Pathogenesis Of Parkinsons Disease
A number of mechanisms have been implicated in PD pathogenesis, with -synuclein aggregation central to the development of the disease. Multiple other processes are thought to be involved, with several studies suggesting that abnormal protein clearance, mitochondrial dysfunction, and neuroinflammation play a role in the onset and progression of PD. However, the relationship between these pathways remains unclear.
Medicines And Dietary Supplements
Some medicines both prescription and over the counter can lead to constipation.
- These include some drugs used to treat depression, antacids containing aluminum or calcium, some allergy medicines , certain painkillers, some medicines for high blood pressure, diuretics, anticholinergics, antispasmodics, anticonvulsants, and drugs used to treat Parkinsons disease.
- Certain dietary supplements, such as iron, can also lead to constipation.
- Anesthesia, which is used during medical procedures to keep a person from feeling pain, can also lead to constipation.
Medicines For Parkinsons Disease
Medicines can help treat the symptoms of Parkinsons by:
- Increasing the level of dopamine in the brain
- Having an effect on other brain chemicals, such as neurotransmitters, which transfer information between brain cells
- Helping control non-movement symptoms
The main therapy for Parkinsons is levodopa. Nerve cells use levodopa to make dopamine to replenish the brains dwindling supply. Usually, people take levodopa along with another medication called carbidopa. Carbidopa prevents or reduces some of the side effects of levodopa therapy such as nausea, vomiting, low blood pressure, and restlessness and reduces the amount of levodopa needed to improve symptoms.
People living with Parkinsons disease should never stop taking levodopa without telling their doctor. Suddenly stopping the drug may have serious side effects, like being unable to move or having difficulty breathing.
The doctor may prescribe other medicines to treat Parkinsons symptoms, including:
- Dopamine agonists to stimulate the production of dopamine in the brain
- Enzyme inhibitors to increase the amount of dopamine by slowing down the enzymes that break down dopamine in the brain
- Amantadine to help reduce involuntary movements
- Anticholinergic drugs to reduce tremors and muscle rigidity
Also Check: Does Everyone With Parkinson’s Get Dementia
What Are The Symptoms
The best-known symptoms of Parkinson’s disease involve loss of muscle control. However, experts now know that muscle control-related issues aren’t the only possible symptoms of Parkinson’s disease.
Motor-related symptoms
Motor symptoms which means movement-related symptoms of Parkinsons disease include the following:
Additional motor symptoms can include:
- Blinking less often than usual. This is also a symptom of reduced control of facial muscles.
- Cramped or small handwriting. Known as micrographia, this happens because of muscle control problems.
- Drooling. Another symptom that happens because of loss of facial muscle control.
- Mask-like facial expression. Known as hypomimia, this means facial expressions change very little or not at all.
- Trouble swallowing . This happens with reduced throat muscle control. It increases the risk of problems like pneumonia or choking.
- Unusually soft speaking voice . This happens because of reduced muscle control in the throat and chest.
Non-motor symptoms
Several symptoms are possible that aren’t connected to movement and muscle control. In years past, experts believed non-motor symptoms were risk factors for this disease when seen before motor symptoms. However, theres a growing amount of evidence that these symptoms can appear in the earliest stages of the disease. That means these symptoms might be warning signs that start years or even decades before motor symptoms.
