Tgm83+/ Mice Subjected To Mcao Continuously Gain Body Weight But Develop Motor Deficits Within 180 Days After Surgery That Further Worsen Over Time
Fig. 1
TgM83+/ mice subjected to MCAO gain weight but develop motor deficits within 180 days. TgM83+/ mice expressing the A53T mutant of human -synuclein were subjected to middle cerebral artery occlusion for 30 min or sham surgery without occlusion of the artery. Groups of treated animals were sacrificed at 14, 30, 90, 180, and 360 days post surgery and neuropathology was analyzed by histology and biochemistry . Additionally, the motor behavior of treated animals was tested at 90, 180, and 360 days post surgery on a rotarod treadmill . TgM83+/ mice subjected to MCAO as well as sham-treated animals gained body weight until the end of the experiment at 360 days post surgery . MCAO- and sham-treated mice were tested for motor impairment using a rotarod at 90, 180, and 360 days post surgery. TgM83+/ mice that had been subjected to MCAO showed significantly reduced motor skills at 180 and 360 days post surgery relative to 90 days post surgery . In contrast, sham-treated control animals did not develop any motor deficits. Six to ten animals were analyzed per group. The data represents the mean latency to fall in seconds±standard error of the mean. P values were computed using two-way ANOVA followed by Tukeys post-hoc test
Subgroup Analysis Of Ischemic Stroke Incidence Rate
In both male and female subgroups, ischemic stroke incidence rate showed difference between the PD and control group . In both age subgroups , ischemic stroke incidence rates were significantly different between the PD and the control group . In both the non-diabetes subgroup and diabetes subgroup, the ischemic stroke incidence rate was significantly different between the PD and control group . In both the non-hypertension and hypertension subgroups, the ischemic stroke incidence rate was significantly different between the PD and control group . In both the non-dyslipidemia and dyslipidemia subgroups, the ischemic stroke incidence rate was also significantly different between the PD and the control group .
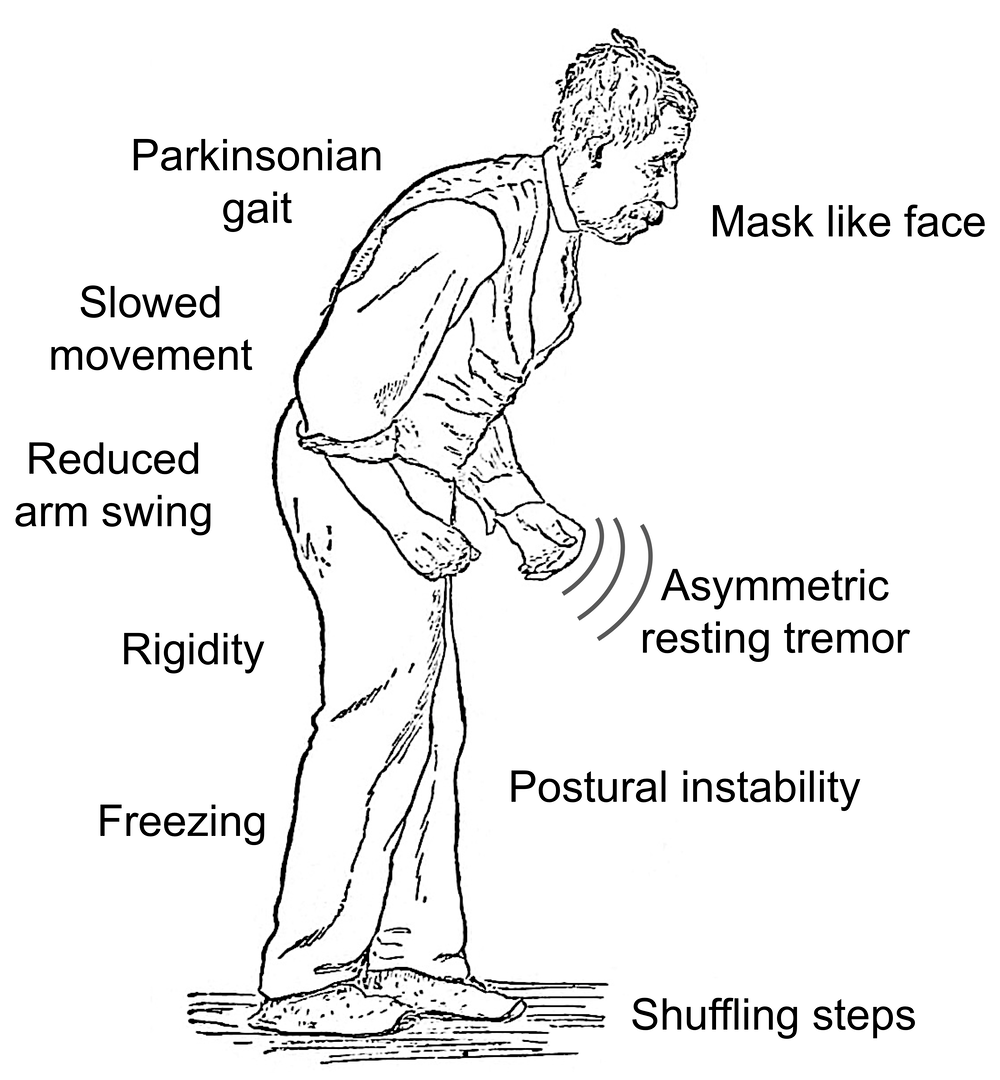
How Is Parkinsons Disease Diagnosed
There are currently no specific tests that diagnose PD. The diagnosis is based on:
- medical history and a neurological examination
- blood and laboratory tests, to rule out other disorders that may be causing the symptoms
- brain scans to rule out other disorders. However, computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging brain scans of people with PD usually appear normal.
In rare cases, where people have a clearly inherited form of PD, researchers can test for known gene mutations as a way of determining an individuals risk of developing the disease. However, this genetic testing can have far-reaching implications and people should carefully consider whether they want to know the results of such tests.
Read Also: Medications Contraindicated In Parkinson’s
Why Does Modern Medicine Know This But Ignore It
Why dont we tackle the inflammation and toxins causes of those nerve cells continually dying in the substantia nigra?
My doctor told me: its cultural.
Most patients especially in western countries want a drug or a procedure for a problem.
Something thats a one-off fix like an operation.
Or an easy, regular thing like a course of tablets.
What they dont want to have to make an effort to heal themselves. So pills it is.
But most inflammatory diseases can be tackled more effectively by lifestyle changes than by drugs.
Whole classes of deadly modern illnesses can be changed by a small number of simple, targeted lifestyle tweaks.
But our medics push meds because they know that, mostly, their patients wont make lifestyle changes.
So they give their patients drugs knowing that theyll at least take them.
Frustratingly, the best solution addressing lifestyle factors isnt at all difficult. Its just that popping a pill is easier.
You May Like: Is The Parkinsonâs Foundation Legitimate
Comparing Risk Factors Of Incident Pd And Coronary Events
With respect to the effects of the risk factors, the differences between PD and coronary events are shown in Table and Fig. . Smoking and LDL were positively associated with risk of coronary events but were inversely associated with risk of PD . Hypertension, lipid-lowering drugs, BMI, ApoB/ApoA1 ratio, and ApoB were positively associated with the risk of coronary events but were not associated with PD . In addition, ApoA1 was inversely associated with the risk of coronary events but was not associated with PD . By contrast, age, male sex, diabetes, NLR, and FBG were common risk factors for coronary events and PD .
You May Like: Herbal Remedy For Parkinson’s Disease
What Causes Parkinsons Disease
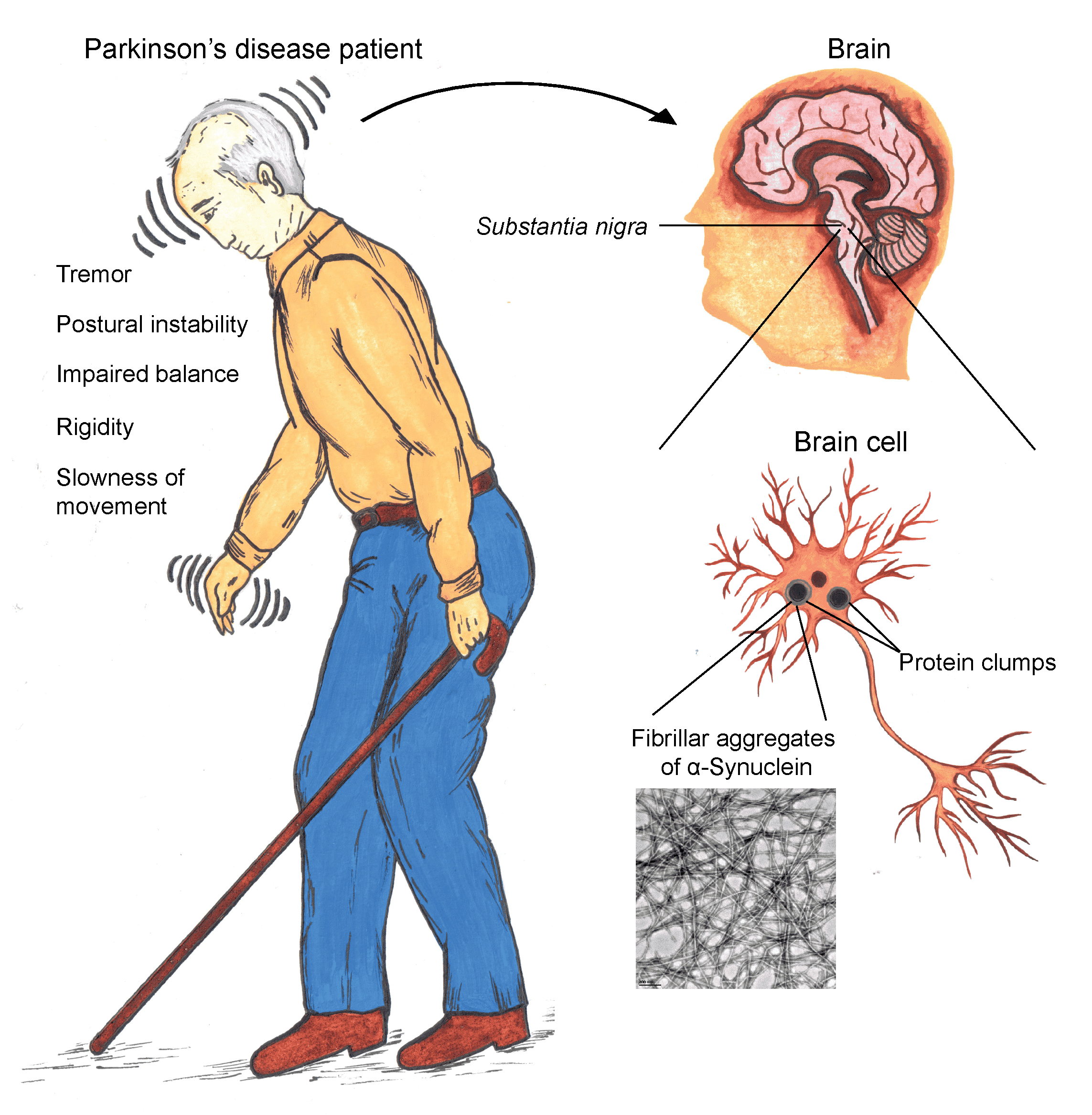
The most prominent signs and symptoms of Parkinsons disease occur when nerve cells in the basal ganglia, an area of the brain that controls movement, become impaired and/or die. Normally, these nerve cells, or neurons, produce an important brain chemical known as dopamine. When the neurons die or become impaired, they produce less dopamine, which causes the movement problems associated with the disease. Scientists still do not know what causes the neurons to die.
People with Parkinsons disease also lose the nerve endings that produce norepinephrine, the main chemical messenger of the sympathetic nervous system, which controls many functions of the body, such as heart rate and blood pressure. The loss of norepinephrine might help explain some of the non-movement features of Parkinsons, such as fatigue, irregular blood pressure, decreased movement of food through the digestive tract, and sudden drop in blood pressure when a person stands up from a sitting or lying position.
Many brain cells of people with Parkinsons disease contain Lewy bodies, unusual clumps of the protein alpha-synuclein. Scientists are trying to better understand the normal and abnormal functions of alpha-synuclein and its relationship to genetic mutations that impact Parkinsons andLewy body dementia.
Establishing Pd Research Priorities
The NINDS-organized Parkinsons Disease 2014: Advancing Research, Improving Lives conference brought together researchers, clinicians, patients, caregivers, and nonprofit organizations to develop 31 prioritized recommendations for research on PD. These recommendations are being implemented through investigator-initiated grants and several NINDS programs. NINDS and the NIHs National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences held the Parkinsons Disease: Understanding the Environment and Gene Connection workshop to identify priorities for advancing research on environmental contributors to PD.
Research recommendations for Lewy Body Dementia, including Parkinsons disease dementia, were updated during the NIH Alzheimers Disease-Related Dementias Summit 2019 .
You May Like: Is Parkinson A Form Of Dementia
Comparison Between Psp And Psn Cohorts
Compared with the PSN cohort, the PSP cohort had overall higher mortality risk . Patients aged 40 to 64, 65 to 74, and 75 years in the PSP cohort had 2.07-, 1.46-, and 1.28-fold higher mortality risks than did those in the PSN cohort, respectively. Compared with the PSN cohort, female and male patients in the PSP cohort had 1.49- and 1.72-fold higher mortality risks. Patients without any and with any one comorbidity in the PSP cohort had 3.02- and 1.38-fold significantly higher mortality risks than did those in the PSN cohort .
Table 4
Parkinsons Disease At A Glance
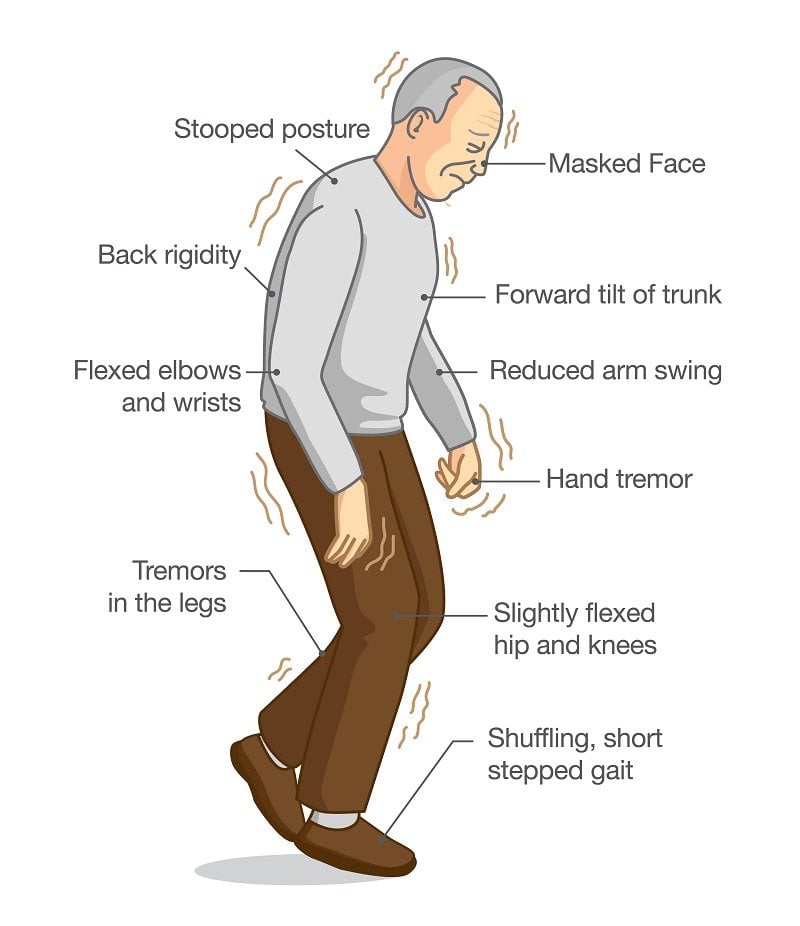
Parkinsonâs disease is a movement disorder that affects at least 500,000 people in the United States. It occurs when brain cells fail to produce enough dopamine, a chemical that helps to control movements, motivation, emotions, and sensations like pleasure. Symptoms of Parkinsonâs begin gradually and become worse over time. They include trembling, stiffness, and poor balance and coordination. As Parkinsonâs progresses, daily tasks like walking, talking, and chewing may become difficult. Depression and sleep problems are common. Itâs unclear why some people develop Parkinsonâs genes may play a role, as well as exposure to chemicals in the environment.
Researchers have studied the following complementary health approaches for Parkinsonâs:
Also Check: Can An Mri Detect Parkinson’s
Thankfully None Of This Is Going To Happen
Which is what I want to tell you about now. So let me start by reassuring you of this:
I feel fine. Absolutely fine.
In some ways, Im happier and more positive than I was before I got that initial shocking diagnosis.
My hands no longer shake. I sleep like a lamb. And I recall all the important details about my life or what I did this morning! with ease.
Second, theres a reason I feel this way. And its to do with how Ive actively worked on my condition.
Respiratory And Heart Diseases Were Common Causes Of Death
These patients had mean age at disease onset of 57, and had been living with Parkinsons for a mean of four years when they entered the study. Fatigue was reported by 52.8% of them, and a majority also engaged in regular physical leisure time exercise.
Over 10 years of follow-up, 50 of these 218 people died 24 men and 26 women representing 22.9% of the total group. The most common causes were respiratory diseases , mainly pneumonia , and heart disease . Other causes were digestive system disorders , stroke , suicide , urinary system disorders , and heat stroke .
These deaths, analyses showed, amounted to an overall SMR of 1.32.
This survival survey in the northern Chinese mainland gave an SMR of 1.32, which means that the 10-year mortality rate for patients is similar to that expected for the general population nationwide, the researchers wrote, noting that there seems to be no survival difference between the South and the North.
Previous studies set the SMR for Parkinsons patients in Shanghai, in southern China, at .87, and that for patients in Hong Kong at 1.10, they also noted.
Recommended Reading: Inhaler For Parkinson’s Disease
Parkinsons Disease Caused By Stroke: Vascular Parkinsonism
A stroke involving the substantia nigra or basal ganglia is called vascular Parkinsonism. Similar to other strokes, damage is caused primarily by a lack of blood supply to these regions of the brain. Generally, the strokes associated with Parkinsonism are termed small vessel strokes as they arenât normally catastrophic. Diagnosis of small vessel strokes can be confirmed with diagnostic tests such as CT or MRI of the brain.
It typically takes several small strokes to produce the symptoms of vascular Parkinsonism. In some cases, small vessel strokes can also produce a type of dementia called vascular dementia. As such, it is not unusual for people who have vascular Parkinsonism to also have vascular dementia.
When Should I See My Healthcare Provider Or When Should I Seek Care
You should see your healthcare provider as recommended, or if you notice changes in your symptoms or the effectiveness of your medication. Adjustments to medications and dosages can make a huge difference in how Parkinsons affects your life.
When should I go to ER?
Your healthcare provider can give you guidance and information on signs or symptoms that mean you should go to the hospital or seek medical care. In general, you should seek care if you fall, especially when you lose consciousness or might have an injury to your head, neck, chest, back or abdomen.
You May Like: How To Tell If Someone Has Parkinson’s
What If You Have Parkinson’s Disease And A Stroke
Stroke is relatively common and so is Parkinson’s disease, so one person can have both. If you or your loved one has a stroke as well as Parkinson’s disease, it is normal for you to be concerned.
The conditions have different causes, but the movement problems of Parkinson’s disease combined with the effects of a stroke can make it even more difficult for you or your loved one to get around than if you only had one of the two problems.
If you have both conditions, it is more important to pay attention to things such as safeguarding your home to prevent falls and getting a walker or a cane in order to avoid falls.
Diagnosis Of Parkinsons Disease
There are currently no blood or laboratory tests to diagnose non-genetic cases of Parkinsons. Doctors usually diagnose the disease by taking a persons medical history and performing a neurological examination. If symptoms improve after starting to take medication, its another indicator that the person has Parkinsons.
A number of disorders can cause symptoms similar to those of Parkinsons disease. People with Parkinsons-like symptoms that result from other causes, such as multiple system atrophy and dementia with Lewy bodies, are sometimes said to have parkinsonism. While these disorders initially may be misdiagnosed as Parkinsons, certain medical tests, as well as response to drug treatment, may help to better evaluate the cause. Many other diseases have similar features but require different treatments, so it is important to get an accurate diagnosis as soon as possible.
Also Check: Risperidone And Parkinson’s Disease
How Do I Take Care Of Myself
If you have Parkinsons disease, the best thing you can do is follow the guidance of your healthcare provider on how to take care of yourself.
- Take your medication as prescribed. Taking your medications can make a huge difference in the symptoms of Parkinsonâs disease. You should take your medications as prescribed and talk to your provider if you notice side effects or start to feel like your medications arenât as effective.
- See your provider as recommended. Your healthcare provider will set up a schedule for you to see them. These visits are especially important to help with managing your conditions and finding the right medications and dosages.
- Dont ignore or avoid symptoms. Parkinsons disease can cause a wide range of symptoms, many of which are treatable by treating the condition or the symptoms themselves. Treatment can make a major difference in keeping symptoms from having worse effects.
Comparing Risk Factors Of Incident Pd And Ischemic Stroke
The comparisons of risk factors for PD and ischemic stroke are presented in Table and Fig. . Female sex was more protective for PD when compared with ischemic stroke . Smoking was positively associated with risk of ischemic stroke but was inversely associated with risk of PD . Age, diabetes, NLR, and FBG were the shared risk factors in PD and ischemic stroke , whereas HDL was a common protective factor for the two outcomes . In addition, hypertension was positively associated with the risk of ischemic stroke but was not significantly associated with the risk of PD . In contrast, LDL was inversely associated with the risk of PD but was not significantly associated with the risk of ischemic stroke .
In sensitivity analyses, similar results were observed when excluding those who developed both PD and coronary events or ischemic stroke during the follow-up .
Don’t Miss: Neuropathy And Parkinson’s Disease
Neurogenesis After Ischemic Injury In Normal And Vehicle
In postischemic brain injury, neuronal cells derived from neural precursor cells are newly born and the cells can be detected by bromodeoxyuridine . The BrdU-immunopositive cells were observed in the postischemic cortex, striatum, and subventricular zone on the ipsilateral side of the ischemic infarct at 1 month and 6 months and 4). The BrdU-positive cells were more frequently observed in the ipsilateral side of the statin-treated mice than in the contralateral side. Especially at 1 month after tFCI, many BrdU- and NeuN-immunopositive cells were detected in the lesioned cortex and striatum at the direct site to ischemic damage by MCAO ). It could be implicated that newborn cells have arisen from the SVZ and migrated into striatum and even into cortical area. Moreover, the proliferation of neural cells is promoted by long-term statin treatment. At 6 months and 8 months after fFCI, the incidence of BrdU-positive cells in the ipsilateral striatum and cortex was significantly diminished compared to that of 1 month after fFCI . The BrdU-positive cells were not detected in either striatum or cortex, but a few BrdU-positive cells were detected in SVZ and corpus callosum.
Who Gets Parkinsons Disease
Risk factors for PD include:
- Age. The average age of onset is about 70 years, and the incidence rises significantly with advancing age. However, a small percent of people with PD have early-onset disease that begins before the age of 50.
- Sex. PD affects more men than women.
- Heredity. People with one or more close relatives who have PD have an increased risk of developing the disease themselves. An estimated 15 to 25 percent of people with PD have a known relative with the disease. Some cases of the disease can be traced to specific genetic mutations.
- Exposure to pesticides. Studies show an increased risk of PD in people who live in rural areas with increased pesticide use.
You May Like: New Cure Parkinson’s Disease
What Is The Prognosis
The average life expectancy of a person with PD is generally the same as for people who do not have the disease. Fortunately, there are many treatment options available for people with PD. However, in the late stages, PD may no longer respond to medications and can become associated with serious complications such as choking, pneumonia, and falls.
PD is a slowly progressive disorder. It is not possible to predict what course the disease will take for an individual person.
One commonly used scale neurologists use for describing how the symptoms of PD have progressed in a patient is the Hoehn and Yahr scale.
What Research Is Being Done
The mission of the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke is to seek fundamental knowledge about the brain and nervous system and to use the knowledge to reduce the burden of neurological disease. NINDS is a component of the National Institutes of Health , the leading supporter of biomedical research in the world. NINDS conducts and supports three types of research: basicscientific discoveries in the lab, clinicaldeveloping and studying therapeutic approaches to Parkinsons disease, and translationalfocused on tools and resources that speed the development of therapeutics into practice. The goals of NINDS-supported research on Parkinsons disease are to better understand and diagnose PD, develop new treatments, and ultimately, prevent PD. NINDS also supports training for the next generation of PD researchers and clinicians and serves as an important source of information for people with PD and their families.
Don’t Miss: Earliest Symptoms Of Parkinson’s Disease