Some Patients May Not Be Eligible To Take Part In The Free Genetic Testing Program
To speed up recruitment for a natural history program we are first focusing on patients who have a higher likelihood of testing positive for the mutated gene from the free genetic testing program. If a patient does not meet the criteria now, we will offer to contact them again should we open up the screening program to a wider population of Parkinsonâs patients.
Age And Genetic Factors Are Not Everything
The rate of Parkinsons disease globally has exceeded far faster than the population has aged according to the American Parkinson Disease Association.
Cases of the disease are up by several multiples over the past decades. From 1990 to 2015, the cases of the disease globally more than doubled, suggesting that there is far more at work. From 2015 to 2040, cases are expected to double once again. This is far higher than the rate of aging in the population.
Omics Analysis Of Patient
To date 10/67 iPSC-PD studies analyzed have used proteomic, transcriptomic, or epigenomic profiling to phenotype PD patient-derived neurons,,,,,,,,. Omics analyses may be less biased and data-driven as opposed to purely hypothesis-driven. Data from omics studies can also help to describe biological relationships between complex intertwined cellular pathways and identify relevant druggable molecular pathways.
Recommended Reading: Does Vitamin B12 Help Parkinson’s
Genetic Principles And Exceptions Thereof In Familial Pd
The majority of PD cases are sporadic, i.e., only about 10% of patients report a positive family history . Out of the six genes unequivocally linked to heritable, monogenic PD, mutations in SNCA , and LRRK2 are responsible for autosomal-dominant PD forms, and mutations in Parkin , PINK1 , DJ-1 , and ATP13A2 are accountable for PD that displays an autosomal recessive mode of inheritance.
In general, the inheritance patterns of human disorders are identified by examining the way the disorders are transmitted in the family of the index patient. Such a pedigree analysis requires a careful assembly of the disease records of the family members over several generations, and if possible, examination and sample collection from affected and unaffected individuals from the pedigree. All of the currently known monogenic PD forms are autosomal , which means that they are linked with regions on autosomes .
Pedigree of a PD family that comprises affected members with and without the LRRK2 p.G2019S mutation. Five mutation carriers are unaffected, showing reduced penetrance, two mutation carriers are affected with dystonia, showing variable expressivity, and one affected family member does not have the p.G2019S mutation in LRRK2. Black symbols – affected individuals white symbols – unaffected individuals half-filled symbols – individuals with dystonia + – mutation carriers.
Who Should Get Genetic Testing
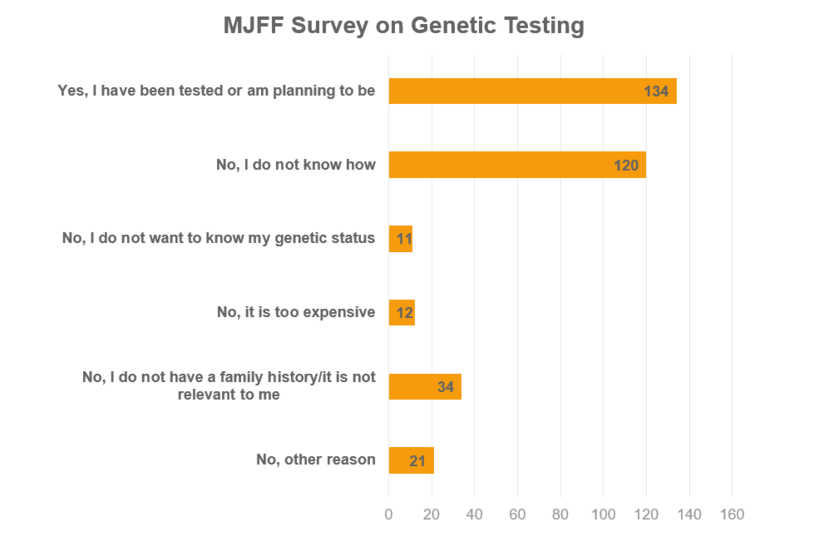
Two groups might consider getting genetic testing, according to Gilbert:
- People with Parkinsons who want to know if they have a mutation they may pass along to their children
- Children and siblings of family members with Parkinsons who want to determine their genetic risk for the disease
Right now its not standard of care for everyone with Parkinsons to get genetic testing, she says. The likelihood that were going to find one of these mutations that is known already is small, and even if you have a mutation associated with Parkinsons, it doesnt mean that youre going to get the disease.
So, at this point, the value of getting tested depends on the individual. Doctors can provide this type of genetic evaluation, or people may turn to direct-to-consumer genetic testing, such as 23andMe. These tests, however, can be limited.
You have to be careful with those panels because theyre not very comprehensive, says Gilbert. They may test for only one or two gene variations.
Currently, 23andMe analyzes DNA from spit samples for a variant in LRRK2 and a variant in the GBA gene associated with the disorder. The company makes it clear that the exam does not diagnose the disease, and there are many other mutations to consider.
Parkinsons patient Paul Cannon, PhD, who works for 23andMe as its Parkinsons research community manager, took the test and found that he had neither of the genetic variations.
Recommended Reading: Cleveland Clinic Parkinson’s Bicycle Study 2017
Is Parkinsons Disease Genetic
Only a relatively small fraction of all Parkinsons cases can currently be explained by genetic causes. As a result, if you have Parkinsons disease, your children are not necessarily at any significantly increased risk for getting the disease. There are exceptions, however, where Parkinsons disease does seem to run in the family, and with the revolutionary advances in the ability to sequence human genes, starting towards the end of the 20th century, it has been possible to figure out why. The insights gained are relevant not just to the patients who have those mutations but to all people with Parkinsons. Here, I will focus only on genes that have been shown to cause Parkinsons there are a number of other genes that have been shown to increase the risk of developing Parkinsons by varying amounts. Both types of genes are potential targets for Parkinsons drug discovery efforts.
The first genetic cause identified for Parkinsons disease is alpha-synuclein. This protein had previously been known as a major component of Lewy bodies, which are identified in the brains of most deceased people who had Parkinsons disease. Because this protein plays such a big role in our understanding of Parkinsons, I discuss it separately in some detail. Only a very small fraction of Parkinsons cases can be explained by abnormalities in this gene, however.
How Environmental Factors Could Cause Parkinsons Disease
Scientists differ about the extent that brain cells are impacted by environmental factors. However, the statistics associated with the disease show that the environment can play a very large role in whether parkinsons disease develops.
Most often, it is exposure to toxic chemicals that could play a role in the development of Parkinsons disease. Usually, these combine with genetic factors to produce the conditions that cause Parkinsons.
Increasing scientific evidence suggests that Parkinsons may be caused by environmental factors such as exposure to herbicides such as Paraquat.
Read Also: Prayer For Parkinson’s Disease
What Is Usually The First Symptom Of Parkinson Disease
Symptoms start gradually, sometimes starting with a barely noticeable tremor in just one hand. Tremors are common, but the disorder also commonly causes stiffness or slowing of movement. In the early stages of Parkinsons disease, your face may show little or no expression. Your arms may not swing when you walk.
Can I be tested for Parkinsons gene?
Currently, genetic testing is available through your doctor for the following genes: GBA, PARK7, SNCA, LRRK2, parkin and PINK1. At-home tests only look for changes in LRRK2 and GBA and do not map the entire gene to look for other mutations, which is a major goal of PD GENEration.
Does coffee affect Parkinsons? For years, drinking coffee has been associated with having a reduced risk of developing Parkinsons disease . In fact, a 1968 study suggested that coffee drinkers were less like to get PD .
Is Parkinsons preventable? Can Parkinsons disease be prevented? Unfortunately, no. Parkinsons disease is long-term disease that worsens over time. Although there is no way to prevent or cure the disease , medications may significantly relieve your symptoms.
Genes Of Unconfirmed Pathogenicity For Parkinsons Disease
Patients carrying variants of unconfirmed pathogenicity and risk variants for Parkinsons disease identified from exome sequencing are reported in Supplementary Table 4, including variants in GIGYF2, CHDCHD2. These variants were detected in cases, as previously described, but also almost all occur in the control population and were not included as pathogenic variants in our analysis.
We found comparable mutation/variant frequencies in our cohort compared to controls, with the exception of well-validated risk variants, such as MAPT . We did not find any patients carrying previously reported mutations in EIF4G1, DNAJC6, FBXO7 and PLA2G6. Further case-control studies are needed to determine the role of variants in SNCAIP, UCHL1 and other genes where we found small differences in allele frequencies from control frequencies, however these variants are unlikely to be pathogenic Mendelian mutations.
Recommended Reading: On And Off Phenomenon
Other Causes Of Parkinsonism
“Parkinsonism” is the umbrella term used to describe the symptoms of tremors, muscle rigidity and slowness of movement.
Parkinson’s disease is the most common type of parkinsonism, but there are also some rarer types where a specific cause can be identified.
These include parkinsonism caused by:
- medication where symptoms develop after taking certain medications, such as some types of antipsychotic medication, and usually improve once the medication is stopped
- other progressive brain conditions such as progressive supranuclear palsy, multiple systems atrophy and corticobasal degeneration
- cerebrovascular disease where a series of small strokes cause several parts of the brain to die
You can read more about parkinsonism on the Parkinson’s UK website.
Page last reviewed: 30 April 2019 Next review due: 30 April 2022
Genetic Risk For Parkinson’s Disease
If you have a genetic mutation associated with Parkinson’s, will you get the disease? Not necessarily. Some mutations carry a greater risk, but none bring a 100 percent chance of developing Parkinson’s disease. There are many Parkinson’s risk genes where a mutation means a very small increased likelihood of Parkinson’s. Researchers are looking for other factors that either push or protect someone with a gene mutation to or from having Parkinson’s. Your doctor and/or a genetic counselor can discuss the risk associated with different Parkinson’s genes and what your results may mean for you and your loved ones.
Don’t Miss: Adaptive Silverware For Parkinson’s
Causal And Associated Genes
The idea that a gene abnormality may cause some cases of Parkinsons dates back to 1997. At that time, scientists at the National Human Genome Research Institute and the National Institutes of Health first precisely identified that an irregularity in the synuclein alpha gene , the gene that provides instructions to make the protein alpha-synuclein, could lead to this movement disorder.
Alpha-synuclein is found in abundance in the brain and is thought to help regulate the release of dopamine, a chemical involved in the transmission of signals between nerve cells . With Parkinsons, the brain doesnt produce enough dopamine. This 1997 research on SNCA confirmed that at least one form of Parkinsons disease is inherited.
Up until 1997, people did not broadly think that Parkinsons could be hereditary or familial, says James Beck, PhD, chief scientific officer with the Parkinsons Foundation. With that discovery, we began to identify a number of genes linked with Parkinsons.
In 2004, scientists discovered the most common genetic contributor to Parkinsons, a mutation in LRRK2, a gene that is active in the brain and pushes a persons risk to 30 percent. Certain ethnic groups are more likely to have this gene irregularity. The faulty LRRK2 gene accounts for 1 percent to 2 percent of all Parkinsons cases, according to a review published in February 2016 in Biochemical Journal.
Who Should Consider A Genetic Test For Parkinsons
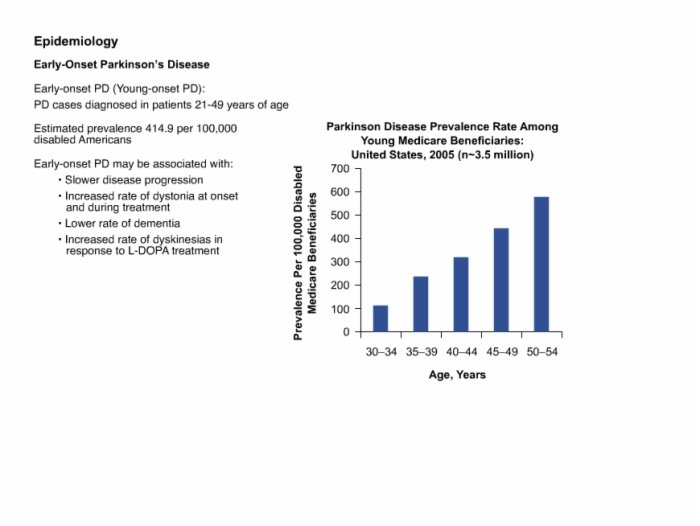
There are two groups of people who might consider getting genetic testing and we will discuss each group separately.
Genetic testing for PD is a common request and a number of commercial labs perform panels of genetic testing for PD. You may ask: How can I test myself for Parksinons? Whether youre considering getting a genetic test through your doctor, or performing one at home, its important to note that at-home test dont map the entire gene for mutations. Genetic testing through your doctor will test for GBA, PARK7, SNCA, LRRK2, parkin and PINK1.
Both groups are faced with two questions: Should I get genetic testing? And if so, what should I do with the results? Before we address these two questions, we need to learn more about the complexity of genetic testing in PD.
Don’t Miss: Diseases Similar To Parkinsons
Common Symptoms Of Parkinsons Disease
Here are some of the early signs and symptoms of Parkinsons disease that you need to be on the lookout for in deciding to see a healthcare professional who can provide medical advice.
- Rigid muscles
- Lack of ability to write
- Slowed movement
- Low blood pressure
If you notice these, or other symptoms involving the nervous system, it is time to see a doctor. If you experience a sudden drop in the bodys ability to execute any of these tasks or control movements, it is a sign that something is wrong. Doctors may be able to give medications or other treatments that could improve symptoms.
Dont Miss: Speech Therapy For Parkinsons Disease
Parkinsons Disease Hereditary Factors
Although a person may have hereditary factors, like a mutation in a certain gene that predisposes them to Parkinsons disease, it does not mean that they will definitely develop the disease.
Only about 10% of cases of Parkinsons have a known genetic contribution to the development of the disease. Two genes that are often found to contribute are the SNCA gene and the LRRK2 gene.
The SNCA gene codes for a protein called alpha-synuclein. Alpha-synuclein is a protein that is abundant in the brain, muscle, heart, and other tissues. Its exact function is still unknown. Studies suggest the alpha-synuclein contributes to the regulation of the release of dopamine from the nerve endings. A mutation in the SNCA gene has been found in many families that have had Parkinsons disease passed down.
A mutation in the LRRK2 gene has also been found in families that have Parkinsons. The LRRK2 gene has been found as the most often genetic factor for Parkinsons disease development. Researchers are unsure of the reason this gene contributes to PD. However, this knowledge is foundational for future breakthroughs in the treatment of Parkinsons.
You May Like: On Off Phenomenon
How Environmental Factors And Aging Can Be Recapitulated In Vitro
An obvious limitation of in vitro models is the lack of environmental context. The influence of nongenetic factors is not recapitulated in the basal phenotype of patient-derived neurons. For example, the influence of head trauma of a boxer with sporadic PD will not be recapitulated by default in reprogrammed neurons. An alternative would be to transplant the patient-derived neurons in animals and simulate the trauma on the animal. Similarly, influence of decades of aging of the human brain is difficult to reproduce in vitro in a few months within the boundaries of feasible experimental design. Brains in a dish will always be an imperfect experimental model. However, many tricks can be used to recapitulate the environmental and aging stress in vitro. Table summarizes a list of reagents that have already been used in iPSC neuronal culture to mimic oxidative stress, proteostatic stress, mitochondrial stress, synaptic stress, ER stress, inflammation, and cellular aging. An interesting example is progerin, a truncated form of lamin A associated with premature aging. Increasing the expression of progerin in iPSC neurons can recapitulate at least some aspect of cellular aging in vitro. Human iPSC-derived dopamine neurons overexpressing progerin displayed specific phenotypes such as neuromelanin accumulation. In addition, PD patient-derived neurons revealed disease-related phenotypes that required both genetic susceptibility and induced-aging in vitro.
The Future Of Pd Genetics
We have identified three key concepts that need to be addressed to speed progress in future PD genetic research ventures. These include identifying and refining heritable risk, predicting the course of disease, and focusing on general data-centric approaches, all of which will facilitate building a bridge to a future intervention.
Also Check: On-off Phenomenon
The Interplay Between Genomic Predispositions And Environmental Factors Leads To Parkinsons
In the mid-1990s, the connection between PD and underlying genetic mutations was established,,. It is now evident that varying degrees of the interplay between genomic predispositions and aging and cellular stressors impose a risk for disease . Previous studies have shown vascular insults to the brain, repeated head trauma, neuroleptic drugs, exposure to pesticides, and manganese toxicity increase the risks of developing symptoms of PD,,. In addition, advancing age can also cause a cascade of stressors within the substantia nigra, which weakens the neurons and their ability to respond to further insults,. Ultimately, the uniqueness of the interactions between genes and the environment makes the development of a single treatment for PD difficult as they give rise to a spectrum of neuronal phenotypes that can be unique to individual patients . The development of a model with the ability to replicate the genomic and epigenetic aspects of the disease is crucial . As increasing evidence suggests that genetic mutations are key modulators of disease initiation and progression, the identification and understanding of the various genomic predispositions are required for the development of better-targeted treatments to slow the disease progression.
Fig. 1: A combinatorial spectrum of genetic risks, cellular stressors, and brain cell dysfunctions causes Parkinsons disease.
Is Parkinsons Hereditary
A MyParkinsonsTeam member recently asked, Should I do genetic testing for PD? Several of my family members have had it Does it run in families?
The short answer is: its complicated. There is still much that scientists do not know about Parkinsons disease . It remains largely unknown why certain people get it and others dont. Based on the available data and research, most scientists believe that PD is due to a combination of nature and nurture genetics plus environmental factors. These factors may include certain drugs or exposures to chemicals like pesticides and herbicides.
About 85 percent of PD cases are thought to be sporadic, meaning that they occur without any genetic factors that can be identified. The other 15 percent of cases are considered potentially familial or genetic, with certain genes and mutations leading to an increased risk of developing PD.
If you know of family members who have PD, you may be wondering if you or others will get it one day as well. Therefore, its important to understand a few key facts about what might prompt PD to develop.
Don’t Miss: Judy Woodruff Parkinson’s