Pearls And Other Issues
Patients with atrial fibrillation and rapid ventricular response are often treated with amiodarone or procainamide. Procainamide and cardioversion are accepted treatments for conversion of tachycardia associated with Wolff Parkinson White syndrome . In acute AF associated with WPW syndrome, the use of IV amiodarone may potentially lead to ventricular fibrillation in some reports and thus should be avoided.
AV node blockers should be avoided in atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter with Wolff Parkinson White syndrome . In particular, avoid adenosine, diltiazem, verapamil, and other calcium channel blockers and beta-blockers. They can exacerbate the syndrome by blocking the heart’s normal electrical pathway and facilitating antegrade conduction via the accessory pathway.
An acutely presenting wide complex tachycardia should be assumed to be ventricular tachycardia if doubt remains about the etiology.
Management Of Asymptomatic And Symptomatic Preexcitation
Blomström-Lundqvist, C, Scheinman, MM, Aliot, EM. ACC/AHA/ESC Guidelines for the Management of Patients With Supraventricular ArrhythmiasExecutive Summary: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines and the European Society of Cardiology Committee for Practice Guidelines . Circulation. vol. 108. 2003. pp. 1871-1909.
Klein, GJ, Gulamhusien, SS. Intermittent preexcitation in the Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome. Am J Cardiol. vol. 52. 1983. pp. 292-6.
Campbell, RWF, Smith, R, Gallagher, JJ. Atrial fibrillation in the preexcitation syndrome. Am J Cardiol. vol. 40. 1977. pp. 514-20.
Auricchio, A, Klein, H, Trappe, HJ. Lack of prognostic value of syncope in patients with Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome. J Am Coll Cardiol. vol. 17. 1991. pp. 152-8.
Wellens, HJ, Bar, FW, Gorgels, AP. Use of ajmaline in patients with the Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome to disclose short refractory period of the accessory pathway. Am J Cardiol. vol. 45. 1980. pp. 130-33.
Brembilla-Perrot, B, Ghawi, R. Electrophysiological characteristics of asymptomatic Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome. Eur Heart J. vol. 14. 1993. pp. 511-15.
Leitch, JW, Klein, GJ, Yee, R, Murdock, C. Prognostic value of electrophysiology testing in asymptomatic patients with Wolff-Parkinson-White pattern. Circulation. vol. 82. 1990. pp. 1718-23.
Safe Practice In Svt With Wpw
So, in summary, what can we safely say about the management of acute SVT in WPW?
- Theoretically, AV nodal blockers should be safe in WPW-associated SVT, be it antidromic or orthodromic. If one thinks for a minute about the epidemiology of SVT, one will come to the conclusion that a large proportion of SVT is in fact caused by WPW or some other sort of preexcitaton syndrome, which is usually not known at the time of their first presentation. Many of these people get adenosine, which then reveals their delta waves to the horrified emergency personnel. Most of them do not die of VF. On the basis of this, we may conclude that it is probably reasonably safe.
- Practically, antidromic SVT in WPW may be difficult to discriminate from AF or VT. Broad complexes and 300+ heart rates could be anything in WPW. Sure, it could be supraventricular, and respond to adenosine. Or it could be AF, and turn into VF. Or it could be VT, which will not benefit from an AV nodal blocker, in which case you have wasted precious time.
The table below has been compiled with the use of the belowlisted references and the UpToDate article on this topic
You May Like: What Percentage Of Parkinson’s Is Hereditary
How Is Wpw Diagnosed
WPW can only be diagnosed by reviewing an ECG . A holter or ambulatory monitor and exercise testing are also helpful in evaluating patients known to have WPW.
In the past, patients with WPW but without symptoms had been observed by a cardiologist for many years. Recently, new guidelines have been published for this group of patients. Your cardiologist may order a holter monitor or stress test to look for a persistent patter of WPW. If the WPW pattern persists, invasive electrophysiology testing is now recommended.
Your doctor will also ask you several questions:
- Do you have symptoms?
- Do you have a history of atrial fibrillation?
- Do you have a history of fainting?
- Do you have a history of sudden cardiac death or does anyone in your family?
- Are you a competitive athlete?
The results of your diagnostic tests and the answers to these questions will help guide your therapy.
