Muscarinic And Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor Agonists
Cholinergic receptors contain muscarinic receptors and nicotinic receptors they function in somatic and autonomic signal transductions in the nervous system . We observed three trials that use muscarinic or nicotinic acetylcholine receptor agonists . ANAVEX2-73 is a small molecule that binds to muscarinic acetylcholine and sigma1 receptors in the low micromolar range developing by Anavex Life Sciences Corp . In October 2019, they started a phase II open-label extension to evaluate the effects of ANAVEX2-73 in 120 PD subjects with dementia on the safety and efficacy of daily treatment . Anavex Life Sciences Corp. estimates the study completion by 31 October 2021. Nicotine is used in two phase-II trials as a transdermal patch and a nasal spray for PD treatment. Unfortunately, the trial data for the nicotine transdermal patch in PD patients is unavailable . Another trial using nicotine nasal spray trial status shows complete under subject recruitment and no results posted . Although the high doses of transdermal nicotine were also tolerated, they failed to show significant improvements in UPDRS scores .
Moreover, the cholinergic drug treatment disadvantages might be less efficient than dopamine receptor agonists or carbidopa-levodopa treatment or even may cause adverse effects on parasympathetic nerve-related organs in PD .
Parkinsons Disease And Gene Therapy: Strategic And Operational Considerations
The gene therapy era can be said to have begun in 1990, when the first gene therapy clinical trial took place. Some 3,000 clinical trials have followed that first study, a resounding affirmation of innovators increasing recognition of gene therapys breakthrough possibilities for treating a diverse range of disorders especially afflictions with limited or no established treatments.
Patients with Parkinsons disease are among the potential beneficiaries of gene therapy. Although there are currently numerous available treatments for PD, these merely target symptomatic relief, leaving disease onset or progression largely unmet and sometimes producing significant adverse effects. Those limitations underscore the need for novel therapeutic approaches.
Compared to conventional pharmacological and surgical approaches to treating PD, gene therapy has several potential advantages including preservation or restoration of dopaminergic neurons addressing underlying pathophysiological imbalances, possibly resulting in less fluctuation in response and reduced risk of dyskinesias.
Challenges inherent in the promise of gene therapy
For all its promise, gene therapy for PD has several potential limitations, including:
The gene therapy regulatory environment
- The product must be of biological origin and contain recombinant nucleic acid
- The recombinant nucleic acid must be directly involved in the mechanism.
Study design considerations
Long-term follow-up
Parkinsons Disease Drug Therapies In The Clinical Trial Pipeline: 2021 Update
Article type: Review Article
Authors: McFarthing, Kevina | Rafaloff, Garyb | Baptista, Marco A.S.c | Wyse, Richard K.d | Stott, Simon R. W.d *
Affiliations: Parkinsons Research Advocate, Oxford, UK | Parkinsons Research Advocate, Marlboro, NJ, USA | The Michael J Fox Foundation, Grand Central Station, New York, USA | Cure Parkinsons, London, UK
Correspondence: Correspondence to: Simon R. W. Stott, Cure Parkinsons, 120 New Cavendish Street, London, UK. E-mail: .
Keywords: Clinical trials, studies, Parkinsons, disease modification, neuroprotection, immunotherapy, inflammation, gene therapy
DOI: 10.3233/JPD-219006
Journal: Journal of Parkinson’s Disease, vol. 11, no. 3, pp. 891-903, 2021
Abstract
Recommended Reading: Parkinson’s Hallucinations Commercial
Effects Of Gene Therapy May Be Long Lasting
We have evidence from a previous study that the gene therapy results in stable expression of the AADC enzyme, said Christine, referencing data demonstrating stability over a five-year duration. We believe that this treatment will allow these patients to more efficiently convert levodopa into dopamine, thereby obtaining greater improvements in mobility with each dose. Since many patients were able to substantially reduce the amount of Parkinsons medications, this gene therapy treatment may also help patients by reducing dose-dependent side effects, such as sleepiness and nausea.
The treatment was generally well tolerated, but one patient experienced a blood clot and irregular heart rhythm likely related to the surgery, said senior author Paul Larson, MD, of the UCSF Department of Neurosurgery.
A Phase II of the study of this gene therapy was recently launched and that study will allow us to better understand the safety and effectiveness of this treatment, Larson said.
While results of this phase I trial are promising, there are a number of non-motor features of Parkinsons disease that may develop over time, such as depression, as well as cognitive changes, said Christine. These conditions do not respond to levodopa and we do not believe that gene therapy will address them.
Funding: Michael J. Fox Foundation for Parkinsons Research and Voyager Therapeutics, Inc.
Other Targets And Strategies
In addition to the above-mentioned peptides for gene therapeutic treatment of PD, several other possible genes deserve attention as potential targets in PD. One such target is the neuron restrictive silencing factor , a zinc finger transcription factor found to be involved in restriction of neuronal factors in non-neural cells and regulation of neurogenesis . Yu and associates reported that NRSF knockout mice were more susceptible to MPTP-induced dopaminergic cell death, as lack of NRSF leads to lower levels of BDNF and TH . It is possible that by upregulating NRSF in conjunction with BDNF, it would be possible to enhance the neuroprotective effects of BDNF. However, sparse data are available on NRSF in PD, but as the role of long coding RNAs have been associated with several neurodegenerative diseases, epigenetic regulation provides a novel interesting avenue of research regarding several diseases .
The transcription factor EB has been found to be a key player in regulating the autophagy-lysosomal pathway which is found to be impaired in PD . By overexpressing TFEB, Decressac et al. reported neuroprotection as well as rescue of a parkinsonian phenotype in a rat model overexpressing SNCA in the SN and ventral tegmental area . These results point to TFEB as another potential future target in the pursuit of therapies for PD.
Read Also: Diseases Similar To Parkinsons
Who Might Be Useful For Gene Therapy And Are There Any Risks
Researchers believe that gene therapy will be useful for a number of people with Parkinsons, irrespective of whether their condition has been genetically caused. However, as with most treatments, it wont be suitable for everyone. As part of the clinical trial process, scientists will establish who this treatment will suit and those for whom it is not recommended.
As with all treatments, there are some risks. It is thought that there may be side effects within the central nervous system that relate to long-term, high levels of exposure to therapeutic genes, or there may be an immune response to the treatment. Current research efforts are directed at implementing further measures to reduce the probability of these risks, even if they are unlikely.
Changes In Motor Function Global Impressions And Quality Of Life
All other clinical outcomes were stable or improved compared with baseline in the âonâ-medication and âoffâ-medication states across all 3 cohorts throughout this 36-month trial. Excluding data from the participant who underwent DBS had a minimal effect on the reported results.
Data shown are mean hours normalized to a 16-hour waking day. Change from baseline at 36 months is reported to the right of each panel. PD diary âoffâ time and good âonâ time were stable or improved from baseline throughout the trial. In a sensitivity analysis that excluded the participant in cohort 1 who underwent deep brain stimulation, âoffâ time and good âonâ time at month 36 were 3.4 ± 1.5 hours and 12.3 ± 1.6 hours, respectively. TD = troublesome dyskinesia.
UPDRS III âoffâ-medication scores improved from baseline in all cohorts at all annual follow-up assessments . Improvements in cohorts 1, 2, and 3 at 12 months were maintained through 36 months, with changes from baseline of â19.0 ± 3.9 points, â12.2 ± 3.3 points, and â10.2 ± 4.6 points, respectively, at the final 36-month follow-up. Improvements in UPDRS III âonâ-medication scores were observed in cohorts 2 and 3 at 12 months, which persisted at the final 36-month follow-up . The UPDRS III âonâ-medication score in cohort 1 remained low and comparable to baseline at all annual follow-up assessments.
You May Like: Parkinson’s Double Vision
Changes In Pd Medication Requirements
Daily PD medication requirements as measured by LED were decreased from baseline in cohorts 2 and 3 throughout the trial . At end of trial , mean changes from baseline in LED of â322 ± 124 mg/day and â441 ± 73 mg/day were documented in cohorts 2 and 3, respectively. In cohort 1, LED remained stable at 12 and 24 months, but then increased by 343 ± 406 mg/day above baseline at 36 months excluding data from the participant who underwent DBS resulted in an increase of 531 ± 465 mg/day from baseline.
Gene Therapy For Parkinsons Disease
You may have read about efforts to use gene therapy as a treatment for Parkinsons disease . Its an exciting prospect and studies are underway, with some positive results so far. Understanding these studies and therapies requires some background information about what genes are and how they work, so Ive included a glossary at the end of this article. You might find it helpful to scroll down and get familiar with the terminology before reading the rest of the article.
You May Like: Adaptive Silverware For Parkinson’s
Study Design And Outcomes
The phase 3 Accordance study is a multi-center , global, randomized, double-blind, double-dummy, active-controlled, parallel-group study in adult subjects with fluctuating PD. The study will have 2 open label titration periods of 6 weeks each prior to the double-blind maintenance period. In the open label periods, all patients will be stabilized on the active comparator, IR-CD/LD and then on AP-CD/LD. The double-blind maintenance period will be 13 weeks long.
The primary outcome is change from baseline through to study completion, an average of 27 weeks, in the percentage of daily Off time during waking hours, based on Hauser Home Diary assessments.
Secondary outcomes, all measured on the same timescale as the primary outcome, are:
- 1.
-
Clinical Global Impression Improvement , as recorded by physician & patient.
- 4.
Change in total UPDRS Score .
CURRENT STUDY STATUS: Enrolment was started in November 2015. Recruitment is closed and while the official primary completion date is August 2019, Intec expects to release top-line data in mid-2019 .
Until disease-modifying therapies are available, people with Parkinsons will welcome any therapy that extends the duration of symptom relief and reduces motor fluctuations. The novel design of the Accordion Pill and the promising safety and efficacy data generated in phases 1 and 2, hold out great hope for the achievement of these benefits.
References
Serotonin Receptor Agonists Or Antagonists
Motor activities, depression, cognitive and autonomic functions are regulated by the serotonergic neurotransmission system . Therefore, drugs targeting serotonergic receptors modulate behavioral qualities and improved motor balances . We found three clinical trials use serotonin receptor agonists or antagonists for PD treatment. Piclozotan is a selective 5-HT1A receptor agonist developing at phase II by Daiichi Sankyo, Inc. A preclinical study showed that serotonin 1A receptor agonists piclozotan ameliorate motor performances in 6-hydroxydopamine-induced models . The trial status shows it completed subject recruitment while results show no serious adverse events compared to the placebo cohort. However, the piclozotan treatment produced few minor adverse events such as headache, nausea, dizziness, and hypertension . Preclinical literature also showed that sarizotan benefits in reducing dyskinesia, respiratory problems . Sarizotan possesses serotonin receptor partial agonist and dopamine D2 receptor agonist activities, developing at phase III by EMD Sereno. The status of this trial shows no results . A study shows that 2 mg/day sarizotan administration had no improvements in dyskinesia compared to placebo subjects . SYN120 is a dual 5-HT6/5-HT2 serotonin receptor antagonist. An update from the American Academy of Neurologys 2019 annual meeting declared that the SYN120 trial in phase II studied with 80 patients has failed to improve cognitive performance .
Read Also: Cleveland Clinic Parkinson’s Bicycle Study 2017
Selection Of Studies And Data Extraction
Abstracts and pertinent full-text articles were independently reviewed for eligibility criteria by one author and double-checked by two additional authors . Duplicated studies were identified and excluded. A data collection form was used to extract variables of interest from the selected studies. Particular attention was paid to studies that shared the same population or published data from the same cohort at different time-points: in these cases, data from all the available manuscripts were reported, specifying how many participants were included in more than one trial. Disagreements were anticipated to be settled by consensus.
Data collected included year of publication study design sample size sex, age, and disease duration at the time of intervention dose, target, and route of administration of the compound delivered follow-up duration and key adverse events . In addition, the following data were acquired for each individual population.
Parkinson Disease
Huntington Disease
Safety and tolerability, with particular attention to AE reporting changes in the Unified Huntington’s Disease Rating Scale and in the Total Functional Capacity Scale . Depending on the endpoints evaluated and the outcome measures used in each trial, we reported changes in functional, cognitive, and psychiatric outcomes, changes in regional metabolic activity , and in pharmacokinetics variables.
Aromatic L-Amino Acid Decarboxylase Deficiency
Phase 3 Study In Focus Intec Pharmas Accordion Pill
TITLE: A Study to Assess the Safety and Efficacy of the Gastric-retentive AP-CD/LD in Advanced Parkinsons Patients .
STATUS: Active, not recruiting.
ENROLMENT: 420.
ESTIMATED COMPLETION DATE: The primary completion date is August 2019.
OBJECTIVE: The purpose of this study is to determine whether the gastric retentive Accordion Pill Carbidopa/Levodopa is more effective than immediate release Carbidopa/Levodopa in reducing motor fluctuations such as off time in advanced Parkinsons Disease patients.
BACKGROUND: Levodopa remains the most potent symptomatic therapy for PD. One of the major limitations of levodopa therapy is the risk of development of motor fluctuations and dyskinesia related to the short half life of the drug, coupled with progressive decline of neuronal dopamine storage capacity. Current formulations of levodopa are generally taken every few hours, leading to a pulsatile profile of peaks and troughs. The peaks can induce troublesome dyskinesia while the troughs can lead to OFF time with significant symptom breakthrough. A steadier and more consistent plasma profile should reduce the incidence of both types of motor fluctuation as well as reducing the number of tablets patients need to take.
Intec Pharma have developed the Accordion Pill, a gastric-retentive capsule containing multiple layers of both immediate release and controlled release levodopa and carbidopa. The pill remains in the stomach for up to 12 hours .
Also Check: Sam Waterston Parkinson’s
Pd Therapeutic Strategies In Clinical Trials
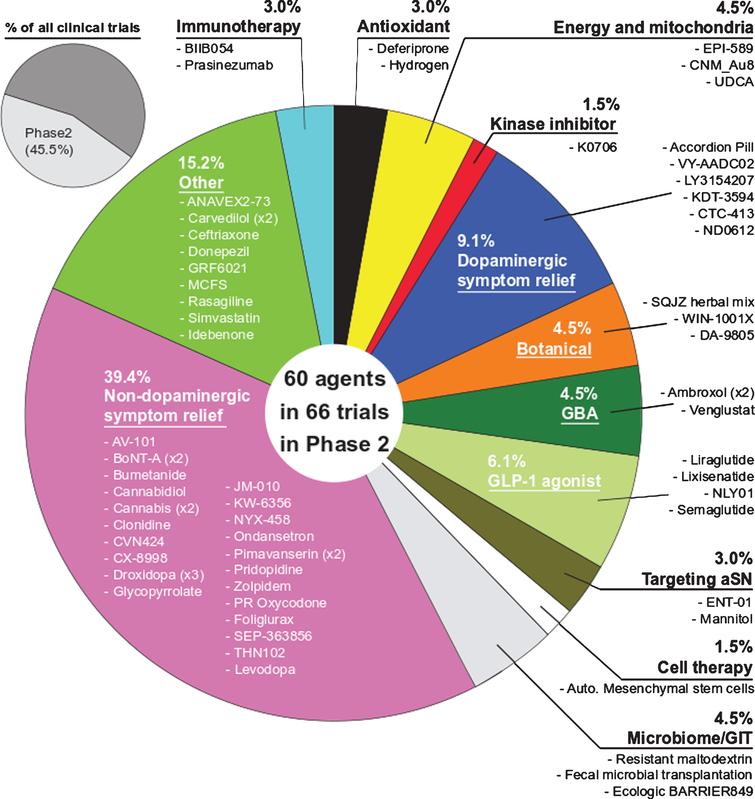
In , we have classified these therapeutic strategies into 15 types: dopamine receptor agonists, anti–synuclein aggregation therapy, convalescent plasma therapy, cell-based therapy, gene therapy, serotonin receptor partial agonists or antagonists, monoamine reuptake inhibitors, muscarinic and nicotinic acetylcholine receptor agonists, N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor modulators, anti-apoptotic drugs, kinase inhibitors, myeloperoxidase inhibitors, adenosine A2A receptor antagonists, antioxidants/botanical-based medication, and others. depicts the type of drug or therapy, mechanisms, and the current drugs/treatments in PD.
The type of therapeutic strategies, mechanism, and the current drugs/therapies in the clinical trials of PD treatment.
After analyzing the data collected from ClinicalTrials.gov, we identified forty-seven registered interventional clinical trials in phases I, II, and III as new PD therapies based on the current trial status that shows ongoing/updated or discontinued as of 16 June 2021. Among the forty-seven trials, 19 trials in phase I, 25 in phase II, and 3 in phase III
The trial phases and therapeutic strategies in the clinical trials for PD treatment. A pie chart shows the individual percentage of phase I, phase II, and phase III trials to the total. The phase I/II or II/III trials on ClinicalTrials.gov are showed as phase I or II, respectively. A pie chart shows the proportions of each therapeutic strategy to the total PD clinical trials.
Time To Initiation Of Symptomatic Therapy
Because of drug complications, symptomatic treatment usually in the form of L-DOPA is often delayed until the severity of motor symptoms results in functional impairment. Unlike the ambiguity in what magnitude change in UPDRS is clinically meaningful, the initiation of symptomatic treatment is considered an early indicator of disease progression and a real-life end point . The time between baseline assessment and the end point can also be conceptualized as survival and is amenable to Kaplan-Meier statistical analysis . A confound of this end point is that when symptomatic therapy should be initiated is largely based on a physicians subjective assessment of the patients status, and may be subject to considerable variation between clinicians.
Don’t Miss: Prayer For Parkinson’s Disease
Clinical Trials In Pd
It is, therefore, crucial that PD clinical trial design be as efficient and robust as possible to ensure the effective identification of any disease-modifying compound. Designing a PD clinical trial for a disease-modifying therapeutic agent depends on the clinical end point being targeted and ensuring that it is also acceptable to regulatory bodies. In 2007, the European Medicines Agency issued draft guidance for PD trials seeking a disease-modifying claim . While recognizing that no universal study design could be recommended, the EMA proposed that clinical trials should be randomized, placebo-controlled, and long-term. Clearly, in established PD cases, the primary goal is to slow further decline in motor function and progression of disability, and to prevent motor and nonmotor complications. Below we consider two possible trial designs to determine a disease-modifying effect.
Hurdles In Pd Drug Development
The drug development pipeline for PD has been, and remains, largely focused on symptomatic treatment. Progress in this area has been steady over the past 10 years . The number of phase I interventional trialsdefined for the purposes of this Perspective as drug, biologic, or genetic therapy aimed at modifying symptoms or disease courseshows a trend toward increasing year over year . The number of phase II and phase III clinical studies has fluctuated from year-to-year but remains essentially stable . A better gauge of the health of the PD drug pipeline, however, comes from examining the number of new molecular entities entering the pipeline annually . Over the last decade, there has been an average of 4.7 new molecular entities entering phase I and phase III clinical trials each year, and 9.6 new molecular entities entering phase II clinical trials annually . However, it should be noted that these data do not discriminate between drugs designed to modify symptoms and those that aim to modify disease trajectory.
The drug pipeline in PD
Recommended Reading: Parkinson Silverware