Pramipexole Dihydrochloride Extended Release
Available Doses: .375 mg, .75 mg., 1.5 mg, 2.25 mg, 3 mg, 3.75 mg, 4.5 mg
Typical Treatment Regimen: 1.5 to 4.5 mg once per day
Side Effects: nausea, lower blood pressure, leg swelling, confusion, sleep attacks, compulsive behaviors like gambling
Indications for Usage: or combination therapy for slowness, stiffness and tremor
Knxv: This Boxing Gym Is Empowering People With Parkinson’s
Members say being around others with Parkinson’s helps them not to feel self-conscious.
“You see your doctor maybe two to four times a year for 15 to 30 minutes, and it’s challenging for patients to go into a doctor’s appointment and be able to quickly communicate what’s going on,” Oslapas said.
Amanda Hare understands that frustration, as a former nurse practitioner who cared for hundreds of Parkinson’s patients.
“And when we’re talking about one thing, and something else is happening, I could be giving them the wrong treatment and actually worsen their symptoms,” Hare said. “So with using StrivePD and having that data to pull up, clinicians can really get to understand what’s going on.”
Hare now works as a senior clinician specialist with Rune Labs. Rune Labs is a precision medicine company that uses StrivePD to capture patient data and help inform drug development companies on creating suitable therapeutics for neurodegenerative diseases like Parkinson’s. Brian Pepin is the founder and CEO.
“We’re taking all of this data that’s generated from people every day as part of clinical care, brain imaging, genetic testing, clinical scoring,” Pepin said. “Now all of this rich data that’s coming off the Apple Watch, and we’re bringing that together in a way that’s actually really helpful for pharma companies to understand how their drugs are working differently in different patients.”
What Other Information Should I Know
Keep all appointments with your doctor and the laboratory. Your doctor will order certain lab tests to check your response to levodopa and carbidopa.
Before having any laboratory test, tell your doctor and the laboratory personnel that you are taking levodopa and carbidopa.
Levodopa and carbidopa can lose its effect completely over time or only at certain times during the day. Call your doctor if your Parkinson’s disease symptoms worsen or vary in severity.
As your condition improves and it is easier for you to move, be careful not to overdo physical activities. Increase your activity gradually to avoid falls and injuries.
Levodopa and carbidopa can cause false results in urine tests for sugar and ketones .
Do not let anyone else take your medication. Ask your pharmacist any questions you have about refilling your prescription
It is important for you to keep a written list of all of the prescription and nonprescription medicines you are taking, as well as any products such as vitamins, minerals, or other dietary supplements. You should bring this list with you each time you visit a doctor or if you are admitted to a hospital. It is also important information to carry with you in case of emergencies.
You May Like: Good Diet For Parkinson’s
Can Dopamine Be Used To Treat Parkinsons
If Parkinsons disease is caused by a drop in dopamine, it might make sense that replacing that dopamine would stop the symptoms and halt the progression of the disorder. But its not that easy.
Dopamine from a medication or injection cant penetrate the blood-brain barrier. That makes it an ineffective treatment.
An amino acid called levodopa can help increase levels of dopamine in the brain. If given as a medication, it can cross the blood-brain barrier. Once in the brain, levodopa is converted to dopamine.
Levodopa wont replace all of the lost dopamine, but it can help to reduce symptoms of Parkinsons disease. Its particularly helpful with movement control.
An Approach To The Treatment Of Parkinsons Disease
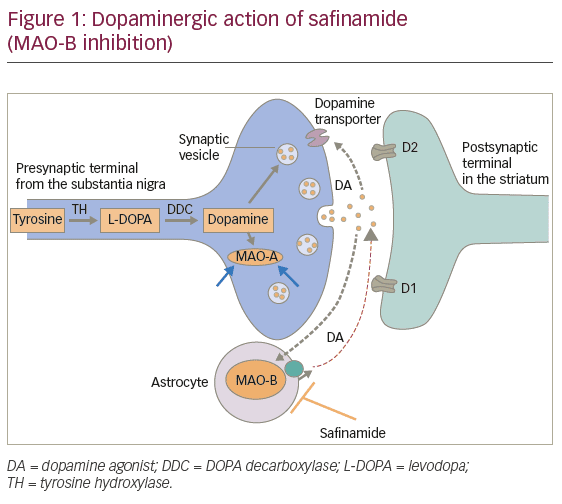
No treatment can arrest or slow neurodegeneration in Parkinsons disease. The aim is to relieve symptoms and avoid the complications of therapy.