How Is It Treated And Managed
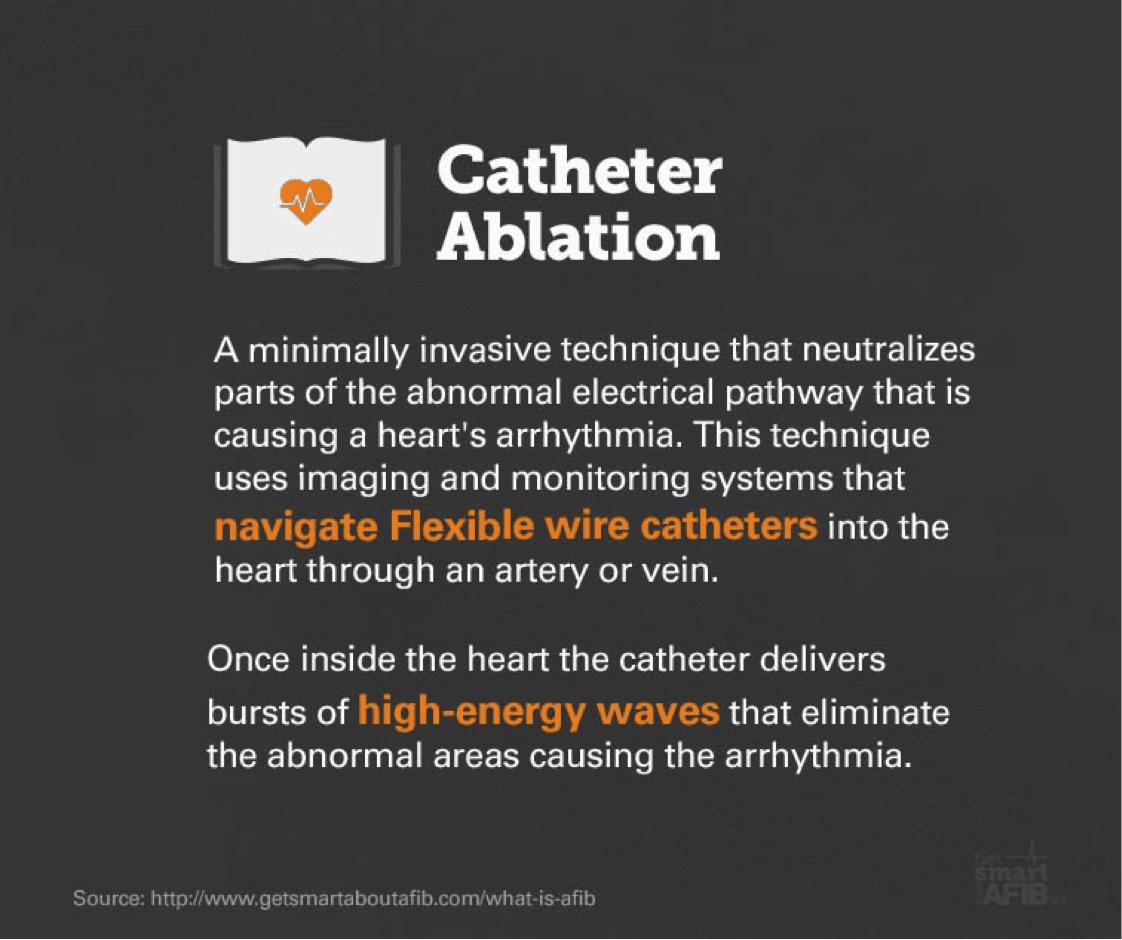
Catheter ablation is the most common treatment for people who have WPW syndrome and symptoms of an arrhythmia. This procedure can cure WPW syndrome in most people. If this treatment works for you, you can go back to your normal activities.
You may need one of more of the following treatments for an irregular heartbeat:
- Medicines that can control or prevent a fast heartbeat
- Cardioversion, which uses an electrical shock to your heart to restore its rhythm
If you have no symptoms of arrhythmias, you may not need any treatment. You may need regular checkups to check for a rapid or irregular heartbeat. Tell your doctor right away if you have any symptoms.
Recommended Reading: Dropping Things Sign Of Parkinson’s
When To See A Doctor
Many things can cause a fast heartbeat. Its important to get a prompt diagnosis and care. Sometimes a fast heartbeat, or heart rate, isnt a concern. For example, the heart rate may increase with exercise.
