What Causes Parkinson Disease
Parkinson disease arises from decreased dopamine production in the brain. The absence of dopamine makes it hard for the brain to coordinate muscle movements. Low dopamine also contributes to mood and cognitive problems later in the course of the disease. Experts don’t know what triggers the development of Parkinson disease most of the time. Early onset Parkinson disease is often inherited and is the result of certain gene defects.
Comparison With Other Dementias
Dementia is the result of physical changes in the brain that can lead to memory loss and an inability to think clearly.
Several types of dementia exist, including:
PD dementia has different symptoms to other types.
Alzheimers dementia, for example, impairs memory and language. PD dementiam on the other hand, affects problem-solving, the speed at which thoughts occur, memory, and mood, alongside other important cognitive functions.
Dementia with Lewy bodies and Parkinsons disease dementia are similar in that the Lewy Bodies might be present in both forms.
However, whether the disease causes Lewy bodies or if Lewy bodies cause the disease symptoms is unclear. Researchers also believe that the way the Lewy bodies form in Parkinsons disease dementia is different from those in Lewy body dementia.
Tip : Whatand Howyou Eat Can Make A Difference
Theres no specific Parkinsons disease diet, but by adjusting your eating habits, you can help protect your brain. Diets that are good for your heart tend to also be good for brain health. Eating habits such as those promoted in the Mediterranean diet can help reduce inflammation, protect neurons, and promote better communication between brain cells.
Primarily, its important to eat plenty of fruit and vegetables, cut down on sugary foods and refined carbs, reduce fried and processed foods, and boost your intake of healthy fats and home-cooked meals. High protein meals may also help to benefit your brain chemistry.
Don’t Miss: Light Treatment For Parkinson’s Disease
Frontotemporal Dementia With Parkinsonism
One form of familial FTD, also known as frontotemporal dementia with Parkinsonism-17 , is caused by genetic changes in the gene for tau protein, located on chromosome 17. No other risk factors for this condition are known.
FTDP-17 is rare and accounts for only three per cent of all cases of dementia. Symptoms progressively get worse over time and usually appear between the ages of 40 and 60. The condition affects both thinking and behavioural skills and movements such as rigidity, lack of facial expression and problems with balance .
It can be distressing to be told that you have a genetic disorder or are at risk of having one. Genetic counselling provides the person and their family with information about a genetic disorder and its likely impact on their lives. This can assist a person with FTDP-17 to make informed medical and personal decisions about how to manage their condition and the challenges it presents to their health and wellbeing. Prenatal genetic counselling is also available for parents to help them decide about a pregnancy that may be at risk of FTDP-17.
Parkinson’s Disease Dementia And Dementia With Lewy Bodies

The key pathological hallmark found in brains of Parkinson’s disease and Parkinson’s disease dementia patients are abnormal microscopic deposits composed of -synuclein. This protein is found widely in the brain and its normal function is not yet well understood. The deposits are called “Lewy bodies”. Lewy bodies are also found in several other neurodegenerative brain disorders, including dementia with Lewy bodies . Evidence suggests that Parkinson’s disease and Parkinson’s disease dementia, and dementia with Lewy bodies, may be linked to the same underlying abnormalities in caused by the deposition of -synuclein.
You May Like: Parkinson’s Early Signs And Symptoms
What Are Pd Dementia Safety Concerns
Safety issues should be considered and monitored from the time of diagnosis. As PDD progresses, ensure that your loved one is not left alone.
- Evaluate driving privileges before safety is a concern. Your doctor can make a driving evaluation referral.
- Work out legal and financial issues and safeguard finances. People with dementia are at greater risk of falling victim to scams and fraud.
- Minimize prescription risks. Confirm with the doctor the medication names and doses of the person with PD. If the person is in dementias early stages and capable, fill up their weekly pill box together and monitor use.
- Medical alert systems can be critical in case your loved one falls or wanders outside of the home. Many types of systems are available, from bracelets and pendants to smart watches with fall detection and one-button connections to 911.
- Evaluate gun safety. If your loved one owns a firearm or has one in the home, consider speaking with their doctor about the subject and taking appropriate safety precautions.
Palliative Care In Parkinson’s Disease
Palliative care for people with PD and their caregivers has progressed over the last 10 years but it is still an upcoming field. Evidence of effects is limited but trials are underway . Qualitative studies on palliative care needs and natural history studies have indicated that the needs of people with advanced PD are complex. Awareness of the potential benefit of palliative care is growing, but we know little about useful components . To the best of our knowledge, there is no clear conceptualization of the specifics of palliative care in PD.
Also Check: Which Parkinson’s Medications Cause Hallucinations
Coping With Cognitive Changes
Some medications used to treat Alzheimer’s disease also may be used to treat the cognitive symptoms of LBD. These drugs, called cholinesterase inhibitors, act on a chemical in the brain that is important for memory and thinking. They may also improve hallucinations, apathy, and delusions. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration has approved one Alzheimer’s drug, rivastigmine, to treat cognitive symptoms in Parkinson’s disease dementia. Several other drugs are being tested as possible treatments for LBD symptoms or to disrupt the underlying disease process.
What Is Aggressive Parkinsons Disease
As written above, Parkinsons dementia aggression is that form of Parkinsons which makes the patient exhibit aggressive behavior. They vent out their aggression either verbally or physically, in the various forms that have been written above. Besides verbal and physical outbursts, PD Dementia patients are also prone to hallucinating caused by the medication administered. Hallucinations in PD Dementia patients primarily occur because of the effects of dopaminergic agents for motor symptoms.
Loss of dopamine neurons in the ventral tegmental area is one of the likeliest of all neuropathological causes as changes in serotonin and norepinephrine systems are not. For the uninitiated, the ventral tegmental area is the origin of the mesolimbic dopaminergic projection. Plenty of studies have gone into analyzing the cause behind the aggression in PD Dementia patients. Depression in PD Dementia patients has been identified due to changes in the medial frontal cortex and the anterior cingulate. Akinetic-rigid variants have been found in patients showing signs of major depression.
Also Check: Will There Ever Be A Cure For Parkinson’s Disease
Treatment Of Behavior And Mood Problems In Lewy Body Dementia
Behavioral and mood problems in people with LBD can arise from hallucinations, delusions, pain, illness, stress, or anxiety. They may also be the result of frustration, fear, or feeling overwhelmed. The person may resist care or lash out verbally or physically.
Medications are appropriate if the behavior interferes with the person’s care or the safety of the person or others. If medication is used, then the lowest possible dose for the shortest period of time is recommended.
The first step is to visit a doctor to see if a medical condition unrelated to LBD is causing the problem. Injuries, fever, urinary tract or pulmonary infections, pressure ulcers , and constipation can worsen behavioral problems and increase confusion.
Certain medications, such as anticholinergics and antihistamines may also cause behavioral problems. For example, some medications for sleep problems, pain, bladder control, and LBD-related movement symptoms can cause confusion, agitation, hallucinations, and delusions. Similarly, some anti-anxiety medicines can actually increase anxiety in people with LBD. Review your medications with your doctor to determine if any changes are needed.
Antidepressants can be used to treat depression and anxiety, which are common in LBD. Many of them are often well tolerated by people with LBD.
Alzheimers And Parkinsons Disease: Similarities And Differences
James M. Ellison, MD, MPH
Swank Center for Memory Care and Geriatric Consultation, ChristianaCare Configure
Explore the similarities and differences between two common degenerative brain disorders.
Ron brings his 78-year-old wife, Sara, to the Memory Clinic, with a pressing concern. Sara is forgetting things more often even though her Parkinsons disease symptoms appear to be under good control with standard medications, healthy diet, and plenty of physical activity. She is losing her train of thought mid-sentence and she became very confused about where she was while driving the well-traveled route to her daughters home. Is she developing dementia? Is that a part of Parkinsons disease? Or is she developing Alzheimers disease? And what are the differences between Alzheimers and Parkinsons?
