How Is Parkinson’s Related To Dementia
While Parkinson’s and dementia are completely independent conditions, people with Parkinson’s have a higher chance of developing certain forms of dementia.
“There are two main types of dementia that affect some people with Parkinson’s: Parkinson’s dementia and dementia with Lewy bodies,” says Fletcher.
How Do Treatments Differ
MS treatments can ease your symptoms during an attack or slow down the diseaseâs effects on your body.
Steroids like prednisone calm the inflammation that damages your nerves.
Plasma exchange is another therapy if steroids donât work. Your doctor will use a machine to remove the plasma portion of your blood. The plasma gets mixed with a protein solution and put back into your body.
Some people with both diseases who take anti-inflammatory medicines like steroids see their Parkinsonâs symptoms get better.
Disease-modifying treatments slow down MS nerve damage and disability. They include:
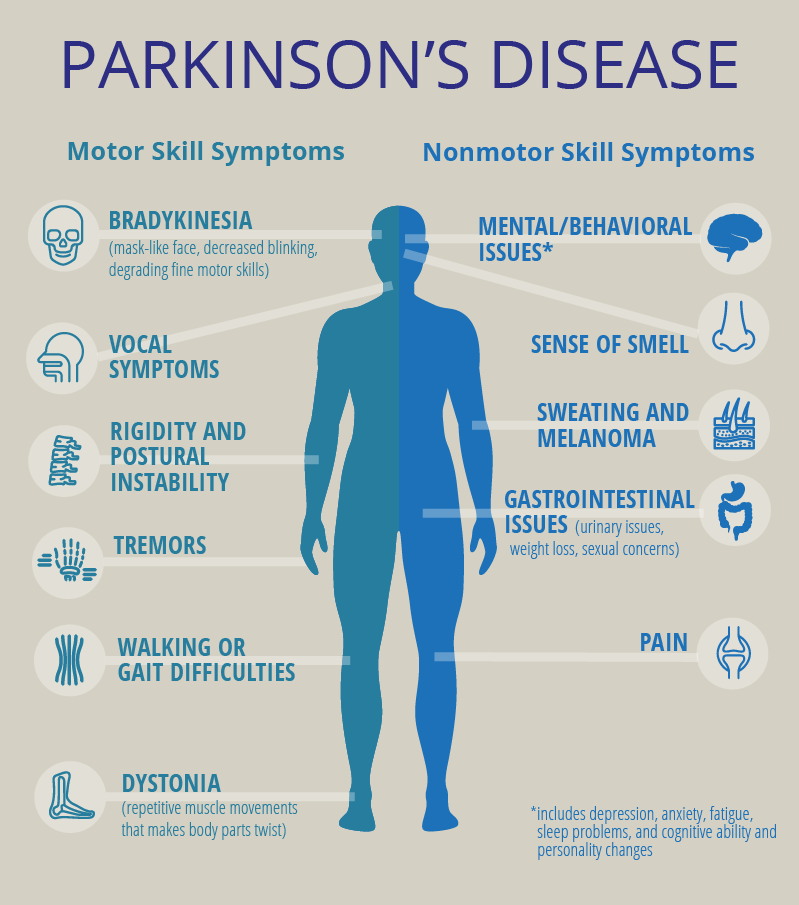
Symptoms Of Parkinsons Disease
Parkinsons disease has four main symptoms:
- Tremor in hands, arms, legs, jaw, or head
- Stiffness of the limbs and trunk
- Slowness of movement
- Impaired balance and coordination, sometimes leading to falls
Other symptoms may include depression and other emotional changes difficulty swallowing, chewing, and speaking urinary problems or constipationskin problems and sleep disruptions.
Symptoms of Parkinsons and the rate of progression differ among individuals. Sometimes people dismiss early symptoms of Parkinsons as the effects of normal aging. In most cases, there are no medical tests to definitively detect the disease, so it can be difficult to diagnose accurately.
Early symptoms of Parkinsons disease are subtle and occur gradually. For example, affected people may feel mild tremors or have difficulty getting out of a chair. They may notice that they speak too softly, or that their handwriting is slow and looks cramped or small. Friends or family members may be the first to notice changes in someone with early Parkinsons. They may see that the persons face lacks expression and animation, or that the person does not move an arm or leg normally.
People with Parkinsons often develop a parkinsonian gait that includes a tendency to lean forward, small quick steps as if hurrying forward, and reduced swinging of the arms. They also may have trouble initiating or continuing movement.
Recommended Reading: 5 Signs You Ll Get Parkinsons
Also Check: Parkinson Bicycle Cleveland Clinic
Parkinsons And Other Movement Disorders
Parkinsons disease is a brain disorder that leads to shaking and difficulty with walking, movement, and coordination. PD encompasses a variety of syndromes, all of which are progressive and degenerative.
In individuals with PD, dopamine- and noradrenaline-producing neurons that normally send signals that coordinate muscle movement are destroyed. As a result, the primary symptoms of the disorder are trembling in hands, arms, legs, jaw, and face rigidity, or stiffness slowness of movement and impaired balance and coordination. The disease most often develops after age 50 and symptoms vary from patient to patient.
PD is the most common among a group of movement disorders called Parkinsonian syndromes, all of which have similar symptoms. According to the Parkinsons Disease Foundation, Parkinsonian syndromes affect approximately 1 million people in the United States and are the second most common neurodegenerative disorder after Alzheimers disease.
With no known cure for the disease, the goal of treatment through medication is to control symptoms. Patients may be prescribed L-DOPA, a drug that can be converted in the brain to dopamine. In some cases, surgery may be appropriate for patients whose disease does not respond to drugs. A therapy called deep brain stimulation has now been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. In DBS, electrodes are implanted in the brain and connected to a small electrical device.
How To Cope When Your Loved One Has Parkinsons Disease

Parkinsons Disease is a serious diagnosis thats extremely difficult for both the patient and their loved ones. Parkinsons Disease is a brain disorder that causes uncontrollable and unintentional movements such as body jerks, shaking, stiffness, and difficulty with balance and coordination. It is a serious illness that starts slowly, and worsens over time. Noticeable symptoms include speech impediments, sleep problems, memory difficulties, fatigue, depression, and tremors.
Parkinsons is caused by the impairment of, or death of, nerve cells in the basal ganglia. The death of these nerve cells in that specific region of the brain hampers dopamine production. Consequently, the neurons produce less dopamine, resulting in movement issues often associated with Parkinsons Disease.
Additionally, Parkinsons patients lose the norepinephrine-producing nerve endings, which act as a messenger of the sympathetic nervous system in charge of numerous bodily functions, such as heart rate and blood pressure. This explains why some Parkinsons patients have non-movement problems such as slow-moving digestion, hypertension, or sleeping problems. Since Parkinsons Disease affects mobility and results in other symptoms, it can also adversely impact the patients mental health.
Read Also: What Foods Should Be Avoided When Taking Levodopa
Whats The Difference Between Multiple System Atrophy And Parkinsons
Parkinsons and MSA both affect the movement control system and the involuntary autonomic control system and early symptoms can make a differential diagnosis a challenge. MSA, however, tends to progress faster than Parkinsons balance problems and a stooped posture happen earlier and get worse more quickly with MSA and autonomic functions such as blood pressure, heart rate, breathing, sweating, bladder function, and sexual problems are more severe in people with MSA.
For more information on multiple symptom atrophy, read this fact sheet.
What Causes Parkinsons Disease
Parkinsons disease occurs when nerve cells, or neurons, in an area of the brain that controls movement become impaired and/or die. Normally, these neurons produce an important brain chemical known as dopamine. When the neurons die or become impaired, they produce less dopamine, which causes the movement problems of Parkinsons. Scientists still do not know what causes cells that produce dopamine to die.
People with Parkinsons also lose the nerve endings that produce norepinephrine, the main chemical messenger of the sympathetic nervous system, which controls many functions of the body, such as heart rate and blood pressure. The loss of norepinephrine might help explain some of the non-movement features of Parkinsons, such as fatigue, irregular blood pressure, decreased movement of food through the digestive tract, and sudden drop in blood pressure when a person stands up from a sitting or lying-down position.
Many brain cells of people with Parkinsons contain Lewy bodies, unusual clumps of the protein alpha-synuclein. Scientists are trying to better understand the normal and abnormal functions of alpha-synuclein and its relationship to genetic mutations that impact Parkinsons disease and Lewy body dementia.
You May Like: Parkinsons Donations In Memory Of
Recommended Reading: Zhichan Capsule
Conditions That Mimic Shuffling Gait Seen In Parkinsons:
Please read the article on shuffling gait. It describes 5 causes of shuffling of gait.
The most crucial mimic to remember is Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus .
The person with NPH feels like he is stuck to the ground. This is a magnetic gait. It is easy to mistake this for Parkinsons disease.
For example, see this video posted by the Hydrocephalus Association of America on youtube:
NPH can be treated by implanting a small shunt pipe. This shunt drains excess water around the brain into the abdomen.
Read Also: Non Shaking Parkinsons Disease
What Are The Different Forms Of Parkinsonism
There are three main forms of parkinsonism, as well as other related conditions.
Most people with parkinsonism have idiopathic Parkinsons disease, also known as Parkinsons. Idiopathic means the cause is unknown.
The most common symptoms of idiopathic Parkinsons are tremor, rigidity and slowness of movement.
Vascular parkinsonism affects people with restricted blood supply to the brain. Sometimes people who have had a mild stroke may develop this form of parkinsonism.
Common symptoms include problems with memory, sleep, mood and movement.
Some drugs can cause parkinsonism.
Neuroleptic drugs , which block the action of the chemical dopamine in the brain, are thought to be the biggest cause of drug-induced parkinsonism.
The symptoms of drug-induced parkinsonism tend to stay the same only in rare cases do they progress in the way that Parkinsons symptoms do.
Drug-induced parkinsonism only affects a small number of people, and most will recover within months and often within days or weeks of stopping the drug thats causing it.
Also Check: Pfnca Wellness Programs
What Is Parkinson Disease
Parkinson disease is a movement disorder. It can cause the muscles to tighten and become rigid This makes it hard to walk and do other daily activities. People with Parkinsons disease also have tremors and may develop cognitive problems, including memory loss and dementia.
Parkinson disease is most common in people who are older than 50. The average age at which it occurs is 60. But some younger people may also get Parkinson disease. When it affects someone younger than age 50, its called early-onset Parkinson disease. You may be more likely to get early-onset Parkinson disease if someone in your family has it. The older you are, the greater your risk of developing Parkinson disease. Its also much more common in men than in women.
Parkinson disease is a chronic and progressive disease. It doesnt go away and continues to get worse over time.
You May Like: Beginning Signs Of Parkinsons
Which Test Can Be Done When The Diagnosis Is In Doubt
I request a small set of tests on almost all patients I diagnose with Parkinsons. These detect some mimics of Parkinsons disease.
Some doctors dont request all these tests. And for a good reason.
The diagnosis of Parkinsons mimics is primarily based on a careful history and examination. Even in my practice, these tests change the diagnosis only in a minority of patients.
I like the additional confirmation provided by these tests. They also have other benefits. For example, they help me determine the proper dosages of medications like Amantadine.
| Simple tests to detect Parkinsons Mimics |
|---|
| 1. MRI-Brain with size measurements of brain parts called the midbrain and pons. I usually also request a unique picture called SWI, which shows iron inside the brain.
2. Blood tests: |
But when the diagnosis s really in doubt, there is another brain scan that can be done.
A Trodat scan. Or even better an F-DOPA scan. Both these scans measure dopamine activity inside the brain.
You can read more about Trodat & F-DOPA scans by clicking here.
These scans are not perfect. Let me tell you why very quickly:
In Parkinsons disease, dopamine activity inside the brain is deficient. This deficiency produces an abnormal scan. If the Trodat/F-DOPA scan is normal, it is unlikely that you have Parkinsons disease.
Read Also: Sam Waterston Parkinson’s
Whats It Like Living With Parkinsons Disease
Whether you’ve just been diagnosed with Parkinsons Disease or you know someone who has, you may wonder what it’s like living with Parkinson’s disease. Life with Parkinson’s disease can be hard to imagine unless you have experienced it. In addition to motor symptoms like tremors, rigidity and slow movement, people with PD may also experience sleep disorders, mood changes, and relationship issues. Here are some of the main challenges of the condition, as well as tips to boost your quality of life or help someone living with Parkinson’s disease.
The Nervous System & Dopamine
To understand Parkinson’s, it is helpful to understand how neurons work and how PD affects the brain .
Nerve cells, or neurons, are responsible for sending and receiving nerve impulses or messages between the body and the brain. Try to picture electrical wiring in your home. An electrical circuit is made up of numerous wires connected in such a way that when a light switch is turned on, a light bulb will beam. Similarly, a neuron that is excited will transmit its energy to neurons that are next to it.
Neurons have a cell body with branching arms, called dendrites, which act like antennae and pick up messages. Axons carry messages away from the cell body. Impulses travel from neuron to neuron, from the axon of one cell to the dendrites of another, by crossing over a tiny gap between the two nerve cells called a synapse. Chemical messengers called neurotransmitters allow the electrical impulse to cross the gap.
Neurons talk to each other in the following manner :
Read Also: On-off Phenomenon
How Is Psp Diagnosed
Currently there are no tests or brain imaging techniques to definitively diagnose PSP. An initial diagnosis is based on the persons medical history and a physical and neurological exam. Identifying early gait problems, problems moving the eyes, speech and swallowing abnormalities, as well as ruling out other similar disorders is important. Diagnostic imaging may show shrinkage at the top of the brain stem and look at brain activity in known areas of degeneration.
General Approach To Management
The primary goal in the management of PD is to treat the symptomatic motor and nonmotor features of the disorder, with the objective of improving the patients overall quality of life. Appropriate management requires an initial evaluation and diagnosis by a multidisciplinary team consisting of neurologists, primary care practitioners, nurses, physical therapists, social workers, and pharmacists., It is also important that the patient and his or her family have input into management decisions.
Effective management should include a combination of nonpharmacological and pharmacological strategies to maximize clinical outcomes. To date, therapies that slow the progression of PD or provide a neuroprotective effect have not been identified., Current research has focused on identifying biomarkers that may be useful in the diagnosis of early disease and on developing future disease-modifying interventions.,
Also Check: On And Off Phenomenon
Gabapentin And Other Parkinsons Medications
Treating Parkinsons disease itself may help alleviate pain. Dopamine agonists like levodopa and other dopaminergic medications or therapies may help. Other people find that medications specifically designed to target nerve function, like gabapentin and amantadine, also help with pain.
Gabapentin worked when I had neck and shoulder pain, shared one member. It helped with the shooting nerve pain. Another wrote, When I had neck and shoulder pain, I took gabapentin. Gabapentin can help with pain in other parts of the body as well. As one member explained, My husband used gabapentin to calm nerve pain in his feet because he was having a lot of pain. It helps.
Others find amantadine to be helpful in managing their pain. One member wrote that they take a prescription called amantadine . This is working well at the moment.
Conditions Related To Parkinsons
No two people have the same Parkinsons disease . With diverse symptoms and varied speeds of progression, PD does not affect every person the same way.
However, people with Parkinsons share many common symptoms and are at greater risk of developing some conditions. Talk to your healthcare team to help understand your risks and learn prevention strategies to help you lead your best life with PD.
Recommended Reading: Voice Amplifiers For Parkinson’s
Review Guide To Diseases Similar To Parkinsons
Some movement disorders have PD symptoms
Parkinsons disease is not related to other well-known neurological conditions such as multiple sclerosis, muscular dystrophy, or Lou Gehrigs disease . However, there is a variety of syndromes and diseases that look like PD but have other clinical features and pathology. The American Parkinson Disease Asso ciation in Staten Island, NY, describes 14 such diseases, as follows:
Benign essential tremor: Essen tial tremor is commonly mistaken for PD, but the tremor quality is different. It is primarily at its worst during action, less severe during posture-holding, and rare at rest. The hands are affected, and there may be a tremor of the head and neck, usually a head nod. Also, the voice has a tremulous quality, which is not seen in PD. The legs are rarely affected, and there is no slowness, stiffness, or other features of PD. Some patients with presumed essential tremor eventually may develop PD.
Multiple systems atrophy: This term refers to three main disorders, called olivopontocerebellar atrophy , Shy-Drager syndrome , and striatonigral degeneration . All of these may be characterized by parkinsonism, although rest tremor is slight or absent. Again, the course is more rapid than PD, and treatment is usually not productive. Distinguishing features are:
Is Parkinsons Painful Describing The Experience
While not everyone diagnosed with Parkinsons disease experiences pain, research indicates that about 60 percent of people with the condition do face this symptom.
Pain can be caused by a number of factors associated with Parkinsons, including:
- Muscle stiffness
- Central pain
- Neuropathy
Its important to understand the different types of pain associated with Parkinsons disease, as well as what can be done for pain management. As always, talk to your health care provider or neurologist about the best ways to manage any pain you experience with Parkinsons.
Also Check: Parkinson’s Hallucinations Commercial
Parkinsons Disease Vs Als: Risk Factors And Complications
Risk factors for Parkinsons disease include being over the age of 50, being male, having a family history of Parkinsons disease, carrying gene variations, experiencing a head injury, being exposed to environmental toxins, and taking certain medications such as anti-anxiety medications or sleeping pills.
Complications associated with Parkinsons disease include difficulty thinking, depression, emotional changes, swallowing problems, sleep problems and disorders, bladder issues, constipation, changes in blood pressure, smell dysfunction, fatigue, pain, and sexual dysfunction.
Studies into ALS have revealed some interesting insight. For example, it may just be that some people with this disease are triggered by certain environmental factors. The environmental triggers under investigation include smoking, lead exposure, and military service. Recent research has indicated that people who have served in the military are at a higher risk of getting ALS.
Studies are also looking at the entire human genome, since research has uncovered a number of genetic variations that people with familial ALS and some with non-inherited ALS have in common. These variations might make people more prone to ALS.