If you feel like your heart is beating too fast, make an appointment to see a health care provider.
- Sensation of a fast or pounding heartbeat
- Difficulty breathing
What To Expect From Your Doctor
Your health care provider is likely to ask you questions, such as:
- How severe are the symptoms?
- How often does the fast heartbeat occur?
- How long do episodes last?
- Does anything, such as exercise, stress or caffeine, seem to trigger the episodes or make symptoms worse?
- Is there a family history of tachycardia or heart disease?
More from the Mayo Library
Read Also: Parkinson’s Dementia End-stage
Key Points About Wpw Syndrome
- WPW syndrome is a rapid heartbeat due to an extra electrical pathway connecting the upper and lower chambers of the heart.
- While some people might not experience WPW syndrome, those who do can experience fainting, tiredness, and shortness of breath. These symptoms can disappear over time but can be treated by your doctor through medication or surgery.
- WPW is caused by a gene mutation or is present at birth.
How Is It Diagnosed
Your doctor may ask you to get tested for WPW syndrome if you have atrial fibrillation or a family history of WPW syndrome. You may need to be screened for WPW syndrome if you are going to play competitive sports.
Your doctor will use your medical history, family history, physical exam, and heart tests to diagnose WPW syndrome. Sometimes WPW syndrome is diagnosed during a routine heart test. Common heart tests to diagnose WPW include an EKG and a Holter monitor. You may also need a stress test to measure your heart rhythm while your heart is working hard and beating fast.
You may also need an electrophysiology study to see whether you are at risk of more serious health problems.
You May Like: Does Heat Affect Parkinson Disease
Preventing An Episode That Has Started
Your doctor can advise on ways to interrupt the abnormal electrical signals and slow down the fast heartbeats. They include actions as simple as coughing in a particular way, or applying an ice pack to your face. Only do these if your doctor recommends them. Your doctor might also recommend medication to treat an episode.
Deterrence And Patient Education
The dysrhythmias causing electrical abnormalities associated with WPW syndrome are a result of a congenital abnormality forming an accessory pathway. There is nothing that can be done to prevent WPW pattern. After WPW syndrome has manifested with the presentation of a tachyarrhythmia, an electrophysiologic study can be performed to map and assess risks of the accessory pathway, and catheter radiofrequency ablation of the pathway can be curative. For patients that this is not an option or preference, antiarrhythmic medications can be a reasonable alternative option.
Also Check: What Causes Parkinson’s Patients To Die
Serotonin Syndrome : Symptoms Causes &
Serotonin syndrome, also known as serotonin toxicity, is a potentially life-threatening condition resulting from having too much serotonin in your body. Learn about serotonin syndrome symptoms, the medications that can cause the condition, and how it can beWebMDWebMD Better information. Better health.Treatment of atrial flutter · After atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter is the most important and most common atrial tachyarrhythmia. Although it was first described 80 years ago, techniques for its diagnosis and management have changed little for decades. The diagnosis rested almost entirely with the 12 lead ECG, and treatment options included only the use of a digitalis compound to slow and control the ventricular
Recommended Reading: What Is The Best Mucuna Pruriens For Parkinsons
Can You Die From Wolff
The incidence of sudden death in patients with WPW is extremely low. To the best of our knowledge, this is the only reported case of sudden death in a man with WPW and myocardial bridge. This case highlights that SCD can occur in WPW patients with mild or unrecognized structural abnormality.
Is WPW life-threatening?
WPW syndrome can sometimes be life-threatening, particularly if it occurs alongside a type of irregular heartbeat called atrial fibrillation. But this is rare and treatment can eliminate this risk.
Don’t Miss: Primidone Used For Parkinson’s
Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome is a rare but dangerous condition. A high index of clinical suspicion and close attention to concerning symptoms may be crucial in making a diagnosis. Once a diagnosis or sufficient concern is established, an interprofessional approach will be necessary for further evaluation and management. This approach, paired with education and shared decision making with patients and their families, will help guide treatment plans.
It is often difficult to develop and carry out well structured and rigorous studies in rare medical conditions. Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome is no exception, and most of the evidence is drawn from case series and population studies. The pathophysiologic basis is well understood, and surgical or catheter ablation has been shown to be successful and low risk. In high-risk patients, ablation is the most definitive treatment, but more future studies would help delineate medical management and ablation thresholds in some low-risk patients.
