Time To Initiate Treatment In Early Pd
The timing of initiation of symptomatic therapy has been one of the most debated subjects in the management of early PD, and there still is no consensus. In the past, the preferred strategy was to delay the initiation of symptomatic treatment due to the concern of potential long-term negative effects of dopaminergic therapy on the rate of PD progression, a concern that stems from the hypothesis of a neurotoxic effect of L-dopa caused by the production of free oxygen radicals that could further potentiate the degenerative process in the substantia nigra . However, several lines of evidence do not support the hypothesis of L-dopa toxicity . While L-dopa has been shown to potentiate cell death in tissue culture, the concentration of L-dopa in those experiments far exceeded the concentrations achieved in humans. Animal data also do not demonstrate a neurotoxic effect of L-dopa at doses that approximate human use . Most importantly, data from the ELLDOPA trial demonstrated clinically that early initiation of L-dopa was not deleterious, but rather resulted in a reduction of disability . However, the imaging component of the trial was potentially consistent with a neurotoxic effect, and an increased risk of dyskinesia was observed. Thus, while L-dopa remains the most efficacious agent for the treatment of PD, the timing of initiation of L-dopa must be balanced against the risk of drug-induced motor complications.
Thanks For Signing Up
We are proud to have you as a part of our community. To ensure you receive the latest Parkinsons news, research updates and more, please check your email for a message from us. If you do not see our email, it may be in your spam folder. Just mark as not spam and you should receive our emails as expected.
Also Check: What New In Parkinson Treatment
Medication Guidelines For Parkinson’s Disease
There is no one best mix of Parkinsonâs medicines. You and your doctor will have to try a few treatment approaches to figure out the best one for you.
But there are some general guidelines for taking your medication. Be sure to ask your doctor or pharmacist for any specific tips for your treatment.
Also Check: Parkinson’s Disease Hand Tremor
Parkinsons Treatment For Motor Symptoms
The majority of medications developed specifically to treat Parkinsons disease target common motor symptoms. Many of these treatments are designed to increase the level of the dopamine, a neurotransmitter that transfers signals between nerve cells. Dopamine is involved in regulating signals for movement, which is reduced in the brains of Parkinsons disease patients.
How Soon After Treatment Will I Feel Better And How Long Will It Take To Recover
The time it takes to recover and see the effects of Parkinsons disease treatments depends strongly on the type of treatments, the severity of the condition and other factors. Your healthcare provider is the best person to offer more information about what you can expect from treatment. The information they give you can consider any unique factors that might affect what you experience.
Read Also: Does Parkinsons Disease Cause Death
Don’t Miss: Best Bed For Parkinson’s Patients
Pharmacological Treatment Of Parkinsons Disease
There is currently no proven disease-modifying or neuroprotective therapy for PD. A summary of previous neuroprotection trials is given in a recent review article. Current evidence-based treatment for PD is symptomatic and mainly based around dopaminergic replacement or modulation . The evidence base is summarised in recent guidelines from the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence and the International Parkinson and Movement Disorder Society. Levodopa, dopamine agonists and monoamine oxidase B inhibitors are all licensed for use as initial therapy in PD. Anticholinergics are no longer routinely used due to the risk of cognitive decompensation.
Pharmacological therapies currently used for initial and adjunctive treatment of motor symptoms in Parkinsons disease
Also Check: Parkinsons Age Of Onset
Early Treatment In Old Patients
In elderly patients L-dopa remains the treatment of choice even in early stages as it is the drug with the best therapeutic window particularly with regard to psychiatric side effects. In view of their high potential of causing confusion anticholinergics should best be avoided but dopamine agonist and amantadine can be tried. Again, selegeline may be considered but the advantage of delaying L-dopa for several months is less meaningful in this age group.
Box 2: Treatment strategiesearly stages
-
None of the currently available drugs has a proved neuroprotective effect. Potential neuroprotective agents are under study.
-
Treatment should be tailored to the individual patient’s needs. The choice of drugs is mainly influenced by age.
-
Young patients are more prone to develop motor complications. L-dopa therapy should therefore be delayed for as long as other drugs, particularly dopamine agonist, adequately relief symptoms.
-
In elderly patients L-dopa has the best therapeutic index and is the first line treatment.
