Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
A detailed cognitive assessment is essential for the detection of late-onset dementia. Regular exercise helps in maintaining physical health. Appropriate interprofessional physiotherapy and rehabilitation measures are necessary. A comprehensive approach from each specialty, including physicians and specialists, palliative care, social worker, physiotherapist, speech therapist, mental health nurse, and pharmacists, are of utmost importance to enhance patient care. These various disciplines need to collaborate across interprofessional lines to optimize care and outcomes for patients with parkinsonism.
Whats The Difference Between Vascular Parkinsonism And Parkinsons
As the name implies, vascular parkinsonism is caused by cerebrovascular disease which affects the blood supply to the brain. Vascular parkinsonism is caused by one or more small strokes, while Parkinsons is caused by a gradual loss of nerve cells. One major difference from Parkinsons is that its not progressive, while Parkinsons becomes worse with time. Another difference is that there are no tremors in vascular parkinsonism.
For more information on vascular parkinsonism, read this journal article.
Consider Tremor Along With Other Symptoms
Parkinsons reputation is that it is a tremor disease, and thats how you can identify it across a crowded room, says Rebecca Gilbert, MD, PhD, chief scientific officer for the American Parkinson Disease Association in New York City.
Although tremors bring people to diagnosis in many cases, defining the condition as a tremor disease may have done patients a disservice over the years because there are more severe symptoms that people struggle with. Tremor is just the one that people can see, according to Dr. Gilbert.
Many think if you dont have a tremor everything is fine, she says. That isnt true.
Over time, other disease features, such as cognitive problems, psychosis, blood pressure irregularities, depression, and lack of desire to do things, can be more devastating.
James Beck, PhD, chief scientific officer with the Parkinsons Foundation, also cautions that tremor may not be the first distinguishing feature.
A person may notice a slowness of movement called bradykinesia, he says. Or someone may be walking down the street and one arm doesnt swing. These symptoms may appear before tremor.
While focusing only on tremor may not be advisable, understanding this abnormal movement and treatment options may help patients improve their quality of life.
Recommended Reading: Parkinson’s And Bad Taste In Mouth
Whats The Difference Between Drug
Parkinsons is a progressive disorder, which will become worse over time, while DIP does not. In DIP, Parkinson-like symptoms can begin within four days to one month of starting the medication. However, all the symptoms could completely subside once the effecting medication is stopped, though it may take up to 18 months for all the symptoms to subside.
For more information on drug-induced parkinsonism, read this journal article and/or information sheet.
Two Types Of Parkinsons Disease

By Amanda Butas 9 am on July 8, 2019
Parkinsons symptoms develop when approximately 80 percent of the neurons that produce dopamine become damaged or die. Statistics indicate approximately one million adults in the United States live with the debilitating disorder. While many people have heard about Parkinsons, few may realize there are two types of the disease.
Don’t Miss: What Causes Shaking In Parkinson’s Disease
What Lifestyle Changes Can I Make To Ease Parkinsons Symptoms
Exercise: Exercise helps improve muscle strength, balance, coordination, flexibility, and tremor. It is also strongly believed to improve memory, thinking and reduce the risk of falls and decrease anxiety and depression. One study in persons with Parkinsons disease showed that 2.5 hours of exercise per week resulted in improved ability to move and a slower decline in quality of life compared to those who didnt exercise or didnt start until later in the course of their disease. Some exercises to consider include strengthening or resistance training, stretching exercises or aerobics . All types of exercise are helpful.
Eat a healthy, balanced diet: This is not only good for your general health but can ease some of the non-movement related symptoms of Parkinsons, such as constipation. Eating foods high in fiber in particular can relieve constipation. The Mediterranean diet is one example of a healthy diet.
Preventing falls and maintaining balance: Falls are a frequent complication of Parkinson’s. While you can do many things to reduce your risk of falling, the two most important are: 1) to work with your doctor to ensure that your treatments whether medicines or deep brain stimulation are optimal and 2) to consult with a physical therapist who can assess your walking and balance. The physical therapist is the expert when it comes to recommending assistive devices or exercise to improve safety and preventing falls.
Trouble Moving Or Walking
Do you feel stiff in your body, arms or legs? Have others noticed that your arms dont swing like they used to when you walk? Sometimes stiffness goes away as you move. If it does not, it can be a sign of Parkinson’s disease. An early sign might be stiffness or pain in your shoulder or hips. People sometimes say their feet seem stuck to the floor.
What is normal?If you have injured your arm or shoulder, you may not be able to use it as well until it is healed, or another illness like arthritis might cause the same symptom.
Also Check: Parkinson’s Age Of Onset
Whats The Difference Between Multiple System Atrophy And Parkinsons
Parkinsons and MSA both affect the movement control system and the involuntary autonomic control system and early symptoms can make a differential diagnosis a challenge. MSA, however, tends to progress faster than Parkinsons balance problems and a stooped posture happen earlier and get worse more quickly with MSA and autonomic functions such as blood pressure, heart rate, breathing, sweating, bladder function, and sexual problems are more severe in people with MSA.
For more information on multiple symptom atrophy, read this fact sheet.
Types Of Parkinsons Tremors
Quivering in these parts of the body can be signs of Parkinson’s:
- Finger Twitching Commonly seen among patients in the early stages of the disease, this symptom is also called a pill-rolling tremor because the fingers and hand appear to be rolling a pill-sized object.
- Jaw Tremors This movement in the jaw may resemble a slow shivering and disappear while eating or talking. In some cases, the teeth chatter. Patients may chew gum to stop the trembling.
- Foot Tremors This shakiness may appear while resting, lying down, or dangling the feet. It stops when standing and walking. It can also extend beyond the feet and cause the whole leg to vibrate.
- Tongue Tremors Although far less reported than other types of tremor, quivering in tongue can be a revealing manifestation of Parkinsons, according to an article published in December 2015 in the journal Movement Disorders Clinical Practice. The shaking can also appear in the chin, lips, and face.
While these types of tremors can help doctor identify Parkinsons, about 30 percent of patients do not have these movements, per prior research. Those people who do not have a resting tremor may not get a diagnosis immediately, says Gilbert. If doctors dont see it, they wont necessarily think a person has Parkinsons.
Also Check: Parkinson’s And Marriage Breakdown
Parkinsons Disease: An Introductory Guide
This guide will help you better understand Parkinsons. Developed and authored with the McGill University Health Centre Patient Education Office with support from Parkinson Canada, it describes the illness, changes in your body over time, treatment and care options, possible health problems, as well as when and where you can find more help.
The focus of this resource is on providing you with the tools to understand Parkinsons, and to live well. You are encouraged to review this guide with your family. Bring it with you to your appointments with your health care team.
Thanks to the generosity of donors like you, Parkinsons Disease: An Introductory Guide is made available to anyone, anywhere in Canada.
How Is Parkinsons Disease Diagnosed
Diagnosing Parkinsons disease is sometimes difficult, since early symptoms can mimic other disorders and there are no specific blood or other laboratory tests to diagnose the disease. Imaging tests, such as CT or MRI scans, may be used to rule out other disorders that cause similar symptoms.
To diagnose Parkinsons disease, you will be asked about your medical history and family history of neurologic disorders as well as your current symptoms, medications and possible exposure to toxins. Your doctor will look for signs of tremor and muscle rigidity, watch you walk, check your posture and coordination and look for slowness of movement.
If you think you may have Parkinsons disease, you should probably see a neurologist, preferably a movement disorders-trained neurologist. The treatment decisions made early in the illness can affect the long-term success of the treatment.
Don’t Miss: Does Parkinson’s Cause Weight Gain
What Medications Are Used To Treat Parkinsons Disease
Medications are the main treatment method for patients with Parkinsons disease. Your doctor will work closely with you to develop a treatment plan best suited for you based on the severity of your disease at the time of diagnosis, side effects of the drug class and success or failure of symptom control of the medications you try.
Medications combat Parkinsons disease by:
- Helping nerve cells in the brain make dopamine.
- Mimicking the effects of dopamine in the brain.
- Blocking an enzyme that breaks down dopamine in the brain.
- Reducing some specific symptoms of Parkinsons disease.
Levodopa: Levodopa is a main treatment for the slowness of movement, tremor, and stiffness symptoms of Parkinsons disease. Nerve cells use levodopa to make dopamine, which replenishes the low amount found in the brain of persons with Parkinsons disease. Levodopa is usually taken with carbidopa to allow more levodopa to reach the brain and to prevent or reduce the nausea and vomiting, low blood pressure and other side effects of levodopa. Sinemet® is available in an immediate release formula and a long-acting, controlled release formula. Rytary® is a newer version of levodopa/carbidopa that is a longer-acting capsule. The newest addition is Inbrija®, which is inhaled levodopa. It is used by people already taking regular carbidopa/levodopa for when they have off episodes .
Tremors In Parkinsons Disease: What They Are Types Of Tremors And More
Getting the trembling associated with Parkinsons under control can be a challenge, but treatments can help.
Nicole Rerk/Shutterstock
Tremors are a defining characteristic of Parkinsons disease, affecting about 8 out of 10 people with this movement disorder. Many people think the involuntary shaking motion is the main problem for patients. While it is certainly an irritating symptom that individuals want to get under control, other characteristics of the disease can be more debilitating.
Don’t Miss: Is There Pain With Parkinson’s
What Is The Outlook For Persons With Parkinsons Disease
Although there is no cure or absolute evidence of ways to prevent Parkinsons disease, scientists are working hard to learn more about the disease and find innovative ways to better manage it, prevent it from progressing and ultimately curing it.
Currently, you and your healthcare teams efforts are focused on medical management of your symptoms along with general health and lifestyle improvement recommendations . By identifying individual symptoms and adjusting the course of action based on changes in symptoms, most people with Parkinsons disease can live fulfilling lives.
The future is hopeful. Some of the research underway includes:
- Using stem cells to produce new neurons, which would produce dopamine.
- Producing a dopamine-producing enzyme that is delivered to a gene in the brain that controls movement.
- Using a naturally occurring human protein glial cell-line derived neurotrophic factor, GDNF to protect dopamine-releasing nerve cells.
Many other investigations are underway too. Much has been learned, much progress has been made and additional discoveries are likely to come.
Optogenetic Stimulation Of Glutamatergic Neurons In The Cuneiform Nucleus Controls Locomotion In A Mouse Model Of Parkinsons Disease
See allHide authors and affiliations
- For correspondence:
Edited by Peter L. Strick, University of Pittsburgh, Pittsburgh, PA, and approved September 7, 2021
You May Like: Parkinson’s Coughing At Night
Clinical Confirmation Of Parkinson Disease
The diagnosis of PD is guided by the Queen Square Brain Bank diagnostic criteria, which require two steps. Step one focuses on the definition of parkinsonism and requires the presence of bradykinesia and of either typical rest tremor, extrapyramidal rigidity, or postural instability . However, postural instability is not an early PD feature and should alert the clinician of an atypical parkinsonian disorder. Step two focuses on features typical of the parkinsonism of PD, such as unilateral onset, excellent response to levodopa therapy, and development of dyskinesia. Exclusion criteria include pyramidal signs, stepwise deterioration of parkinsonism , repeated head injury, history of encephalitis or oculogyric crisis, neuroleptic treatment at the onset of symptoms, strictly unilateral features after 3 years, supranuclear gaze palsy, cerebellar signs, early severe autonomic dysfunction, early severe cognitive dysfunction, negative response to levodopa, and imaging evidence of communicating hydrocephalus.
What Are The Symptoms Of Atypical Parkinsonian Disorders
Like classic Parkinsons disease, atypical Parkinsonian disorders cause muscle stiffness, tremor, and problems with walking/balance and fine motor coordination.
Patients with atypical Parkinsonism often have some degree of difficulty speaking or swallowing, and drooling can be a problem. Psychiatric disturbances such as agitation, anxiety or depression may also be part of the clinical picture.
Dementia with Lewy bodies can cause changes in attention or alertness over hours or days, often with long periods of sleep during the day. Visual hallucinations typically of small animals or children, or moving shadows in the periphery of the visual field are common in DLB. DLB is second only to Alzheimers disease as a cause of dementia in the elderly, and it most commonly affects patients in their 60s.
Patients with progressive supranuclear palsy may have difficulties with eye movements, particularly when looking downward, and with balance when descending stairs, for instance. Backward falls are common and may occur during the early course of the disease. PSP is not usually associated with tremor, unlike Parkinsons disease.
Parkinson’s Disease and Movement Disorders Center
Don’t Miss: Is Drooling A Sign Of Parkinson’s Disease
Parkinsonism Vs Parkinson’s Disease
Often confused as one and the same, Parkinsons disease is actually the most common kind of Parkinsonism, accounting for nearly 80% of all cases.2 PD is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder characterized by the same motor conditions as Parkinsonisms including tremor, rigidity, bradykinesia, and impaired balance. Other contributing causes of Parkinsonism include multiple system atrophy, progressive supranuclear palsy, and corticobasal degeneration. PD has no directly attributable cause or cure.