Are There Different Types Of Accessory Pathways
Lown, B. The syndrome of short P-R interval, normal QRS complex and paroxysmal rapid heart action. Circulation. vol. 5. 1952 May. pp. 693-706.
James, TN. Morphology of the human atrioventricular node, with remarks pertinent to its electrophysiology. Am Heart J. vol. 62. 1961. pp. 756-71.
Lev, M, Leffler, WB, Langendorf, R. Anatomic findings in a case of ventricular preexcitation terminating in complete atrioventricular block. Circulation. vol. 34. 1966. pp. 718-33.
Murdock, CJ, Leitch, JW, Teo, WS. Characteristics of accessory pathways exhibiting decremental conduction. Am J Cardiol. vol. 67. 1991. pp. 506-10.
Ross, DL, Uther, JB. Diagnosis of concealed accessory pathways in supraventricular tachycardia. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. vol. 7. 1984. pp. 1069-85.
Anderson, RH, Becker, AE, Brechenmacher, C. Ventricular pre-excitation: a proposed nomenclature for its substrates. Eur J Cardiol. vol. 3. 1975. pp. 27-36.
Mahaim, I, Benatt, A. Nouvelles recherches sur les connections superieures de la branche du faisceau de His-Tawara avec cloison interventriculaire. Cardiologia. vol. 1. 1937. pp. 61
Recommended Reading: Lewy Body Dementia Vs Parkinsons
What Are The Symptoms Of Wolff
Symptoms occur only when the heart beats abnormally fast, so most of the time people have no symptoms. Episodes can start suddenly and last for a few seconds or several hours. They often happen during exercise. When symptoms do occur, they include rapid heartbeat, heart palpitations or heart fluttering, lightheadedness, chest pain, fatigue, fainting, dizziness, anxiety, loss of consciousness, and breathing problems. Sudden death can occur.
Catheter Ablation Of Accessory Pathways
Lesh, MD, Van Hare, G, Scheinman, MM. Comparison of the retrograde and transseptal methods for ablation of left free-wall accessory pathways. J Am Coll Cardiol. vol. 22. 1993. pp. 542-9.
Jackman, WM, Wang, X, Friday, KJ. Catheter ablation of accessory atrioventricular pathways by radiofrequency current. N Engl J Med. vol. 324. 1991. pp. 1605-11.
Kuck, KH, Schluter, M, Geiger, M. Radiofrequency current catheter ablation of accessory atrioventricular pathways. Lancet. vol. 337. 1991. pp. 1557-61.
Calkins, H, Langberg, J, Sousa, J. Radiofrequency catheter ablation of accessory atrioventricular connections in 250 patients: abbreviated therapeutic approach to Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome. Circulation. vol. 85. 1992. pp. 1337-46.
Kay, GN, Pressley, JC, Packer, DL. Value of 12-lead electrocardiogram in discriminating atrioventricular nodal reciprocating tachycardia from circus movement atrioventricular utilizing a retrograde accessory pathway. Am J Cardiol. vol. 59. 1987. pp. 296-300.
Tchou, PJ, Lehmann, MJ, Donga, J. Effect of sudden rate acceleration on the human His-Purkinje system: adaptation of refractoriness in a damped oscillatory pattern. Circulation. vol. 73. 1986. pp. 920-9.
Drago, F, DeSantis, A, Grutter, G, Silverti, MS. Transvenous cryothermal catheter ablation of re-entry circuit located near the atrioventricular junction in pediatric patients. J Am Coll Cardiol. vol. 45. 2005. pp. 1096-103.
Recommended Reading: Drugs To Treat Parkinsons
You May Like: Sound Therapy For Parkinson’s Disease
When To Seek Medical Advice
See a GP if you keep getting a fast or noticeable heartbeat . It’s important to get it checked out in case it could be something serious.
Dial 999 for an ambulance if:
- your heartbeat doesn’t go back to normal in a few minutes
- you have chest pain that lasts more than 15 minutes you may also have pain in your arms, back or jaw
- you have chest pain and other symptoms like feeling sick, being sick , shortness of breath or sweating
- someone passes out and doesn’t regain consciousness
If you’ve been diagnosed with WPW syndrome and you experience an episode, first try the techniques you’ve been taught or take any medication you’ve been given.
Dial 999 or go to your nearest accident and emergency department if these measures don’t stop the episode within a few minutes, or if someone you know has WPW syndrome and collapses or faints.
Home Remedies: Vagal Maneuvers
Sometimes, a persons rapid heartbeat corrects itself. Alternatively, some simple physical movements may help to correct the heartbeat.
These exercises include:
- bearing down as if having a bowel movement
- massaging the sides of the neck over the carotid artery
- holding an ice pack on the face
- gagging or forceful coughing
Therapists call these exercises vagal maneuvers because they affect the vagus nerve that runs from the abdomen to the brain. A branch of it runs to the heart.
Stimulation of the vagus nerve can cause a variety of results, depending on what organ it affects. If the heart is beating too fast, it acts as a brake and slows the heart rate down.
If vagal maneuvers do not normalize the heart rhythm, a doctor may inject an antiarrhythmic drug to bring the heartbeat back to normal.
Another option is a procedure known as cardioversion. This intervention is when a doctor places paddles or patches on the persons chest and applies an electric shock to the heart, to restore normal heart rhythm.
Doctors usually use cardioversion for people who have not responded to vagal maneuvers or medication.
Also Check: What Supplements Are Good For Parkinson’s
Orthodromic Tachycardia With Concealed Accessory Pathway
Some APs are unable to conduct in an antegrade fashion. These are called concealed APs, because “manifest” preexcitation is a delta wave that is visible on a surface 12-lead ECG. They account for about 30% of all SVTs induced on EPS.
Although no evidence of the pathway is present during sinus rhythm , orthodromic tachycardias can occur. Orthodromic tachycardia may also occur when there are two or more accessory connections, and in that case, the retrograde conduction may occur through the AV node, through one of the accessory connections, or through both.
This type of SVT may be difficult to distinguish from the usual AV nodal reentrant tachycardia on a standard surface ECG. In adults, if the heart rate is higher than 200 bpm or a retrograde P wave is visible in the ST segment , a concealed AP-mediated orthodromic reentrant tachycardia may be the diagnosis. However, this determination is most accurately made with electrophysiologic studies , or if SVT terminates with a single PVC. Other differentiating factors include the following :
How Do Doctors Treat Wpw Syndrome

To slow your heart rate, your doctor may ask you to try one of the following:
-
Strain as if having trouble passing stool
-
Rub your neck just below the angle of your jaw
-
Plunge your face into a bowl of ice-cold water
If these don’t work or you’re having severe symptoms, doctors will:
-
Give you medicine directly into your vein
If you keep having episodes of rapid heart rate from WPW, doctors may recommend:
-
An ablation procedure
Recommended Reading: Gene Therapy For Parkinson’s Disease An Update
What Drugs To Avoid In Wpw
Do not give digoxin or nondihydropyridine calcium channel blockers to patients with atrial fibrillation and Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome because these drugs may trigger ventricular fibrillation.
How long does WPW surgery take?
The procedure used to be really longaround ten hourswhich is why this myth persists, Dr. Arkles explains. Thanks to advances in technology and expertise, ablations today generally last between 2 and 3 hours. Ninety percent of ablation patients go home the next day.
Antidromic Svt In Wpw
In antidromic SVT, the action potential conducts to the ventricle initially via the accessory pathway, then wanders shambolically around the ventricles producing a weird wide QRS, and then propagates up the AV node in an unnatural retrograde manner. It then goes straight back down into the ventricle via the accessory pathway, and the whole thing repeats cyclically.
So, consider what might happen if the AV node were blocked. The ventricle is now only depolarised by the accessory pathway, so the QRS will be weird and wide, but now that the AV node is blocked, theoretically the block should have the exact same effect as in orthodromic SVT, i.e. the cycle is broken and the SVT should be aborted.
However, the authorities are not convinced. UpToDate hold forth that:
Even though retrograde AV node conduction may be a weak link during antidromic AVRT, intravenously administered AV node-specific blocking drugs such as adenosine, verapamil, and beta blockers should be avoided unless the tachycardia is definitely known to be antidromic AVRT. If the diagnosis is not certain, the patient should be considered to have an undiagnosed wide QRS tachycardia
Which brings us to
Dont Miss: Wolf Parkinsons White Disease Treatment
You May Like: Local Support Groups For Parkinson’s Disease