Memory And Thinking Problems
You may experience forgetfulness, slowed thinking and difficulty concentrating. You might find it harder to follow conversations, and remember some words and names. This can make communication difficult.
You may also find it increasingly difficult to make decisions, plan activities and solve problems. This can make everyday activities harder.
Recommended Reading: What Are The Very First Signs Of Parkinsons Disease
What Is Parkinsons Disease Dementia
Parkinsons disease dementia is a term specifically used for those who have suffered with Parkinsons for multiple or several years and eventually develop dementia. Almost always in the early stages of Parkinsons, patients will experience inhibited motor skills and even sometimes cognitive change. Non-motor symptoms of Parkinsons may appear over time, such as memory loss, anxiety, fatigue, cognitive dysfunction, and more. However, not all individuals who are diagnosed with Parkinsons will receive a dementia diagnosis, and it is not yet possible to determine which Parkinsons patients will develop dementia as well.
Read Also: Parkinsons Disease Foundation Grants
Dopamine Concentration And Metabolism
The dopamine concentration in control cases was greatest at coronal levels 1113 in the caudate and putamen while the concentration of HVA displayed no gradient in the caudate but peaked in the putamen at coronal level 12. The HVA : dopamine ratio in the posterior striatum was higher in the putamen than in the caudate, as previously reported .
Comparing disease groups, dopamine was significantly reduced in the caudate in DLB and Parkinson’s disease relative to controls and Alzheimer’s disease cases . The loss of dopamine in the caudate in DLB was uniform along the rostrocaudal axis , but in Parkinson’s disease the dopamine reduction in the posterior caudate was much more extensive . In the putamen, the dopamine concentration was significantly reduced in both DLB and Parkinson’s disease compared with controls and Alzheimer’s disease cases . In the putamen in both DLB and Parkinson’s disease, dopamine loss was more extensive caudally. In the putamen in DLB, dopamine was reduced by 35% rostrally and 72% caudally, while in the putamen in Parkinson’s disease dopamine was reduced by 79% rostrally and 90% caudally.
Also Check: Parkinson’s Disease Exercise Program
Movement Problems And Lewy Body Dementia
Some people with LBD may not experience significant movement problems for several years. Others may have them early on. At first, movement symptoms, such as a change in handwriting, may be very mild and easily overlooked. Movement problems may include:
- Muscle rigidity or stiffness
Behavioral And Mood Symptoms Of Lewy Body Dementia
Changes in behavior and mood are possible in LBD and may worsen as the persons thinking abilities decline. These changes may include:
- Apathy, or a lack of interest in normal daily activities or events and less social interaction
- Anxiety and related behaviors, such as asking the same questions over and over or being angry or fearful when a loved one is not present
- Agitation, or restlessness, and related behaviors, such as pacing, hand wringing, an inability to get settled, constant repeating of words or phrases, or irritability
- Delusions, or strongly held false beliefs or opinions not based on evidence. For example, a person may think his or her spouse is having an affair or that relatives long dead are still living.
- Paranoia, or an extreme, irrational distrust of others, such as suspicion that people are taking or hiding things
Also Check: Parkinson’s Disease Gene Therapy Clinical Trial
Wait So What Is Parkinsonism
Parkinsonism refers to the motor symptoms that are typically associated with PD, such as tremors, stiffness, and walking/balance problems. Both PD and LBD are forms of Parkinsonism, meaning that PD patients and LBD patients may experience these motor symptoms.2 Because the Parkinsonism motor symptoms of PD and LBD can be very similar, it can be difficult to differentiate between the two conditions.