Non-motor symptoms include:
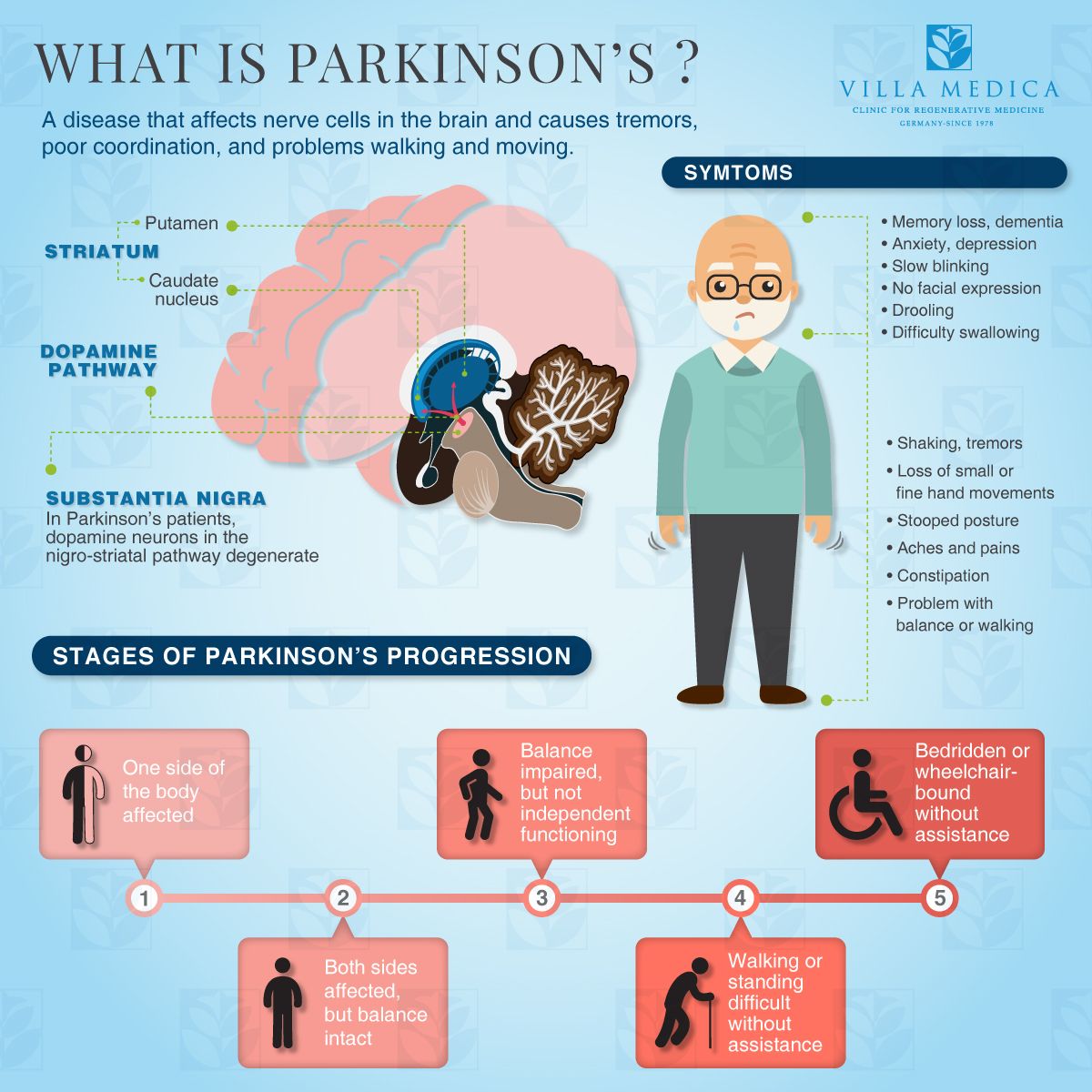
Stages of Parkinsons disease
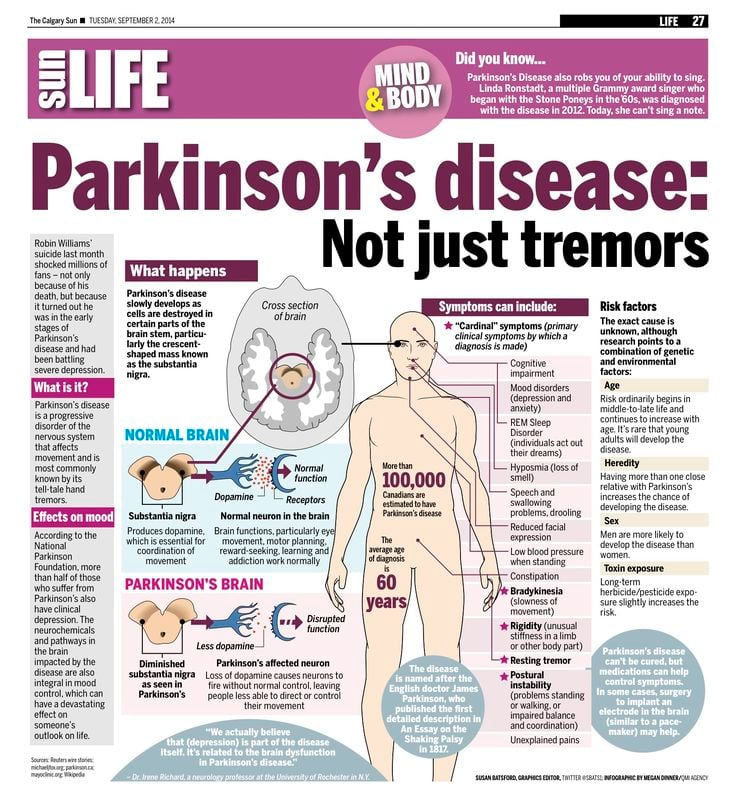
What Are The Causes
The cause of Parkinson’s is largely unknown. Scientists are currently investigating the role that genetics, environmental factors, and the natural process of aging have on cell death and PD.
