Parkinsons Protein Blueprint Could Help Fast
Researchers have solved a decade-long mystery about a critical protein linked to Parkinsons disease that could help to fast-track treatments for the incurable disease.
The research, published in Nature, has for the first time produced a live action view of the protein, called PINK1, in exquisite molecular detail.
The discovery explains how the protein is activated in the cell, where it is responsible for initiating the removal and replacement of damaged mitochondria. When the protein is not working correctly, it can starve brain cells of energy, causing them to malfunction and in the long term die, as happens to dopamine-producing cells in Parkinsons disease.
The discovery is the culmination of a project spanning eight years and provides the first detailed blueprint for the discovery and development of therapeutic agents that could help to slow or even stop the progression of Parkinsons disease.
Led by PhD student Mr Zhong Yan Gan and Professor David Komander, the multidisciplinary team at WEHI used innovative cryo-electron microscopy facilities and research to make the discovery.
Common Scale Of Motor Symptom Severity May Have Flaws: Study
A commonly used measure of how motor symptoms are affecting daily life could also for people in early stages of Parkinsons disease be taking into account the contribution of their non-motor symptoms, a study suggests. This is a likely reason for the discrepancies seen in evaluations made by patients
Aiming For Timely Diagnosis
As with many chronic conditions, earlier recognition of Parkinsons disease can help people experience an enhanced quality of life.
2016 statistics reflect that around 6.1 million people worldwide had Parkinsons, more than double than in 1990. However, this increase doesnt necessarily mean that Parkinsons disease is more common now.
The rise could be the result of increasing awareness of the disease, causing more people to contact a doctor about potential symptoms. The global population is , meaning more adults are in the at-risk age category for Parkinsons disease.
A of research findings suggests a timely diagnosis of Parkinsons disease can provide the following benefits, among others:
- support your right to know about the disease as soon as possible
- enable you to take an active role in your health and well-being surrounding disease management and treatment options
- allow you to engage with ongoing research into Parkinsons disease
- help you understand that the symptoms of Parkinsons arent just part of aging but a specific health condition
by The Scripps Research Institute
Parkinsons disease may be driven in part by cell stress-related biochemical events that disrupt a key cellular cleanup system, leading to the spread of harmful protein aggregates in the brain, according to a new study from scientists at Scripps Research.
Explore further
Also Check: Brain Stem Stimulation Parkinson’s
Advanced And Future Treatments For Parkinsons
While theres no cure for Parkinsons disease, recent research has led to improved treatments.
Scientists and doctors are working together to find a treatment or prevention technique. Research is also seeking to understand who is more likely to develop the disease. In addition, scientists are studying the genetic and environmental factors that increase the chance of a diagnosis.
Here are the latest treatments for this progressive neurological disorder.
