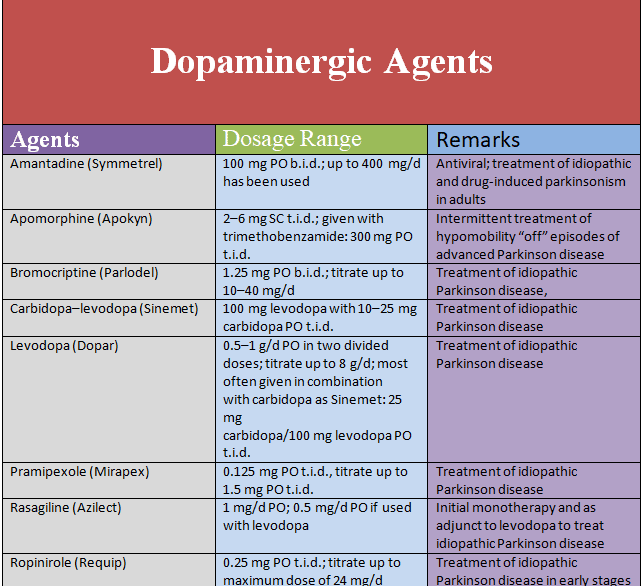
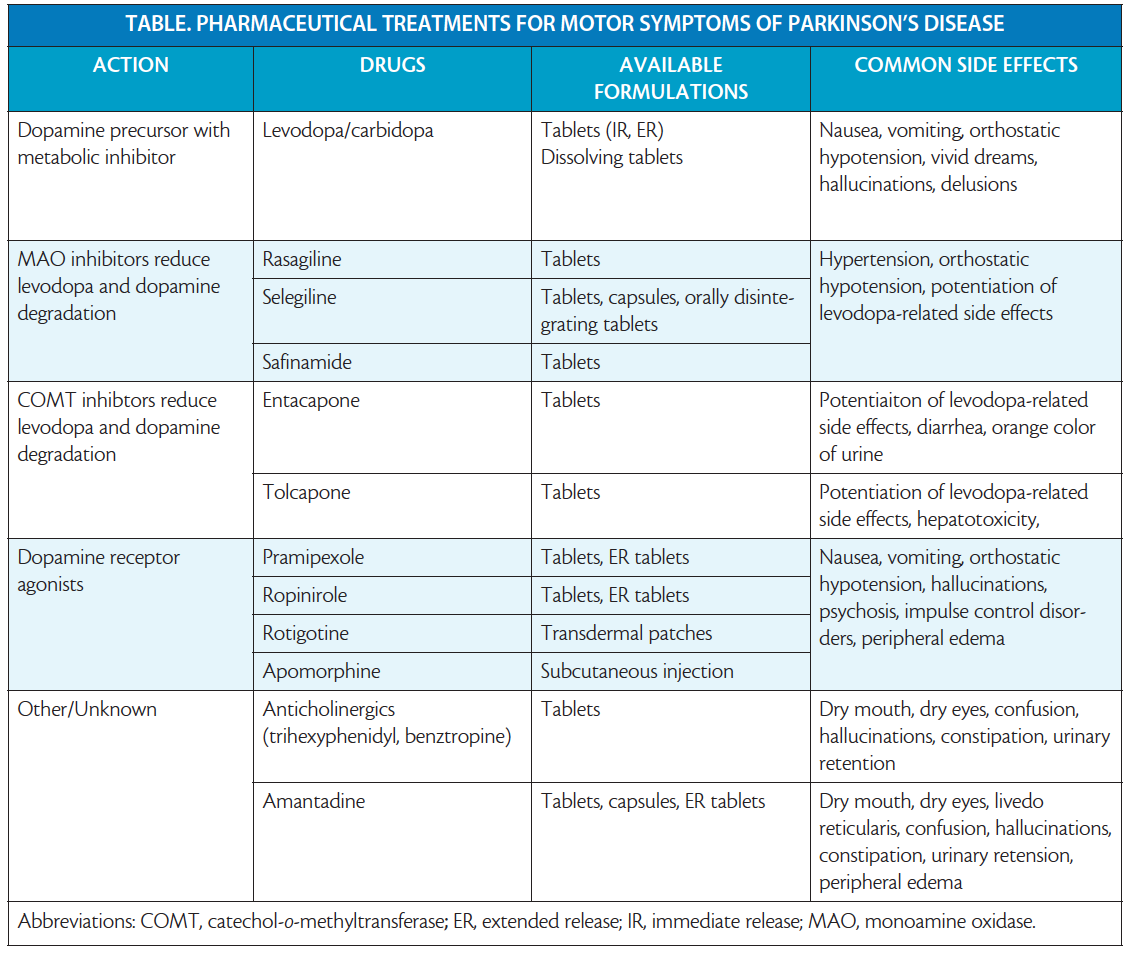
What Are Dopaminergic Antiparkinsonism Agents
Dopaminergic antiparkinsonism agents aim to replace dopamine or prevent the degradation of dopamine.Antiparkinson drugs that aim to replace dopamine in the central nervous system, either release dopamine or mimic the action of dopamine. Drugs that replace dopamine are generally given with peripherally acting dopa carboxylase inhibitors, to prevent the metabolism of levodopa to dopamine peripherally. Dopamine receptor agonists bind to dopamine receptors and mimic the action of dopamine.Selective monoamine oxidase inhibitors bind to the enzyme MAO-B and prevent dopamine from being broken down. Antiparkinson agents are used to treat Parkinson’s disease, which is a degenerative disorder of movement that occurs due to dopamine deficiency in the brain, particularly in the basal ganglia.
Early Use Of Levodopa
The first clinical application of Carlssons discoveries was for extrapyramidal side effects of reserpine and phenothiazines. Degkwitz et al. found that levodopa produced moderate improvement in reserpine-induced parkinsonism and McGeer et al. thought that levodopa was less effective than the anti-histamine and mildly anti-cholinergic diphenhydramine for dystonia and parkinsonism caused by antipsychotics.
When levodopa was administered to patients with PD in single dose studies by intravenous and oral routes, it appeared to produce unequivocal improvement in motor function. More physicians experimented with the drug, and not all were as impressed by its therapeutic effects. In the mid-1960s, two double blind, placebo-controlled trials of levodopa were published. Fehling gave intravenous D,L-dopa to 27 parkinsonian patients, while McGeer and Zeldowicz gave both oral and intravenous levodopa doses to 10 individuals. Neither group of researchers could detect much difference between active and placebo treatment. In retrospect, these trials had probably been using doses of levodopa that were too low for periods that were too short.
Treatment Of Late Stage Complications Of Parkinsons Disease
Postural hypotension
Levodopa and dopamine agonists worsen postural hypotension and it may be necessary to lower the dose of levodopa or withdraw the agonist. Treatment is difficult, but patients should be advised to sleep with the head of the bed raised by one or two bricks and to add salt to their diet. Fludrocortisone can then be added at a dose of 0.1 mg in the morning, increasing if necessary up to 0.5 mg in the morning. If these measures are ineffective, the alpha agonist midodrine 10-20 mg four hourly can be useful but it is experimental and only available via the Special Access Scheme. Patients treated for postural hypotension need to have electrolytes, renal function and supine blood pressures closely monitored.
Parkinsonian psychosis, depression and dementia
Psychotic symptoms such as visual hallucinations and persecutory delusions occur most commonly in the setting of dementia, which may be mild and therefore easily missed. Most drugs for Parkinsons disease make these symptoms worse. Depression is also common and requires treatment in its own right.
Recommended Reading: How To Tell The Difference Between Essential Tremor And Parkinson’s
Taking Dopamine Agonist Drugs: Pramipexole And Ropinirole
Below we have included the different forms of pramipexole medication and an overview of how to take them.
The most recent and complete information on your specific drug will be on your patient information leaflet that comes with your medication packet. Always read it carefully before you start your treatment.
For detailed information you should follow the advice of your specialist or Parkinsons nurse about how to take pramipexole so that it works well for your Parkinsons.
Pramipexole drugs are also used to help your symptoms when your levodopa medication causes you to experience wearing off and dyskinesia. This could be motor fluctuations, or wearing off before your next dose of levodopa is due.
What Should I Know About Parkinsons Disease And Medications
There have been rapid and remarkable changes over the past decade in treating Parkinsons disease . The development of new medicines and the understanding of how best to use them and the older drugs have significantly improved the quality of life for people with the disease.
There is currently no treatment that has been proven to affect the disease progression or development of medication that can slow the disease process. There are two general approaches to the treatment of PD improve the symptoms with medications and engage in physical therapy. Most patients with PD can be adequately treated with medicines that alleviate their symptoms. For the approximately 15% of patients for whom medicines are not sufficiently effective, new, highly effective, and safe surgical treatments are available.
Choices about medicines made early in the course of the disease have a strong impact on the long-term course of the illness. Therefore, you should seek the advice of doctors specially trained in treating PD even when the illness is only suspected. Movement disorders specialists are neurologists who have completed their training in neurology and have received special advanced training in treating PD and other related diseases.
Don’t Miss: Are Seizures Common With Parkinson’s
Assessing The Robustness Of Model Findings
To examine the robustness of our findings, we used a more conservative linear regression approach to explain choice behavior and found results consistent with our learning model analysis. This approach is often used to study value-based decision making in animals . We also confirmed that behavioral results were comparable for young adult subjects and young adult monkeys performing a similar task . If subjects learn values according to standard RL models, reward weights estimated by linear regression, although not constrained to do so, will decay exponentially. Reward weights across our groups bear a striking resemblance to the exponentially weighted average of reward history in RL models. Reward weights for Parkinson’s patients decayed significantly more quickly on than off dopaminergic medication, consistent with higher learning rates in patients on than off dopaminergic medication. Finally, we used model comparison methods to show that the RL model explains the data better than the more general linear regression approach, although results using the two different modeling approaches were consistent.
Deferiprone Is Associated With Worsening Parkinsons Symptoms In Patients Nave To Dopaminergic Drugs
1.Deferiprone was associated with an increase in MDS-Unified Parkinsons Disease Rating Scale scores compared to placebo, indicating worsening symptoms.
2. The deferiprone group had faster disease progression and more adverse events than the placebo group.
Evidence Rating Level: 1
Relevant Reading: A double-blind, delayed-start trial of Rasagiline in Parkinsons disease
Read Also: Does Parkinson’s Cause Weight Gain
What Are The Possible Side Effects
Side effects can vary depending on the specific drug you are taking. The most common side effects of dopamine agonists include:3,4
- Sudden sleepiness
- Dizziness or light-headedness
Dopamine agonists may also cause dyskinesia, or sudden and uncontrollable movements. Although dopamine agonists are less likely to cause dyskinesia than carbidopa-levodopa therapy, dyskinesias can greatly affect a persons quality of life.3,4
A less common side effect of dopamine agonists is impulse control behaviors. Examples include increased gambling urges, increased sexual urges, or other intense urges.3,4
These are not all the possible side effects of dopamine agonists. Talk to your doctor about what to expect or if you experience any changes that concern you during treatment with dopamine agonists.
Dopamine Substitution And Non Motor Symptoms
Dopaminergic drugs improve the mainly dopamine related motor symptoms in PD. They only partially influence non motor symptoms . The drug therapy of non motor features is complex due to possible occurrence of drug interactions, interference with side effects and induction of altered pharmacokinetic behaviour of dopamine substituting compounds. But drug treatment of non motor symptoms in PD gains more and more interest. Thus trials showed a moderate positive effect of the dopamine agonist pramipexole on depression in PD . These investigations reflect a changing attitude from the focus on the effects of centrally acting compounds on the dopaminergic neurotransmission towards a more general view of PD with consideration of neuropsychiatric features under long-term aspects. However, PD drugs themselves may also contribute to onset of non motor symptoms, such as visual hallucinations. This complicates the differentiation from the disease process itself.
Don’t Miss: What Medications Can Cause Parkinson’s
Role Of Imaging In Diagnosis
For a patient presenting with symptoms of typical idiopathic Parkinsons disease and no other abnormal exam findings, imaging is usually not necessary.
Dr. Hung notes that he will typically order an MRI in the following situations:
- Atypical symptoms some atypical parkinsonian syndromes can have particular MRI correlates that mary be useful
- Lower-body predominant parkinsonism For patients with significant lower-body parkinsonism without significant tremor or upper-body bradykinesia, an MRI is important to obtain to rule out the following causes of lower-body parkinsonism : 1) Vascular disease significant frontal white matter disease can cause symptoms of lower-body parkinsonism, and 2) Normal pressure hydrocephalus can cause parkinsonian symptoms involving the gait.
What Future Medications May Be Available For Parkinsons
There are numerous studies investigating new treatments for Parkinsons disease.
There has been new information about the role of autoimmunity and T-cells in the development of Parkinsons disease, possibly opening the door to a role for biologics.
Stem cells are also being investigated as a treatment option for Parkinsons disease.
Recommended Reading: Can Essential Tremor Become Parkinsons
Don’t Miss: Acupressure Points For Parkinson’s Tremors
What Are The Most Common Medicines Used To Treat Pd
Sinemet®
Levodopa is the most commonly prescribed and most effective medicine for controlling the symptoms of PD, particularly bradykinesia and rigidity.
Levodopa is a chemical found naturally in our brains. When given as a medicine, it is transported to the nerve cells in the brain that produce dopamine. It is then converted into dopamine for the nerve cells to use as a neurotransmitter.
Sinemet is made up of levodopa and another drug called carbidopa. Levodopa enters the brain and is converted to dopamine while carbidopa prevents or lessens many of the side effects of levodopa, such as nausea, vomiting, and occasional heart rhythm disturbances. It is generally recommended that patients take Sinemet on an empty stomach, at least ½ hour before or one hour after meals.
There are two forms of Sinemet: controlled-release or immediate-release Sinemet. Controlled-release Sinemet and immediate-release Sinemet are equally effective in treating the symptoms of PD, but some people prefer the controlled release version. Ask your doctor which approach is best for you.
Dopamine agonists
Dopamine agonists are medicines that activate the dopamine receptor. They mimic or copy the function of dopamine in the brain.
Parlodel®, Requip®, and Mirapex® are all dopamine agonists. These medicines might be taken alone or in combination with Sinemet. Generally, dopamine agonists are prescribed first and levodopa is added if the patient’s symptoms cannot be controlled sufficiently.
Symmetrel®
What Is Parkinson’s Disease
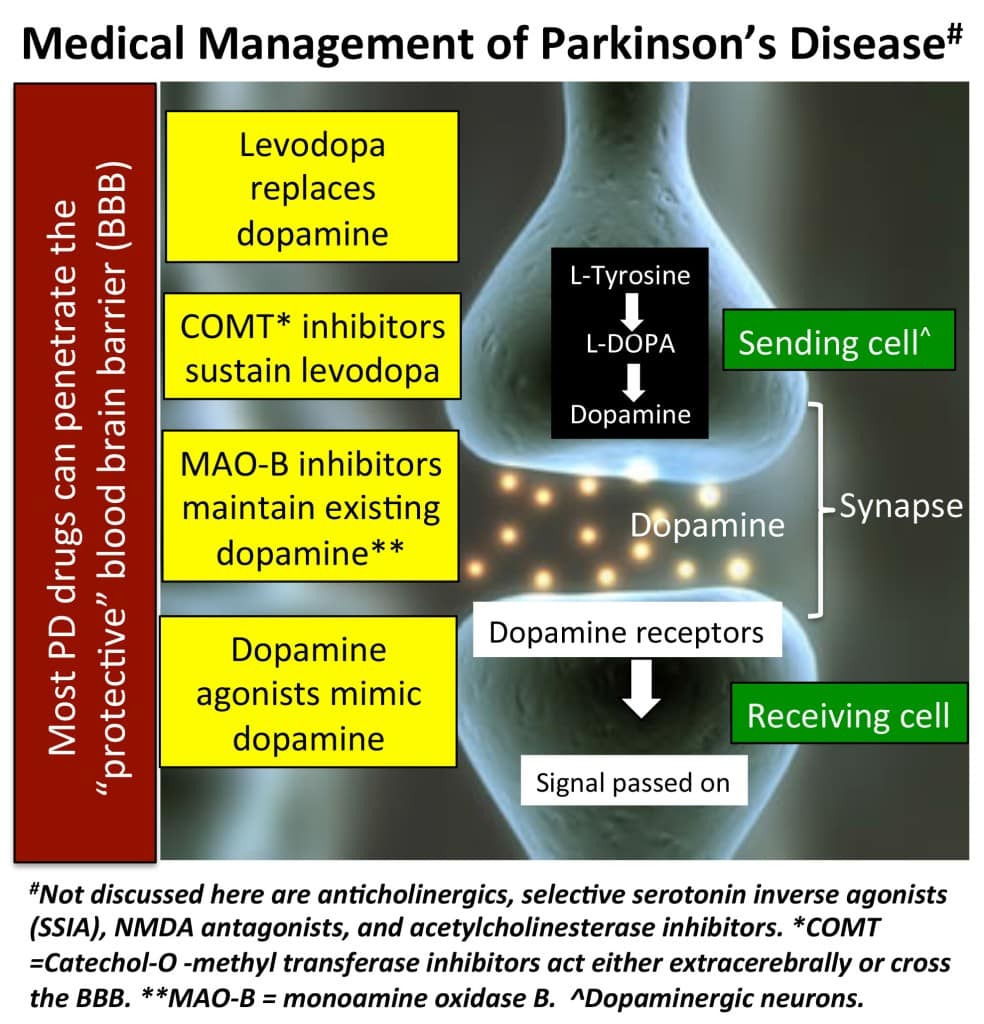
Parkinsonâs disease is an illness in the brain that affects many different parts of the body.
Your brain has different areas that deal with separate body parts. Cells in these brain areas are called neurons.
Neurons send electrical signals to each other to direct your body. Signals between neurons tell your body to move, make you feel pain and other sensations, manage your breathing, and perform many more needed functions.
Chemicals called neurotransmitters help these electrical signals travel between neurons throughout the brain. For example, dopamine is a chemical that plays a role in movement, motivation, and other behaviors.
The part of the brain that helps with movement and produces dopamine is called the basal ganglia. In cases of Parkinsonâs disease, cells in this area of the brain become damaged and produce less dopamine and other important neurotransmitters. This can cause problems with moving, thinking, and other functions.
Parkinsonâs disease isnât contagious. It usually appears in people around age 60 and older. People as young as their early twenties can get diagnosed with Parkinsonâs disease, though.
Don’t Miss: Advanced Parkinson’s Home Care
Pramipexole Dihydrochloride Extended Release
Available Doses: .375 mg, .75 mg., 1.5 mg, 2.25 mg, 3 mg, 3.75 mg, 4.5 mg
Typical Treatment Regimen: 1.5 to 4.5 mg once per day
Side Effects: nausea, lower blood pressure, leg swelling, confusion, sleep attacks, compulsive behaviors like gambling
Indications for Usage: or combination therapy for slowness, stiffness and tremor
How Dopamine Agonists Are Used
Dopamine agonists are used at all stages of Parkinsons. You might take them alone when treatment is being started, or alongside levodopa to provide a more effective treatment with fewer side effects.
Treatment with dopamine agonists has to be started carefully to minimise the risk of side effects, with the dose gradually increasing until you and your specialist or Parkinsons nurse are happy that your symptoms are under control. Some dopamine agonists are available as one a day tablets. These can be a better option for the body and may help both movement and other symptoms of Parkinsons.
You May Like: How Long Does A Person Live With Parkinson’s Disease
How Anticholinergics Are Used
These medications are older and are not used very often for Parkinsons today. Sometimes they are prescribed for reducing tremor and muscle stiffness. They can be used on their own, especially in the early stages of your Parkinsons when symptoms are mild, before levodopa is prescribed.
Anticholinergics can also be used with levodopa or a glutamate antagonist. They are taken as tablets or as a liquid.
Discussing A New Diagnosis Of Parkinsons With Patients
In discussing a new diagnosis of Parkinsons with a patient, Dr. Hung said he makes sure patients understand that there are medications that can help with symptoms, and while we cant currently cure the disease, we will do our very best to keep them at a high quality of life for as long as possible. Dr. Hung refers his patients to a variety of online resources, including the Parkinsons Foundation, the Michael J Fox Foundation, and the American Parkinsons Disease Association.
In an initial visit, Dr. Hung also stresses the importance of exercise , and recommends early referral to physical therapists specializing in Parkinsons Disease. There is growing evidence that exercise not only helps with mobility / motor symptoms in Parkinsons, but may actually also have neuroprotective effects, and an ongoing trial is randomizing patients to moderate or vigorous exercise to investigate the impact on clinical disease progression and DaT scans.
Recommended Reading: Parkinson’s Disease Stage 1 Symptoms
How Should This Medicine Be Used
The combination of levodopa and carbidopa comes as a regular tablet, an orally disintegrating tablet, an extended-release tablet, and an extended-release capsule to take by mouth. The combination of levodopa and carbidopa also comes as a suspension to be given into your stomach through a PEG-J tube or sometimes through a naso-jejunal tube using a special infusion pump. The regular and orally disintegrating tablets are usually taken three or four times a day. The extended-release tablet is usually taken two to four times a day. The extended-release capsule is usually taken three to five times a day. The suspension is usually given as a morning dose and then as a continuous dose , with extra doses given no more than once every 2 hours as needed to control your symptoms. Take levodopa and carbidopa at around the same times every day. Follow the directions on your prescription label carefully, and ask your doctor or pharmacist to explain any part you do not understand. Take levodopa and carbidopa exactly as directed. Do not take more or less of it or take it more often than prescribed by your doctor.
Swallow the extended-release tablets whole do not chew or crush them.
To take the orally disintegrating tablet, remove the tablet from the bottle using dry hands and immediately place it in your mouth. The tablet will quickly dissolve and can be swallowed with saliva. No water is needed to swallow disintegrating tablets.
History And Physical: The Cardinal Signs
There are four cardinal signs of parkinsonism that are important to assess for when taking a history and performing a physical exam on a patient with suspected Parkinsons disease: tremor, bradykinesia, rigidity, and postural instability . The Movement Disorder Society Unified Parkinsons Disease Rating Scale provides a framework for evaluating parkinsonism on physical exam . Dr. Hung shares pearls for assessing for each of these cardinal symptoms on history and physical exam:
During the office visit, Dr. Hung also stresses that it is important to always ask a patient to walk in order to assess their gait and posture. In early Parkinsons, gait changes may be subtle, and may manifest with slight slowness, a bit of a stooped posture, and reduced arm swing on the side more affected by parkinsonism. The classic shuffling gait or freezing gait of Parkinsons disease is usually seen at more advanced stages.
Don’t Miss: Ddt And Parkinson’s Disease
Levodopa Vs Das Vs Mao
Recommendation 1 Rationale
Clinical trials have failed to provide evidence of disease modification when the initial therapy prescribed is levodopa, a DA, or an MAO-B inhibitor. Studies comparing treatment with levodopa to treatment with MAO-B inhibitors early in the disease course provide Class IV evidence. These studies demonstrate greater improvement in mobility with levodopa than with MAO-B inhibitors, a higher risk of AE-related discontinuation with MAO-B inhibitors, and that > 60% of individuals randomized to MAO-B inhibitors will require additional therapy within 2 to 3 years.
Initial treatment of early PD with levodopa provides greater benefit for motor symptoms than initial treatment with DAs, as shown in the majority of studies that demonstrate greater improvement in the UPDRS part III score for the first 5 years of follow-up. Initial treatment with levodopa is more likely to induce dyskinesia than initial treatment with DAs for up to 5 years of follow-up, but the prevalence of severe or disabling dyskinesia during this 5-year period is low. Although initial treatment with DAs is possibly more likely to cause hallucinations than treatment with levodopa, the difference between treatments for this outcome is small for the first 5 years of treatment. Treatment with DAs in early PD is associated with a higher risk of ICDs.
Recommendation 1 Statements
Searching To Control Symptoms: New Methods Of Delivery
In recent months, symptomatic treatment of PD has had some new developments as well. A new drug for PD, rotigotine, has been introduced in Europe and elsewhere as Neupro. This compound is a dopaminergic agonist, a class of drugs that also includes drugs that have been available for many years in the U.S., including Mirapex, Requip, and Permax . Neupro is unique in how it is delivered: it is absorbed through the skin and so has been marketed as a transdermal patch with continuous delivery over 24 hours. So far, experience with Neupro suggests that it is effective and well tolerated. However, whether this drug or its unique mode of delivery will offer a significant advantage over currently marketed medications of the same class still remains to be learned.
PD still presents many challenges for the medications of the future. Among the unmet needs are ways to reverse the problem of imbalance, especially falling backward. The flexed posture of PD, swallowing and speech difficulties, and situation-specific freezing are all challenges for improved drug therapy. Scientists have not yet determined where in the brain and what types of biochemical disturbance underlie these problems.
Don’t Miss: Apple Watch Parkinson’s App