There are also secondary forms of PD that are caused by medications such as haloperidol , reserpine , and metoclopramide .
Also Check: Fluid Retention And Parkinson’s
The Facts About Parkinsons Disease
Parkinson’s disease is a progressive neurogenerative disease that causes nerve cells in the area of the brain that controls movement to weaken and/or die. While healthy neurons produce a chemical called dopamine, which the brain needs a certain amount of in order to regulate movement, weakened neurons produce lower levels of dopamine. What causes these neurons to weaken is currently unknown.
Some patients with Parkinson’s disease also suffer from a decline in norepinephrine, a chemical that transmits signals across nerve endings and controls various functions, such as blood pressure and heart rate.
More than 10 million people worldwide are currently living with Parkinson’s disease and nearly one million will be living with the disease in the United States this year, according to the Parkinson’s Foundation.
Symptoms Of Parkinsons Disease
Parkinsons has four main symptoms:
- Tremor in hands, arms, legs, jaw, or head
- Muscle stiffness, where muscle remains contracted for a long time
- Slowness of movement
- Impaired balance and coordination, sometimes leading to falls
Other symptoms may include:
The symptoms of Parkinsons and the rate of progression differ among individuals. Early symptoms of this disease are subtle and occur gradually. For example, people may feel mild tremors or have difficulty getting out of a chair. They may notice that they speak too softly, or that their handwriting is slow and looks cramped or small. Friends or family members may be the first to notice changes in someone with early Parkinsons. They may see that the persons face lacks expression and animation, or that the person does not move an arm or leg normally.
People with Parkinson’s disease often develop a parkinsonian gait that includes a tendency to lean forward take small, quick steps and reduce swinging their arms. They also may have trouble initiating or continuing movement.
Symptoms often begin on one side of the body or even in one limb on one side of the body. As the disease progresses, it eventually affects both sides. However, the symptoms may still be more severe on one side than on the other.
Also Check: Is Joint Pain A Symptom Of Parkinson’s
What Can I Expect If I Have This Condition
Parkinsons disease is a degenerative condition, meaning the effects on your brain get worse over time. However, this condition usually takes time to get worse. Most people have a normal life span with this condition.
You’ll need little to no help in the earlier stages and can keep living independently. As the effects worsen, youll need medication to limit how the symptoms affect you. Most medications, especially levodopa, are moderately or even very effective once your provider finds the minimum dose you need to treat your symptoms.
Most of the effects and symptoms are manageable with treatment, but the treatments become less effective and more complicated over time. Living independently will also become more and more difficult as the disease worsens.
How long does Parkinsons disease last?
Parkinsons disease isnt curable, which means its a permanent, life-long condition.
Whats the outlook for Parkinsons disease?
Parkinson’s disease isn’t fatal, but the symptoms and effects are often contributing factors to death. The average life expectancy for Parkinson’s disease in 1967 was a little under 10 years. Since then, the average life expectancy has increased by about 55%, rising to more than 14.5 years. That, combined with the fact that Parkinson’s diagnosis is much more likely after age 60, means this condition doesn’t often affect your life expectancy by more than a few years .
Impact On Families And Carers
Informal carers spendmany hours dailyproviding care for people living with PD.This can be overwhelming. Physical, emotional and financial pressures can cause great stress to families and carers, and support is required from the health, social, financial and legal systems. Useful support resources from other conditions can be drawn upon, such as WHOs iSupport programme for dementia.
Also Check: Woman Who Can Smell Parkinson’s Disease
How Is A Diagnosis Made
Because other conditions and medications mimic the symptoms of PD, getting an accurate diagnosis from a physician is important. No single test can confirm a diagnosis of PD, because the symptoms vary from person to person. A thorough history and physical exam should be enough for a diagnosis to be made. Other conditions that have Parkinsons-like symptoms include Parkinsons plus, essential tremor, progressive supranuclear palsy, multi-system atrophy, dystonia, and normal pressure hydrocephalus.
