Why Are They Not Helpful
Most people in the last stage of Alzheimers disease have difficulty eating and drinking. At this time, families may wonder if a patient needs a feeding tube.
Families want to do everything possible for someone who is ill. But they often get little information about feeding tubes. And they may feel pressure from doctors or nursing home staff, because feeding is simpler with a feeding tube.
But feeding tubes sometimes do more harm than good. Heres why:
Feeding tubes usually arent helpful for severe Alzheimers disease.
People with severe Alzheimers disease can no longer communicate or do basic things. Chewing and swallowing is often hard. This can cause serious problems, such as weight loss, weakness, and pressure sores. Or food can get into the lungs, and cause pneumonia. So people often need help to eat.
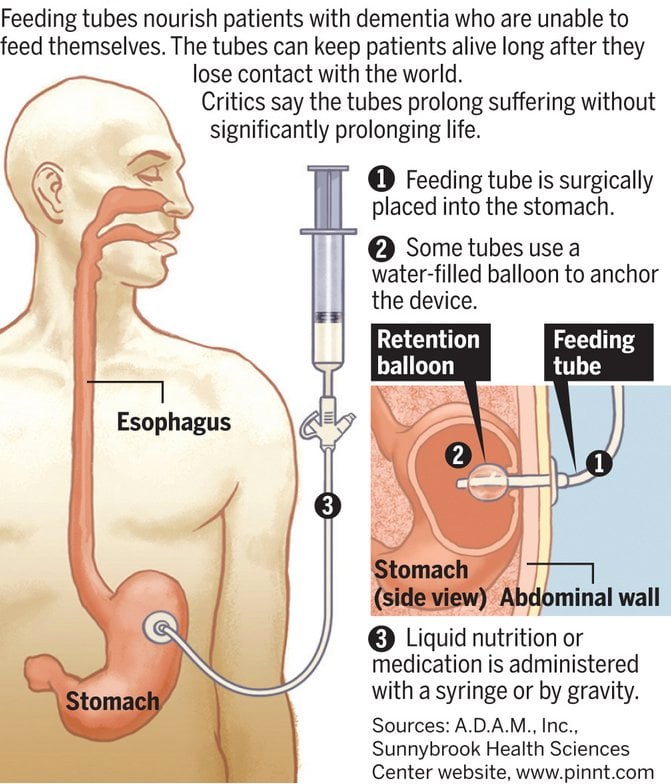
In many cases, a decision is made to use a feeding tube. The tube may be put down the throat. Or it may be put through a small cut in the abdominal wall, into the stomach. The patient is then given liquid nutrition through the tube.
But tube feeding is not better than careful hand feedingand it may be worse. It does not help people live longer, gain more weight, become stronger, or regain skills. And it may increase the risk of pneumonia and pressure sores.
Strategy For Rapidly Progressive Dysphagia In Prd Psp And Msa
Dysphagia symptoms in PRD, PSP, and MSA appear earlier after the onset than in PD . The median dysphagia latencies were reported to be 42 months in PSP, 67 months in MSA, and 130 months in PD. This suggests that early dysphagia symptoms in PRD are distinguishable from those in PD.
In PSP, the most common cause of death is pneumonia that occurs subsequent to silent aspiration . The reported prevalence of dysphagia in PSP is up to 80%, and the early development of dysphagia leads to repeated aspiration pneumonia and a short survival time . Medication, adjustment of food consistency, feeding techniques, and PEG feeding should be attempted in order to prevent pneumonia. Relative to PD patients, PSP patients exhibit a poorer response to medications with mild improvement in dysphagia , and the management of dysphagia in the later stages of PSP is more challenging than in the earlier stages. The early deterioration of the cognitive function or dementia may influence the treatment difficulty. However, despite adjusting the food consistency and feeding techniques, most PSP patients ultimately require PEG feeding within a few months after the initial development of pneumonia . Nevertheless, whether or not PEG placement prolongs the survival time is unclear .
The authors state that they have no Conflict of Interest .
Progression And Management Of Dysphagia In Pd
Unlike stroke, dysphagia in PRD degenerates with disease progression. Although their swallowing dysfunction is assessed by using VFSS or FEES, rehabilitation is required for determining PD patients’ quality of life. A transdisciplinary approach, including physicians, nurses, physical therapists, speech pathologists, and nutritionists, is required for long-term management.
Two specific questionnaires have been developed to detect dysphagia in PD: the swallowing disturbance questionnaire and the Munich Dysphagia test-Parkinson’s disease . The SDQ containing 15 questions is more basic and an easier screening test for asking about specific symptoms with dysphagia and their frequencies. The MDT-PD can detect the beginning of oropharyngeal symptoms and the risk of laryngeal penetration or aspiration. It consists of 26 items divided into 4 categories: difficulty in swallowing food and liquids, difficulty in swallowing independent of food intake, further swallowing-specific and associated problems, swallowing-specific health questions.
You May Like: Parkinson’s Bike Therapy
Single Centre Experience Of Peg Feeding In Parkinsons Disease
H. Fairclough, H. Bashir, R. Beekman, M. Lee, E. Johns, C. Mcdonald
Session Time: 1:15pm-2:45pm
Location: Les Muses Terrace, Level 3
Objective: To determine factors influencing mortality in patients who receive percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy in Parkinson s disease .
Background: PD is a progressive neurological disease associated with dysphagia and risk of aspiration. In these circumstances PEG insertion may be considered. However, data is limited related to outcomes following PEG in PD or the factors associated with favourable outcomes.
Method: We retrospectively reviewed case notes for all patients with PD undergoing PEG between 2014 and 2018 at the Queen Elizabeth Hospital in Gateshead. Patient demographics and clinical characteristic prior to PEG insertion were collected. Duration of survival post PEG was recorded.
Survival post PEG in PD is very variable. In this small case series there were no clear predictors of outcome. Notably 50% of the cohort were unable to consent to procedure at time of PEG. This demonstrates the need for earlier discussion re patients wishes. Further studies will need to gather data from multiple centres in order to reliably determine factors associated with favourable outcome following PEG in PD.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Mov Disord.
End Of Life Ethical Issues
Palliative care recognises that we all have a right to say what care we would like and for those wishes, wherever possible, to be respected. It upholds the belief that we should not be forced to undergo any treatment against our will and should be consulted if possible when choices are made regarding our care.
Many ethical issues arise in the final stage of life and each country has agreed practices to follow. Ethical frameworks vary depending on where you live so it is advisable to talk to your family doctor or other members of your care team to get more information on local guidelines.
Recommended Reading: Similar To Parkinsons
Thanks For Signing Up
We are proud to have you as a part of our community. To ensure you receive the latest Parkinsons news, research updates and more, please check your email for a message from us. If you do not see our email, it may be in your spam folder. Just mark as not spam and you should receive our emails as expected.
Limb Deformities And Contractures
Hand and foot deformities as well as other abnormal body postures such as flexion at the waist or tilting of the torso are common in advanced PD. There is a range of severity of these deformities. As the severity increases, it is more difficult to maneuver the limb into a normal position. The reasons for development of these deformities are not well understood but are likely a combination of rigidity , dystonia as well as factors that we dont fully understand.
A contracture is a permanent tightening or shortening of a muscle and can result from a persistent limb deformity or abnormal body posture. This results in an inability to even passively move or manipulate a body part through the normal range of motion. Once a contracture is present, these deformities do not typically respond to treatment.
Treatments of limb deformities :
- PD medication optimization early on, limb deformities may respond to an increase in PD medication
- Regular range of motion exercises
- Physical therapy
- Botulinum toxin injections
Read Also: Sam Waterston Tremor
Oral Dysfunction In Parkinsons: Swallowing Problems And Drooling
Two common and distressing problems that can develop in Parkinsons disease are swallowing dysfunction and drooling. I want to help you better understand these issues and learn what you can do to improve them so read on!
Thank you to Christine Sapienza, PhD, CCC-SLP and Bari Hoffman Ruddy, PhD, CCC-SLP for providing some of the material below.
Artificial Feeding And Hydration Are They Compulsory
Artificial feeding is an alternative feeding method that can be used in some situations to sustain life if eating and swallowing are no longer possible. Artificial hydration involves introducing additional fluid into the body to ensure that adequate levels are maintained.
Some people feel uncomfortable about both procedures as they can be intrusive at a difficult time. The right to refuse these will depend on the country in which you live, but in most cases, you have the right to choose or refuse any treatment. If no preference has been expressed and you are not well enough to make a decision, the doctor will always decide what is in your best interests, weighing up the potential advantages and disadvantages. They will consult with your carer and relatives and all decisions will be recorded and reviewed on an ongoing basis.
Whilst artificial feeding or hydration can be very beneficial in some cases, it may not always be appropriate and there is no evidence that nutrition or hydration actually prolongs life when death is imminent.
Read Also: Cleveland Clinic Parkinson’s Bicycle Study 2017
Feeding Tube Placement For Parkinsons Often Precedes Move To Nursing Home
Fully a third of patients who have certain feeding tubes placed for Parkinsons disease-related dysphagia are discharged to an eldercare facility, a new outcomes study has found.
Investigators analyzed 83 cases of adults with a median age of 78 who received percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy procedures . Among 56 patients admitted to the hospital from home, 32% were moved to a nursing home after the procedure, reported first author Lisa Brown, BSc, RN, from the University Hospitals of Derby and Burton, United Kingdom.
Other outcomes included a median survival of 422days, and a 30-day mortality rate of 6%. Survival rates were not significantly influenced by age, sex, diagnosis, or comorbidities, among other factors. Longer survival was linked to discharge to the community and follow up by an enteral feeding team, the researchers noted. The most common complication was aspiration pneumonia.
Discussions about percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy feeding should include information about survival, complications, and the potential need for long-term care, the investigators concluded.
The study was published in the journal Movement Disorder Clinical Practice.
When You Need Themand When You Dont
Most people in the last stage of Alzheimers disease have difficulty eating and drinking. At this time, families may wonder if their family member needs a feeding tube.
Families want to do everything possible for someone who is ill. But they often get little information about feeding tubes. And they may feel pressure from doctors or nursing home staff, because feeding is simpler with a feeding tube.
But feeding tubes sometimes do more harm than good. Heres why:
Feeding tubes usually arent helpful for severe Alzheimers disease.
People with severe Alzheimers disease can no longer communicate or do basic things. Chewing and swallowing is often hard. This can cause serious problems, such as weight loss, weakness, and pressure sores. Or food can get into the lungs, and cause pneumonia. So people often need help to eat.
In many cases, a decision is made to use a feeding tube. The tube may be put down the throat. Or it may be put through a small cut in the abdominal wall, into the stomach. The person is then given liquid nutrition through the tube.
But tube feeding is not better than careful hand feedingand it may be worse. It does not help people live longer, gain more weight, become stronger, or regain skills. And it may increase the risk of pneumonia and pressure sores. Hand feeding gives human contact and the pleasure of tasting favorite foods.
Feeding tubes can have risks.
Tube feeding has many risks.
Feeding tubes can cost a lot.
So when are feeding tubes a good idea?
Also Check: Judy Woodruff Parkinson’s
How Does One Make These Decisions
When a person is diagnosed with a chronic and degenerative illness, it is important for the patient and family members to discuss these topics early in the illness, while the patient is still in a position to let family members know what his/her wishes are regarding these decisionsâit is much more difficult to make a decision under the pressure of an acute episode. If the ill person has begun to choke when swallowing, it is a good time for the family, the patient, and, if possible, the physician, to discuss the âwhat ifs,â and how to think about the choices, keeping in mind the patientâs values. Consultation with clergy may also be helpful.
Can I Leave My Brain For Medical Research

You may wish to help the future treatment of Parkinsons by leaving your brain for medical research but it is always a good idea to discuss this possibility with family, your doctor and the executors of your will.
Because organs need to be collected within a few hours of death it is important to register your willingness to donate tissues with a hospital or tissue bank. Many institutions have a consent form which must be signed and it is advisable to put your wishes in writing and have this document signed in the presence of a witness.
Some countries have a national organ donor register with a card that can be carried indicating consent to donate in the event of death. However, do check that organs donated in this way can be used for research as well as for transplant as this may not automatically be the case.
Your national Parkinsons association may be able to provide further information or you can talk to your care team or look online.
Also Check: Judy Woodruff Health Problems
Short Communicationoutcome Of Gastrostomy In Parkinsonism: A Retrospective Study
This is a retrospective study conducted on 33 patients.
-
We investigated the outcome of gastrostomy tube insertion in Parkinsonian syndromes.
-
The median survival following the gastrostomy tube insertion was 6 months.
-
Being totally dependent was associated with a shorter survival.
-
Aspiration pneumonia is no prevented by gastrostomy tube insertion.
How Do You Know If You Or Your Loved One Has A Problem With Swallowing
Swallowing difficulties can start very subtly and initially not be obvious to either the person with PD or their loved ones. There are signs to look out for before swallowing difficulty becomes overt . Some of the signs you should pay attention to include:
- Slow rate of eating people with difficulty swallowing may slow down their eating in order to avoid coughing or choking
- Fatigue during eating or decreased enjoyment of food
- A sensation that food is sticking in the throat
- Coughing or excessive throat clearing during eating
- Difficulty in swallowing pills
- Unexplained weight loss people with difficulty swallowing may reduce their consumption in an attempt to eat without coughing or choking
- Change in dietary habits people with difficult swallowing may alter their diet in order to avoid foods that cause difficulty. This may not be a choice made consciously
- Diagnosis of a pneumonia this could be caused by aspiration, or entry of a foreign substance into the airway
If you think there might be a swallowing issue, it is important to speak with your doctor about it. There are steps you can take to properly assess the situation and improve your swallowing function. This can in turn reduce your risk of choking, make eating more enjoyable, and lessen the chances of unwanted weight loss and/or other discomforts.
Don’t Miss: On And Off Phenomenon
Nutritional Supplement And Hydration
As many types of neurological illnesses progress, the muscles of the throat gradually cease to work properly. This can cause swallowing difficulties, gagging, choking, trouble coughing, loss of voice, or difficulty catching oneâs breath. Receiving proper nutrition is difficult if someone is having trouble swallowing, which is usually accompanied by eating less. The danger of choking while swallowing is that the food can âgo down the wrong pipeââin other words, the food is aspirated into the lungs. Gagging can also cause vomiting, which may cause some of the stomach contents to enter the lungs. All of these possibilities can lead to an illness called aspiration pneumonia, which occurs when bacteria causes infection in the lungs which have been damaged by food or stomach material.
With or without feeding tubes, patients can learn swallowing techniques to reduce the likelihood of aspirating. Caregivers can also help by preparing âthick liquidâ diets , that are easier to swallow, and by avoiding thin liquids and things that require chewing. Some people can enjoy eating small amounts this way, even when they are receiving their primary nutrition through a tube.
In many cases, feeding tubes help prevent illness and prolong life. In diseases like ALS, feeding tubes can be a normal part of treatment, as swallowing may be compromised before a person is in the end stages of the disease.
Swallowing Difficulties In Parkinsons Disease
The act of swallowing involves a complex series of activities that begin in the mouth, continue in the pharynx and end in the esophagus. These include chewing, using the tongue to move the bolus of food to the back of the throat and then coordinating the muscles that both propel the food into the esophagus and protect the airway or trachea from food penetration. Swallowing dysfunction can be considered both a motor and a non-motor symptom of PD. Loss of dopamine neurons in the substantia nigra area of the brain can cause the motor dysfunction that impairs swallowing. However, loss of neurons in other areas of the brain, such as the cortex and lower brain stem can also affect the overall control and coordination of swallowing, and can be thought of as a non-motor symptom of PD. Swallowing issues are very important to diagnose. Impacts on your daily life and your health can range from difficulties with meals to more extreme cases where it could lead to choking and aspiration which can be very serious or even fatal.
You May Like: Weighted Silverware
When You Take Medicine
In most cases, you can crush your pills and mix them with applesauce or pudding. But crushing some drugs, like Sinemet CR, can affect how the drugs work. There are some medications that should never be crushed. Ask your pharmacist which meds you can crush and which you can get as a liquid.
Show Sources
What Are The Risks
Tube feeding has many risks.
- It can cause bleeding, infection, skin irritation, or leaking around the tube.
- It can cause nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea.
- The tube can get blocked or fall out, and must be replaced in a hospital.
- Many people with Alzheimers disease are bothered by the tube and try to pull it out. To prevent that, they are often tied down or given drugs.
- Tube-fed patients are more likely to get pressure sores.
- Tube-fed patients are more likely to spit up food, which may lead to pneumonia a term called aspiration pneumonia.
- At the end of life, fluids can fill the patients lungs, and cause breathing problems.
So when are feeding tubes a good idea?
Feeding tubes can be helpful when the main cause of the eating problem is likely to get better. For example, they can help people who are recovering from a stroke, brain injury, or surgery.
The tubes also make sense for people who have problems swallowing and are not in the last stage of an illness that cant be cured. For example, they can help people with Parkinsons disease or amyotrophic lateral sclerosis .
Don’t Miss: Pfnca Wellness Programs