Historical Perspective Of Deep Brain Stimulation
Prior to the discovery of levodopa, surgical interventions were the most efficacious treatment for PD symptoms, but primarily focused on the reduction of bothersome tremor. Early approaches targeted the pyramidal tracts, with lesioning either at the point of origin in the cortex or the descending pathways through the brainstem and cervical spinal cord . Although tremor was reliably improved following surgery, hemiparesis was an inevitable consequence. However, in 1952, Dr. Irving Cooper inadvertently interrupted the anterior choroidal artery while performing a mesencephalic pedunculotomy in a patient with PD. Ligation of the vessel was required, though what resulted was a serendipitous reduction in rigidity and tremor with preservation of motor and sensory function. Cooper reasoned the favorable outcomes were due to infarction of the medial globus pallidus. An expansion of ablative stereotactic surgery followed, aided by the earlier development of the stereotactic frame and methods of targeting deep brain structures, including the basal ganglia and thalamus. However, the success of these approaches was limited, partly because of inaccurate, imprecise, and inconsistent targeting. Moreover, intentionally created bilateral brain lesions frequently led to irreversible deficits in speech, swallowing, and cognition.
Deep Brain Stimulation: A Paradigm Shifting Approach To Treat Parkinson’s Disease
- Department of Neurology, Duke University Medical Center, Durham, NC, USA
Parkinson disease is a chronic and progressive movement disorder classically characterized by slowed voluntary movements, resting tremor, muscle rigidity, and impaired gait and balance. Medical treatment is highly successful early on, though the majority of people experience significant complications in later stages. In advanced PD, when medications no longer adequately control motor symptoms, deep brain stimulation offers a powerful therapeutic alternative. DBS involves the surgical implantation of one or more electrodes into specific areas of the brain, which modulate or disrupt abnormal patterns of neural signaling within the targeted region. Outcomes are often dramatic following DBS, with improvements in motor function and reductions motor complications having been repeatedly demonstrated. Given such robust responses, emerging indications for DBS are being investigated. In parallel with expansions of therapeutic scope, advancements within the areas of neurosurgical technique and the precision of stimulation delivery have recently broadened as well. This review focuses on the revolutionary addition of DBS to the therapeutic armamentarium for PD, and summarizes the technological advancements in the areas of neuroimaging and biomedical engineering intended to improve targeting, programming, and overall management.
You Are About To Exit The Abbott Family Of Websites For A 3rd Party Website
Links which take you out of Abbott worldwide websites are not under the control of Abbott, and Abbott is not responsible for the contents of any such site or any further links from such site. Abbott is providing these links to you only as a convenience, and the inclusion of any link does not imply endorsement of the linked site by Abbott.The website that you have requested also may not be optimized for your screen size.
Read Also: Prayer For Parkinson’s Disease
Deep Brain Stimulation For Parkinsons Disease: What You Need To Know
Parkinsons disease is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder, affecting more than 10 million people worldwide. There are several theories on the cause of Parkinsons Disease and there are a variety of treatments available today. Deep brain stimulation for Parkinsons Disease is a surgical approach to manage Parkinsons symptoms and improve the quality of life of Parkinsons patients.
Deep brain stimulation, also known as DBS, began in the late 1980s when Alim Benabid identified that electric stimulation of the basal ganglia improved Parkinsons disease symptoms. Since the late 1980s, many advancements to deep brain stimulation have been made. In 1997, DBS was approved by the FDA as a treatment for Parkinsons Disease.
Deep brain stimulation is typically reserved for Parkinsons patients that are in the more advanced stages of the disease process. Early in the progression of Parkinsons disease, most Parkinsons patients respond well to L-Dopa containing medications. After years of medication use, the same Parkinsons medications may no longer provide the same amount of relief. In this case, deep brain stimulation may offer a benefit to help relieve Parkinsons symptoms and improve the quality of life.
WHAT EXACTLY IS DEEP BRAIN STIMULATION?
IS DEEP BRAIN STIMULATION RIGHT FOR ME?
DBS may not be considered if a patients symptoms are well controlled with his/her medication regimen.
DBS may be a good consideration for patients who satisfy one or more of the following:
Resources For More Information
- Surgical option a potential life-changer for patients with OCD: Read and watch Erins story as she, a lively 21-year-old woman, fought her battle with OCD. This article explores how deep brain stimulation gave Erin her life back. The procedure was the first of its kind performed at Albany Medical Center the only facility offering this treatment between New York and Boston. In Erins own words, “Now, I can be who I really am and tell people my story and hopefully inspire people and help people along the way.
- Karen and Jims Story: A Shared Journey of Life, Love and DBS: Read about Karen and Jim. They were each diagnosed with Parkinsons before they met. Follow them on their journey as they fall in love after meeting each other from an online support group. See how they embraced each other and DBS.