Early Parkinsons disease
Many studies have shown that early treatment with dopamine agonists reduces the incidence of dyskinesia.1Fewer motor fluctuations were shown in some but not all of the studies. We recommend a dopamine agonist as the first treatment in younger patients who have mild disease and no cognitive deficit. It is necessary to add levodopa within 1-5 years in most patients. In more severe disease, treatment begins with levodopa but a dopamine agonist may be added to keep the daily dose of levodopa in the lower range if there is no cognitive deficit. Dopamine agonists are used infrequently and with caution in patients more than 70 years old because of the risk of neuropsychiatric adverse effects and postural hypotension. They are contraindicated in the presence of dementia.
Isolated resting tremor is rarely disabling, but if it interferes with function it can usually be managed with levodopa. When this is ineffective at low to moderate doses, the addition of an anticholinergic can sometimes be useful.
Patients with motor fluctuations
Role of physical therapy and surgery
You May Like: Does Restore Gold Work For Parkinson’s
Where Is It Made In The Brain
Dopamine is produced in the substantia nigra, ventral tegmental area, and hypothalamus.1 You may not remember these complicated names. That is fine! It is probably more important to know what these areas of the brain do:1,4-6
- The substantia nigra is part of the brain known as the basal ganglia. This part of the brain is responsible for making movement possible.
- The ventral tegmental area is the part of the brain that is responsible for reward and reinforcement.
- The hypothalamus has many functions. It is responsible for sleep, appetite, body temperature, and sexual arousal, among other things. The hypothalamus helps control the autonomic nervous system.
Recommended Reading: Questions About Parkinsons Disease
Strongest Association Seen For Sodium Valproate
byKate Kneisel, Contributing Writer, MedPage Today December 27, 2022
Taking antiepileptic drugs was associated with a subsequent diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease , a U.K.-based case control study suggested.
There was a significant association between AED prescriptions and incident Parkinson’s disease , and the magnitude of the association rose with an increasing number of prescriptions and for those who took more than one AED, Alastair Noyce, PhD, of Queen Mary University of London, and colleagues reported in JAMA Neurology.
Of the four most commonly prescribed AEDs in the U.K., carbamazepine wasn’t significantly associated with Parkinson’s, but three AEDs did have a significant relationship:
- Sodium valproate
Previous work — including a study from Noyce’s own group — has shown a link between epilepsy and Parkinson’s disease, and it’s “plausible that may account for some or all of the apparent association between epilepsy and PD,” the researchers wrote.
To further explore that potential relationship, Noyce and colleagues conducted a nested case-control study using data from the U.K. Biobank, which began collection in 2006. Cases were defined as individuals with a hospital-coded diagnosis of PD.
Ultimately, they assessed 1,433 Parkinson’s cases and 8,598 matched controls. Among patients with Parkinson’s, 60.9% were male, median age at diagnosis was 71 years, and about 98% were white.
-
Kate Kneisel is a freelance medical journalist based in Belleville, Ontario.
Don’t Miss: How To Manage Parkinson’s
Data Synthesis And Confidence In Evidence Statements For Levodopa Vs Das
-
1. In people with early PD, what is the comparative efficacy of levodopa vs DAs vs MAO-B inhibitors for motor symptoms?
-
2. In people with early PD, what is the comparative risk of adverse effects of levodopa vs DAs vs MAO-B inhibitors?
UPDRS Part III Score
The change in the UPDRS part III score from baseline to endpoint was extracted from studies comparing levodopa to DAs and the RMD between treatments was calculated . Negative values favored levodopa. Where possible, estimates were combined using meta-analysis at specific time points. The minimal clinically important difference in the UPDRS part III score was determined by consensus to be 3 points changes of 1 point or less were considered unimportant.
Long-Acting vs Immediate-Release Levodopa: Change in Unified Parkinsons Disease Rating Scale Part III Score From Baseline to Endpoint, Risk of Dyskinesia, Hallucinations, and Adverse EventRelated Discontinuation
The available evidence is insufficient to make conclusions regarding the relative efficacy of long-acting vs IR levodopa for improvement in motor function or the risk of hallucinations. There do not appear to be major differences between long-acting and IR levodopa in the risk of dyskinesia or AE-related discontinuation.
You May Like: Parkinsons Life Center Of Southern New Jersey
Ways To Boost Dopamine
Dopamine is a neurotransmitter thats great to have in abundance. When you do, your brain is flooded with pleasurable feelings and a sense of satisfaction and reward.
While increasing your natural dopamine wont prevent or stop the progression of Parkinsons disease, it might help stave off early symptoms of the disorder. For some people, natural dopamine boosts may be helpful alongside other treatments.
Don’t Miss: What To Expect As Parkinson’s Progresses
What Future Medications May Be Available For Parkinsons
There are numerous studies investigating new treatments for Parkinsons disease.
There has been new information about the role of autoimmunity and T-cells in the development of Parkinsons disease, possibly opening the door to a role for biologics.
Stem cells are also being investigated as a treatment option for Parkinsons disease.
Parkinsons Disease Medications Are Designed To Increase Dopamine Levels In The Brain Or Slow The Breakdown Of The Brains Dopamine Lessening The Tremors And Other Symptoms
Story by: David Steen Martin on September 17, 2021
Parkinsons disease medications are designed to increase dopamine levels in the brain or slow the breakdown of the brains dopamine, lessening the tremors and other symptoms.
Dopamine is a chemical involved in movement, and its decrease in the brain is central to Parkinsons disease. By the time someone starts experiencing symptoms, dopamine levels in the basal ganglia already have dropped an estimated 50% to 75%.
Walking, movement and tremor can be managed better with Parkinsons disease medications.
Levodopa, which the brain converts to dopamine through a natural process, is the gold standard for treatment, according to Justin T. Phillips, M.D., medical director of movement disorders at the Norton Neuroscience Institute Cressman Parkinsons & Movement Disorders Center.
Common misconceptions about levodopa prompt some patients to wait before taking. Some patients worry they will develop a tolerance for the drug and it will stop working, it is only effective for a certain amount of time or that will cause the disease to progress faster.
All of these are myths, Dr. Phillips said. In addition to being the most effective medication, levodopa also tends to have fewer side effects, particularly in the long term.
Levodopa should be started as soon as troubling symptoms begin, according to Dr. Phillips. It will lessen disability in the long run, though it will require adjustments over time.
Recommended Reading: New Info On Parkinson’s Disease
Dopaminergic Features And Their Treatment
Patients with PD usually present with features indicative of degeneration of nigrostriatal pathways. A useful clinical definition for PD is asymmetric onset of an akinetic rigid syndrome with resting tremor and a good response to levodopa. When applied by neurologists with an interest in movement disorders, this definition has a pathological correlation exceeding 98%. When treatment is considered appropriate, and this is a topic discussed in detail below, a variety of options is available. The use of dopaminergic drugs improves motor function, significantly reduces both the morbidity and mortality of PD, and improves quality of life.
Levodopa remains the drug most commonly used in PD. It is very effective in improving bradykinesia and rigidity, and in practice remains the gold standard against which other drugs are judged. Some studies, predominantly in vitro, have suggested that levodopa may be toxic. However, such data are conflicting, and some laboratory studies have suggested a growth factor-like effect for levodopa. Overall, the pre-clinical evidence for levodopa toxicity is not convincing and there are no data to indicate that any toxic action is of clinical relevance.
Table 1
Percentage of patients remaining on dopamine agonist monotherapy at years 14 and years 15 during treatment trials
Dopamine Agonist Drugs: An Introduction
Dopamine agonist drugs trick your brain into thinking they are dopamine. This means they can mimic the way dopamine works which can reduce your symptoms.
Dopamine agonists are typically prescribed in the earlier stages of Parkinsons but everyone is different and you could be prescribed them at any time if it is right for you.
Treatment with dopamine agonists has to be started carefully. The dose is gradually increased until you and your specialist team are happy that your symptoms are under control.
Recommended Reading: Parkinson’s Phlegm At Night
Medication Tips For Treating Parkinsons Disease
Your doctor will determine the best combination of Parkinsons disease medications for you, as well as how and when to take them. There are also some general guidelines to consider:
- Keep a Parkinsons disease medication list and note down how and when you should take each drug. This can be helpful if memory problems crop up and someone else has to administer medications for you.
- Always take your medications as your doctor prescribes. Write it down or bring a family member to your appointment if you think youll forget.
- Store your medications in a dry, safe place, unless your doctor advises you to keep them in the fridge.
- Throw away expired medications.
- Remember to order your prescriptions in advance.
- Always take extra medication with you when you travel.
- Dont change your dose or stop taking your medication unless your doctor tells you to.
- Take your medication at the same time every day. Keep them in a pill case and set an alarm to remind yourself to take them, especially if you live alone.
- Physical exercise can help the body absorb medication, so try to move as much as possible.
If you have any questions about this Parkinsons disease medication list, consult your doctor. He or she will be able to answer your questions and advise you on how and when to take your medication. You should also seek medical advice if youre struggling with the side-effects of a particular drug or you want to try something different.
See Also:
What Are The Possible Side Effects
Side effects can vary depending on the specific drug you are taking. The most common side effects of dopamine agonists include:3,4
- Sudden sleepiness
- Dizziness or light-headedness
Dopamine agonists may also cause dyskinesia, or sudden and uncontrollable movements. Although dopamine agonists are less likely to cause dyskinesia than carbidopa-levodopa therapy, dyskinesias can greatly affect a persons quality of life.3,4
A less common side effect of dopamine agonists is impulse control behaviors. Examples include increased gambling urges, increased sexual urges, or other intense urges.3,4
These are not all the possible side effects of dopamine agonists. Talk to your doctor about what to expect or if you experience any changes that concern you during treatment with dopamine agonists.
Recommended Reading: Parkinson’s And Urinary Retention
Proliferation Gliosis And Serotonergic Contamination In The Grafts
Importantly, in agreement with our previous studies, we observed low levels of continued proliferation in the grafts after 6 months, as determined via unbiased stereology performed on sections stained for hKi-67 . We estimated 2402±1006 hKi-67-ir cells in MFD grafts 1038±741 in high-dose grafts 532±745 in medium-dose grafts and 0±5 hKi-67-ir cells in low-dose grafts, representing 0.4, 0.4, 1.2, and 0.0% of estimated hNuclei-ir cells, respectively. We calculated significant differences for MFD compared to high , medium , and low dose as well as low compared to high and medium dose groups for total number of hKi-67-ir cells and for percentages of low compared to high and maximum feasible dose using KruskalWallis and Dwass, Steel, Critchlow-Fligner method. Again, we report no evidence of teratoma formation.
Fig. 8: Non-dopaminergic cell types observed in grafts.
Representative A micrographs of graft sections stained for hKi-67 and B stereological estimates for each group. C Representative images of graft sections stained for hGFAP , D, Iba1 , and E 5-HT . Scale bar A=100M C=200 M D=500M E=1mm =25M. P< 0.05 for medium vs. low dose P< 0.005 for all other comparisons by KruskalWallis test with Dwass, Steel, Critchlow-Fligner method. *p< 0.05 **p< 0.001.
Taking Dopamine Agonist Drugs: Pramipexole And Ropinirole
Below we have included the different forms of pramipexole medication and an overview of how to take them.
The most recent and complete information on your specific drug will be on your patient information leaflet that comes with your medication packet. Always read it carefully before you start your treatment.
For detailed information you should follow the advice of your specialist or Parkinsons nurse about how to take pramipexole so that it works well for your Parkinsons.
Pramipexole drugs are also used to help your symptoms when your levodopa medication causes you to experience wearing off and dyskinesia. This could be motor fluctuations, or wearing off before your next dose of levodopa is due.
Also Check: How To Manage Parkinson’s Symptoms
What Are Dopaminergic Antiparkinsonism Agents
Dopaminergic antiparkinsonism agents aim to replace dopamine or prevent the degradation of dopamine.Antiparkinson drugs that aim to replace dopamine in the central nervous system, either release dopamine or mimic the action of dopamine. Drugs that replace dopamine are generally given with peripherally acting dopa carboxylase inhibitors, to prevent the metabolism of levodopa to dopamine peripherally. Dopamine receptor agonists bind to dopamine receptors and mimic the action of dopamine.Selective monoamine oxidase inhibitors bind to the enzyme MAO-B and prevent dopamine from being broken down. Antiparkinson agents are used to treat Parkinsons disease, which is a degenerative disorder of movement that occurs due to dopamine deficiency in the brain, particularly in the basal ganglia.
How Does Pd Affect Dopamine
Doctors believe that PD affects the brains ability to create dopamine.7 Since the brain cannot produce the dopamine it needs, a persons movement begins to be affected. PD can also cause other symptoms as the brain begins to create less dopamine.8
People with PD can have issues with sleep, depression, and blood pressure. Younger people with PD can also have issues with impulse control.9 As you can see, these are all related to the parts of the brain that create dopamine. Doctors are not sure why this happens, or what causes PD.
PD causes the neuron cells in the substantia nigra to break down and die. People with PD have 80 percent fewer dopamine-producing cells in their substantia nigra than people without PD have.7
Doctors are not sure why this happens. If doctors can figure out why PD causes the brain to stop producing dopamine, they think they may be able to find a better treatment for PD.
Recommended Reading: Parkinsons Double Vision
Recommended Reading: Food For Parkinson’s Disease