You May Like: Sinemet Dosage For Parkinson’s
Parkinson’s Dementia And Dementia With Lewy Bodies
“Both of these types of dementia involve abnormal protein deposits called Lewy bodies forming in brain cells. Because they are so similar, you may hear both of them being called Lewy body dementia.”
According to Fletcher, the symptoms of Parkinson’s dementia and dementia with Lewy bodies can be very similar. These include both motor and cognitive symptoms:
Physical symptoms could include:
“However, the order in which movement and mental symptoms appear is different,” adds Fletcher. “If there have been motor symptoms for at least one year before dementia symptoms occur, specialists will often give a diagnosis of Parkinson’s dementia.
“If dementia symptoms occur before or at the same time as motor symptoms, specialists will usually give a diagnosis of dementia with Lewy bodies.”
Lewy Body Dementia Research
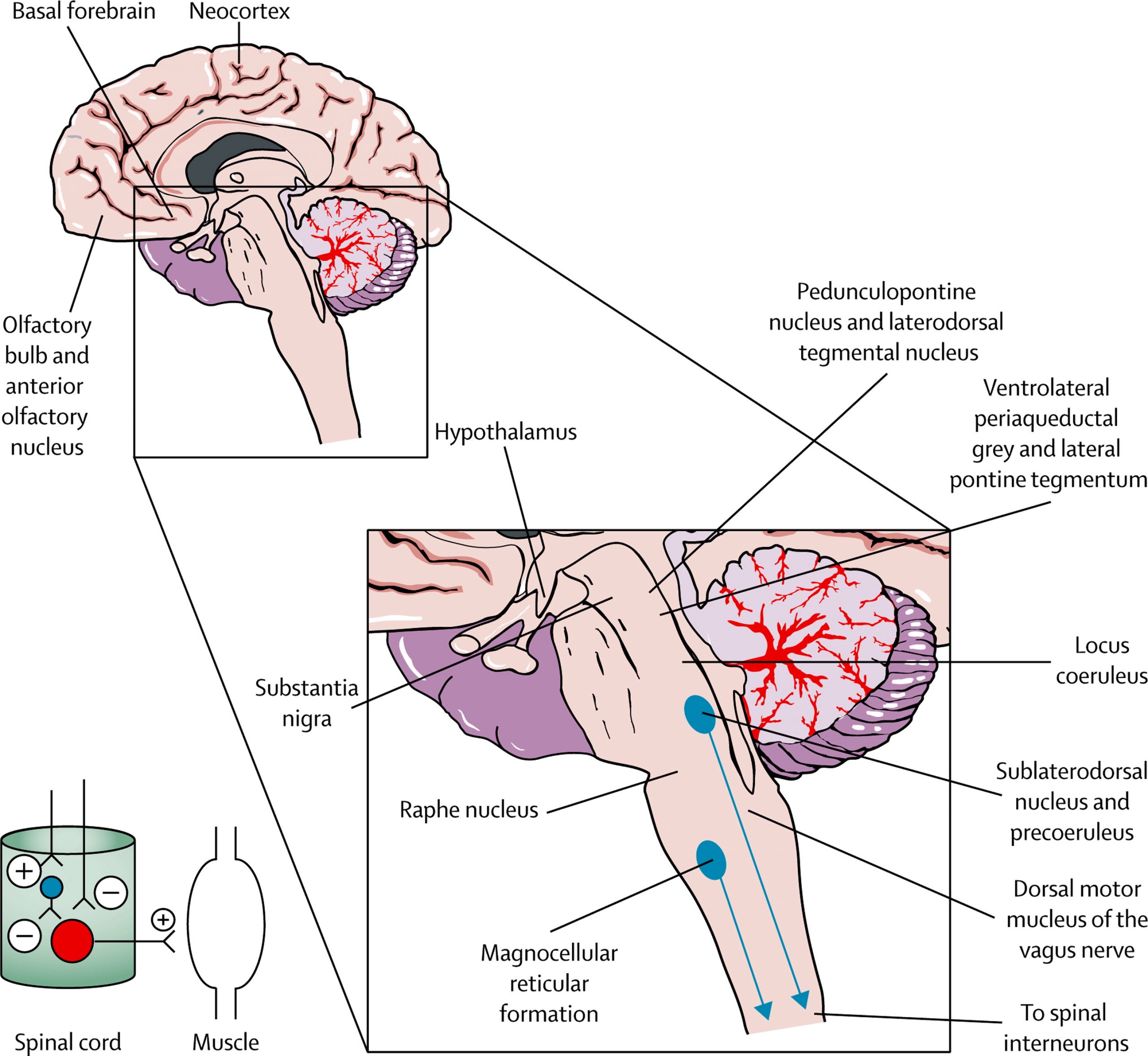
Many avenues of research are being explored to improve our understanding of LBD. Some researchers are working to identify the specific differences in the brain between the two types of LBD. Others are looking at the disease’s underlying biology, genetics, and environmental risk factors. Still other scientists are trying to identify biomarkers , improve screening tests to aid diagnosis, and research new treatments.