- Kays Story A Parkinsons Disease Patient: Read about Kay, a 68-year-old woman suffering from Parkinsons disease. The article and video explore how DBS helped her regain her life. In Kays own words, Its like I had been turned on again. It was like a miracle.
You May Like: Weighted Silverware
Deep Brain Stimulation Surgery
A team of experts, including a movement disorder specialist and a brain surgeon, conducts an extensive assessment when considering DBS for someone. They review your medications and symptoms, examine you when you’re on and off Parkinson’s medication, and take brain imaging scans. They also may do detailed memory/thinking testing to detect any problems that could worsen with DBS. If your doctors do recommend you for DBS and you are considering the surgery, discuss with your care team the potential benefits as each person’s experience is unique. It’s also critical to discuss the potential surgical risks, including bleeding, stroke and infection.
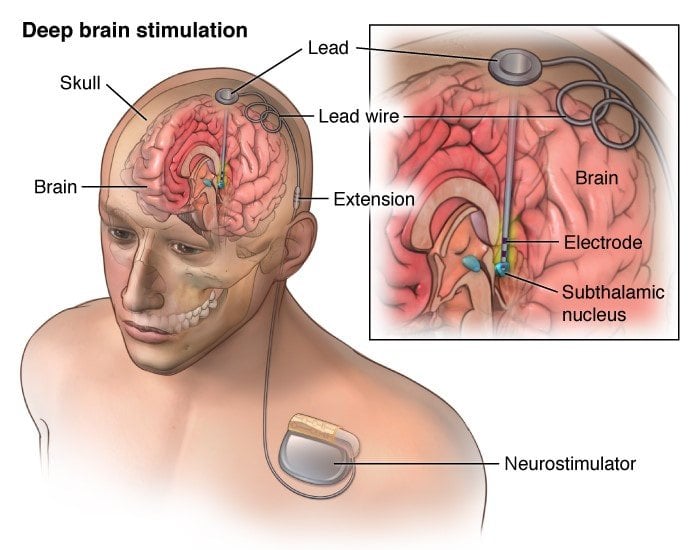
In DBS surgery, the surgeon places thin wires called electrodes into one or both sides of the brain, in specific areas that control movement. Usually you remain awake during surgery so you can answer questions and perform certain tasks to make sure the electrodes are positioned correctly. Some medical centers now use brain imaging to guide the electrodes to the right spot while a person is asleep. Each method has its pros and cons and may not be suitable for everyone or available everywhere.
Once the electrodes are in place, the surgeon connects them to a battery-operated device , which usually is placed under the skin below the collarbone. This device, called a neurostimulator, delivers continuous electrical pulses through the electrodes.
Research To Improve Deep Brain Stimulation
Researchers are working to improve upon existing DBS devices and methods to help treat more symptoms and more people. Some researchers are putting electrodes in a different area of the brain the pedunculopontine nucleus to treat walking and balance problems that don’t typically improve with present-day DBS. Others are developing a “smart” DBS device that can record a person’s unique brain signals and deliver electrical stimulation only when needed, such as when symptoms return, rather than continuously, as the current systems do. This could help reduce side effects such as numbness and weakness and lengthen the battery life of the neurostimulator, which would result in a longer time between battery replacement procedures.
Scientists also are planning to test deep brain stimulation in the first years after a Parkinson’s diagnosis to see if the therapy may slow or stop disease progression. Testing in Parkinson’s models showed the therapy may help protect brain cells, and a small human trial showed motor symptoms improved after early-stage DBS.
Don’t Miss: Sam Waterston Tremor
The Role Of Dbs In An Era Of Novel Treatment Options For Pd
Novel treatment options for PD have been introduced, which may not only address motor symptoms but rather reduce progression of the disease. Such treatment strategies include for example monoclonal antibodies, small molecules, or chelating agents.149 So far, it is unclear, if and to what degree such treatment methods are able to act as disease-modifying agents. In the case of successful applications, deceleration of disease progression may delay the occurrence of motor fluctuations, the classical indication for DBS. While the gradual decrease of DBS surgery may be expected from such development, patients who are treated with DBS may also benefit from such treatments combined with DBS due to delayed manifestation of DBS-refractive symptoms like cognitive decline or frequent falls.
The Pros And Cons Of Microelectrode Recording For Precise Neuro Navigation
It is an old debate whether MER increases the accuracy of the DBS lead placement.37 MER may help identify anatomical targets via the detection of characteristic cellular firing patterns.38 Experienced centers on MER report that an alternative trajectory is preferred over the initially predefined target in about 25% of cases, leading to more preferable motor outcomes.39 Also, intraoperative test stimulation via microelectrodes may predict the risk of early capsular side effects at a given target and therefore may also enhance decision-making on the DBS electrode placement.40 Consequently, MER is a useful technique to optimize placement of the final DBS electrode and routinely utilized in most DBS centers, including our own.