Don’t Miss: Core Exercises For Parkinson’s
Treatment Of Motor Fluctuations
A number of strategies can reduce motor fluctuations in patients with PD. Optimising the amount of levodopa delivered to the brain is the main approach and can be achieved by increasing the levodopa dose, adjusting the timing of administration and/or adding adjunctive agents., Administering levodopa with a low protein meal or empty stomach, if tolerated, can improve absorption. Smaller, more frequent dosing may also help. Changing to a controlled-release formulation could theoretically improve fluctuations however, studies have shown no difference in symptoms compared to immediate-release preparations.
Adjunctive agents such as dopamine agonists, catechol-o-methyltransferase inhibitors and monoamine oxidase-B inhibitors have been shown to improve fluctuations. Direct head-to-head studies comparing these medications are lacking however, a Cochrane review involving 44 randomised controlled trials suggested dopamine agonists were most effective in reducing âoffâ time . In older people, choice of adjunctive agent should be based on factors including comorbidities, adverse effects and patient preference.
Dopamine Agonists
COMT Inhibitors
MAO-B Inhibitors
How Is It Diagnosed
Diagnosing Parkinsons disease is mostly a clinical process, meaning it relies heavily on a healthcare provider examining your symptoms, asking you questions and reviewing your medical history. Some diagnostic and lab tests are possible, but these are usually needed to rule out other conditions or certain causes. However, most lab tests arent necessary unless you dont respond to treatment for Parkinsons disease, which can indicate you have another condition.
You May Like: Psychotherapy For Parkinson’s Disease
Monoamine Oxidase B Inhibitors
Selegeline is an example of this class of drug. It selectively and irreversibly inhibits intracellular and extracellular monoamine oxidase B and therefore reduces or delays the breakdown of dopamine to dihydroxyphenylacetic acid and hydrogen peroxide. The latter has been implicated in oxidative damage in dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra. It also inhibits reuptake of dopamine from the synaptic cleft. Adding selegeline to L-dopa may allow a reduction of the L-dopa dose of 10%15%, occasionally up to 30%.Mild L-dopa response fluctuations can often be reduced by adding selegeline. Monotherapy in de novo patients delays the need for additional treatment by approximately a year.Possible neuroprotective effects will be discussed later . Side effects of L-dopa, including dyskinesias and psychiatric problems, are potentially enhanced by selegeline. Orthostatic hypotension may also occur.
Manual Therapy And Exercise
Chiropractic manipulation, osteopathic manipulation, and Trager therapy have been suggested to benefit patients with Parkinsons disease. No studies exist, however, to refute or confirm this position. The Alexander technique has shown some benefit and patient improvement has been noted in some studies.
Standard physical therapy, as well as occupational therapy, did result in improved functional outcomes, but the benefit was small and was not sustained when the exercise therapy stopped.
Read Also: Parkinson’s Foundation Support Groups
What Future Medications May Be Available For Parkinsons
There are numerous studies investigating new treatments for Parkinsons disease.
There has been new information about the role of autoimmunity and T-cells in the development of Parkinsons disease, possibly opening the door to a role for biologics.
Stem cells are also being investigated as a treatment option for Parkinsons disease.
Pathophysiology And Risk Factors

The loss of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra and presence of alpha-synuclein clumps known as Lewy bodies and Lewy Neurites are the pathological hallmarks of PD. The resultant deficiency in dopamine and relative cholinergic excess lead to motor symptoms. When symptoms present, it is estimated that 60â70% of neurons are already lost. Other neurotransmitters in nondopaminergic areas of the brain are also affected, which likely accounts for the non-motor features.,
Age is the leading risk-factor, with most diagnoses occurring after age 65., Gender ratios vary between studies but overall there is a slight male predominance. Some studies have suggested a genetic link, but this only accounts for 5â10% of PD cases, typically with younger onset., Environmental factors such as pesticide and heavy metal exposure are also suspected, but are not conclusive risk-factors. Caffeine and cigarette smoking are associated with less risk of developing PD.,
Don’t Miss: Last Stages Of Parkinson’s Disease
When Is It Best To Start The Parkinsons Drug Levodopa
This is a plain English summary of an original research article
Earlier treatment with levodopa provides symptomatic relief to those with symptoms but does not appear to slow Parkinsons disease from progressing. Therefore, timing is best determined by symptoms.
The treatment of Parkinsons disease is complex. Levodopa is the main drug used to reduce tremors and muscle stiffness. Whether it modifies the course of the disease or becomes less effective over time is debated, and it can have side effects, so patients and clinicians sometimes prefer to delay starting treatment.
