Thanks For Signing Up
We are proud to have you as a part of our community. To ensure you receive the latest Parkinsons news, research updates and more, please check your email for a message from us. If you do not see our email, it may be in your spam folder. Just mark as not spam and you should receive our emails as expected.
Tic And Tourette Syndrome:
Motor tics are repetitive, usually quick movements that can usually be suppressed by the person who has them, at least for a few seconds. They are not a nervous habit, but are believed to be neurological in their origin. Tourette syndrome is the name applied when motor tics associated with vocal tics begin in childhood, last longer than a year, and change over time. Most people who have Tourette syndrome do not have the famous symptom of uttering obscenities.
Tic is common, particularly in childhood, and may improve or cease altogether as one grows older. Occasionally it is sufficiently troubling that medication is warranted. Teasing from other children, or misunderstanding and criticism from parents and teachers are sometimes more problematic than the tic itself.
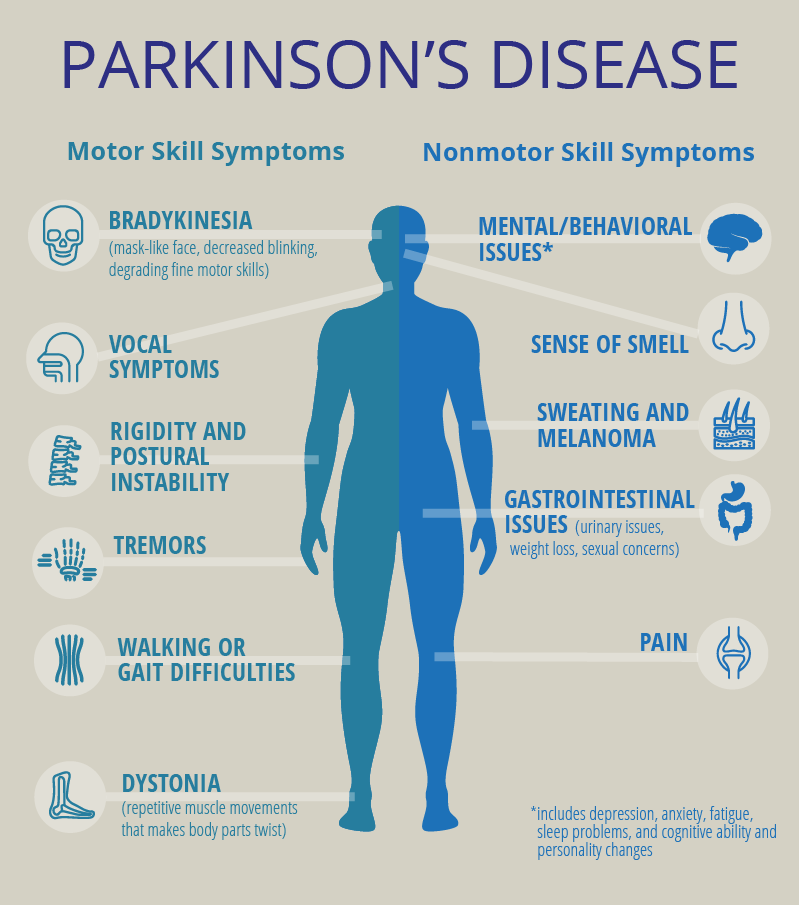
Some Experts Estimate That Forty Percent Of People Living With Parkinsons Disease Experience Dystonia As An Early Symptom Or As A Complication Of Treatment
What is the relationship between Parkinsons and dystonia?
Dystonia and Parkinsons disease are movement disorders that are closely related. Parkinsonism is a term used to describe any clinical presentation that manifests in the cardinal symptoms of Parkinsons disease .
Main Types of Dystonia
There are two main categories of dystonia: primary and secondary . Primary dystonia is a condition in which dystonia is the only clinical feature. There is no evidence of cell death or a known cause. It is also known as idiopathic torsion dystonia. Primary dystonia is thought to have greater genetic contribution, even in the absence of a family history of dystonia. Among forms of primary dystonia, the most common is generalised dystonia, which affects the legs or one leg and the trunk, plus other regions, most commonly the arms.
Outside the context of Parkinsons disease, there are several other types of secondary dystonia, in which other symptoms are also present. In this category are:
- Myoclonus dystonia, characterised by dystonia and myoclonus , with onset in childhood or adolescence.
- Dopa-responsive dystonia, a genetic disorder of childhood-onset and may have features of parkinsonism or exaggerated reflex responses.
- Rapid-onset dystonia parkinsonism, a rare inherited disorder characterised by sudden development of dystonia and parkinsonism.
- Paroxysmal dystonia, neurological conditions characterised by discrete and sudden episodes of involuntary movements.
Read Also: What Is The Difference Between Parkinson’s And Alzheimer’s
Therapies To Manage Dystonia
Physical and occupational therapy are also options for managing dystonia. It may be difficult to exercise when you are in pain. However, if you are in pain while moving and suddenly stop, the pain can get worse. A physical or occupational therapist can recommend exercises or techniques to target the source of your pain and to stretch and strengthen the body parts most affected by dystonia.
Dystonia Vs Dyskinesia In Parkinson’s Disease
Claudia Chaves, MD, is board-certified in cerebrovascular disease and neurology with a subspecialty certification in vascular neurology.
Dystonia and dyskinesia are movement problems that commonly occur in Parkinsons disease . You may experience one or both of them, particularly in late-stage PD. Dystonia is muscle stiffening caused by PD, while dyskinesia is a type of muscle twisting caused by some PD medications.
Dystonia and dyskinesia can both cause distress, and they are distinguished from each other based on their visible features. They can be managed with medication or surgery, typically with a moderate improvement of symptoms.
PD is characterized by four primary symptoms:
- Resting tremor
- Postural instability
- Rigidity
While they can fluctuate in severity, the primary symptoms of PD tend to be present most of the time.
Dystonia and dyskinesia are recurrent, abrupt, and short-lived muscle movements. Not everyone who has PD experiences dystonia and dyskinesia. If they do, the symptoms they experience can be telling.
-
Affects large muscle groups
-
Smooth, repetitive movement often described as a rolling or writing motion
-
Can begin suddenly and stop after several minutes
-
Not typically painful
-
More likely to occur when PD medication effects are at their peak
With dyskinesia, you may experience a snakelike twisting of your arm or movements of your head and neck that appear like dancing in slow motion.
Don’t Miss: University Of Florida Parkinson’s Center
Treating Dystonia In Parkinsons
Treatment options for dystonia include:
- Dopaminergic medication adjustment as discussed above
- Botulinum toxin injections of the affected muscles
- Physical therapy to loosen and strengthen the dystonic body part
- Trying other medications that target the dystonia directly such as muscle relaxants or anti-cholinergic medications
- Use of a device to provide a sensory trick*.
- Deep brain stimulation can be considered in difficult-to-treat situations
*To minimize their dystonia, some people have success using an interesting tactic called a sensory trick. A sensory trick is defined as a physical gesture that mitigates the production of the dystonia. For example, touching the eyebrow may help keep the eyes open, or touching the chin may keep the neck from twisting. In my clinical practice, one woman wears metals rings on her dystonic fingers to help them assume a more normal position. Another man wears 5-toed shoes to prevent dystonic toe curling
How Can I Reduce My Muscle Cramps
Cramps can result from excess or lack of movement. Some cramps may be connected to particular positions, such as at night, or specific activities. By avoiding these situations, you can reduce the occurrence of these cramps.
Cramps may also be related to a lack of hydration and vitamin B. Drink more fluids and consult your doctor to assess whether you need to take vitamin supplements.
You can also try to:
- Stretch longer before your daily activities
- Massage your muscles
Recommended Reading: Parkinson’s And Swollen Feet And Ankles
What Is The Difference Between A Parkinson’s Disease Patient With Dystonia And A Dystonia Patient With Parkinson’s Symptoms
Parkinson’s disease is a neurological movement disorder with a wide array of symptoms that includes slowness of movement, rigidity of muscles, tremor, loss of balance, memory impairment, personality changes, and others. The movement symptoms of Parkinsons disease may be called parkinsonism. Parkinsonism is one aspect of Parkinsons disease.
Symptoms of dystonia and parkinsonism can occur in the same patient because both of these movement disorders seem to arise from involvement of the basal ganglia in the brain. Both parkinsonism and dystonia can each be caused by a great many disorders, and some of these disorders includes features of both parkinsonism and dystonia.
For example, there are the disorders known as dopa-responsive dystonia and x-linked dystonia-parkinsonism . DRD commonly begins in children as a dystonia predominately affecting the feet and being first manifested by an abnormal gait. In these children, features of parkinsonism tend to develop such as slowness of movement and also decreased muscle tone.
When DRD begins in adults, it usually appears first as parkinsonism and can be mistaken for Parkinson’s disease. XDP can also first develop as either dystonia or parkinsonism, and the symptoms of other disorder may occur.
What Are The Symptoms Of Dystonia
The symptoms of dystonia may vary from person to person. Various types of dystonia can affect only one muscle, groups of muscles or muscles throughout the body. In childhood or early-onset dystonia, the symptoms often start in the limbs and may progress to involve other parts of the body. Symptoms may occur after periods of exertion. They may fluctuate throughout the course of the day.
In adult-onset dystonia, the symptoms usually affect one or adjacent parts of the body, most often involving the neck and/or facial muscles.
Involuntary muscle contractions may affect a single area such as the leg, jaw or arm.
Recommended Reading: Parkinson’s Leaning To One Side
Whats The Difference Between Dystonia And Dyskinesia
Both dystonia and dyskinesia affect your muscles and joints however, there are distinct differences between them that require unique treatments. Dystonia is a movement disorder that can occur with or without a Parkinsons diagnosis, while dyskinesia is often a side effect people experience as a result of taking Parkinsons medications. Though both involve similar abnormal movements of the arms, legs, neck, and face, dystonia is characterized by more sustained muscle contractions and pain.
Other Causes Of Dyskinesia And Dystonia
There are many types of dystonia unrelated to Parkinsons disease. Many forms of dystonia occur with no known cause. Some causes of dystonia are hereditary, while brain injury can also cause dystonia.
Huntingtons disease is a rare, genetic condition in which nerve cells in the brain degenerate over time. This disease causes movement disorders similar to Parkinsons, including chorea and dystonia.
Multiple system atrophy and progressive supranuclear palsy are other rare, degenerative disorders that affect muscle movements. Dyskinesia can occur when people with MSA or PSP are treated with levodopa, and untreated MSA or PSP can lead to the development of dystonia.
Recommended Reading: Possible Causes Of Parkinson’s Disease
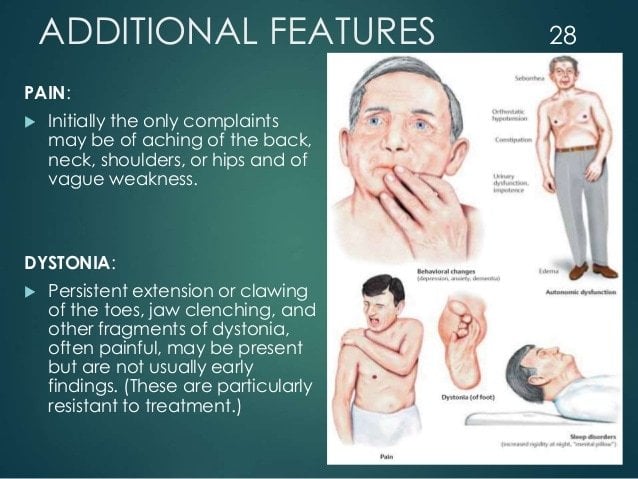
What Dystonia Looks Like In Pd
The involuntary muscle movements of dystonia can be subtle or very noticeable. They may manifest as:
-
Blepharospasm , squinting or repeated blinking
-
Grimacing or repeated jaw clenching
-
Thin, hoarse or shaky voice
-
Twisting of the neck into an abnormal posture
-
Twitching and cramping of the hands, fingers, feet or toes
If you experience symptoms of cervical dystonia, you should notify your doctor right away. Keeping a log of your dystonia symptoms can be helpful in finding the right treatment.
Is Dystonia A Form Of Parkinson’s
Dystonia can be one of the symptoms of Parkinsons disease . PD is a long-term neurological movement disorder with various symptoms ranging from slowness of movement , rigidity of muscles, tremor, loss of balance, memory impairment, personality changes and others. In young-onset PD, foot dystonia may be the first feature. Later, other symptoms such as personality changes and memory impairment become noticeable.
Dystonia may sometimes develop as an isolated symptom in individuals who do not have PD. It may be seen in people who suffer from Huntingtons chorea, birth injury, stroke, brain infections, etc. Sometimes, a person with Parkinsons may develop dystonia due to the drug Leva Dopa that is given as a part of PD treatment.
Dystonia is a neurological disorder that purely affects movement and is characterized by involuntary contractions of the muscles causing repetitive or twisting movements or abnormal postures. Dystonia can occur in isolation or as a symptom of PD. It, however, does not affect everyone with PD.
Both PD and dystonia seem to occur due to the involvement of a part of the brain called the basal ganglia. Thus, the symptoms of both can occur in the same person.
Read Also: How Serious Is Parkinson’s Disease
S Of The Body Affected By Dystonia
- Arms, hands, legs and feet: Involuntary movements, spasms or twisting and “curling”
- Neck: May twist uncomfortably, causing the head to be pulled down or to the side. This is called cervical dystonia or spasmodic torticollis
- Muscles around the eyes: May squeeze involuntarily, leading to a person to blink too much or to have difficulty opening the eyes. This is also called blepharospasm
- Vocal chords and swallowing muscles: May cause a person’s voice to sound softened, hoarse or breathy
- Jaw: May open or close forcefully or there may be grimacing of the face
- Abdominal wall: May cause sustained contractions and involuntary, writhing movements of the abdominal wall
Ssrt Is Not A Predictor Of Disease Severity
Although all groups of movement disorders patients tested showed prolonged SSRT, within a particular disease group there was no correlation between SSRT and clinical measures of disease severity. Previous studies also failed to find a relation between the prolonged SSRT of PD patients and global measures of cognitive impairment or severity of disease,. By contrast, a more specific assessment of the severity of levodopa-induced dyskinesia in PD patients does show a correlation with SSRT. The disease severity demonstrated no significant correlation with RT. This is expected as the major deficit in PD is bradykinesia and not the prolongation of reaction time. It is likely that a multitude of changes to cortical and sub-cortical networks result from disease pathology and attempts at compensation to restore function. Global disease severity probably results from a myriad of different interactions and impairments, with many possible routes to generate a similar level of impairment. Only a sub-set of these networks will affect response inhibition as measured by SSRT these may overlap with the circuits responsible for dyskinesia. Interestingly, the ocSSRT was significantly prolonged even in a sub-set of patients with early stage of disease, suggesting that ocSSRT might be developed as an early disease marker.
You May Like: Parkinson’s Disease And Brain Function
How Can I Treat Episodes Of Dystonia
You first need to determine the cause of your muscle pain and make sure it is not cramps.Secondly, you must determine when dystonia occurs in regard to your levodopa dose intakes. The best way to do this is by keeping a diary for a few days. You will then be able to explain this phenomenon in full detail to your neurologist, who will be able to optimize your treatment with you.