Scientists hope that new knowledge about LBD will one day lead to more effective treatments and even ways to cure and prevent the disorder. Until then, researchers need volunteers with and without LBD for clinical studies.
NIH and other groups help people learn about clinical trials and studies and find research opportunities near them. Visit the following websites for details:
Recommended Reading: Is Hip Pain An Early Sign Of Parkinson’s
What Causes Parkinsons Disease Dementia
A chemical messenger in the brain called dopamine helps control and coordinate muscle movement. Over time, Parkinsons disease destroys the nerve cells that make dopamine.
Without this chemical messenger, the nerve cells cant properly relay instructions to the body. This causes a loss of muscle function and coordination. Researchers dont know why these brain cells disappear.
Parkinsons disease also causes dramatic changes in a part of your brain that controls movement.
Those with Parkinsons disease often experience motor symptoms as a preliminary sign of the condition. Tremors are one of the most common first symptoms of Parkinsons disease.
As the disease progresses and spreads in your brain, it can affect the parts of your brain responsible for mental functions, memory, and judgment.
Over time, your brain may not be able to use these areas as efficiently as it once did. As a result, you may begin experiencing symptoms of Parkinsons disease dementia.
You have an increased risk of developing Parkinsons disease dementia if:
Dementia Outcomes According To Baseline Motor Features
Among motor variables , the proportion of gait involvement at baseline , falls , and freezing predicted dementia. Poor performance on the Purdue Pegboard Test and alternate tap test , but not the UPDRS predicted dementia. Patients developing dementia were more likely to report bilateral onset of motor symptoms . There was no association between dementia status and PD subtype, although the dementia-converted group had slightly more patients with akinetic-rigid Schiess scores than the group without dementia . Baseline UPDRS part III scores, total UPDRS scores, Timed Up and Go, Hoehn and Yahr stage, and axial-limb ratio were not predictive of dementia status.
Read Also: Laser Cane For Parkinson’s
What Is Parkinsons Disease Dementia
Parkinsons disease dementia is a brain disorder that occurs in somebut not allpeople living with Parkinsons disease. The brain cell damage caused by the disease can lead to a loss of memory and other cognitive functions such as problem solving and speed of thinking. These changes in thinking and behavior can impact your daily living, independence, and relationships.
In those who do develop Parkinsons disease dementia, there is at least one yearand usually 10 to 15 yearsbetween the Parkinsons diagnosis and the onset of dementia. According to estimates by the Alzheimers Association, 50% or more of people with Parkinsons disease eventually experience dementia, although there are a number of risk factors that impact the likelihood of developing symptoms:
- Parkinsons patients who experience hallucinations, excessive daytime sleepiness, and more severe motor control problems are at higher risk for dementia.
- Dementia is more common in people who are older at onset of Parkinsons.
- Dementia is a bigger risk factor in non-tremor predominant Parkinsons.
- Overwhelming stress, cardiovascular disease, and adverse reactions to the Parkinsons disease drug levodopa can also indicate an increased risk for developing dementia.
- Dementia is relatively rare in people who develop Parkinsons before age 50, no matter how long they have had the disease.