Don’t Miss: Cleveland Clinic Parkinson’s Bicycle Study 2017
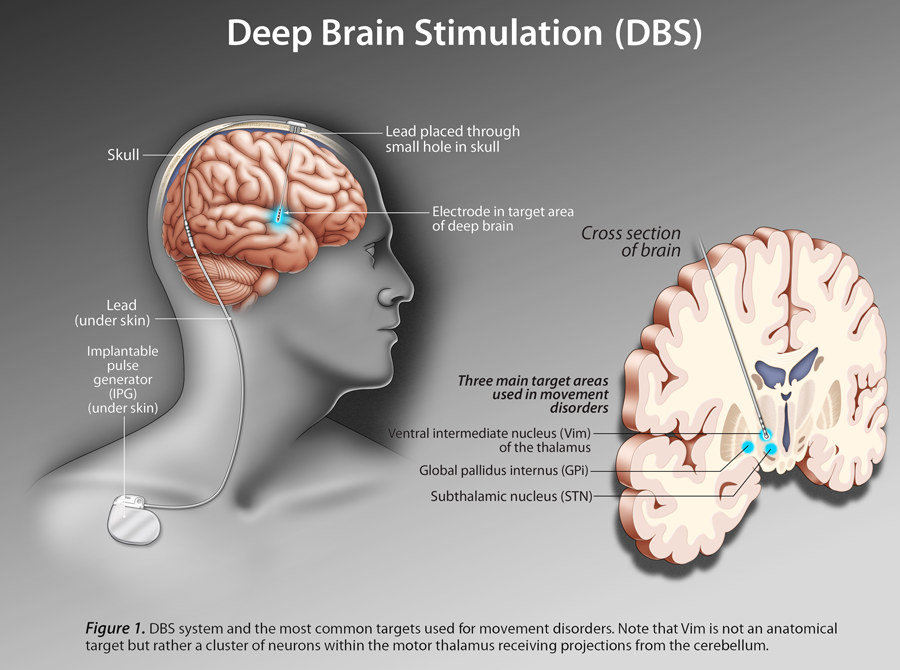
Sites Of Deep Brain Stimulation And Symptom Control
While both subthalamic nucleus and globus pallidus internus stimulation help improve the motor symptoms of Parkinsons disease, studies have found a few differences.
DBS of the third target, the ventral intermediate nucleus, can be beneficial for controlling tremors but does not work as well at addressing the other motor symptoms of Parkinsons disease.
In a Canadian study, targeting the subthalamic nucleus allowed people to reduce the doses of their medications to a greater degree, while targeting the globus pallidus internus was more effective for abnormal movements .
In another study, STN deep brain stimulation also led to a greater reduction in medication dosages. However, GPi stimulation resulted in greater improvement in quality of life, and also appeared to help with the fluency of speech and depression symptoms.
Side effects of DBS can sometimes include subtle cognitive changes . A different study compared these effects with regard to these different areas.
GPi showed smaller neurocognitive declines than STN, though the effects were small with both. On a positive note, both procedures seemed to reduce symptoms of depression following surgery.
What Benefits Does The Procedure Offer
DBS is not a cure for Parkinsons, but it may help control motor symptoms while allowing a reduction in levodopa dose. This can help reduce dyskinesias and reduce off time. DBS does not usually increase the peak benefits derived from a dose of levodopa the best levodopa response before DBS is a good indicator of the best response after DBS. But it can help extend the amount of on time without dyskinesias, which may significantly increase quality of life.
DBS does not provide most patients benefit for their non-motor symptoms, such as depression, sleep disturbance, or anxiety. DBS also does not usually improve postural instability or walking problems. If a symptom you have does not respond to levodopa, it is not likely to respond to DBS.
Read Also: On Off Phenomenon
Recommended Reading: Parkinson’s Bike Therapy
Some Common Concerns And Misconceptions About Dbs
My condition is not bad enough to necessitate DBS.In Parkinsons disease, there is a window of opportunity wherein one can undergo DBS. If a patient has progressed to moderate or severe dementia, DBS is not an option. Furthermore, DBS is appropriate when medication still has a positive effect but is becoming less reliable, or, when side effects are intolerable. Once medications are ineffective, DBS will not be a treatment option. One should inquire about DBS when PD symptoms and effectiveness of medications change, and before dementia sets in. A neurosurgeon or neurologist can help to monitor your symptoms. DBS does not cure PD, and if it progresses we can fine tune programming for continued effectiveness.
The battery needs to be replaced often and will include an invasive procedure.Generator replacement takes 15 minutes, can be accomplished under local anesthesia and is done every three-to-five years on average.
I cannot afford DBS.DBS is covered by all major insurances, including Medicare and Medicaid.