This Dutch trial involved 445 participants with a recent diagnosis of Parkinsons disease, enrolled over five years. About half took levodopa for 80 weeks, and half placebo for the first 40 weeks and levodopa for the last 40 weeks. There was no difference in symptoms between the groups at the end of the study.
This evidence supports current guidance to start levodopa when symptoms begin to affect the quality of life and confirm that it has insufficient impact on disease progression to justify earlier treatment.
Brain Connectomic Studies And Improved Precision Of Neuromodulation Targets
The process of altering brain function through direct manipulation of neural activity has long been used to treat patients with neuropsychiatric disorders and deep brain stimulation has provided clinical benefit to more than 150 000 patients with PD, dystonia and essential tremor . Apart from the conventional application in advanced PD, DBS has also been suggested to exert disease-modifying traits . In multiple preclinical studies on rat models, chronic STN electrical stimulation was shown to result in preservation of SNpc dopaminergic neurons and an increase of brain-derived neurotrophic factors followed by activation of the tropomyosin receptor kinase type B receptor signaling in the nigrostriatal system . Although preclinical experiments suggest potential neuroprotective effects of DBS, results from clinical studies have shown that dopaminergic neuron degeneration remains unaltered , and -syn burden is not reduced in PD patients treated with DBS .
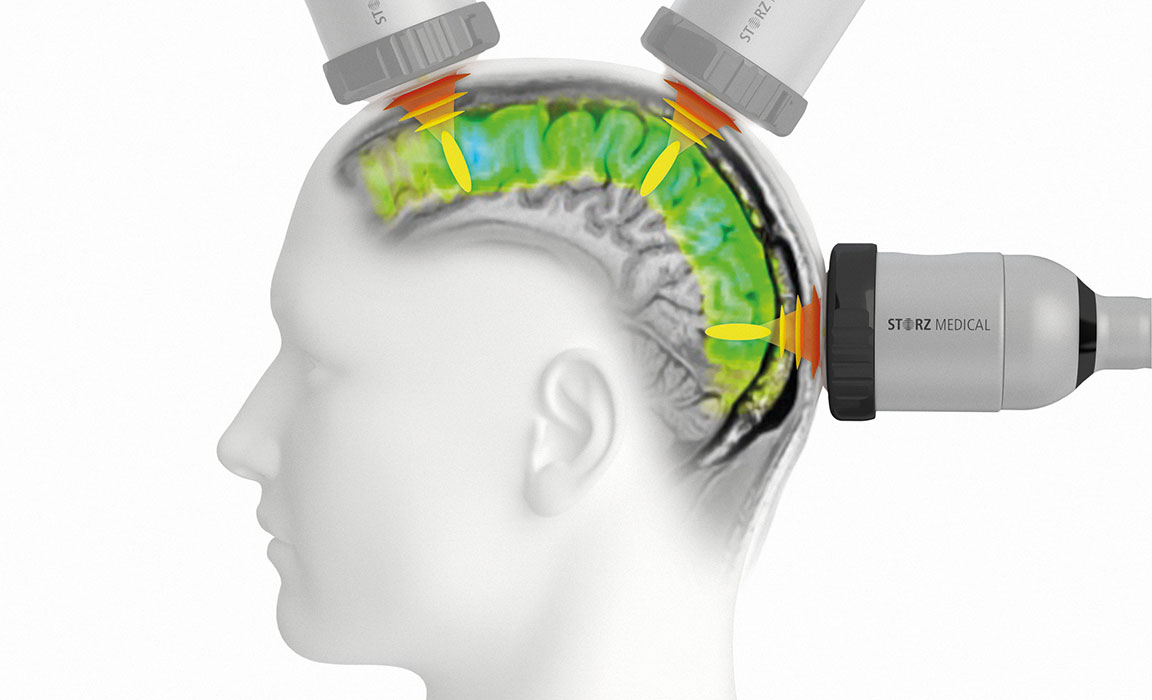
Focused ultrasound as a newly developed neuromodulation technique
Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation
Few studies have investigated the effect of rTMS on levodopa-induced dyskinesias, showing only short-lasting or no beneficial effect.
Don’t Miss: What Are Some Causes Of Parkinson’s Disease
Parkinsons Disease: Management And Guidance
An overview of Parkinsons disease management, including discussion of the updated National Institute for Health and Care Excellence guidelines.
Nervous system diseases
DR. MICHAEL SOUSSAN/ISM/SCIENCE PHOTO LIBRARY
Parkinsons disease is a chronic, progressive neurodegenerative condition resulting from the loss of the dopamine-containing cells of the substantia nigra, and its prevalence increases with age. Using primary care data from 2015, a Parkinsons UK report of the Clinical Practice Research Datalink found that the prevalence of PD is 45 per 100,000 people who are aged 3039 years, compared with 1,696 per 100,000 people who are aged 8084 years. Prevalence rates almost double at each five-year interval between the ages of 50 and 69 years for both men and women. The lifetime risk of being diagnosed with PD is 2.7% equating to 1 in every 37 people being diagnosed at some point in their lifetime. Owing to population growth and an increasing ageing population, the estimated prevalence of PD is expected to increase by 23.2% by 2025.
What Drugs Are Available For Initial Treatment Of Parkinsons Disease
Parkinsons disease is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder characterised by tremor, rigidity, bradykinesia, and a wide spectrum of non-motor symptoms including sleep disorders, hyposmia, bladder and bowel dysfunction, fatigue, dementia, and other neuropsychiatric symptoms.1
Although the disease has no cure, available treatments effectively control motor symptoms and improve quality of life.23 Several drug classes are licensed for use as monotherapy in early Parkinsons disease and adjuvant therapy in later disease:
-
Levodopa is the main precursor in dopamine synthesis and has been the mainstay of treatment for decades
-
Dopamine agonists simulate dopamine by binding directly to post-synaptic dopamine receptors in the striatum.4 They include:
-
-Non-ergot dopamine agonists
-
-Ergot derived dopamine agonists : their use requires frequent monitoring for complications of heart valve and retroperitoneal fibrosis, so the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence guidelines recommend non-ergot dopamine agonists instead5
Monoamine oxidase B inhibitors selectively inhibit
Recommended Reading: Parkinson’s Vs Multiple Sclerosis
Common Drugs For Parkinson’s Disease
Levodopa and carbidopa . Levodopa is the most commonly prescribed medicine for Parkinsonâs. Itâs also the best at controlling the symptoms of the condition, particularly slow movements and stiff, rigid body parts.
Levodopa works when your brain cells change it into dopamine. Thatâs a chemical the brain uses to send signals that help you move your body. People with Parkinsonâs donât have enough dopamine in their brains to control their movements.
Sinemet is a mix of levodopa and another drug called carbidopa. Carbidopa makes the levodopa work better, so you can take less of it. That prevents many common side effects of levodopa, such as nausea, vomiting, and irregular heart rhythms.
Sinemet has the fewest short-term side effects, compared with other Parkinsonâs medications. But it does raise your odds for some long-term problems, such as involuntary movements. An inhalable powder form of levodopa and the tablet istradefylline have been approved for those experiencing OFF periods, OFF periods can happen when Parkinsonâs symptoms return during periods between scheduled doses of levodopa/carbidopa.
People who take levodopa for 3-5 years may eventually have restlessness, confusion, or unusual movements within a few hours of taking the medicine. Changes in the amount or timing of your dose will usually prevent these side effects.
Dopamine agonists. These drugs act like dopamine in the brain. They include pramipexole , rotigotine , and ropinirole , .
Anosmia And Other Sensory Manifestations Of Pd
Loss of smell has long been reported to be an early sign of PD, present in 70100% of PD patients . As the loss of smell frequently can precede the onset of motor symptoms, recent research has focused on the role of smell-testing in the early identification of PD . If proven to be sensitive and specific, a smell test would be an easy-to-administer inexpensive screening tool that would be useful for identifying populations at risk of PD and for enrollment in neuroprotection clinical trials. Anosmia does not improve with dopaminergic therapy, and thus cannot be used as a measure of efficacy for dopaminergic agents.
Pain is another common manifestation of PD . The pattern and distribution of pain varies, but a subset of patients experiencing pain is responsive to dopaminergic therapy . The nature of pain in PD is likely multifactorial, and more data on the mechanisms of pain and potential disease-specific treatment interventions are necessary.
Also Check: Parkinsons Disease Typically Causes
Don’t Miss: How Long Does Parkinson’s Take To Develop
A Review On Parkinsons Disease Treatment
5214526Tori K. Lee Eva L. Yankee
Department of Biology, Angwin, CA 94508, USA .
Received:First Decision:Revised:Accepted:Available online:Academic Editors:Copy Editor:Production Editor:
© The Author 2021. Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, for any purpose, even commercially, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
Recommended Reading: What Benefits Can You Claim For Parkinsons Disease
The Evolution Of Treatments
The history of Parkinsons disease is tightly linked to therapeutic interventions, ranging from serendipitous observations to controlled clinical trials of specifically designed agents.
Parkinson devoted a chapter of his monograph to considerations respecting the means of cure . In humility and perhaps with a vision toward current concepts of neuroprotection, he hoped for the identification of a treatment by which the progress of the disease may be stopped . To this end, he advocated very early therapeutic intervention when signs were largely confined to the arms without balance and gait impairments. Reflecting therapeutic approaches of the early nineteenth century, Parkinson recommended venesection, specifically advocating bloodletting from the neck, followed by vesicatories to induce blistering and inflammation of the skin. Small pieces of cork were purposefully inserted into the blisters to cause a sufficient quantity of purulent discharge . All these efforts were designed to divert blood and inflammatory pressure away from the brain and spinal cord, and in this way, decompress the medulla that Parkinson considered the seat of neurological dysfunction.
You May Like: Effect Of Exercise On Parkinson’s Disease
Advanced Therapies For Parkinsons Disease
When significant off-time or dyskinesia persists despite optimised oral treatment, advanced therapies should be considered. Apomorphine, a potent dopamine agonist given by continuous subcutaneous infusion, is the least invasive and most straightforward of these. Following on from extensive clinical experience, the recent double-blind TOLEDO study confirmed a significant reduction in off-time and improved on-time with apomorphine versus placebo.
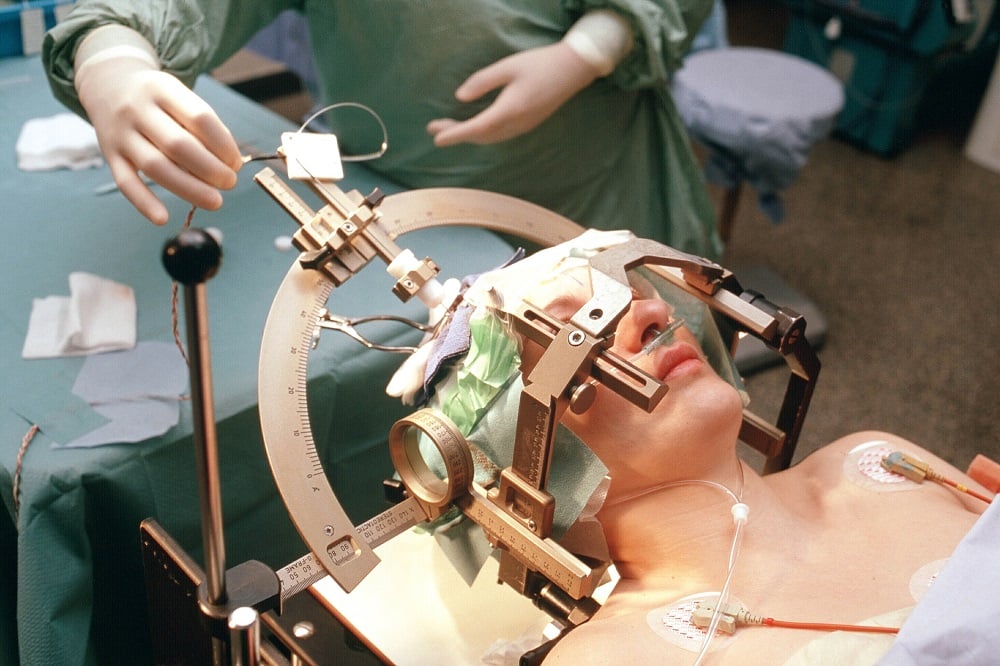
Deep-brain stimulation involves surgical placement of electrodes into brain regions such as the subthalamic nucleus to improve motor fluctuations or refractory tremor. DBS is typically considered in patients without significant axial or neuropsychiatric problems. It improves motor function, off-time and QoL in patients with PD, and provides significant benefits over medical therapy even in patients with an average disease duration of 7 years. The benefits of DBS on motor function, fluctuations and activities of daily living have been demonstrated up to 10 years postoperatively, although axial features continue to progress. Infusion of levodopacarbidopa intestinal gel via jejunostomy has also been shown to improve off-time compared to oral levodopa, and is commissioned in specialist centres where other advanced therapies are ineffective or contraindicated. Further information on the decision-making process for advanced therapies is summarised in a dedicated review.