Many people with episodes of dystonia reduce the intensity of their pain by:
- Gently touching the affected body part with their finger or with other objects of different textures
- Touching a part of the body close to the part affected by the contraction
- Stretching the part of the body affected by the contraction
Relaxation techniques can also help relax muscles affected by dystonia.
What Causes Dyskinesia And Dystonia
Dyskinesia is a common side effect of the Parkinsons drug levodopa. This drug is used to help increase the level of dopamine in the brain, alleviating symptoms of the disease. However, levodopa is taken intermittently throughout the day, causing dopamine levels to rise and fall over time. These fluctuations are thought to be the cause of dyskinesia. There are two types of dyskinesia:
- Peak-dose dyskinesia, which occurs when the level of levodopa is at its highest
- Diphasic dyskinesia, which occurs when levels of levodopa are rising or falling
While dystonia can be a symptom of Parkinsons disease itself, it can also be caused by levodopa treatment, similar to dyskinesia. Dystonia symptoms occur when there is a decrease in brain dopamine levels, which can occur before medication is taken in the mornings or as it is wearing off during the day. This off and on dystonia can be addressed by taking an extended-release form of levodopa, or increasing the number of doses taken per day.
Dystonic dyskinesia can occur when the movements caused by levodopa are more sustained and twisting than in typical dyskinesia. When this occurs, it is important to determine the cause whether the movement occurs at peak-dose levels of dopamine or it is off and on dystonia.
Read Also: Is Parkinson’s A Form Of Cancer
Standard Treatments Partially Normalise Ssrt
Although SSRT did not correlate with disease severity, when patients were treated SSRT was reduced. In PD patients, the SSRT was significantly reduced by levodopa treatment. This is in agreement with past work which showed an improvement in response inhibition in the ON phase, although two previous studies failed to find a decrease specifically in SSRT with dopaminergic medications,. It is possible that our improved approach to estimation of SSRT allowed us to detect a relation, which could otherwise be masked by measurement variability.
It is perhaps not unexpected that treatment with a centrally-acting drug such as levodopa could modulate response inhibition. Interestingly, the patients with more prolonged OFF ocSSRT demonstrated a positive correlation with change in ocSSRT after levodopa administration. This differential correlation could suggest that RT and ocSSRT may be measuring underlying processes which are differently affected by the disease.
How Dystonia Is Caused In Parkinsons Cases
First and foremost, dystonia can be a symptom of Parkinsons disease itself. Particularly in young onset PD, foot dystonia may appear as the first motor symptom that is experienced. If dystonia occurs in isolation, the diagnosis of PD may only become clear as other symptoms appear. If dystonia occurs as the predominant symptom of PD, the patient and his/her doctor must decide how to treat it either by starting dopaminergic medications to see if this helps the dystonia or by targeting the dystonia itself, possibly with Botulinum toxin injections.
Once medications for PD have been started, dystonia may appear when there is a decrease in brain dopamine levels, which could occur first thing in the morning before taking medication or when a dose of medication is wearing off. If this is the pattern that is noted, there are various strategies that can be implemented to decrease OFF time. Depending on when the OFF time occurs, these approaches may include taking a long-acting Levodopa formulation before bed, increasing the number of doses per day or adding a medication to lengthen the amount of time that a dose works.
Don’t Miss: How Close To A Cure For Parkinson’s
Dystonia Or Muscle Cramps
Muscle cramps and dystonia occur when one of your muscles, or a group of muscles, tightens or shortens involuntarily.
Muscle cramps and dystonia can be confusing as they can feel very similar. You may not always be able to tell the difference between them, but they are caused by separate problems and are therefore treated differently.
Muscle cramps in Parkinsons are generally caused by muscular rigidity and reduced movement rather than by muscles contracting. But, like dystonia, cramps can also be painful and very distressing.
Normal painkillers do not usually relieve them, but cramps often respond well to massage and the use of a hot water bottle or heated pad. Movement and exercise may also help to release cramps and reduce stiffness. If these do not help, then your doctor may prescribe muscle relaxants.