- Categories
Deep Brain Stimulation Doctors
Our expert restorative neurosurgeon Dr. JP Langevin has many years of experience with DBS. He was the first to implant and program PerceptTM PC with BrainSenseTM technology DBS system to treat patients with Parkinsons disease among Providence hospitals, the 3rd largest healthcare system in the United States.
You May Like: On Off Phenomenon
Potential Benefits Risks And Side Effects
DBS is not suitable for everyone, so it’s important to talk with your doctor about the potential benefits and risks. You should also discuss with a DBS neurologist the potential risks relating to not treating Parkinson’s, Parkinsons medication and other types of therapies. This information will enable you to make an informed decision on whether DBS is the right treatment to most effectively manage your specific symptoms.
Levodopa And Deep Brain Stimulation For Parkinsons Disease
Symptoms that do not respond to levodopa are unlikely to improve with Deep Brain Stimulation . Also if a patient with Parkinsons Disease has no response when taking adequate doses of levodopa, they are unlikely to experience any benefit from DBS. Sometimes patients would have a good response to levodopa, but they cannot tolerate the optimal dose.
This can be determined by doing a pre- and post-medication examination while the patient is in the clinic, giving a high dose of medication on an empty stomach. Patients who have good benefit to levodopa but cannot tolerate it may be good candidates for DBS. Patients should expect DBS to provide the same benefit as their best response to levodopa, but in a more consistent and reliable way. Please note that DBS is not a cure, and does not benefit imbalance, cognition, or freezing.
The only exception to the rule that DBS provides the same benefit as the best response to levodopa is tremor. Many patients with tremor-predominant PD find that while other motor symptoms improve with medication, the tremor may not respond as much, or at all.
These patients do still enjoy significant benefit in tremor reduction with DBS, by about 75%.
You May Like: Diseases Similar To Parkinsons
What Happens Before Surgery
In the doctor’s office you will sign consent forms and complete paperwork to inform the surgeon about your medical history, including allergies, medicines, anesthesia reactions, and previous surgeries. Presurgical tests may need to be done several days before surgery. Consult your primary care physician about stopping certain medications and ensure you are cleared for surgery.You may also need clearance from your cardiologist if you have a history of heart conditions.
Stop taking all non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medicines and blood thinners 7 days before surgery. Stop using nicotine and drinking alcohol 1 week before and 2 weeks after surgery to avoid bleeding and healing problems.
You may be asked to wash your skin and hair with Hibiclens or Dial soap before surgery. It kills bacteria and reduces surgical site infections.
No food or drink, including your Parkinson’s medication, is permitted after midnight the night before surgery.
Try to get a good night’s sleep. The DBS surgery involves multiple steps and lasts most of the day, during which you may be awake and off medication.
Morning of surgery
Arrive at the hospital 2 hours before your scheduled surgery time to complete the necessary paperwork and pre-procedure work-ups. An anesthesiologist will talk with you and explain the effects of anesthesia and its risks.
Can I Use Electrical Devices
While you should be able to use most electronic devices, you should be aware that:
- Some devices, such as theft detectors and screening devices, like those found in airports, department stores, and public libraries, can cause your neurotransmitter to switch on or off. Usually, this only causes an uncomfortable sensation. However, your symptoms could get worse suddenly. Always carry the identification card given to you. With this, you may request assistance to bypass those devices.
- You will be able to use home appliances, computers, and cell phones. They do not usually interfere with your implanted stimulator.
- You will be provided with a magnet to activate and deactivate your stimulator. This magnet may damage televisions, credit cards, and computer discs. Always keep it at least 1 foot away from these items.
Also Check: Parkinson’s Hallucinations Commercial
What Would Happen If I Have Dbs
The duration and surgical steps may vary depending on the type of system used but typically, surgery to implant the DBS system lasts several hours. Your hospital stay is usually a few days and includes a pre-operative assessment, the surgery itself and initial healing before you return home.
Your surgical team will include a neurologist, a DBS specialist neurosurgeon, an anaesthetist, a radiologist and other healthcare professionals.
The components of a DBS system are:
- Neurostimulator this pacemaker-like device is the power source for the system. There are several rechargeable and non-rechargeable stimulators. Each contains a small battery and a computer chip programmed to send electrical pulses to control Parkinson’s symptoms.
- Lead an insulated wire terminating in four electrodes which transfer electrical current to your brain .
- Extension an insulated wire placed under your scalp and outside your skull to connect to the lead and run behind the ear, down the neck, and into the chest below the collar- bone where it connects to the neurostimulator.
- Programmer the doctor uses this external programmer to set the parameters for stimulation. Each person responds to DBS in their own way so the programmer will be used to customise the signals to your brain.
- Patient controller in some DBS systems you can use this to turn the neurostimulator on and off. It may also be used to adjust stimulation settings within the limits set by your doctor.