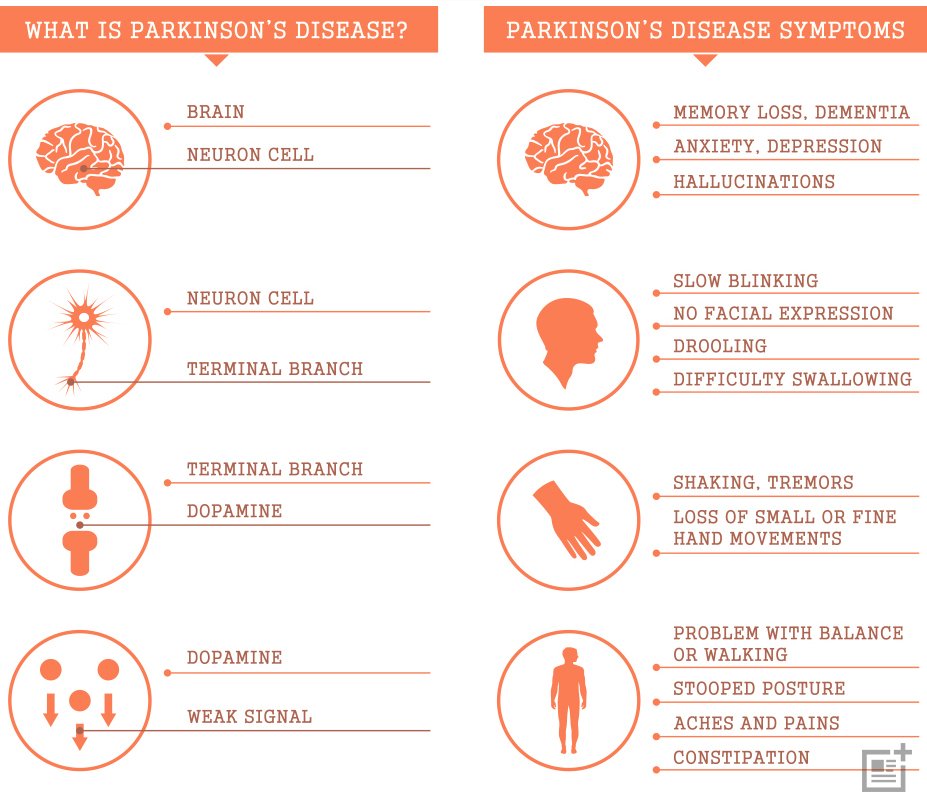
Symptoms Of Parkinsons Disease
Parkinson’s disease has four main symptoms:
- Tremor in hands, arms, legs, jaw, or head
- Stiffness of the limbs and trunk
- Slowness of movement
- Impaired balance and coordination, sometimes leading to falls
Other symptoms may include depression and other emotional changes difficulty swallowing, chewing, and speaking urinary problems or constipation skin problems and sleep disruptions.
Symptoms of Parkinsons and the rate of progression differ among individuals. Sometimes people dismiss early symptoms of Parkinson’s as the effects of normal aging. In most cases, there are no medical tests to definitively detect the disease, so it can be difficult to diagnose accurately.
Early symptoms of Parkinson’s disease are subtle and occur gradually. For example, affected people may feel mild tremors or have difficulty getting out of a chair. They may notice that they speak too softly, or that their handwriting is slow and looks cramped or small. Friends or family members may be the first to notice changes in someone with early Parkinson’s. They may see that the person’s face lacks expression and animation, or that the person does not move an arm or leg normally.
People with Parkinson’s often develop a parkinsonian gait that includes a tendency to lean forward, small quick steps as if hurrying forward, and reduced swinging of the arms. They also may have trouble initiating or continuing movement.
Also Check: Do You Get Pain With Parkinson’s
How Is Parkinsonism Diagnosed
You should be referred to a Parkinsons specialist for the diagnosis of any parkinsonism. They may wish to explore different things before giving you a diagnosis.
Your specialist will look at your medical history, ask you about your symptoms and do a medical examination.
Telling the difference between types of parkinsonism isnt always easy, for the following reasons:
- The first symptoms of the different forms of parkinsonism are so similar.
- In many cases, parkinsonism develops gradually. Symptoms that allow your doctor to make a specific diagnosis may only appear as your condition progresses.
- Everyone with parkinsonism is different and has different symptoms.
Find out more: see our information on symptoms of Parkinsons, and diagnosing Parkinsons.
One of the most useful tests to find out what sort of parkinsonism you may have is to see how you respond to treatment.
If your specialist thinks you have idiopathic Parkinsons, theyll expect you to have a good response to Parkinsons drugs such as levodopa . A good response means that your symptoms will improve. Sometimes, it will only be clear that youve responded to medication when the drug is reduced or stopped, and your symptoms become more obvious again.
If you dont have any response to Parkinsons medication, your specialist will have to look again at your diagnosis.
Although not routinely available, your specialist may wish to carry out some of the tests below.
Current tests available include: