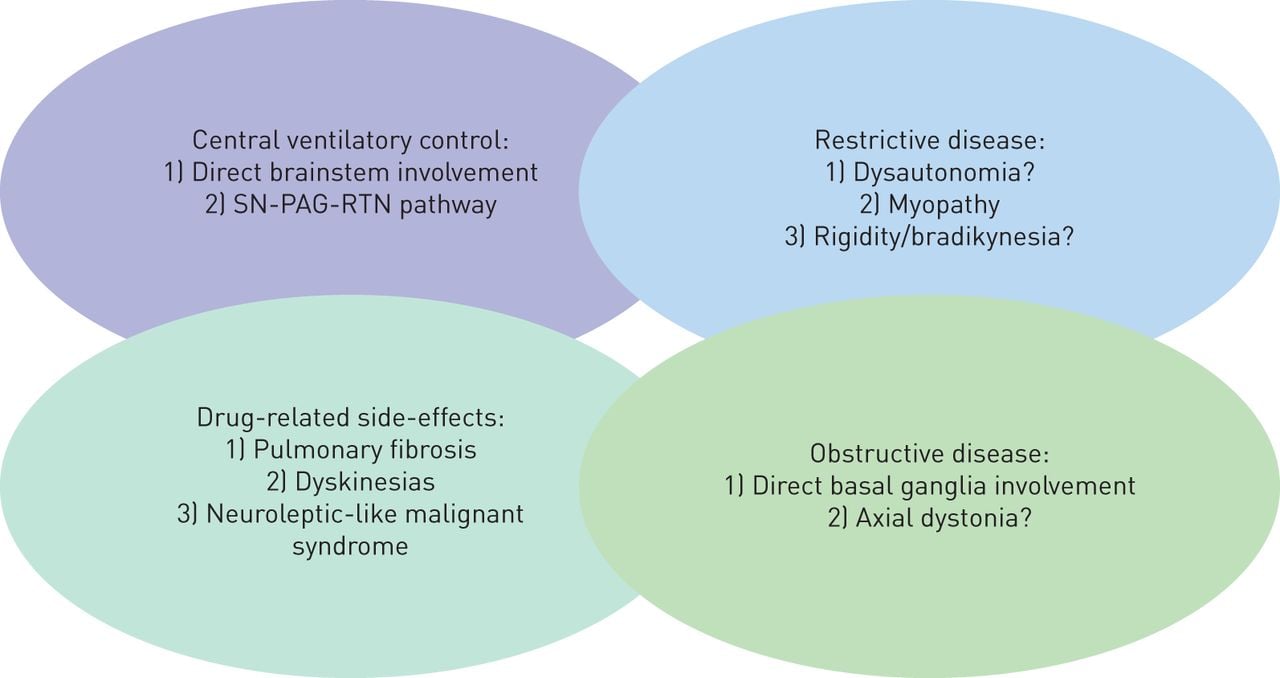
Several different patterns of breathing abnormality may be found in PD:
KM Torsney, D Forsyth
Also Check: Similar To Parkinsons
Deep Brain Stimulation And Respiratory Failure
DBS is an effective strategy for the treatment of advanced PD, thus improving motor fluctuations and bradykinesia.
Nonetheless, the classical target of the subthalamic nucleus -DBS reserves stimulation-induced side effects in the long-term period, comprising gait and speech impairment, as well as a progressively worsening of tremor. In this scenario, only few papers have specifically investigated respiratory failure. In particular, STN-DBS may increase the risk of a fixed epiglottis and modify velopharyngeal control these effects seem to strictly depend on frequency parameters, with low-frequency stimulation leading to a clinical improvement, whereas higher frequencies are associated with a detrimental effect on velopharyngeal control .
In support of this view, Hammeret al. have recently found that in STN-DBS patients, respiratory changes do not correlate with limb function, but speech-related respiratory and laryngeal control may benefit when the stimulation is delivered at low frequencies and shorter pulse width . In addition to stimulation frequency, other factors may account for these correlations, including variability in localisation of the active DBS electrodes, individual variability in somatotopic organisation of STN, stimulation fields and potential current spread beyond the STN target . Data on the relationship between respiratory changes and novel DBS targets, such as the pedunculopontine nucleus , have not been extensively reported so far.
Apnoea In Parkinson’s Disease
The presence of apnoea syndrome has been studied in PD as well. Apnoea syndrome is probably related to a central dysfunction of the brainstem respiratory centres and/or a peripheral airways involvement. However, different studies have produced conflicting results, probably according to the different samples of patients and methods used.
Apnoea occurring during sleep could be classified as central , obstructive and mixed nonetheless, these patterns have not been studied systematically in PD and a clear stratification is not available in the current literature. Most studies focused on obstructive apnoea rather than central.
Conflicting results have been reported about the prevalence of obstructive apnoea syndrome in PD patients Mariaet al. identified a higher prevalence of obstructive apnoea in PD populations, whereas others found less occurrence of obstructive apnoea compared to controls , or even no apnoea or sleep abnormalities . De Cocket al. tried to explain this phenomenon, postulating a possible protective contribution due to rapid eye movement sleep behaviour disorder , in which the physiological muscle atonia during REM sleep is absent and may prevent upper airway closure.
You May Like: Parkinson’s Bike Therapy
Occurrence Of Sleep Apnea Syndrome In Pd
It has been known for decades that PD is associated with sleep disorders such as insomnia, excessive daytime sleepness, REM and sleep behavioral disorders. However, there is still debate as to the prevalence of sleep apnea syndrome in PD patients . According to Shill et al. , the presence of restrictive or obstructive patterns in PD could be a predisposition to SAS. Some researchers have reported an abnormally high prevalence of SAS in PD , whereas others have reported normal or below-normal values . The body mass index was a major source of bias in these studies, and most of the patients included were suffering from late-stage PD. Moreover, no predictive clinical features of SAS have been identified . Some researchers have mentioned peripheral SAS caused by upper airway obstruction . However, an occurrence of 48% of sleep breathing disorders with a predominance of central SAS has been observed .
Blood Sampling And Assessment Of Inflammatory Markers
All the patients underwent blood sampling by venipuncture of forearm veins.
Assessment of inflammatory markers
The serum concentrations of TBARS and thiol were measured in all the patients in order to detect lipid peroxidation and determine anti-oxidative defense capability, respectively . In addition, the level of EPCs was measured by flow cytometry based on a previous report . First, mononuclear cells were incubated for 30 min at 4 °C in a dark room with monoclonal antibodies against kinase insert domain-conjugating receptor and fluorescein isothiocyanate-conjugated CD34 and CD133, by which the EPC surface markers of CD133/CD34 and KDR/CD34 were determined. The control ligand was then added. Quantitative two-color flow cytometric analysis was performed using an Epics XL flow cytometer . In these arrays, each analysis included 10,000 cells per sample and was performed in duplicate, with mean level reported.
Assessment of serum adhesion molecules
To assess serum sICAM-1, sE-selectin, and sP-selectin levels, commercially available enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays were used . The dual wavelength absorbance, from which the degree of enzymatic turnover of the substrate was estimated, was measured at 450 and 620 nm. Absorbance was directly proportional to the concentration of antigens present. To determine the antigen concentrations of the unknowns, a standard curve of absorbance of standard antigen versus the given antigen concentration was plotted.
Don’t Miss: Sam Waterston Tremor
Correlation Between Pneumological Drugs And Pd
In this scenario, the effects of drugs commonly used by the pneumologist should also be considered. For instance, some studies recently reviewed by Hopfneret al. postulated the possible correlation between -adrenoreceptors and PD . Anticholinergic drugs are frequently used for obstructive pulmonary disorders and systemic anticholinergics may play a part in PD . Acetylcholine has a key role in modulating dopaminergic activity in the basal ganglia, and its inhibition may increase central dopaminergic tone . Anticholinergic bronchodilators might have central effects, as reported by some authors . An effect on motor disturbances in PD may be reasonable, even if to our knowledge this has not been investigated in the current literature. However, it should be considered that anticholinergics may be associated with cognitive impairment and delirium , and these adverse effects may be even more common in the advanced stage of PD, when dementia is a very common feature.
The Issue Of Pneumonia In Parkinson’s Disease
Aspiration pneumonia represents a dramatic complication that may explain the acute/subacute onset of fever and respiratory insufficiency in a PD patient. Physiologically, swallowing requires adequate coordination between pharyngeal and respiratory musculature, but this mechanism is frequently impaired in PD . Dysphagia is typical in the advanced stages of disease, on average 1011years after motor symptoms onset , when bradykinesia, rigidity and dyskinesias are predominant however, a cough dysfunction in more than 50% of asymptomatic PD patients has been demonstrated and this may also contribute to silent aspiration and increased risk of pneumonia . Moreover, in these patients the cough mechanism becomes weak because of cough reflex impairment and chest wall rigidity, further increasing the risk of aspiration . A blunted urge to cough , a respiratory sensation that precedes the cough reflex, is also present and correlates with the severity of dysphagia and consequently, with an increased risk of aspiration .
Also Check: Zhichan Capsule
Chapter : Respiratory Dysfunction And Cardiovascular Conditioning
Breathing issues and respiratory dysfunction are a common issue within the Parkinsons population. They are at risk of complications for a couple of reasons underlying disease pathology and the side effects of medication. The degeneration of the substantia nigra and loss of dopaminergenic neurons can cause changes in ventilatory parameters. Overtreatment with levodopa can cause respiratory dyskinesia which can be difficult to differentiate from complications of the disease itself. Therapy using ergo derivatives may cause pleuropulmonary fibrosis. Pneumonia resulting from respiratory issues remains a leading cause of morbidity in the Parkinsons population.
In the following text, we will learn more about respiratory dysfunction from two experts in the neurology world, Dr. Ingrid Estrada-Belleman and Dr. Fernando Carrera. Lets have a look at these insights they have so generously provided.
Introduction
Parkinsons disease has been associated with respiratory dysfunction since its discovery by James Parkinson. It is known to be an important cause of morbidity and mortality. Parkinsons disease is characterized by cardinal symptoms such as: rigidness, tremor, slowness in movement , and postural instability in late stages of the disease.
Clinical manifestations
Respiratory Physiology
Upper Airway Obstruction
Pulmonary Restrictive Pattern
Central Ventilatory Control
Complications
Rehabilitation