Other Causes Of Parkinsonism
Parkinsonism is the umbrella term used to describe the symptoms of tremors, muscle rigidity and slowness of movement.
Parkinsons disease is the most common type of parkinsonism, but there are also some rarer types where a specific cause can be identified.
These include parkinsonism caused by:
- medication where symptoms develop after taking certain medications, such as some types of antipsychotic medication, and usually improve once the medication is stopped
- other progressive brain conditions such as progressive supranuclear palsy, multiple systems atrophy and corticobasal degeneration
- cerebrovascular disease where a series of small strokes cause several parts of the brain to die
You can read more about parkinsonism on the Parkinsons UK website.
Page last reviewed: 30 April 2019 Next review due: 30 April 2022
Pesticide And Herbicide Exposure
A strong link has been shown between PD and exposure to pesticides and herbicides. We need more Parkinsons-specific research to better understand what causes PD and to work to prevent it and help eliminate the risk of getting the disease, when it comes to all environmental risk factors and whether genetics can cause an increased risk in developing Parkinsons.
One herbicide that has been linked to Parkinsons is paraquat, a widely used commercial herbicide in the U.S. that is banned in 32 countries, including the European Union and China. The Parkinsons Foundation, along with the Unified Parkinsons Advocacy Council, signed two letters to the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency encouraging them to cancel the registration of paraquat based on strong scientific research linking the herbicide to Parkinsons disease. In October 2020, the EPA re-approved paraquat for use in the U.S. Without additional action, paraquat will remain legal for sale and use in the U.S. for the next 15 years.
Want To Learn More About The Latest Research In Parkinsons Disease Ask Your Questions In Our Research Forum
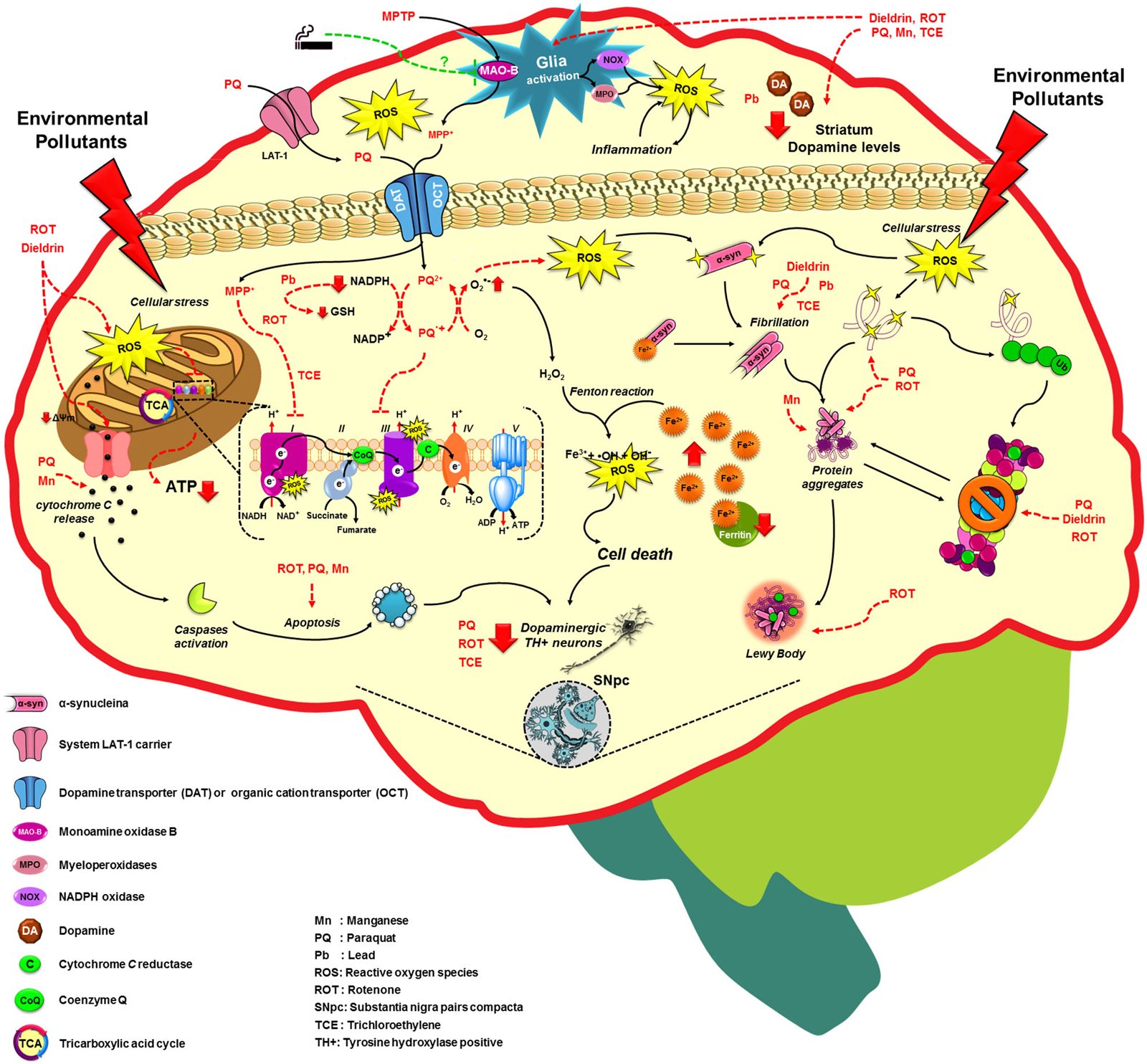
Environmental factors may trigger Parkinsons or modify its progression during the prodromal stage, in which early symptoms or signs are present, but clinical diagnosis is not yet possible. Among the reported factors, smoking, coffee, exercise, plasma urate, and use of ibuprofen have been linked to a lower risk of Parkinsons, while pesticide exposure and traumatic brain injury have been associated with a greater risk.
Apart from two pesticides known as rotenone and paraquat, researchers have had difficulties in providing evidence that other risk factors can cause the disease. Reverse causation meaning that Parkinsons changes lifestyle and behavior before a clinical diagnosis rather than the other way around has been proposed as an explanation for the link between these environmental triggers and Parkinsons in its early stages.
