A New Toilet Or An Alternative
If you have real difficulties getting to the toilet, it may be possible to get a grant to build a new one, perhaps downstairs. An occupational therapist can advise you on this.
Not all homes are suitable for building new toilets, so a commode might be needed. A commode is a moveable toilet that doesnt use running water. It looks like a chair, with a container underneath that can be removed and cleaned after someone has used it. They can be very discreet.
Urinary Issues In Advanced Parkinsons Disease
Urinary dysfunction and symptoms in PD are most commonly caused by overactivity of the detrusor muscle, or the muscle of the bladder, which contracts excessively despite the fact that it is not filled with urine. This causes an increased urge to urinate and/or an increased frequency of urination, which can be especially prominent at night. In advanced PD, this could culminate in urinary incontinence, or involuntary release of urine. Mobility issues which make getting to the bathroom slower and more cumbersome, compound the problem.
Always remember that people with advanced PD may have other medical problems that affect their urination such as an enlarged prostate. Make sure to have a complete evaluation before assuming that the problem is only related to PD. It is also essential to keep in mind that if changes in urination occur suddenly, there could be a urinary tract infection present.
Once other medical issues and urinary tract infection are ruled out, there are a number of approaches to the issue of urinary incontinence in a person with advanced PD:
Unfortunately, for some, the above available options may not be sufficient to effectively treat urinary incontinence in advanced PD. If this is the reality, it becomes extremely important to keep the skin dry with frequent changes of incontinence products to prevent skin breakdown and the potential development of skin infection.
Treatment For Over Active Bladder In Parkinsons
Overactive bladder affects up to 27% of men and 43% of women of the global population. Now, add a neurological condition and the problem becomes more challenging. First, there is a list of medications which make the problem worse, so should be avoided. Then, a thorough evaluation and physical exam. Treatment depends on the cause, but evaluating all medications and an adjustment of dopamine medication is often necessary. If you are still having problems, five further treatment options are included.
Read Also: Parkinson’s And Memory Loss
Parkinsons Disease And Your Bladder
Many diagnosed with Parkinsons disease experience urinary tract issues. A Michigan Medicine urologist discusses treatment options for patients to consider.
Anne Pelletier-Cameron, M.D., often jokes to her patients that shes a female plumber of the lower urinary tract. On a more professional note, however, shes a urologist in the Michigan Medicine Department of Urology.
In this role, Pelletier-Cameron treats patients with a variety of lower urinary tract symptoms. Some of her patients have been diagnosed with Parkinsons disease, a progressive nervous system disorder that impacts movement. But the breakdown of nerve cells that characterize Parkinsons disease can also cause non-movement symptoms, including bladder issues.
Half of all women and 17% of men will experience urinary incontinence, or the inability to hold urine, she says, noting that for Parkinsons disease patients, those numbers escalate.
Many of my PD patients end up having other bladder problems, including issues with urgency and frequency, says Pelletier-Cameron. Nocturia, or the need to urinate many times during the night, is also common, along with difficulty in emptying the bladder.
Pelletier-Cameron says the impact of bladder symptoms cant be ignored.
Thanks For Signing Up
We are proud to have you as a part of our community. To ensure you receive the latest Parkinsons news, research updates and more, please check your email for a message from us. If you do not see our email, it may be in your spam folder. Just mark as not spam and you should receive our emails as expected.
You May Like: Physical Therapy For Parkinson’s Disease
Prevalence Of Nocturia In Pd
Questionnaire based studies generally report a high prevalence of nocturia, with figures ranging between 76% and 86%,, though one study reported a prevalence of only 34.6%. In a study of 115 PD patients using a questionnaire on pelvic organ functions, Sakakibara et al. reported nocturia in 53% of men and 63% of women with PD.
Nocturia has been reported in 34.6% of PD patients using a semistructured interview in 1,072 consecutive patients with PD in the large, multicentric PRIAMO study.
This apparent variability in prevalence between studies could be put down to several factors, including differences in the demographic features of the cohort of patients being studied, and the occurrence of medical comorbidities. LUT symptoms are more prevalent with advancing disease and were most frequent in patients at H & Y stage 4 to 5 with a reported prevalence of around 90%. Moreover, the term nocturia has been applied differently in studies and the prevalence varies according to the definition being used. The International Continence Society made an attempt to standardize the definition of nocturia in 2002 and, based on a consensual approach, put forward the complaint that the individual has to wake at night one or more times to void.
Warning Disclaimer Use For Publication
WARNING: Please DO NOT STOP MEDICATIONS without first consulting a physician since doing so could be hazardous to your health.
DISCLAIMER: All material available on eHealthMe.com is for informational purposes only, and is not a substitute for medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment provided by a qualified healthcare provider. All information is observation-only. Our phase IV clinical studies alone cannot establish cause-effect relationship. Different individuals may respond to medication in different ways. Every effort has been made to ensure that all information is accurate, up-to-date, and complete, but no guarantee is made to that effect. The use of the eHealthMe site and its content is at your own risk.
If you use this eHealthMe study on publication, please acknowledge it with a citation: study title, URL, accessed date.
Also Check: Keto Diet And Parkinson’s Disease
Difficulty Emptying The Bladder
- Some people with Parkinsons find it difficult to pass urine if the bladder fails to contract when required, or because the sphincter does not let urine out or a combination of the two. This is a result of reduced dopamine levels interfering with the efficiency of the bladder muscles and causing a residual amount of urine to be left in the bladder. This reduces the total amount the bladder can hold and creates a feeling of wanting to empty the bladder very often. Unfortunately, there is an increased risk of urinary infection if the bladder is not emptied completely.
- In some older people, constipation which is often associated with Parkinsons can result in faeces collecting in the rectum. This can result in difficulties in bladder emptying, which may be because of pressure on the urethra, or mediated by the nerves in the region. The bladder is then unable to empty and may continue distending, causing dribbling incontinence.
- Anticholinergic medications can also make emptying problems worse.
Fecal Incontinence In Advanced Parkinsons Disease
Fecal incontinence is a very debilitating symptom that can occur in advanced PD and refers to the involuntary release of fecal matter.
Once again, fecal incontinence, especially if it is a new symptom, should be fully evaluated to determine if there is a cause unrelated to PD. Diseases of the gut such as inflammatory bowel disease or compression of the lower spine cord can be the reason.
If related to PD, there are typically two situations to consider. One possibility is that severe constipation with impacted bowel movement allows loose stool from higher up in the gastrointestinal tract to escape around the edges of the obstruction. In this situation, fecal incontinence could be a harbinger of bowel obstruction. Aggressive and continuous treatment of constipation can help avoid this potential scenario.
Fecal incontinence can also be related to nerve dysfunction of the anal sphincter, or the ring of muscle that controls when feces is released. Cognitive dysfunction and mobility issues may further interfere with getting to the bathroom in time. Some treatment options are similar to urinary incontinence including the use of bedside equipment to minimize mobility issues and introduction of pelvic floor exercises to strengthen the musculature that keeps feces in place.
As with urinary incontinence, frequent and rapid exchange of dirtied incontinence products can keep skin intact and prevent infection.
Tips and Takeaways
Dr. Rebecca Gilbert
Don’t Miss: Parkinson’s Vs Multiple Sclerosis
Management Of Sexual Dysfunction
Management of sexual dysfunction in patients with PD includes both behavioural and pharmacological options depending on the nature of the sexual dysfunction. Behavioural therapy may be used to treat SD, if considered as a learned maladaptive behaviour and may involve the use of psychodynamic psychotherapy and cognitive behavioural therapy . Pharmacological treatment of SD, on the other hand, requires either the reduction or elimination of drugs interfering with the sexual function or the introduction of drugs that improves sexual function . Ultimately, treatment options for SD may require multidisciplinary input from neurologists and psychologists for optimum results . Although phosphodiesterase 5 inhibitors are standard treatment option for erectile dysfunction , intracavernosal alprostadil 1.2510 g injections can be used.
The management of hypersexuality as part of an impulse control disorder includes reduction/stopping of dopamine receptor agonist and practical therapeutic strategies including psychological therapies but not limited to counselling, psychotherapy, sex, couple and behavioural therapies . Hormonal treatment specifically testosterone has been tried in PD .
