Apda In Your Community
APDAParkinson’s TreatmentsUnderstanding Stem Cell Therapy in Parkinsons Disease Treatment
On published an article examining commercial stem cell clinics in the United States that market non-FDA approved treatments directly to the public for a variety of health issues, including arthritis, macular degeneration and of particular note to us, Parkinsons disease .
What Are The Advantages Of Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- Abundant supply containing up to 10 times more stem cells than bone marrow or adipose derived stem cells
- hUC-MSC have immunosuppressors and immunomodulatory properties that allow their use in any individual without rejection- Human Leukocyte Antigen matching is not necessary
- Greater proliferation ability than adult autologous stem cells
- They regenerate at a very rapid rate
- They are young and very adaptive
- They have not been impacted by the aging process
- They have not been affected by environmental toxins
- Umbilical cord stem cells can be administered multiple times over the course of days
- Eliminates the need to collect stem cells from the patients fat or hip bone reducing pain and recovery time
Proof Of Concept: Fetal Tissue Grafts
In the late 1990s and early 2000s, more than 300 people with PD were transplanted with brain tissue from 6-10 week old fetuses.
The results were variable, but in some cases symptoms were reversed and sustained for more than 20 years.
Issues related to fetal tissue transplants:
- Insufficient tissue
- Cannot comprehensively analyze tissue before transplant
- Graft-induced dyskinesias
Freed, CR et. al. New Engl. J. of Med. 344, 710-719 Grealish, et. al. Cell Stem Cell 15, 653-665 Olanow CW, et. al. Ann Neurol. 54:403-414 Wen Li, et. al. PNAS 113:6544-6549
You May Like: Does Vitamin B12 Help Parkinson’s
What Are Researchers Investigating Can Stem Cell Therapy Improve The Symptoms Of Parkinsons Disease
Frustration from limited treatment options has led to an increased focus on stem cell replacement therapy, treatment intending to provide long-lasting relief from symptoms of Parkinsons disease.
Approximately 5% of patients diagnosed with Parkinsons disease have an inherited genetic mutation.
Researchers are currently investigating the underlying cause of Parkinsons disease in the other 95% of cases.
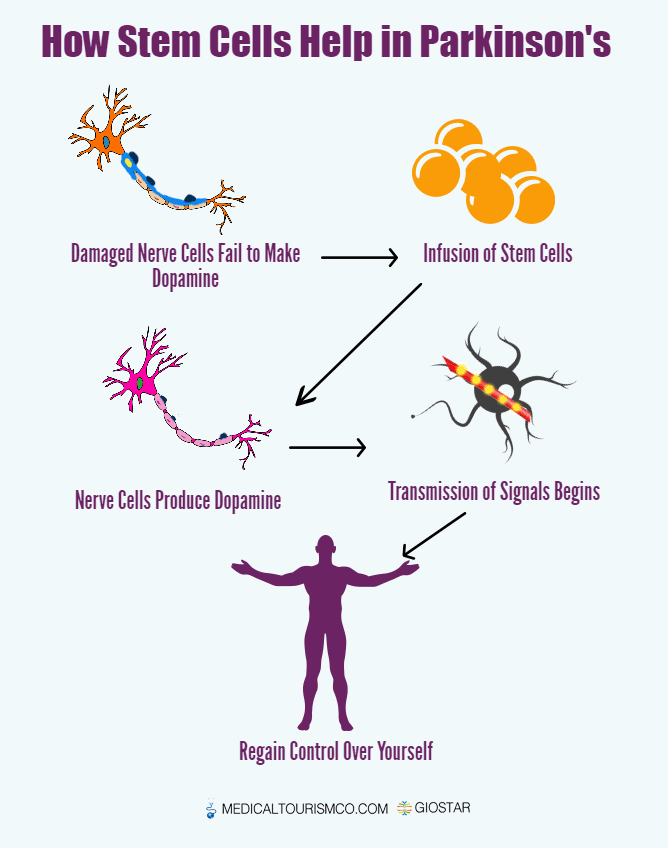
When dopamine was reintroduced into the central nervous system, symptoms were decreased or reversed. This means, if stem cells can be induced into becoming dopamine producing neurons and then transplanted in affected zones, they could replace impaired cells, improving function.1,2
Researchers have shown transplanting young brain cells derived from human umbilical cord into patients with Parkinsons disease resulted in an improvement in disease related symptoms.
Animal studies have shown mesenchymal stem cells promote neuroprotection and neurodifferentiation, by modulating neural stem cells, neurons and glial cells and axonal growth.3-11 They have the ability to repair and regenerate neurons in the brain, reduce levels of free radicals, improve synaptic connection from damaged neurons and regulate inflammation.
Animal models have shown stem cell therapy has been shown to be safe and effective.
When Will Stem Cell Therapy Be Available As A Parkinson’s Treatment
Whilst there has been considerable progress in stem cell research in the last decade, particularly for the treatment of blood and immune system disorders, scientists are still some way from being able to start clinical trials using stem cell therapy for Parkinsons. No-one can predict how long it is likely to take for stem cell therapy to be a viable treatment for Parkinsons.
Also, even if a therapy is approved, it is unlikely to work for everyone just as no one medication is suitable for everyone.
At this stage, scientists do not know which type of stem cell, if any, may eventually lead to a successful treatment or cure.
The key challenges for scientists at present are:
- to understand the way cells grow and differentiate
- to identify methods to differentiate the stem cells into the cell types needed in the brains of people with Parkinsons
- to establish the best ways of getting stems cells into the right part of the brain.
Read Also: Diseases Similar To Parkinsons
Is There Any Guarantee That A Stem Cell
There is no therapy, be it an experimental or established treatment, for which your treating physician can promise or even guarantee a therapeutic success. In the case of innovative and experimental therapies such as stem cell therapy, doctors must perform a benefit-to-risk-analysis for each individual case and ensure that the therapy is beneficial to the patient and these benefits outweigh the risks. Only when this is the case, your doctor will suggest treatment with stem cells.
Fetal Ventral Mesencephalon Tissue
Fetal ventral mesencephalon consists of distinct neuronal populations including DA neurons of the SN and VT areas, oculomotor neurons, and reticular neurons . In the late 1970s and 1980s, the first open-label clinical trial transplanting fetal VM cells to the brains of PD patients was performed . DA neurotransmission recovery initiates at six months, with its progressive restoration suggesting the continuing evolution of the transplanted cells . However, postmortem analysis of patients who had received fetal VM grafts revealed evidence of LB pathology in the transplanted cells in some patients , leading to the hypothesis that LB pathology may spread from host to graft . The early fetal VM transplantation trials used tissues from surgical terminations of pregnancy, but medical terminations are often used in recent clinics .
You May Like: Parkinson Bicycle Cleveland Clinic
Proper Patterning Of Mda Precursors Beyond Establishing Floor
Studies, using bulk-RNA sequencing of mDA neurons at the time of grafting demonstrated a correlation of improved in vivo graft outcome, across > 30 batches, for mDA neuron populations expressing more caudal floor-plate markers including expression of EN1 . Furthermore, the same study showed that FGF8b treatment after floor-plate induction could more reliably induce caudal marker expression. These results were consistent with previous work suggesting the need for FGF8 treatment at later time points of differentiation during non-human primate mDA neuron induction . In contrast, earlier exposure of FGF8b during mDA patterning may not impact the robustness of midbrain marker expression . One challenge of protracted FGF8b treatment is the fact that FGF8b is highly expressed in the hindbrain during early development . Therefore, induction of hindbrain markers, such as HOXA2 and GBX2, can occur following high dose FGF8b treatment . Thus, the use of FGF8 needs to be very carefully timed and titrated to avoid hindbrain and potentially other FGF8-driven proliferative contaminants. Alternatively, it may be possible to find alternative strategies such as the use of midbrain-specific FGFs to substitute for late FGF8b treatment or to develop strategies to selectively enrich for the desired phenotype for translational applications.
How Much Does Stem Cell Treatment Cost
Our treatments are always tailored to your specific situation, disease, stage and other factors. The therapies differ in the product used , the frequency of treatment as well as the further examinations and your sedation and anesthesia wishes. A treatment for PD will cost above ten thousand euros. You will receive a cost estimate for all treatments in advance so that you can accurately estimate what a treatment would cost in your individual case.
Also Check: Do You Get Pain With Parkinsons
You May Like: Fitflop Shoes For Parkinson’s
Brief History On Mda Neuron Protocol Development
The initial approach to generate mDA neurons from hPSCs was based on adapting protocols from mouse ESC, which generate the neuronal-rosette like intermediates by co-culturing with feeder such as MS5 and PA6 and then further differentiate mDA neurons . While the rosette-based protocols could yield dopamine neurons that express TH, the rate-limiting enzyme for dopamine production, and showed dopamine release in vitro, those cells unlikely represented the correct cell type of origin as they barely expressed floorplate markers, such as FOXA2 and LMX1A. Importantly, rosette-derived dopamine neuron protocols displayed a considerable risk of neural overgrowth , and resulted in only limited in vivo DA neuron survival and function .
Figure 1. Comparison of published differentiation protocols for dopamine neuron derivation from human pluripotent stem cells. While all protocols use comparable strategies for neural induction and for midbrain floor plate induction , there are differences in the use of FGF8 and the timing and concentration of the WNT activating compounds .
Table 1. Comparison of dopamine neuron transplantation paradigm in preclinical studies.
Stem Cell Therapy For Parkinson Disease In Pakistan
Stem cells are cells that have the ability to differentiate into any other cell type. They can also divide and renew themselves, meaning they can be used for regenerative purposes. It has been found stem cells are of particular importance in cases of Parkinsons disease because these stem cells produce dopamine. This is important because Parkinsons patients suffer from a lack of dopamine production which leads to tremors, speech problems, and more! Additionally Stem cells are the bodys true multi-potentiality cells to treat diseases like diabetes, heart problems and now Parkinsons treatment is possible through stem cell therapy. Stem Cells have developed rapidly and provided a new ray of hope to many patients all over the world suffering from Parkinsons disease.
Read Also: Voice Amplifiers For Parkinson’s
Location Of The Cell Injected
Cell transplantation in PD has mainly focused on ectopic placement of cells within the striatal target region, far away from the site of degeneration in the SN. The rationale for this approach arose from the concern that the extent of the mDA axonal outgrowth from the graft may not suffice to efficiently innervate the human caudate or putamen. Additionally, in some of the studies, DA neurons did not survive as well when grafted in the midbrain compared to striatum . Furthermore, grafting studies over the last decade have demonstrated that intra-striatal grafting of fetal tissue is sufficient for restoring striatal dopamine release and inducing recovery from PD-relevant symptoms at least a subset of patients . Ectopic transplantation, however, raises the concern that grafted cells may lack major afferent inputs of endogenous mDA neurons in SN, inputs known to play important roles in phasic regulation of nigrostriatal neuron activity. This lack of afferent control may restrict the ability of the cells to improve more complex motor behaviors . Furthermore, there is increasing evidence that DA released from dendrites locally in the SN may have important physiological functions distinct from striatal DA release . Therefore, several groups have pursued a long-term goal of orthotopic transplantation using hPSCs-derived mDA cells into the SN.
What Is The Cost Of Stem Cell Treatments For Parkinsons Disease
The cost of the initial treatment ranges from $5,000 to $10,000. The range in cost is dependent on the complexity of delivering the cells back to you. For example, some Parkinsons Disease patients desire stem cells directly into the fluid surrounding their brain and spinal cord referred to as the cerebrospinal fluid . When this occurs, special imaging and an additional specialist are necessary. For many people the initial treatment is all that is needed however, for some conditions, subsequent treatments may be required and these are done at a reduced fee.
Innovations Medical provides Stem Cell Therapy procedures at both our Dallas and Fort Worth practice locations. Learn more about the benefits of fat stem cell therapy for Parkinsons disease and other neurological conditions by calling for more information or to schedule a consultation.
You May Like: Zhichan Capsule
Stem Cell Therapy In Parkinson’s Disease
Embryonic stem cells : ES cells have attracted great attention as an alternative source for the generation of dopamine neurons because they can be continually expanded with high potential for differentiation. As they are pluripotent stem cells, they are able to form all three embryonic germ layer lineages following induced differentiation. Many studies have focused on optimizing the differentiation of ES cells into dopamine neurons. Among them, systematic and efficient induction systems for dopamine neurons have been reported by several groups , The prospect that ES cells can produce a sufficient number of dopamine neurons for transplantation therapy is particularly appealing, both for clinical and industrial use. At the same time however, their clinical application is limited because of their ability to form tumors and the ethical problems surrounding the use of using fertilized human eggs to establish the ES cell lines .
Mesenchymal stem cells :
Figure 9: Strategy for MSC transplantation in PD patients. View Figure 9
These findings stimulated the advancement of regenerative medicine aimed at the generation of desired cells from MSCs. To date, various cell types, such as mesodermal lineage cells , as well as endodermal lineage cells and ectodermal lineage cells have been induced from MSCs in vitro by the use of cytokines, trophic factors or gene introduction .
Figure 10: Production release of dopamine. View Figure 10
Pathophysiology Of The Disease
Basal ganglia motor circuitry: Parkinson’s disease is predominantly a disorder of the basal ganglia, which are a group of nuclei situated at the base of the forebrain . The striatum, composed of the caudate and putamen, is the largest nuclear complex of the basal ganglia. The striatum receives excitatory input from several areas of the cerebral cortex, as well as inhibitory and excitatory input from the dopaminergic cells of the substantia nigra pars compacta . These cortical and nigral inputs are received by the spiny projection neurons, which are of 2 types: those that project directly to the internal segment of the globus pallidus , the major output site of the basal ganglia and those that project to the external segment of the globus pallidus , establishing an indirect pathway to the GPi via the subthalamic nucleus . The actions of the direct and indirect pathways regulate the neuronal output from the GPi, which provides tonic inhibitory input to the thalamic nuclei that project to the primary and supplementary motor areas .
Figure 2: Anatomy of basal ganglia. View Figure 2
Two pathways exist within the basal ganglia circuit, the direct and indirect pathways , as follows:
Figure 3: Basal ganglia circuitry in Parkinson’s disease. View Figure 3
â¢In the direct pathway, outflow from the striatum directly inhibits the GPi and SNr striatal neurons containing D1 receptors constitute the direct pathway and project to the GPi/SNr
Common symptoms:
b.Terminates with movement
Read Also: Does Sam Waterston Have Parkinsons
Stem Cells And Parkinsons Disease
In many of my previous posts, I have mentioned that one of the reasons that I am so passionate about stem cell research is the possibility that terminal or debilitating diseases can be cured. One of the diseases that scientists are trying to cure with stem cells is Parkinsons Disease which is a disease that progressively attacks the nervous system. One of the main issues with the disease is that the symptoms appear gradually and then worsen as the disease progresses. There is no cure for Parkinsons Disease, but patients have the choice to take medication to control the symptoms of the disease.
However, a study posted on Monday revealed that a specific stem cell technique has cured Parkinsons disease when tested in mice. This technique involves the implantation of stem cells into the dead nerve or brain cells. The mice tested in the laboratory setting had the version of Parkinsons Disease that is exhibited in mice and had only a few more weeks before the disease would completely inhibit their motor skills. However using methods used in stem cell research, the researchers were able to restore the brain cells that were dying and causing the onset of Parkinsons Disease. The mice even began to regain motor functions that were lost before the treatment.
The picture below shows the effect that Parkinsons disease has on the dopamine receptors in the human brain.
A Patient Disease Model
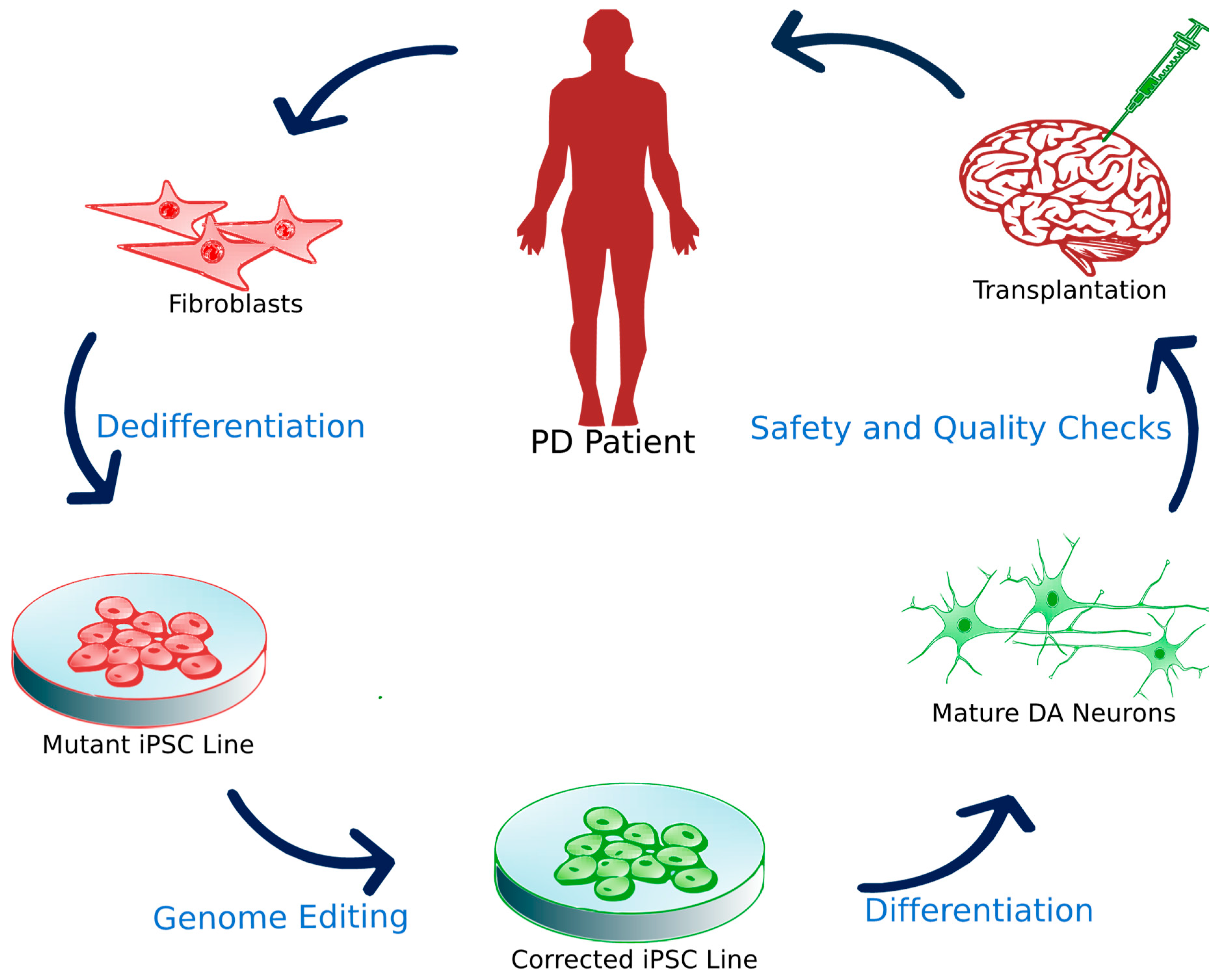
HSCI Principal Faculty member and Director of the Neuroregeneration Research Institute at McLean Hospital Ole Isacson, MD, with funding from HSCI, the Harvard Miller Consortium for the Development of Nervous System Therapies, and the National Institutes of Health, has generated brain cells that produce dopamine, collected from the skin cells of patients with Parkinsons.
Isacson orchestrated the transformation by biologically reprogramming the mature skin cells into induced pluripotent stem cells, and then encouraging the stem cells to become dopaminergic neurons. Neurons were also made from skin cells collected from individuals with genetic mutations associated with high risk for Parkinsons disease.
The creation of this in vitro disease model provides a powerful platform for studying Parkinsons outside of the body. In the journal Science Translational Medicine, Isacson and his team reported that many of the mutations implicated in Parkinsons affect the function of the mitochondria, the cellular organelle responsible for energy production. In collaboration with HSCI Director of Translational Medicine Lee Rubin, PhD, Isacsons lab started to identify compounds that could eliminate disease symptoms in cell lines derived from people carrying Parkinsons mutations.
Don’t Miss: Is Double Vision A Symptom Of Parkinson’s
Results Of Cell Surgical Network For First 201 Patients Receiving Stem Cells For Parkinsons Disease
The improvement does appear to reduce after about 1 year, so repeated treatments appear to be warranted. Remember when looking at these results that most of these patients have been on standard Parkinsons Disease medications for several years. Some patients note increased effectiveness of their Parkinsons Disease medications after stem cell therapy.
Which Stem Cells To Use In Cell Therapies
Stem cells are found throughout the body from development through to adulthood. They are defined by two main properties: self-renewal and the ability to become mature cell types.
Stem cells range from being:
Pluripotent can differentiate into any cell type in the body. Multipotent have a more restricted lineage, e.g. neural stem cells form neurons and glia of the . Unipotent/bipotent make one or two cell types, respectively.
Stem cell therapies branch in two main forms:
Autologous: Same donor and recipient. This is a personalized medicine that avoids immune rejection. Stem cells can either be re-programmed in situ or removed from a patient, manipulated and returned in a transplant.
Allogeneic: Different donor and recipient. The advantage here is that these could be derived from more diverse sources, e.g. embryonic stem cells. Matching will be required for immune compatibility: it is estimated that a cell bank of 150 embryonic stem cell lines would be required to cover 85% of the British population .
Identification is only the first step to achieving high yields of specific cell types from stem cells. A major challenge with developing optimal cells for therapies is recreating the complex spatial and temporal signalling processes that are required to create specific mature cells within organised three-dimensional tissues and structures.
Read Also: Sam Waterston Parkinson’s