This prodromal stage is of major interest for prevention efforts, the researchers said in the release, adding that the discovery of Lewy bodies protein aggregates mainly composed of alpha-synuclein that are characteristic of Parkinsons in the olfactory pathway and the digestive tract made targeting factors that enter the body via the nose or gut even more important.
We are at an exciting moment to unveil environmental contributions to development and progression by taking a life-course approach, and utilizing novel tools to assess environmental exposures, the researchers said.
You May Like: Yopd Life Expectancy
You May Like: Sam Waterston Parkinson’s
Lack Of Exercise/physical Activities
The idea that exercise might have a role in Parkinsons disease is not new. Researchers have been trying to find a connection between Parkinsons and exercise for many years. They think that those who do regular exercise are less likely affected by the disease than those who dont.
A study published in the Journal of Neurology suggests that higher levels of physical activity may reduce the risk of developing Parkinsons disease. In this study, 125,828 provided information on physical activity in early adulthood. During the follow-up, a total of 387 Parkinsons cases were identified. The study found that the people who didnt develop the disease were mostly involved in some sort of higher levels of physical activity.
Similarly, one meta-analysis that included data from 8 prospective studies has concluded that moderate to vigorous physical activity may have an inverse relationship with a risk of Parkinsons.
Although it is not known how exercise could protect someone from developing Parkinsons, researchers think that it may inhibit abnormal changes in dopamine neurons and contribute to the healthy functioning of brain parts involved in body movement.
Investigating Environmental Factors That Increase The Risk For Parkinsons Disease
This funding program supported projects to investigate environmental exposures, such as chemicals or toxic emissions, that increase the risk of PD and/or influence disease progression.
While there are reports linking a variety of environmental factors with risk of PD, much remains unknown regarding the identification of specific environmental factors, their role in disease, and quantification of their contributions. A better understanding of such factors could lead to efforts to reduce or prevent such exposures in order to reduce the risk of PD.
Read Also: On And Off Phenomenon
Genetics: Insights Into Etiology
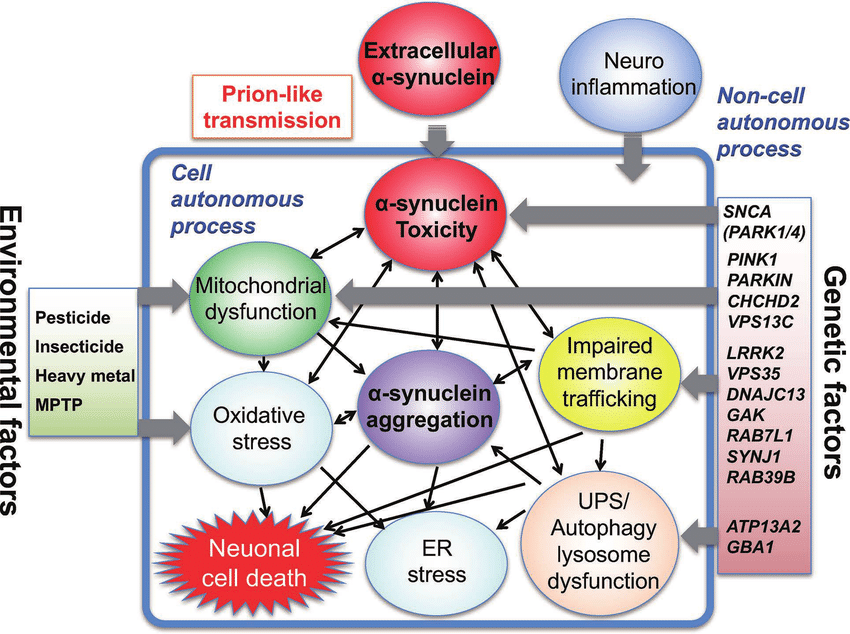
Improvement in genetic analysis techniques in the 1990s led to the discovery of the first genetic cause of PD: mutations in the SNCA gene encoding -synuclein . At around the same time, -synuclein was found to be the major constituent of LB, the pathological hallmark of PD . Subsequently, multiplications of the SNCA gene have been found to cause PD with penetrance increasing with gene dosage . These discoveries brought -synuclein to center stage in the study of the pathogenesis of PD and led to the hypothesis that during different stages of the disease, -synuclein spreads in a stereotypical way within the nervous system in a prion-like fashion .
Table 2 Examples of genes associated with PD risk
What Causes Parkinsons Disease
Parkinsons disease is a chronic, progressive neurological disease that currently affects about 1 million Americans. Parkinsons disease involves a small, dark-tinged portion of the brain called the substantia nigra. This is where you produce most of the dopamine your brain uses. Dopamine is the chemical messenger that transmits messages between nerves that control muscle movements as well as those involved in the brains pleasure and reward centers. As we age, its normal for cells in the substantia nigra to die. This process happens in most people at a very slow rate.
But for some people, the loss happens rapidly, which is the start of Parkinsons disease. When 50 to 60 percent of the cells are gone, you begin to see the symptoms of Parkinsons.
You May Like: Parkinson’s Bike Therapy
How Do Genetics Contribute To The Development Of Parkinsons Disease
Genes are like an instruction manual. They code the synthesis of molecules that make up the body. A change in these instructions can lead to different effects and potentially to diseases.
Some of these modifications or mutations have been identified in people living with Parkinsons disease. They increase the risk of developing the disease but are not common. Moreover, they do not always lead to the development of the disease.
Risk Factors For Parkinson’s Disease
While the exact causes arent fully understood, researchers have identified characteristics that increase a persons risk of developing Parkinsons, including gender, age, race, and genetic factors. However, it is worth noting that the vast majority of cases of PD are considered idiopathic Parkinsons disease. Idiopathic means a condition that arises spontaneously or for which the cause is currently unknown. Major advances in research and science are continuing to reveal more underlying causes for PD.1,2
Read Also: On-off Phenomenon
Environmental Factors: Etiological And Disease
From 1817 when Dr. James Parkinson first described 6 patients with the condition that would later bear his name , much progress was made in the following 150years. It became known that the SN was the site affected by PD pathology together with the presence of cytoplasmic inclusions, and levodopa became available as the first effective symptomatic drug treatment of PD in 1960s . However, the etiology of PD remained elusive.
Table 1 Examples of environmental factors and their biologic correlates
The most robust beneficial environmental factor associated with PD is cigarette smoking which has been seen in early case-control studies and then confirmed in more recent large prospective cohorts. Active smokers have 50% lower risk of PD compared to never smokers . There is a strong dose-response relationship including duration, intensity, pack-years and years since last smoking: PD risk decreases with increasing duration of smoking and increases again with time since quitting . Preliminary reports also support an inverse relationship between passive smoking, smokeless tobacco use and PD .
Environmental Risk Factors For Parkinsons Disease And Parkinsonism: The Geoparkinson Study
Dick, F D, De Palma, G., Ahmadi, A., Scott, N W, Prescott, Gordon ORCID: 0000-0002-9156-2361, Bennett, J, Semple, S, Dick, S, Counsell, Cet al, Mozzoni, P., Haites, N, Wettinger, S. Bezzina, Mutti, A., Otelea, M., Seaton, A, Söderkvist, P. and Felice, A.Environmental risk factors for Parkinsons disease and parkinsonism: the Geoparkinson study. Occupational and Environmental Medicine, 64 . pp. 666-672. ISSN 1351-0711
Full text not available from this repository.
Official URL:
You May Like: Does Vitamin B12 Help Parkinson’s
Family History And Genetics
Approximately 15 percent to 25 percent of people with PD have a relative with the disease.5 People with a close family member with Parkinsons have a small increased risk of developing the disease. About 15 percent to 25 percent of people with PD have a known relative with the disease.5 A number of genetic mutations have been identified that are associated with PD. Some of these appear to be more causal, while others simply increase a persons risk for the disease.5
What Are Other Parkinsons Disease Risk Factors

- Age: Parkinsons disease mainly affects people over 60 years of age and the risk of developing the disease increases over the years.
- Population: Parkinsons disease is more common among people with white skin.
- Sex: More men have Parkinsons disease than women.
- Career: Some occupations, such as farmers or factory workers, may be more exposed to certain chemicals or toxins that increase the risk of developing Parkinsons disease.
- Serious head injuries: Different types of serious head and brain injuries, such as concussions, increase the risk of developing the disease.
- Location: The number of people living with the disease in rural areas is higher. This seems to be related to agricultural pesticide exposure.
Recommended Reading: What Foods Should Be Avoided When Taking Levodopa
Don’t Miss: Voice Amplifiers For Parkinson’s
How You Lose Dopamine Production
Damaged nerve cells can be what results in a decreased ability of the brain to create dopamine. Generally, some kind of degradation of the brain cells will reduce dopamine production.
There is some genetic link to parkinsons disease. For example, specific genetic mutations can impact the dopamine production. Far more common is that exposure to something in the environment can impact the brain.
You May Like: Fitflop Shoes For Parkinsons
Is Parkinsons Disease Hereditary
Hereditary diseases are passed from parents to their children, but cases of familial Parkinsons disease are very rare . The vast majority of Parkinsons cases are not transmissible.
Having Parkinsons disease does not affect your childrens risk of developing the disease. Similarly, your risk is not increased if your brother or sister has the disease. However, your risk may be increased if more than one person in your family has the disease.
Exposure to certain environmental factors or toxins may contribute to the development of Parkinsons disease.
The main environmental factors involved in Parkinsons disease are:
You May Like: Zhichan Capsule
Interplay Of Aging Genetics And Environment: What Animal Models Show
Aging is recognized to be the primary risk factor for PD with incidence rising exponentially with advancing age. Nevertheless, most elderly over 85years do not have PD. Familial PD due to monogenic causes account for about 5% of all PD but the majority of known mutations have incomplete and variable penetrance. It is hypothesized that genetic risk factors may render the individual more sensitive to the pathologic influence of other factors. For example, the cumulative risk of PD in carriers of LRRK2 p.G2019S, the most common LRRK2 mutation in PD, rises exponentially from the age of 50 onwards , suggesting that aging interacts with LRRK2 mutations to initiate disease. This observation is corroborated in a LRRK2 G2019S knock-in mouse model which showed dysfunctions in plasma membrane and vesicular DA transporters, and accumulation of serine129-phosphorylated -synuclein, the predominant form of -synuclein in Lewy bodies, in 12-month-old KI mice compared to age-matched wild-type mice. These changes were not present in young 3-month-old KI mice, suggesting a progressive response relying on the interaction of the mutation and aging . Similarly, another LRRK2 KI mouse model, LRRK2 R1441G, showed a progressive, age-dependent accumulation of oligomeric -synuclein in the striatum and cortex compared with age-matched WT mice this higher rate of oligomeric -synuclein accumulation in KI than WT mice was first apparent at 15months and became significant at 18months of age .
Snp Selection And Genotyping
Thirteen SNPs that have been associated with PD in at least one out of the 5 large GWAS meta-analysis studies for PD in the European population were selected for genotyping . The selection criteria for the SNPs were based on the estimates of the association and on the frequency of the minor allele , in order to ensure the maximum statistical power for their investigation. There was an estimation of the power of the study at a value of 0.05 to detect ORs similar to those previously reported in the GWAS, given the allele frequencies observed in the Cypriot population.
DNA was extracted from peripheral blood lymphocytes as described elsewhere . SNP genotyping was performed using Taqman genotype assays . Each assay was carried out using 10 ng genomic DNA in a 5 μl reaction using Taqman Universal PCR Master Mix . The fluorescence profile was read on an ABI PRISM 7900HT instrument and the results analyzed with Sequence Detection Software .
Dont Miss: Adaptive Silverware For Parkinsons
You May Like: Adaptive Silverware For Parkinson’s
No One Definitive Cause Of Parkinsons
There are no biomarkers or objective screening tests that indicate one has Parkinsons. That said, medical experts have shown that a constellation of factors are linked to it.
Parkinsons causes are likely a blend of genetics and environmental or other unknown factors. About 10 to 20 percent of Parkinsons disease cases are linked to a genetic cause, says Ted Dawson, M.D., Ph.D., director of the Institute for Cell Engineering at Johns Hopkins. The types are either autosomal dominant or autosomal recessive .
But that leaves the majority of Parkinsons cases as idiopathic, which means unknown. We think its probably a combination of environmental exposure to toxins or pesticides and your genetic makeup, says Dawson.
Age. The biggest risk factor for developing Parkinsons is advancing age. The average age of onset is 60.
Gender. Men are more likely to develop Parkinsons disease than women.
Genetics. Individuals with a parent or sibling who is affected have approximately two times the chance of developing Parkinsons. Theres been an enormous amount of new information about genetics and new genes identified over the past 10 or 15 years that have opened up a greater understanding of the disease, says Dawson.
Fecal Microbiota Transplantation In Neurodegenerative Diseases
Germ-free wild-type mice and their offspring had ASD-like symptoms and displayed alternative splicing of ASD-relevant genes when FMT was performed with stool from children with ASD. ASD symptoms decreased when GABA receptor agonists were administered to the ASD model. Decreased cerebral oxidative stress was observed in another study after FMT from a normal hamster in an ASD hamster model.
FMT may reverse the decrease in cognitive function induced by antibiotics. Wild-type mice showed a cognitive decline after broad-spectrum antibiotic therapy. However, memory and spatial learning were improved after receiving anti-aging mouse feces. Human microbiome transplantation protected germ-free mice from death caused by acute arsenic toxicity. According to our research, Mn exposure increased A and inflammatory factor production in the brain and caused hippocampal degeneration and necrosis,. FMT from normal rats alleviated the neurotoxic effects of Mn exposure by altering the gut microbiota.
Recommended Reading: Parkinson Bicycle Cleveland Clinic
Advancing Age And Parkinsons Disease
Age is perhaps the biggest risk factor for the onset of Parkinsons disease. The average age at which people will develop this movement disorder is 60. This is not usually something that affects younger people. The brain ages as people get older.
Even without external factors, cells in the substantia nigra can die on their own as an individual ages, causing symptoms to develop as the person gets older.
Recommended Reading: On And Off Phenomenon
Environmental Risk Factors For Parkinson’s Disease: The Epidemiologic Evidence
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 05 January 2016
- Bruce S. Schoenberg*
- Affiliation:Neuroepidemiology Branch, Intramural Research Program, National Institute of Neurological and Communicative Disorders and Stroke, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, Maryland and the Department of Neurology, Georgetown, University School of Medicine, Washington, D.C.
- *
Read Also: Pfnca Wellness Programs
Genetic And Environmental Risk Factors For Neurodegenerative Diseases
Mutations in the gene encoding leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 are the most common cause of hereditary PD. LRRK2 activity promotes -synuclein propagation via the phosphorylation of RAB35. A genetic component for the apparently sporadic disease was not obvious in the early days of PD research. LRRK2 mutations can cause familial PD with age-dependent but variable penetrance variants of the gene are also risk factors for sporadic PD. Individuals with mutations in the genes PARKIN, PINK1, SNCA, GBA1, and LRRK2 show an increased risk of developing familial PD . In addition, multiple mutations in genes such as C9orf72, TARDBP, and SOD1 are mainly expressed in a variety of nonneuronal cells which enhance immune dysregulation and neuroinflammation in the pathogenesis of ALS.
Fig. 3: Implications of metals in A neurotoxicity.
APP binds to metals . Under acceleratory conditions, A self-aggregates and forms several types of oligomers finally forming insoluble aggregates , and tight binding to the surface of neurons and form fibrillar deposits.