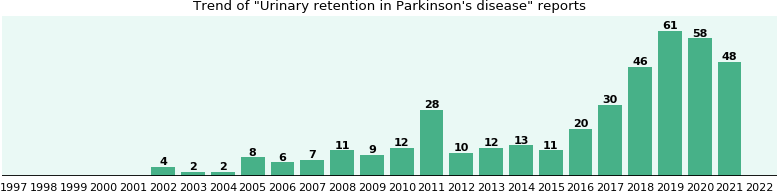
Symptoms Of Urinary Retention
The symptoms of urinary retention are not always obvious but may include
- Hesitancy really having to strain to pass urine
- Strong feelings of urgency and frequency and when passing urine only a small amount comes out
- A urinary stream that is very weak and intermittent
Whilst your bladder is not emptying properly there is a risk that the residual urine in the bladder will become infected. This could cause further complications and problems if it isnt removed regularly. It is important to seek help if you experience any of the above symptoms.
It is a good idea to keep a record of your bladder activity in a bladder diary for a few days before your appointment with your doctor or nurse.
Your Doctor or Healthcare Professional may recommend the following tests:
Recommended Reading: Cialis And Parkinson’s Disease
Addressing Practical Aspects Of Eating And Drinking
Some people with Parkinsons have problems chewing and swallowing. This can make it difficult to eat a diet with plenty of fibre. A speech and language therapist can give advice about this. Ask your GP, specialist or Parkinsons nurse for a referral. If it takes a long time to eat and your meal goes cold, eat smaller portions and go back for seconds that have been kept warm. You can also get special plates that keep your meals hot the Disabled Living Foundation has more information.
An occupational therapist will also be able to give you some tips and practical advice.
Clean Intermittent Self Catheterization

The finding of a high post-void residue is unusual in patients with PD. If the PVR volume is consistently more than 100 mL, clean intermittent catheterization has been advocated. Specific issues related to dexterity in PD may make this challenging. Experienced health-care professionals, such as a continence adviser, should be involved in teaching the technique and exploring possible barriers to successful catheterization. Complications include UTI and trauma .
Don’t Miss: What Happens If Parkinson’s Is Left Untreated
How Might Parkinson’s Affect Bladder Problems
Bladder difficulties can be common in Parkinsons, particularly in the later stages of the condition. The loss of dopamine and the resulting interruption of signals from the brain can mean that messages telling the bladder to retain or expel urine are disrupted.
However, it is important to stress that bladder problems are not inevitable in Parkinsons. If difficulties do arise, especially in older people, they may be caused by factors totally unrelated to the condition, so a thorough medical evaluation should be carried out with any appropriate tests.
Bladder problems associated with Parkinsons include:
Evaluating And Treating Urinary Issues In Parkinson’s Disease Multiple System Atrophy And The Other Atypical Parkinsonism Disorders
In this hour-long webinar, neuro-urologist Ekene Enemchukwu, MD focuses on urinary incontinence, overactive bladder, urinary retention, and other urinary issues in PD, MSA, and the atypical parkinsonism disorders. Following the presentation, moderator Candy Welch, Brain Support Networks MSA caregiver support group leader, asks Dr. Enemchukwu many questions submitted by webinar participants.
Recommended Reading: Stretching Exercises For Parkinson’s Disease
What Examinations May I Need To Have
Your GP or specialist will probably ask a series of questions to find out what the problem is. These may include:
- When did the trouble start?
- How often does it happen?
- Can you feel when your bladder or bowel is full?
- Are you having difficulty emptying your bladder or bowel?
- How often are you using the toilet?
Parkinson’s symptoms, such as slowness of movement and rigid muscles, affect the muscles in the bowel wall. This can make it harder to push stools out of the body. You may be asked to keep a chart for several days of how often you use the toilet and how much you drink.
You may also be asked for a urine sample to test for infection and they will normally carry out a physical examination.
Bladder or bowel problems can be complex in Parkinson’s, so sometimes specialist tests or X-rays may be needed. All of these can usually be done in an outpatient department or clinic.