In 2002, the FDA approved deep brain stimulation as a treatment for Parkinsons disease. But advances in DBS were limited because only one company was approved to make the device used for the treatment.
In June 2015, the FDA approved the
Support For People Living With Parkinsons Disease
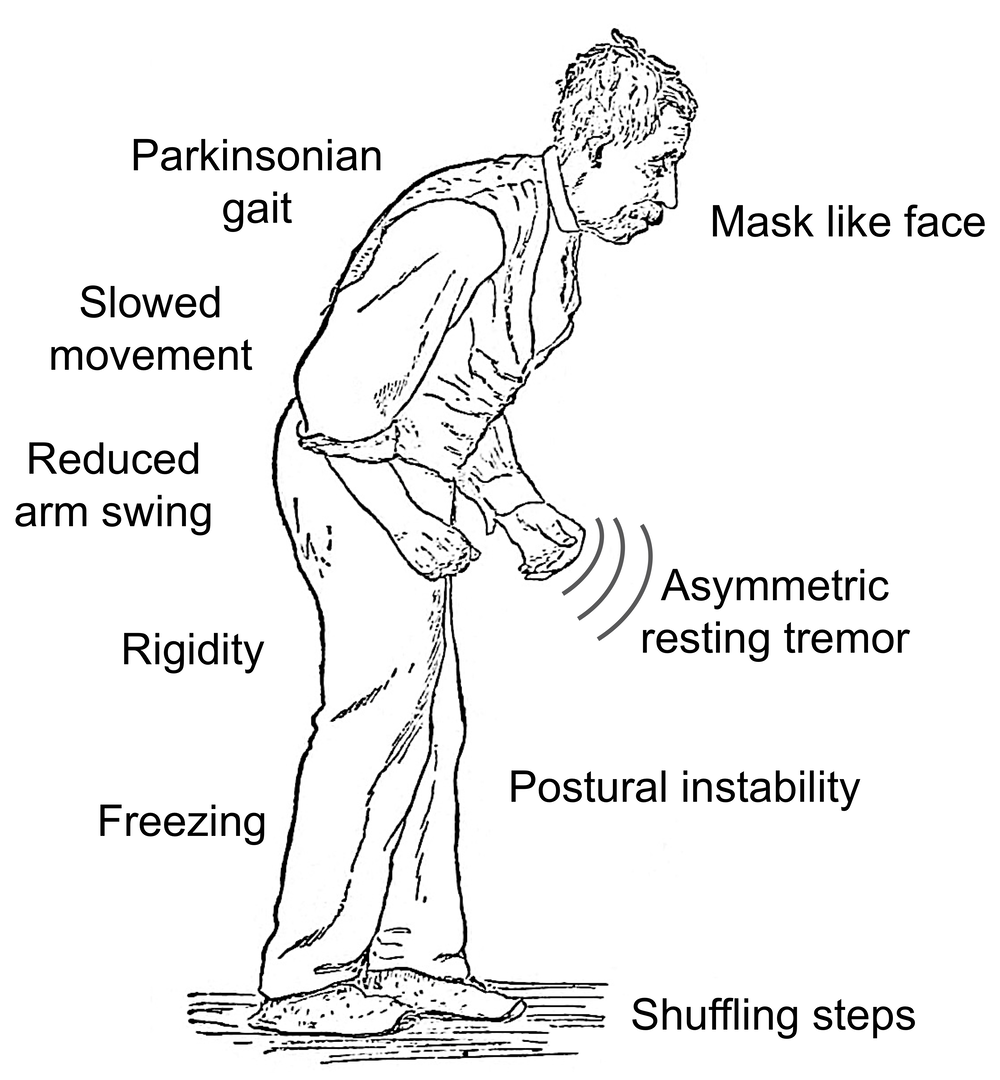
While the progression of Parkinsons is usually slow, eventually a persons daily routines may be affected. Activities such as working, taking care of a home, and participating in social activities with friends may become challenging. Experiencing these changes can be difficult, but support groups can help people cope. These groups can provide information, advice, and connections to resources for those living with Parkinsons disease, their families, and caregivers. The organizations listed below can help people find local support groups and other resources in their communities.
You May Like: What Medication Is Given For Parkinson’s
How Could Stem Cells Help People With Parkinsons
Stem cells are the parent cells of all tissues in the body. This means they can turn into any type of cell. The hope is that they will eventually be able to make these cells into specific types of cells, like dopamine-producing neurons, that can be used to treat Parkinsons disease. However, there are concerns that patients may have the same risk of increased involuntary movements as those who undergo fetal cell transplantation. And, like fetal cell transplantation, stem cell therapy is surrounded by moral and ethical controversy.
What The Research Data Tells Us
Over the past eight months, physicians and scientists with expertise in PD have gathered their preliminary data on the experience of people with PD with COVID-19. These findings have been published in journals for others to learn from. This type of work is not unique to PD of course. Physicians are collating the data on how COVID-19 affects different people with the entire array of human conditions.
Recommended Reading: Parkinson’s Seborrheic Dermatitis Treatment
Researchers From Johns Hopkins Create A Nanobody Capable Of Penetrating Brain Cells And Preventing Misshapen Proteins From Spreading Halting The Progression Of Neurocognitive Diseases
Image caption: The structure of alpha-synuclein clumps was disrupted by the nanobody PFFNB2. The debris from the disrupted clump is shown on the right.
- Office phone
- 410-955-8236
Researchers from the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine have helped develop a nanobody capable of getting through the tough exterior of brain cells and untangling misshapen proteins that lead to Parkinson’s disease, Lewy body dementia, and other neurocognitive disorders.
The research, published last month in Nature Communications, was led by Xiaobo Mao, an associate professor of neurology at the School of Medicine, and included scientists at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor. Their aim was to find a new type of treatment that could specifically target the misshapen proteins, called alpha-synuclein, which tend to clump together and gum up the inner workings of brain cells. Emerging evidence has shown that the alpha-synuclein clumps can spread from the gut or nose to the brain, driving the disease progression.
The researchers had to shore up the nanobodies to help them keep stable within a brain cell. To do this, they genetically engineered them to rid them of chemical bonds that typically degrade inside a cell. Tests showed that without the bonds, the nanobody remained stable and was still able to bind to misshapen alpha-synuclein.
What Causes Parkinsons Disease
The most prominent signs and symptoms of Parkinsons disease occur when nerve cells in the basal ganglia, an area of the brain that controls movement, become impaired and/or die. Normally, these nerve cells, or neurons, produce an important brain chemical known as dopamine. When the neurons die or become impaired, they produce less dopamine, which causes the movement problems associated with the disease. Scientists still do not know what causes the neurons to die.
People with Parkinsons disease also lose the nerve endings that produce norepinephrine, the main chemical messenger of the sympathetic nervous system, which controls many functions of the body, such as heart rate and blood pressure. The loss of norepinephrine might help explain some of the non-movement features of Parkinsons, such as fatigue, irregular blood pressure, decreased movement of food through the digestive tract, and sudden drop in blood pressure when a person stands up from a sitting or lying position.
Many brain cells of people with Parkinsons disease contain Lewy bodies, unusual clumps of the protein alpha-synuclein. Scientists are trying to better understand the normal and abnormal functions of alpha-synuclein and its relationship to genetic mutations that impact Parkinsons andLewy body dementia.
You May Like: What’s The Signs Of Parkinson’s Disease
The Latest In Nutrition And Parkinson’s Disease
Eating well can help you take control of your health. In fact, choosing to eat healthy foods can improve your Parkinsons disease symptoms. And some research suggests that sound nutritional choices could have disease-modifying effects, meaning that they could potentially slow PD progression. Changing your eating habits can be a challenge, but there are many small adjustments you can make to your diet that will add up to big benefits. Learning about them is the first step.
The following article is based on the latest research and a Parkinsons Foundation Expert Briefings about nutrition, hosted by John E. Duda, M.D., from Philadelphia VA Parkinsons Disease Research, Education & Clinical Center .
A New Era For Parkinsons Disease Treatment
March 2, 2022 | By
A non-invasive ultrasound treatment for Parkinsons disease that was tested in a pivotal trial led by University of Maryland School of Medicine researchers is now broadly available at the University of Maryland Medical Center .
Howard Eisenberg, MD, Dheeraj Gandhi, MD, MBBS, Paul Fishman, MD, PhD, Bert W. OMalley, MD.
The device, called Exablate Neuro, was approved in November by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration to treat advanced Parkinsons disease on one side of the brain. The approval was based on findings from the UMSOM clinical trial and effectively expands access to focused ultrasound beyond clinical trial participation.
Rapid Reversal of Symptoms
Focused ultrasound is an incisionless procedure, performed without the need for anesthesia or an in-patient stay in the hospital. Patients, who are fully alert, lie in a magnetic resonance imaging scanner, wearing a transducer helmet. Ultrasonic energy is targeted through the skull to the globus pallidus, a structure deep in the brain that helps control regular voluntary movement. MRI images provide doctors with a real-time temperature map of the area being treated. During the procedure, the patient is awake and providing feedback, which allows doctors to monitor the immediate effects of the tissue ablation and make adjustments as needed.
Patient: Focused Ultrasound Changed My Life
A New Era for Parkinsons Disease Treatment
You May Like: Is Parkinson’s Disease An Autoimmune Disease
Studies That Investigate The Relationship Between Pd And Covid
Apda Funds $235m In New Cutting
The American Parkinson Disease Association will fund a host of Parkinsons disease research projects for the coming year, including one that will examine the molecular underpinnings of anxiety and another that proposes a treatment for freezing of gait, for a total funding package of $2.35 million, a 25%
Read Also: Do Parkinson Patients Shake During Sleep
Medicines For Parkinsons Disease
Medicines can help treat the symptoms of Parkinsons by:
- Increasing the level of dopamine in the brain
- Having an effect on other brain chemicals, such as neurotransmitters, which transfer information between brain cells
- Helping control non-movement symptoms
The main therapy for Parkinsons is levodopa. Nerve cells use levodopa to make dopamine to replenish the brains dwindling supply. Usually, people take levodopa along with another medication called carbidopa. Carbidopa prevents or reduces some of the side effects of levodopa therapy such as nausea, vomiting, low blood pressure, and restlessness and reduces the amount of levodopa needed to improve symptoms.
People living with Parkinsons disease should never stop taking levodopa without telling their doctor. Suddenly stopping the drug may have serious side effects, like being unable to move or having difficulty breathing.
The doctor may prescribe other medicines to treat Parkinsons symptoms, including:
- Dopamine agonists to stimulate the production of dopamine in the brain
- Enzyme inhibitors to increase the amount of dopamine by slowing down the enzymes that break down dopamine in the brain
- Amantadine to help reduce involuntary movements
- Anticholinergic drugs to reduce tremors and muscle rigidity
Parkinsons Disease Diagnosis And Prognosis
A Parkinsons disease diagnosis cannot be determined by a single test but is rather assigned based on a patients medical history, symptoms, and a series of neurological and physical exams. Each patients Parkinsons disease prognosis is different, as the disease is unique to each person. While all patients will experience some degree of motor dysfunction, the severity and course that the disease takes may differ from person to person.
Also Check: Art Therapy Parkinson’s Disease
What New Treatments Are Being Developed
Thanks to the progress weve already made, new treatments are being tested in clinical trials that have the potential to slow, stop or even reverse Parkinsons.
These include:
- stem cell therapies, which aim to use healthy, living cells to replace or repair the damage in the brains of people with Parkinsons
- gene therapies, which use the power of genetics to reprogramme cells and change their behaviour to help them stay healthy and work better for longer
- growth factors , which are naturally occurring molecules that support the growth, development and survival of brain cells.
And were developing treatments that aim to improve life with the condition, including new drugs that can reduce dyskinesia.
What Are The Different Stages Of Parkinsons Disease
Each person with Parkinsons disease experiences symptoms in in their own unique way. Not everyone experiences all symptoms of Parkinsons disease. You may not experience symptoms in the same order as others. Some people may have mild symptoms others may have intense symptoms. How quickly symptoms worsen also varies from individual to individual and is difficult to impossible to predict at the outset.
In general, the disease progresses from early stage to mid-stage to mid-late-stage to advanced stage. This is what typically occurs during each of these stages:
Early stage
Early symptoms of Parkinsons disease are usually mild and typically occur slowly and do not interfere with daily activities. Sometimes early symptoms are not easy to detect or you may think early symptoms are simply normal signs of aging. You may have fatigue or a general sense of uneasiness. You may feel a slight tremor or have difficulty standing.
Often, a family member or friend notices some of the subtle signs before you do. They may notice things like body stiffness or lack of normal movement slow or small handwriting, lack of expression in your face, or difficulty getting out of a chair.
Mid stage
Mid-late stage
Standing and walking are becoming more difficult and may require assistance with a walker. You may need full time help to continue to live at home.
Advanced stage
Recommended Reading: Yopd Life Expectancy
Recommended Reading: Ejercicios Para Personas Con Parkinson
The Motor Network In Parkinsons Disease And Dystonia: Mechanisms Of Therapy
open to eligible people ages 21-75
This is an exploratory pilot study to identify neural correlates of specific motor signs in Parkinsons disease and dystonia, using a novel totally implanted neural interface that senses brain activity as well as delivering therapeutic stimulation. Parkinsons disease and isolated dystonia patients will be implanted unilaterally or bilaterally with a totally internalized bidirectional neural interface, Medtronic Summit RC+S. This study includes three populations: ten PD patients undergoing deep brain stimulation in the subthalamic nucleus , ten PD patients with a globus pallidus target and five dystonia patients. All groups will test a variety of strategies for feedback-controlled deep brain stimulation, and all patients will undergo a blinded, small pilot clinical trial of closed-loop stimulation for thirty days.
San Francisco, California
You May Like: Similar To Parkinsons
Can Eating Well Alter The Course Of Pd
Scientists know a lot about the molecular changes that underlie Parkinsons. You may have heard of alpha-synuclein, the protein that forms clumps in brain cells, oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, and inflammation. The search is intense for therapies that can stop or reverse these processes. Can nutrition or dietary choices do anything to change them or alter the course of PD?
Some laboratory and animal research suggest that diet could have an effect, especially plant-based foods like fruits, vegetables, legumes, nuts and seeds. Every plant-based food contains hundreds of chemicals called phytochemicals. These are not nutrients, but substances that may, alone or in combination, affect many of the processes thought to be involved in PD including oxidation, chronic inflammation, protein aggregation and mitochondrial dysfunction.
Phytochemicals have not been proven to change disease progression in people with PD, but neither is there typically any harm in eating a diet that includes whole, unprocessed plants. This diet has proven benefits for preventing heart and vascular disease and can reduce PD symptoms, like constipation and risk of cognitive change.
Don’t Miss: Big Physical Therapy For Parkinson’s
Latest Research On Covid
UPDATE: This post has been updated with the latest information available.We will continue to keep this post up-to-date as new information develops.
As citizens of the world, we all continue to grapple with the COVID-19 pandemic. And as members of the Parkinsons disease community, we continue to have specific concerns about COVID-19 and how it relates to PD. There is so much information out there, some of it misinformation, so it is important to rely on credible, trusted sources. In this post, I will cover the latest information that investigates the relationship between PD and COVID-19.