Vocal Changes In A Zebra Finch Model Of Parkinsons Disease Characterized By Alpha
- Cesar A. Medina,
Roles Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Validation, Visualization, Writing original draft, Writing review & editing
Affiliations Graduate Interdisciplinary Program in Neuroscience, University of Arizona, Tucson, Arizona, United State of America, Department of Neuroscience, University of Arizona, Tucson, Arizona, United States of America
-
Contributed equally to this work with: Eddie Vargas, Stephanie J. Munger
Roles Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Validation, Writing review & editing
Affiliation Department of Neuroscience, University of Arizona, Tucson, Arizona, United States of America
-
Contributed equally to this work with: Eddie Vargas, Stephanie J. Munger
Roles Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Writing review & editing
Affiliation Department of Neuroscience, University of Arizona, Tucson, Arizona, United States of America
-
* E-mail:
Affiliations Graduate Interdisciplinary Program in Neuroscience, University of Arizona, Tucson, Arizona, United State of America, Department of Neuroscience, University of Arizona, Tucson, Arizona, United States of America, Department of Speech, Language, and Hearing Sciences, University of Arizona, Tucson, Arizona, United States of America, Department of Neurology, University of Arizona, Tucson, Arizona, United States of America, BIO5 Institute, University of Arizona, Tucson, Arizona, United States of America
You May Like: Can Parkinson’s Symptoms Come And Go
Managing And Treating Rigidity
Your doctor will diagnose rigidity by having you demonstrate various motor functions, like joint extension and flexing your muscles. â
Treatment options for managing Parkinsonâs disease work for managing rigidity. But if youâve caught the rigidity early and want to get ahead of future discomfort, there are treatment options available. â
Exercise. Specifically, exercise that focuses on flexibility and stretching your muscles. Itâs recommended that you stretch at least once per day. You can do this by having a stretching routine or using a program like yoga.
It can be difficult to start exercising when your muscles feel tight. This can compound and make you feel worse for not exercising. Break that cycle, take the first step, and work toward your overall health.
Soaks. Warm baths with Epsom salts help relax your muscles. This can provide instant relief for muscle stiffness and prolong your muscle effectiveness.
Physical therapy. Physical therapy can help target rigidity and soothe stiffness. It can also help you find routines and exercises that work for you. Speech therapy can be used to treat face muscle rigidity.
Medications. Your doctor can recommend medications to help with muscle stiffness. Many medications can be used to treat Parkinsonâs disease. Your doctor will work with you to develop a treatment plan.
Show Sources
Davis Phinney Foundation for Parkinsonâs: âRIGIDITY AND PARKINSONâS: WHAT IT IS AND HOW TO TREAT IT.â
Learn More About Parkinsons Disease
Parkinsons Disease: The Essentials
If youre new to Parkinsons disease and would like a good overview to help you better understand the disease, please view our Parkinsons Disease: The Essentials presentation. Its a great place to get started with reliable and concise information.
Causes
The exact cause of Parkinsons is still unknown, but there is an enormous amount of research being done to learn more. This research has led scientists to formulate a number of theories on the cause of this disease.
Diagnosing
While there is no definitive test that can be taken to determine whether a person has Parkinsons disease, movement disorder specialists look for symptoms and use brain imaging technology to accurately diagnose Parkinsons.
Symptoms
Even though Parkinsons is classified as a movement disorderand its motor symptoms are the most discussed and well-knownthere are many non-motor symptoms that display in people with Parkinsons as well.
Treatments
As of today, there is no cure for Parkinsons disease. But there are many ways in which the disease can be treated to make symptoms more manageable.
Living With Parkinsons
Also Check: Parkinson’s Stem Cells Cost
Changes In Cognition And Parkinsons Disease
Some people with Parkinsons may experience changes in their cognitive function, including problems with memory, attention, and the ability to plan and accomplish tasks. Stress, depression, and some medications may also contribute to these changes in cognition.
Over time, as the disease progresses, some people may develop dementia and be diagnosed with Parkinsons dementia, a type of Lewy body dementia. People with Parkinsons dementia may have severe memory and thinking problems that affect daily living.
Talk with your doctor if you or a loved one is diagnosed with Parkinsons disease and is experiencing problems with thinking or memory.
How Do I Take Care Of Myself
If you have Parkinsons disease, the best thing you can do is follow the guidance of your healthcare provider on how to take care of yourself.
- Take your medication as prescribed. Taking your medications can make a huge difference in the symptoms of Parkinson’s disease. You should take your medications as prescribed and talk to your provider if you notice side effects or start to feel like your medications aren’t as effective.
- See your provider as recommended. Your healthcare provider will set up a schedule for you to see them. These visits are especially important to help with managing your conditions and finding the right medications and dosages.
- Dont ignore or avoid symptoms. Parkinsons disease can cause a wide range of symptoms, many of which are treatable by treating the condition or the symptoms themselves. Treatment can make a major difference in keeping symptoms from having worse effects.
Recommended Reading: What Tests Are Done For Parkinson’s Disease
Possible Causes Of Parkinsonism
For many types of parkinsonism, the exact cause isnt known. Genetic and environmental factors are both believed to play a role.
Parkinsons disease has been linked to exposure to pesticides and herbicides, as well as living close to industrial plants. Some genes are also associated with an elevated risk of developing Parkinsons.
Conditions that cause brain damage, like traumatic injuries, tumors, and exposure to certain toxins, are also potentially contributing factors to the development of parkinsonism.
Symptoms Of Parkinson’s Disease
These common symptoms of Parkinson’s disease often begin gradually and progress over time:
- Shaking or tremor
- Slowing of body movements
As the disease continues to progress, additional symptoms can occur such as slurred or soft speech, trouble chewing and/or swallowing, memory loss, constipation, trouble sleeping, loss of bladder control, anxiety, depression, inability to regulate body temperature, sexual dysfunction, decreased ability to smell, restless legs and muscle cramps.
You May Like: Mucuna Pruriens Dosage For Parkinson’s
Motor Circuit In Parkinson Disease
The basal ganglia motor circuit modulates the cortical output necessary for normal movement .
Signals from the cerebral cortex are processed through the basal ganglia-thalamocortical motor circuit and return to the same area via a feedback pathway. Output from the motor circuit is directed through the internal segment of the globus pallidus and the substantia nigra pars reticulata . This inhibitory output is directed to the thalamocortical pathway and suppresses movement.
Two pathways exist within the basal ganglia circuit, the direct and indirect pathways, as follows:
-
In the direct pathway, outflow from the striatum directly inhibits the GPi and SNr striatal neurons containing D1 receptors constitute the direct pathway and project to the GPi/SNr
-
The indirect pathway contains inhibitory connections between the striatum and the external segment of the globus pallidus and between the GPe and the subthalamic nucleus striatal neurons with D2 receptors are part of the indirect pathway and project to the GPe
The STN exerts an excitatory influence on the GPi and SNr. The GPi/SNr sends inhibitory output to the ventral lateral nucleus of the thalamus. Dopamine is released from nigrostriatal neurons to activate the direct pathway and inhibit the indirect pathway. In Parkinson disease, decreased striatal dopamine causes increased inhibitory output from the GPi/SNr via both the direct and indirect pathways .
Causes Of Parkinson Disease
Parkinson disease results from complex interplay of non-genetic and genetic factors. However, genetic factors are increasingly recognized as causative.
Typically Parkinson disease occurs in only one family member less commonly it occurs in several family members . Historically, about 15% of individuals with Parkinson disease have a positive family history of PD.
An estimated 5%-10% of all Parkinson disease is attributed to pathogenic variants in single genes . In addition to these variants, other genetic and environmental factors â known and unknown â may contribute to overall risk .
You May Like: Gdnf Gene Therapy Parkinson’s Disease
Tips To Keep Your Bladder Healthy
People rarely talk about bladder health, but everyone is affected by it. Located in the lower abdomen, the bladder is a hollow organ, much like a balloon, that stores urine. Urine contains waste and extra fluid left over after the body takes what it needs from what we eat and drink. Each day, adults pass about a quart and a half of urine through the bladder and out of the body.
As people get older, the bladder changes. The elastic bladder tissue may toughen and become less stretchy. A less flexible bladder cannot hold as much urine as before and might make you go to the bathroom more often. The bladder wall and pelvic floor muscles may weaken, making it harder to empty the bladder fully and causing urine to leak.
While you cant control everything that affects your bladder, here are 15 steps you can take to keep it as healthy as possible: