Newly Diagnosed: Treatment Strategies For Parkinson’s
While there is no cure for Parkinsons disease yet, there are therapeutic approaches that can help to ease symptoms and improve quality of life. Experimental treatments are also being explored that could prove beneficial for patients. Check out the information below to explore more about therapeutic strategies your doctor may recommend and what therapies are in the pipeline for potential future use.
What Is Parkinsons Disease
Parkinsons disease is a condition where a part of your brain deteriorates, causing more severe symptoms over time. While this condition is best known for how it affects muscle control, balance and movement, it can also cause a wide range of other effects on your senses, thinking ability, mental health and more.
How Could Stem Cells Help People With Parkinson’s
Stem cells are the parent cells of all tissues in the body. This means they can turn into any type of cell. The hope is that they will eventually be able to make these cells into specific types of cells, like dopamine-producing neurons, that can be used to treat Parkinson’s disease. However, there are concerns that patients may have the same risk of increased involuntary movements as those who undergo fetal cell transplantation. And, like fetal cell transplantation, stem cell therapy is surrounded by moral and ethical controversy.
Don’t Miss: Sole Support For Parkinson’s
Brain Connectomic Studies And Improved Precision Of Neuromodulation Targets
The process of altering brain function through direct manipulation of neural activity has long been used to treat patients with neuropsychiatric disorders and deep brain stimulation has provided clinical benefit to more than 150 000 patients with PD, dystonia and essential tremor . Apart from the conventional application in advanced PD, DBS has also been suggested to exert disease-modifying traits . In multiple preclinical studies on rat models, chronic STN electrical stimulation was shown to result in preservation of SNpc dopaminergic neurons and an increase of brain-derived neurotrophic factors followed by activation of the tropomyosin receptor kinase type B receptor signaling in the nigrostriatal system . Although preclinical experiments suggest potential neuroprotective effects of DBS, results from clinical studies have shown that dopaminergic neuron degeneration remains unaltered , and -syn burden is not reduced in PD patients treated with DBS .
Focused ultrasound as a newly developed neuromodulation technique
Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation
Few studies have investigated the effect of rTMS on levodopa-induced dyskinesias, showing only short-lasting or no beneficial effect.
Parkinsons Disease Therapy With Stem Cells: How Can Stem Cells Help
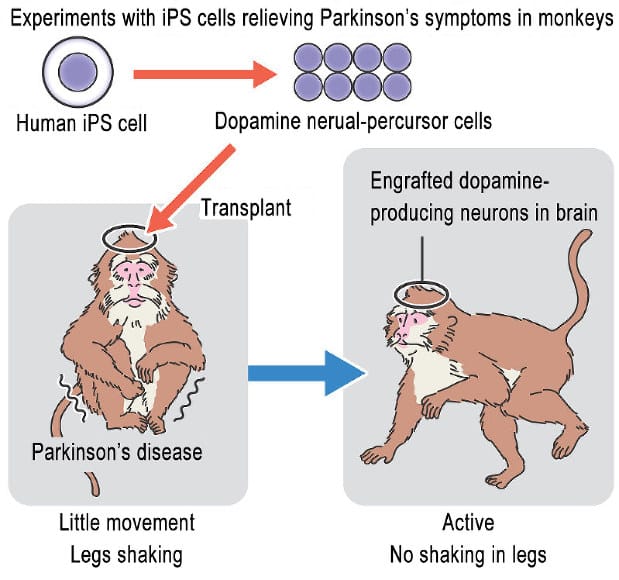
Diverse stem cell types are under scientific investigations, some of which are in clinical trials, for the safety and efficacy of stem cell-based therapies for treating Parkinsons disease. They include:
- Dopamine-producing Embryonic Stem Cells for Parkinsons disease
- Induced pluripotent stem cells for Parkinsons disease
- Neural stem cells for Parkinsons disease
- Stromal Vascular Fraction for Parkinsons disease
- Lab-grown Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Parkinsons disease
Read Also: Best Parkinson’s Doctors In Florida
Treatments In Phase Ii Trials
Another strategy in the therapeutic research space is drug repurposing. This is when an existing medication for one condition is repurposed to treat an entirely different condition. Working with repurposed medications comes with many advantages including understanding its general safety. Repurposing an existing medication, rather than starting from scratch, typically requires fewer tests for safety as the drug has already met these requirements. This can reduce costs and speed up the process through the clinical trial pipeline. It can also lead to faster approvals, getting much-needed treatments into the hands of people with Parkinsons as soon as possible. There are a total of 74 therapies in Phase II trials and 44% are repurposed medications.
One exciting takeaway from Phase II trials this year is the progress made with stem cell therapies. While there are nine stem cell therapies being explored in Phase I, two stem cell therapies graduated to Phase II trials this year! Moving into Phase II means these treatments are being administered to a larger group of people to monitor their effectiveness and further evaluate their safety.
How Much Does Stem Cell Treatment Cost
Our treatments are always tailored to your specific situation, disease, stage and other factors. The therapies differ in the product used , the frequency of treatment as well as the further examinations and your sedation and anesthesia wishes. A treatment for PD will cost above ten thousand euros. You will receive a cost estimate for all treatments in advance so that you can accurately estimate what a treatment would cost in your individual case.
Also Check: Exercises For Someone With Parkinson’s Disease
Disadvantages Of Stem Cell Approaches
While the stem cell approaches described potentially offer promising treatment approaches, a number of problems must be overcome in order for them to be used as a mainline treatment for PD.
Of course, any grafting therapy will require a neurosurgical procedure, and it must be demonstrated that this can be achieved safely, with minimal risk. Additionally, for allogenic grafts a period of immunosuppression will be required, with the associated risk of infection and malignancy. Having said this, there is postmortem evidence of FVM graft survival for over two decades, with only a transient period of immunosuppression, and taking into account the fact that the central nervous system is an immune-privileged site, it is unlikely that this will be a major problem .
It has been estimated that generating iPSCs from 150 human leukocyte antigen -typed individuals could allow for the development of haplobanks which would be able to provide HLA-matched cell products for over 90% of a population . This would mean that rather than an autologous grafting product being produced for each patient, that an iPSC line could be selected with which they were HLA compatible to generate a matched cell product. However, in order to achieve this, a degree of HLA mismatch would be necessary, and a period of immunosuppression would therefore probably be required. Additionally, this would still have significant economic costs .
Complementary And Supportive Therapies
A wide variety of complementary and supportive therapies may be used for PD, including:
A healthy diet. At this time there are no specific vitamins, minerals, or other nutrients that have any proven therapeutic value in PD. The National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke and other components of the National Institutes of Health are funding research to determine if caffeine, antioxidants, and other dietary factors may be beneficial for preventing or treating PD. A normal, healthy diet can promote overall well-being for people with PD just as it would for anyone else. Eating a fiber-rich diet and drinking plenty of fluids also can help alleviate constipation. A high protein diet, however, may limit levodopas absorption.
Exercise. Exercise can help people with PD improve their mobility, flexibility, and body strength. It also can improve well-being, balance, minimize gait problems, and strengthen certain muscles so that people can speak and swallow better. General physical activity, such as walking, gardening, swimming, calisthenics, and using exercise machines, can have other benefit. People with PD should always check with their doctors before beginning a new exercise program.
Alternative approaches that are used by some individuals with PD include:
You May Like: Effect Of Exercise On Parkinson’s Disease
How Are Clinical Trials Conducted
Clinical trials that test drugs or interventions are conducted in a series of carefully monitored phases designed to answer specific questions.
Phase I trial: researchers test a new drug or treatment in people for the first time. A small group of people, typically fewer than 100, are monitored to evaluate the drug or treatments safety, determine a safe dosage range, and identify side-effects.
Phase II trial: study the effectiveness of a drug or treatment in a larger group of people.
Phase III trial: the study drug or treatment is given to a large group of several hundred to several thousand people. This large-scale testing gives more detailed information about the drugs benefits, effectiveness, range of possible side effects, and compare it with standard treatment or placebo.
Phase IV trial: usually conducted on treatments that have already been Food and Drug Administration approved and is available to the general population. These trials help monitor the safety of the intervention in a larger population and obtain additional information about the benefits and use of the intervention.
Experimental Drug Stops Parkinsons Disease Progression In Mice
Researchers say they have developed an experimental drug that slows the progression of Parkinsons disease itself
Johns Hopkins researchers say they have developed an experimental drug, similar to compounds used to treat diabetes, that slows the progression of Parkinsons disease itself as well as its symptoms in mice. In experiments performed with cultures of human brain cells and live mouse models, they report the drug blocked the degradation of brain cells that is the hallmark of Parkinsons disease. The drug is expected to move to clinical trials this year.
It is amazingly protective of target nerve cells, says Ted Dawson, M.D., Ph.D., director of the Institute for Cell Engineering and professor of neurology at the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine.
A report of the studys results was published June 11 in Nature Medicine.
According to the investigators, NLY01 works by binding to so-called glucagon-like peptide-1 receptors on the surface of certain cells. Similar drugs are used widely in the treatment of type 2 diabetes to increase insulin levels in the blood. Though past studies in animals suggested the neuroprotective potential of this class of drugs, researchers had not shown directly how it operated in the brain.
They explored this hypothesis by testing the drugs effectiveness in mice engineered to have a rodent version of Parkinsons disease.
Read Also: Support Services For Parkinsons Disease
Also Check: Parkinson’s Support Group Los Angeles
Gene Therapy For Modulating The Synthesis Of Neurotransmitter
Adeno-Associated Virus -Glutamate Decarboxylase
Aromatic Amino Acid Decarboxylase and Tyrosine Hydroxylase/Aromatic Amino Acid Decarboxylase/Guanosine Triphosphate Cyclohydrolase Gene Therapy
The beneficial effect of oral administration of L-dopa will soon be complicated by motor symptoms. Olanow et al. find that continuous dopamine stimulation might counter balance these long-term effects of drug . Based on these theories, researchers focused on increasing dopamine level through enhancing the chemical synthesis of dopamine from levodopa. The conversion of levodopa to dopamine needs the enzyme acromatic L-amino acid decarbocylase . With the PD advancing, activities of AADC diminished, this further limiting dopamine level and resulted a larger need for the dosage of levodopa . The transduction of AADC gene to intrinsic striatal neurons could enhance the synthesis of dopamine and might improve the dopamine level in brain. The continuous existence of DA might reduce the need of levodopa in advancing PD , and with the reduction of levodopa, the side effect like LIDs might be alleviated. A phase I clinical trial of gene transfer of AAV mediated gene delivery of AADC into putamen of 6 PD patients was launched. using multiple measures, including UPDRS, motor state diaries and PET trace for AADC, 6 months after surgery, the off-state of motor function was improved by 46% based on UPDRS scores, PET shows a 56% increase in FMT activities, both effect last 96 weeks .
Deep Brain Stimulation For The Treatment Of Pd Patients
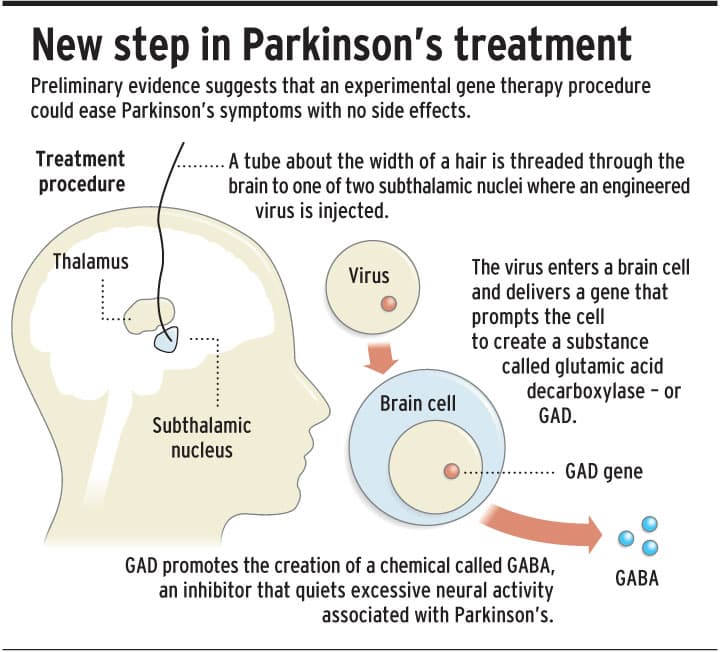
Current surgical indications for PD include reducing motor fluctuations, off time, dyskinesias, tremor, and improvement of levodopa-responsive symptoms. Deep brain stimulation is probably the most critical advance in treatment of PD since the introduction of levodopa. The beneficial effects of DBS on motor symptoms and quality of life in advanced PD have been shown in randomized, controlled studies6666. Deuschl G, Schade-Brittinger C, Krack P, Volkmann J, Schäfer H, Bötzel K, et al. A randomized trial of deep-brain stimulation for Parkinsons disease. N Engl J Med. 2006 Aug 31 355:896-908. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa060281 ,6767. Williams A, Gill S, Varma T, Jenkinson C, Quinn N, Mitchell R, et al. Deep brain stimulation plus best medical therapy versus best medical therapy alone for advanced Parkinsons disease : a randomised, open-label trial. Lancet Neurol. 2010 Jun 1 9:P581-91. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-442270093-4 .
Don’t Miss: Deep Brain Stimulation For Parkinson’s Disease
How Long Does A Stem Cell Therapy Take
The initial analyses and counseling can be done without you having to travel to Offenbach . This period can be 2 weeks up to months depending on the availability of patients slots. If you live further away, we will conduct the initial discussions by telephone or video conference. For the actual treatment, you will travel to Offenbach.
Drug And Medication Therapies
The purpose of treating Parkinsons is to reduce the effect of symptoms on your daily life. Without treatment, you will eventually find that the symptoms make it hard to perform daily activities. Symptoms, such as shaking and stiffness, may cause discomfort the risk of injury from falls may increase, and swallowing may become more difficult. People are encouraged to maintain open and ongoing discussions with their Parkinsons healthcare team when exploring treatment options.
Medication will help you function, but may cause side effects. It is important to find the right balance between the medications benefits and side effects. Everyone with Parkinsons is unique and will experience different symptoms, which means the treatment you receive will be geared to your specific needs. Drugs for Parkinsons work on the brains complex chemistry and may need to be taken several times a day. Use them as prescribed and do not alter your doses without consulting your doctor. Current treatment neither cures Parkinsons nor stops it from advancing.
You May Like: Drugs Contraindicated In Parkinsons Disease
Don’t Miss: How Close Are We To Curing Parkinson’s
Bacteria Engineered To Produce Parkinsons Disease Drug In The Gut
New research presented at the American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics annual meeting has demonstrated the potential for genetically engineered bacteria to be an effective Parkinsons disease treatment. The researchers created a bacteria that can synthesize a consistent source of medicine inside a patients gut, and animal tests have demonstrated it is safe and effective.
The idea of engineering bacteria to serve as medical treatments is not new. For years scientists have experimented with ways of modifying bacteria to fit our needs, from engineering bacteria to eat up excess ammonia in a human body to helping bacteria hunt down colorectal cancer cells.
Of course, before an idea like this is ready for mainstream clinical uses a number of hurdles need to be overcome. Its one thing to offer a patient controlled doses of a drug via a pill, but limiting the growth of living microbes engineered to synthesize those same therapeutic molecules in the human gut is a whole different challenge.
New research from a team of scientists has presented an incremental step forward in engineering a novel strain of the human probiotic E.coli Nissle 1917 that has been developed to continually synthesize a Parkinsons disease drug known as L-DOPA.
Why Should I Participate In A Clinical Study
We can only reach breakthroughs in treatment and care if people participate in the studies.
Participating is safe and can help you
Every clinical study is reviewed thoroughly before your doctor asks you to participate. Clinical trials carry some risks, but your doctor is required by law to explain the risks to you clearly and make sure that you understand them. If your doctor tells you about the risks of participating in the study, ask yourself, What are the risks of not participating in the study? Most of the time, if you balance the possible benefits from participating against the risks, it is about the same as the risks of not being in the study.
On the other hand, the study may be of a new drug or treatment that could help you. If you dont participate, it may be years before you have a chance to try that drug.
Some people do not participate because there is no guarantee they will get the experimental therapy they might get the placebo. Again, think carefully about the risks and benefits of entering the study and getting the new treatment, entering the study and getting the placebo or not entering the study at all.
Your participation can help others
If you have PD or any other disease, the drugs, procedures and therapies you use now were scientifically tested, likely by thousands of volunteers. Participating in a clinical trial is your way to pay it forward for people diagnosed with Parkinsons in the future.
You May Like: Simple Explanation Of Parkinson’s Disease
What New Treatments Are Being Developed
Thanks to the progress weve already made, new treatments are being tested in clinical trials that have the potential to slow, stop or even reverse Parkinsons.
These include:
- Stem cell therapies. These aim to use healthy, living cells to replace or repair the damage in the brains of people with Parkinsons.
- Gene therapies. These use the power of genetics to reprogramme cells and change their behaviour to help them stay healthy and work better for longer.
And were developing treatments that aim to improve life with the condition, including new drugs that can reduce dyskinesia.
What The Experiments Showed
Initially, the researchers tested the nanobody on mouse brain tissue in vitro. They found that PFFNB2 could bind to aggregates of alpha-synuclein, but could not prevent the formation of clumps.
Further experiments revealed that the nanobody could bind to and disrupt fibrils of alpha-synuclein that had already formed, destabilizing the misshapen proteins.
The researchers then tested this in live mice and found that the nanobody prevented alpha-synuclein from spreading to the cortex of the brain. The cortex is the largest part of the brain and is responsible for most higher brain functions.
Dr. Petrossian explained for MNT that he results showed that they were able to specifically target the preformed fibrils of alpha-synuclein in cell and mouse models, that they were able to reduce the clumping of alpha-synuclein in cell models, and they were able to reduce alpha-synuclein pathology in mouse models.
Recommended Reading: Do You Capitalize Parkinson’s Disease