Recommended Reading: Parkinson Silverware
Treatments For Parkinsons Disease Dementia And Dementia With Lewy Bodies
Treatments for DLB are similar to PDD and are aimed at symptom control. The motor symptoms of slowness, stiffness and walking difficulties can be treated with Levodopa. However, Levodopa can cause or exacerbate hallucinations, making it difficult to use it as a treatment for patients who have or are at risk of having hallucinations. Sometimes, clinicians will need to treat the hallucinations more aggressively in order for a patient to tolerate Levodopa given to help the motor symptoms. On the flipside, anti-psychotic medications to control hallucinations can worsen motor symptoms, so treating all the symptoms of LBD simultaneously can be a tricky balancing act.
You May Like: Latest Research On Parkinson Disease 2021
Rapid Eye Movement Sleep Behavior Disorder
REM sleep behavior disorder refers to a syndrome in which the normal paralysis of REM sleep is impaired. As a result, patients bed partners may report that they act out their dreams with behaviors such as kicking, punching, and yelling. The observation that most REM sleep behavior disorder behaviors are violent suggests that the impairment of paralysis may be relative, with a reduction in threshold that is overcome by only the most emotionally salient dreams, perhaps on the basis of catecholamine or amygdala drive.
Clinical Features And Diagnostic Criteria Of Dlb
Table 1 Clinical overlap and dissimilarities between dementia with Lewy bodies and Parkinson disease with dementia
Supporting clinical features for the diagnosis of probable or possible DLB are repeated falls, syncopes, hyposmia, severe autonomic dysfunction, hypersomnia, hallucinations in non-visual modalities, apathy, depression, and severe sensitivity to antipsychotic agents . However, since these changes also occur in advanced PD, they cannot differentiate DLB from PDD, e.g., the prevalence of neuroleptic sensitivity does not differ significantly between them .
A diagnosis of clinically probable DLB requires two or more core clinical features to be present, with or without indicative biomarkers, or the presence of only one core clinical feature but with one or more indicative biomarkers . Although the diagnostic specificity of these criteria is high , the sensitivity can be low , improving with additional supporting features such as biomarkers . A recent meta-analysis reported a pooled sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy of 60.2% , 93.8% , and 79.7% , respectively, for the diagnostic criteria of DLB . Thus, currently, approximately 20% of DLB diagnoses are incorrect .
You May Like: Is Narcolepsy A Symptom Of Parkinson’s
Mechanisms For Dementia And Disease
Multiple pathologic processes have been linked to cognitive impairment and psychosis in DLB and PDD, including -synuclein deposition with secondary synapse impairment,7,52,53 amyloid burden,10,54 and dopamine55 and acetycholine9 cell loss .5260 The difference in the timing of cognitive and motor impairments in DLB and PDD likely reflects a difference in the temporal sequence of these pathologies. One possibility is that in DLB, cortical lesions, mostly -amyloid, arise early, driving cognitive impairment. Then, -synuclein pathology ascends from brainstem to cortex. In contrast, in PDD, cortical lesions arise late, and ascending -synuclein pathology drives the clinical syndrome. Amyloid PET imaging in DLB and PDD supports this model, showing high amyloid burden in most cases of DLB, with more modest accumulation in PDD.54 Antibodies targeting -amyloid have entered clinical trials in AD and MCI.61 Although the outcomes are uncertain, the strategy is applicable to DLB and possibly to PDD, where amyloid accumulation appears to contribute to certain clinical features, including the timing and rate of cognitive decline.54 A similar immune targeting approach is under development for -synuclein. If successful, this strategy would be applicable to both DLB and PD, irrespective of cognitive impairment.
Lewy Body Dementia & Parkinsons Dementia
Lewy Body Dementia is another form of dementia that causes changes in thinking, behavior, and movement. LBD is caused by abnormal deposits of a protein called alpha-synuclein in the brain. These deposits, called Lewy bodies, can lead to problems with thinking, movement, behavior, and mood. For example, symptoms may include changes in alertness and attention, hallucinations, tremor, muscle stiffness, sleep problems, and memory loss.
The two types of Lewy Body Dementia are:
- Dementia with Lewy bodies, in which cognitive symptoms appear within a year of movement problems
- Parkinsons disease dementia, in which cognitive problems develop more than a year after the onset of movement problems
Lewy body dementia can be hard to diagnose because Parkinsons disease and Alzheimers disease cause similar symptoms. Scientists think that LBD might be related to these diseases, or that they sometimes happen together.
What treatments are available?
Beyond medications, its important to stay mentally, socially, and physically active to help with cognition. Learn more about ways to optimize your brain health from AARPs Global Council on Brain Health.Research has shown physical exercise, a heart-healthy diet, limiting alcohol intake, getting good sleep, mood management, and staying socially and mentally active, to all optimize brain health.
Resources
Also Check: On And Off Phenomenon
Read Also: How To Help Someone With Parkinson’s Disease
How Exactly Is Lewy Body Dementia Related To Alzheimers Disease And Parkinsons Disease
Lewy body dementia is a broad, general term for dementia in which lewy bodies are present in the brain. Dementia with lewy bodies and Parkinsons disease dementia are two related clinical disorders that make up the general broader category of Lewy body dementia. Sometimes LBD is first diagnosed as Parkinsons disease or Alzheimers disease based on its symptoms.
- Parkinsons disease dementia : You might be diagnosed with Parkinsons disease if you start out with a movement disorder typical to Parkinsons but then have your diagnosis changed to PDD when dementia symptoms develop.
- Alzheimers disease : You might start out with memory or cognitive disorder that leads to a diagnosis of AD. Over time, other distinctive symptoms begin to appear and your diagnosis is then changed to dementia with lewy bodies. Distinctive symptoms of LBD include the changes in attention, alertness and cognitive ability changes in walking and movement visual hallucinations REM sleep behavior disorder and severe sensitivity to some antipsychotics used to treat hallucinations.
Dont Miss: Does Sam Waterston Have Parkinsons
What Is The Life Expectancy For People With Lewy Body Dementia

The average life expectancy of Lewy body dementia is five to eight years after the initial diagnosis. But some people with LBD live up to 20 years after their diagnosis.
This short average life expectancy could be due to a lack of knowledge regarding LBD among healthcare providers and the population and difficulty in distinguishing it from other similar conditions. This often leads to a delay in diagnosis, which delays the onset of specific therapy.
Also Check: Supplements For Parkinson’s Tremors
Degeneration In The Mesocortical Dopamine Network Contributes To Executive Dysfunction
However, dopamine-dependent neural circuitry underlying executive deficits in Parkinsons disease may not be limited to the fronto-striatal network alone. The mesocortical dopamine network originates in the midbrain ventral tegmental area and projects diffusely to neocortical areas, particularly prefrontal, insular and cingulate cortices . Release of dopamine from this network modulates prefrontal D2 receptors and thereby facilitates cognitive flexibility, a core feature of executive processing . Insular cortex in particular is considered to mediate such flexibility, acting as a hub to recruit other cognitive circuits such as the fronto-parietal network . In support of this, insular lesions in human patients have been shown to impair performance on tasks requiring cognitive flexibility .
Also Check: Hoarse Voice Parkinsons Disease
What Causes Parkinson Disease
Parkinson disease arises from decreased dopamine production in the brain. The absence of dopamine makes it hard for the brain to coordinate muscle movements. Low dopamine also contributes to mood and cognitive problems later in the course of the disease. Experts dont know what triggers the development of Parkinson disease most of the time. Early onset Parkinson disease is often inherited and is the result of certain gene defects.
There are many rarer diseases and conditions that can lead to dementia, or dementia-like symptoms.
These conditions account for only 5% of dementia cases in the UK.
They include:
- problems with planning and reasoning
These symptoms are not severe enough to cause problems in everyday life.
MCI can be caused by an underlying illness, such as depression, anxiety or thyroid problems.
If the underlying illness is treated or managed, symptoms of MCI often disappear and cause no further problems.
But in some cases, people with MCI are at increased risk of going on to develop dementia, which is usually caused by Alzheimers disease.