Cardiovascular Dysautonomia And Nocturia
An association is known to exist between orthostatic hypotension and nocturia, and nocturnal polyuria. In health, blood pressure is known to decrease at night, and this is often absent in patients with PD reporting autonomic failure. This may be mediated through inappropriate mineralocorticoid receptor activation. Consequent to this, pressure natriuresis occurs, resulting in increased urine output and the patient reports nocturia. OH and supine hypertension frequently coexist in PD, and older age, akinetic-rigid motor subtype, and pre-existing hypertension are independent risk factors for supine hypertension. Improvement of nocturia, however, has not been a consistent finding in studies evaluating treatments for supine hypertension,, , and therefore cardiovascular dysautonomia is likely to be only one of several mechanisms responsible for nocturia in PD.
Don’t Miss: Parkinson’s Disease Symptoms And Treatment
Increased Risk Of Overactive Bladder In Patients With Idiopathic Parkinsons Disease: Insight From A Nationwide Population
-
Roles Conceptualization, Investigation, Methodology, Writing original draft
Affiliation Department of Neurology, China Medical University Hospital, China Medical University School of Medicine, Taichung, Taiwan
-
Affiliation Department of Neurology, China Medical University Hospital, China Medical University School of Medicine, Taichung, Taiwan
- Cheng-Li Lin,
Roles Data curation, Formal analysis, Project administration
Affiliations College of Medicine, China Medical University, Taichung, Taiwan, Management Office for Health Data, China Medical University Hospital, Taichung, Taiwan
-
* E-mail:
Affiliations National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences, National Health Research Institutes, Miaoli, Taiwan, Institute of Occupational Medicine and Industrial Hygiene, College of Public Health, National Taiwan University, Taipei, Taiwan, Ph.D. Program in Environmental and Occupational Medicine, Kaohsiung Medical University, Kaohsiung, Taiwan
Reduced Functional Bladder Capacity At Night
Functional bladder capacity is diminished if the bladder wall compliance is reduced, the detrusor is involuntarily contracting , or if the bladder has incompletely emptied following a void. All three of these are known to occur in PD. Nocturia results whenever the urine volume produced at night exceeds the functional bladder capacity. Urodynamic evidence for detrusor overactivity has been reported in 45% to 93% of PD patients, , and correlates with scores in overactive bladder questionnaires. In urodynamic studies, 81.0% had storage disorder, 54.8% had abnormalities of storage and voiding, whereas 19.0% had only a voiding disorder.,
A likely mechanism for DO in PD is disruption of the dopamine D1-GABAergic direct pathway and its GABAergic collateral to the micturition circuit,, resulting in loss of inhibition of the micturition reflex and OAB. Severity of OAB symptoms has been shown to correlate with impairments observed on urodynamic testing and dopaminergic deficiency observed in dopamine transporter scans.,
You May Like: Pre Parkinson’s Disease Symptoms
Why Do Urgency And Frequency Occur
Bladder difficulties in Parkinsons are related to changes in the level of dopamine affecting the function of the bladder muscle. Parkinsons is also thought to affect the nerve pathway between the bladder and the part of the brain controlling bladder function. Some of the symptoms that affect bladder control are related to the level of dopamine in your body which will rise and fall depending on your medication level.
Other conditions such as weak pelvic floor muscles or an enlarged prostate will contribute to bladder symptoms. Constipation can also worsen bladder symptoms by putting pressure on the bladder.
Sexual Dysfunction In Parkinsons Disease

People with PD may experience sexual dysfunction, including loss of desire, inability to orgasm, erectile dysfunction in men, decreased lubrication in women, or pain with intercourse in women. Some studies have found that sexual dysfunction may occur in 60-80% of men and women with PD. Older patients with PD have more sexual dysfunction than younger patients, although sexual dysfunction is also greater in older adults who do not have PD. In addition to age, conditions such as diabetes, hypertension, and depression can factor into sexual dysfunction.3,4
There are several factors that can lead to sexual dysfunction in people with PD. In addition to the motor symptoms of PD, which may create practical barriers to engaging in sexual activity, non-motor symptoms like depression, anxiety, or sleep disturbances can also impact a persons sex drive. Many people with PD express dissatisfaction with their sexual life.3,5
Some people with PD who are treated with dopamine agonists develop impulse control disorders, like hypersexuality. Hypersexuality can lead to unusual or increased sexual behavior, which may have devastating effects on relationships. Changing medications or reducing the dose of medication can help, and people who experience any side effects such as impulse control disorders should bring it to the attention of their doctor.3
Recommended Reading: Emotional Symptoms Of Parkinson’s