What Are The Treatments For Lewy Body Dementia
There is no cure for LBD, but treatments can help with the symptoms:
- Medicines may help with some of the cognitive, movement, and psychiatric symptoms
- Physical therapy can help with movement problems
- Occupational therapy may help find ways to more easily do everyday activities
- Speech therapy may help with swallowing difficulties and trouble speaking loudly and clearly
- Mental health counseling can help people with LBD and their families learn how to manage difficult emotions and behaviors. It can also help them plan for the future.
- Music or art therapy may reduce anxiety and improve well-being
Support groups can also be helpful for people with LBD and their caregivers. Support groups can give emotional and social support. They are also a place where people can share tips about how to deal with day-to-day challenges.
NIH: National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke
Recommended Reading: Parkinson’s Physical Therapy Evaluation
Secondary Symptoms Of Parkinsons Disease
In addition to the major symptoms of Parkinsons, there are many secondary motor symptoms associated with the disease. Again, not everyone with Parkinsons will necessarily develop all or even any of these symptoms.
- Freezing when walking, usually occurring when taking the first step.
- Small, cramped handwriting that gets worse the more you write.
- A less expressive face. People may comment that you look serious or mad. You may have a blank stare or blink less often.
- Speech may become slow, whispery, or slurred.
- Emotional changes such as anxiety, depression, and fear.
- Fatigue and loss of energy.
- Loss of sense of smell.
- Trouble chewing or swallowing, drooling and excess saliva.
- Sleep problems, including waking up frequently during the night or suddenly falling asleep during the day.
What Happens In Pdd
People with PDD may have trouble focusing, remembering things or making sound judgments. They may develop depression, anxiety or irritability. They may also hallucinate and see people, objects or animals that are not there. Sleep disturbances are common in PDD and can include difficulties with sleep/wake cycle or REM behavior disorder, which involves acting out dreams.
PDD is a disease that changes with time. A person with PDD can live many years with the disease. Research suggests that a person with PDD may live an average of 57 years with the disease, although this can vary from person to person.
Read Also: Vascular Parkinson’s Disease Treatment
Dementia And Cognitive Change
Cognition or cognitive function is a term used to describe the thought processes of your brain.
Cognition includes judgement, reasoning, problem-solving and memory. It is thought that the majority of people with Parkinsons experience some changes to their cognition. This is known as cognitive impairment. In people living with Parkinsons the level of cognitive impairment is mild in most cases.
Environmental Risks Of Parkinsons Disease

Environmental factors can lead to an increased risk that causes Parkinsons Disease. These include:
- Significant exposure to pesticides
- Certain heavy metals
- Repeated head injuries
Because many years pass between these environmental factors and when the first Parkinsons Disease symptoms appear, it is difficult to establish a direct correlation. Although the connection is difficult to connect, scientists still believe that these environmental factors do play a role in the cause of Parkinsons Disease developing.
Recommended Reading: Best Books On Parkinson’s Disease
How Is Parkinson Disease Diagnosed
Parkinson disease can be hard to diagnose. No single test can identify it. Parkinson can be easily mistaken for another health condition. A healthcare provider will usually take a medical history, including a family history to find out if anyone else in your family has Parkinson’s disease. He or she will also do a neurological exam. Sometimes, an MRI or CT scan, or some other imaging scan of the brain can identify other problems or rule out other diseases.
How Is Parkinson Disease Treated
Parkinson disease can’t be cured. But there are different therapies that can help control symptoms. Many of the medicines used to treat Parkinson disease help to offset the loss of the chemical dopamine in the brain. Most of these medicines help manage symptoms quite successfully.
A procedure called deep brain stimulation may also be used to treat Parkinson disease. It sends electrical impulses into the brain to help control tremors and twitching movements. Some people may need surgery to manage Parkinson disease symptoms. Surgery may involve destroying small areas of brain tissue responsible for the symptoms. However, these surgeries are rarely done since deep brain stimulation is now available.
Recommended Reading: Side Effects Of Parkinson Disease Medicine