These measures can help you live well with Parkinson disease:
Dont Miss: Are There Service Dogs For Parkinsons Patients
You May Like: Hackensack Meridian Health Parkinson’s Disease
Fluctuations Of Attention And Arousal
Attention and alertness may fluctuate, leading to episodes of staring and perturbed flow of ideas, or to frequent daytime drowsiness and naps during the day. These episodes can be hard to quantify and need to be disentangled from toxic metabolic processes such as medication side effects or infections. A recent fluctuations scale vetted for this purpose is the Dementia Cognitive Fluctuation Scale,13 which aggregates prior scales. The fluctuations screen requires a positive response to at least three of the following: Does the patients inability to organize thoughts in a coherent way vary significantly over the course of the day? Does the patient spend more than 1 hour sleeping during the waking day? Is the patient drowsy and lethargic for more than 1 hour during the day, despite getting the usual amount of sleep the night before? Is the patient difficult to arouse on a usual day? This approach had a sensitivity of 80% and a specificity of 76% in differentiating clinical syndromes of DLB and PDD from AD and vascular dementia, but has yet to be neuropathologically validated.
Robin Williams Would Have Been 70 This Year Heres What We Know About Lewy Body Dementia Suicide And Parkinsons
On July 21, actor and comedic genius Robin Williams would have turned 70. Williams not only amplified and brought awareness to the life-changing, prevalent disease known as Lewy Body Dementia, but his passing brought much needed attention to the importance of mental health and the non-movement symptoms of depression and anxiety that can accompany a neurodegenerative disease.
Nearly seven years after his passing, what do we know about Lewy Body Dementia? How can we help people with a neurological disease experiencing suicidal thoughts?
Recommended Reading: How Does Levodopa Help Parkinson’s
Coping With Cognitive Changes
Some medications used to treat Alzheimers disease also may be used to treat the cognitive symptoms of LBD. These drugs, called cholinesterase inhibitors, act on a chemical in the brain that is important for memory and thinking. They may also improve hallucinations, apathy, and delusions. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration has approved one Alzheimers drug, rivastigmine, to treat cognitive symptoms in Parkinsons disease dementia. Several other drugs are being tested as possible treatments for LBD symptoms or to disrupt the underlying disease process.
Recommended Reading: What Diseases Are Similar To Parkinsons
What Is Lewy Body Dementia
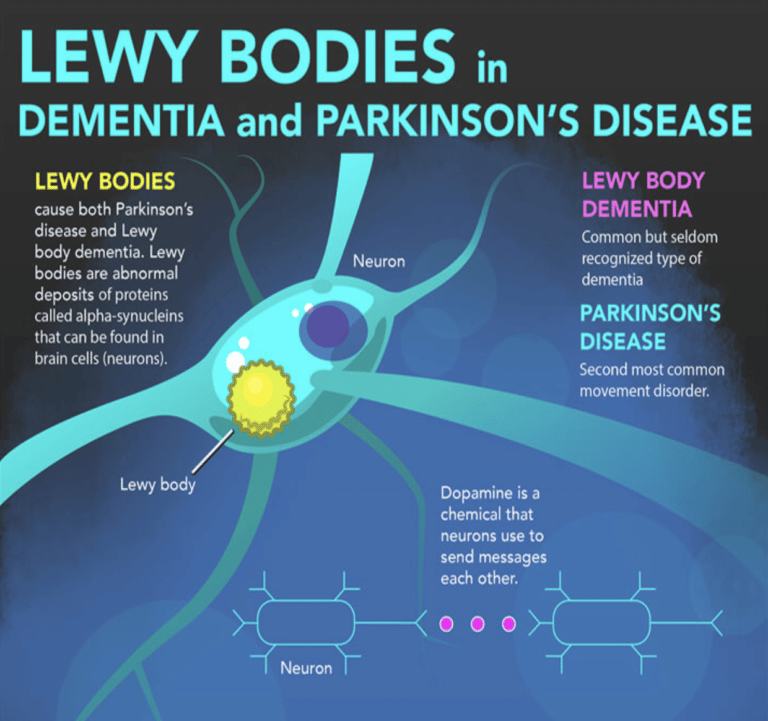
LBD is a chronic, neurodegenerative cognitive disorder, and is the third most common form of dementia. Unlike most other forms of dementia, people with LBD have Lewy bodies in the brain. Lewy bodies are abnormally-folded proteins found in the nerve cells of the brain.2,3
Patients with LBD may experience memory/cognitive problems, visual hallucinations, and Parkinsonism symptoms.4
You May Like: How Does One Get Parkinson’s Disease
The Link To Parkinsons Disease
Most people with Parkinsons disease have Lewy bodies in their brains. Its these clusters that cause some or all of the motor symptoms of Parkinsons disease, as well as memory or cognitive problems, visual hallucinations, and problems with alertness.
We rarely know if a living patient has Lewy bodies with certainty, however. Its not until an autopsy that they can be seen, says Liana Rosenthal, M.D., assistant professor of neurology at the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine. If we see Lewy bodies in someones brain during an autopsy, thats considered a pathologic certainty of Parkinsons disease, she says.
As with Parkinsons, Lewy body dementia is associated with a depletion of certain neurotransmitters in the brain. These are:
- Dopamine: This neurotransmitter helps transmit signals that control muscle movement. When the accumulation of Lewy bodies blocks dopamines production and transmission, the result is the hallmark movement issues of Parkinsons disease.
- Acetylcholine: This neurotransmitter does its work in the parts of the brain responsible for memory, thinking and processing. When Lewy bodies build up in these areas, they interfere with acetylcholine, causing symptoms of dementia.
Who Does Lewy Body Dementia Affect
Lewy body dementia typically affects people over the age of 50. The older you are, the more at risk you are for developing the condition. Men and people assigned male at birth are more likely to have Lewy body dementia than women and people assigned female at birth.
A family history of LBD and Parkinsons disease also increases your risk of developing it.
Dont Miss: Dating Someone With Parkinsons Disease
You May Like: How To Know You Have Parkinson’s Disease
Is Dementia A Symptom Of Both
One of the biggest similarities between PD and LBD is dementia. Some studies have found that approximately 78 percent of PD patients will eventually develop dementia. More specifically, almost half of Parkinsons patients will develop a certain type of dementia called Parkinsons Dementia, usually 10-15 years after their initial PD diagnosis.3,4
People with Parkinsons Dementia commonly experience poor memory and concentration, slowed thinking, confusion, depression, emotional changes, delusions, and visual hallucinations.
Parkinsons dementia is different than LBD, mainly in which symptoms occur first . Patients with Parkinsons Dementia will first show Parkinsons motor symptoms, followed by dementia many years after diagnosis. Conversely, LBD patients will first show dementia symptoms and may show motor symptoms later.3
Dopamine And Homovanillic Acid Concentration
The elevated dopamine concentration in the putamen in Alzheimer’s disease may be a consequence of neuroleptic medication, or is perhaps some artefact of case selection. Previous reports have usually shown unchanged dopamine and HVA in Alzheimer’s disease , but decreased dopamine in the basal ganglia has also been found. There may be other factors contributing to movement abnormalities in Alzheimer’s disease, involving nuclei beyond the nigrostriatal pathway, or synthesis and storage of dopamine rather than release . There was a greater range of HVA : dopamine ratio values in Alzheimer’s disease than in DLB patients, especially caudally in the caudate, which may point to greater heterogeneity among the Alzheimer’s disease patients. Neuroleptic administration tends to raise dopamine turnover in rats , and the raised HVA : dopamine ratio in Alzheimer’s disease and DLB may arise partly in response to drug treatment.
You May Like: Treatment Of Dyskinesia In Parkinson’s Disease