Types Of Dopamine Agonist Drugs
Below are the types of dopamine agonist drugs. The generic names are written in bold and the brand names are written underneath in bullet points.
Pramipexole
- Mirapexin prolonged release
- Pipexus
- Ralnea XL
- Requip
- Requip XL
- Spiroco XL
- Ipinnia XL
- Raponer XL
- Repinex XL
- Ropilynz XL
Rotigotine
- Apo-go pre-filled pen for Intermittent injection
- Dacepton cartridge for Intermittent injection
- Apo-go pre-filled syringe for infusion
- Dacepton Vial
Dopamine Agonist Withdrawal Syndrome In Parkinsons
Some remedies are worse than the disease. Publilius Syrus
Each patient carries his own doctor inside him. Norman Cousins
Summary: Dopamine agonists are widely used in the treatment of Parkinsons, especially as a first-line therapy. Some patients on a dopamine agonist experience side-effects that require either tapering or discontinuation of the drug. First described in 2010, dopamine agonist withdrawal syndrome is a complication of ~20% of Parkinsons patients who are either lowering or stopping the dopamine agonist. DAWS presents as a cluster of physical and behavioral symptoms . There is no known standard-of-care in dealing with DAWS in Parkinsons. Presented here is a brief overview of DAWS in Parkinsons including dopamine agonists, clinical description, risk factors and prevalence, mechanism of action, treatment/management, and key publications.
To heal illness, begin by restoring balance. Caroline Myss
I enjoy convalescence. It is the part that makes the illness worth while. George Bernard Shaw
What both cases shared were prominent psychiatric symptoms, poor response to both additional carbidopa/levodopa and psychiatric medication however, both had rapid improvement in their new symptoms when placed back on the DA. The majority of DAWS symptoms are presented in the the Table below.The secret of learning to be sick is this: Illness doesnt make you less of what you were. You are still you. Tony Snow
Key References:
Benefits Of Dopamine Agonists As A Frontline Treatment
The advantages of dopamine agonists over l-dopa are several. They are not dependent upon a transporter for entry or absorption into the brain therefore, their effects are not influenced by food they do not require metabolic conversion for their therapeutic effects several dopamine agonists have long plasma half lines and unlike l-dopa, they do not produce free radicals upon metabolism and some dopamine agonists can be given by injection. Some specific dopamine receptors exist only in the central nervous system, allowing in principle the design of drugs to target specific brain neurons without peripheral side effects. Apomorphine is an injectable dopamine agonist with a broad receptor profile of activity that produces an acute anti-Parkinsonian effect, but is too rapidly metabolized and short acting for general use.
Read Also: Is Restless Leg Syndrome Related To Parkinson’s
Ways To Boost Dopamine
Dopamine is a neurotransmitter thats great to have in abundance. When you do, your brain is flooded with pleasurable feelings and a sense of satisfaction and reward.
While increasing your natural dopamine wont prevent or stop the progression of Parkinsons disease, it might help stave off early symptoms of the disorder. For some people, natural dopamine boosts may be helpful alongside other treatments.
What Are Dopaminergic Antiparkinsonism Agents
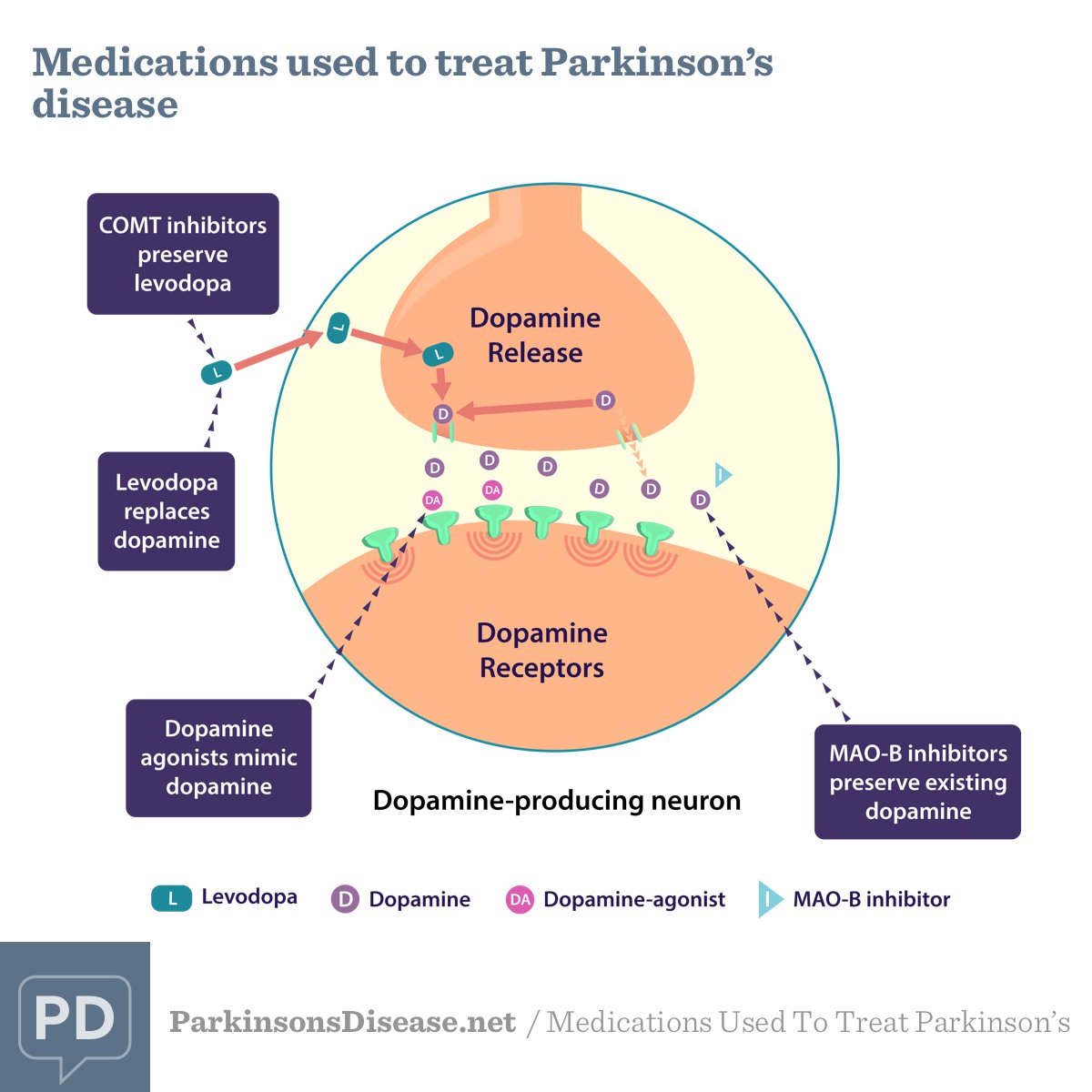
Dopaminergic antiparkinsonism agents aim to replace dopamine or prevent the degradation of dopamine.Antiparkinson drugs that aim to replace dopamine in the central nervous system, either release dopamine or mimic the action of dopamine. Drugs that replace dopamine are generally given with peripherally acting dopa carboxylase inhibitors, to prevent the metabolism of levodopa to dopamine peripherally. Dopamine receptor agonists bind to dopamine receptors and mimic the action of dopamine.Selective monoamine oxidase inhibitors bind to the enzyme MAO-B and prevent dopamine from being broken down. Antiparkinson agents are used to treat Parkinson’s disease, which is a degenerative disorder of movement that occurs due to dopamine deficiency in the brain, particularly in the basal ganglia.
Recommended Reading: How Long Will A Person Live With Parkinson’s Disease
Sudden Onset Of Sleep
Prominent warnings have been in place for daytime drowsiness since 2001 when sudden onset of sleep was reported as an adverse effect associated with dopamine receptor agonists. Patients were to be advised that they should avoid driving or operating machinery until any sudden drowsiness problem experienced was resolved.
What Are The Benefits Of Dopamine Agonists For Parkinsons Disease
Dopamine agonist effects can make life easier for people with Parkinsonâs disease by treating symptoms. They can reduce movement problems like trembling hands, slow walking, and stiff limbs. Other benefits of dopamine agonists for Parkinsonâs disease include:
Fewer side effects. Levodopa can cause uncontrollable body movements over time. Dopamine agonists are less likely to cause this.
Dopamine agonists are helpful on their own during the early years of Parkinsonâs disease when symptoms may not be severe. People diagnosed with Parkinsonâs disease early in life may start out taking only dopamine agonists. This can reduce the amount of uncontrollable movement that comes with taking levodopa for a long time.
No dietary restrictions. Medications like levodopa can be less potent if youâre eating lots of foods that are high in protein. Your body absorbs dopamine agonists in a different way, though, that doesnât interfere with your diet.
They can help levodopa be more effective. Levodopa or other medications for Parkinsonâs disease can wear off before itâs time for another dose. Dopamine agonists last longer and help manage symptoms when taken alongside levodopa.
Recommended Reading: Parkinson’s Disease Causes Death
Benzylhydrazine And Blma5 Inhibit Intestinal Bacteria In Vitro
The intestinal contents of three male SD rats were collected and added to 20mL of sterilized anaerobic medium per gram of intestinal contents. After mixing and filtering, the intestinal contents were incubated for 1h at 37°C, and the corresponding concentration of benzylhydrazine was added at final concentrations of 0, 50, and 100µM. The samples were incubated for 12h at 37°C under anaerobic conditions. Each sample was diluted by 103, 104, and 105-fold. Then, these samples were coated on nutrient agar plates and cultured at 37°C overnight. The colonies were counted and calculated according to the dilution factor. The experimental procedure to test the effect of BLMA5 on inhibiting the growth of the intestinal bacteria in vitro was consistent with the above.
What Are Some Possible Side Effects Of The Dopamine Receptor Agonists
Dopamine agonists have many of the side effects of other dopaminergic agents. These include hallucinations and orthostatic hypotension . Leg swelling can also occur. Dopamine agonists can induce sleepiness as well as sleep attacks and must be used with great caution in those patients who are driving. Compulsive behavior is a well described side effect and could take the form of over-shopping, over-eating, gambling or hyper-sexuality.
In some patients, a withdrawal syndrome can be experienced as the dopamine agonist is lowered and stopped. Symptoms of the withdrawal syndrome can include anxiety, pain, depression, and even suicidality. Patients should be warned about the possibility of experiencing withdrawal when a dopamine agonist is tapered so if they experience these symptoms, they can modify how the medication is weaned off.
Recommended Reading: What Are Complications From Parkinson’s Disease
On Time Without Troublesome Dyskinesia
To provide patients with increased ON time without dyskinesia, 5/6 drugs were significantly more efficacious than the placebo . No significant difference was observed among these drugs. The top three ranked drugs were apomorphine , pramipexole_IR , and ropinirole_PR .
Figure 2. Forest plot of primary outcome on time without troublesome dyskinesia. The size of the node corresponds to the weight in the comparison. MD, mean difference CrI, credible interval.
Figure 3. The surface under the cumulative ranking curve for competing interventions based on ON time without troublesome dyskinesia, on time, OFF time, UPDRS III, UPDRS II, and TEAE. The x-axis represents the ranking, and the y-axis represents cumulative probabilities. The greater the surface under the cumulative ranking, the greater the benefit of the intervention. SUCRA, surface under the cumulative ranking curve.
Are There Different Types Of Dopamine Agonists
There are several different kinds of dopamine agonists that people with Parkinsons may be prescribed.
These include apomorphine, ropinirole and pramipexole. Some forms also have branded names.
Patient Information Leaflets and the Summary of Product Characteristics can tell you more about individual types of dopamine agonists.
Dopamine agonists can be administered in different ways orally, transdermal and subcutaneously .
Pavese says that different patients may be prescribed different forms of the medication: Oral or transdermal dopamine agonists are generally prescribed to younger patients in the early stages of the disease with mild to moderate symptoms, or to more established patients as an adjunct to levodopa preparations to provide a better control of motor symptoms without significantly increase the doses of the former.
In these cases, the advantage of dopamine agonists is that they are all available in long-acting preparations that can be taken once a day. In more advanced patients with motor fluctuations, apomorphine is administered through a subcutaneous pump that provides a continuous delivery of the drug during the day and a better control of the motor symptoms.
Recommended Reading: Tai Chi Exercises For Parkinson’s Disease
Fast Facts About Dopamine Agonists
- mimic the actions of dopamine in the body to aid in symptom relief
- useful for early treatment of Parkinsons symptoms, especially in people less than 60 years old
- fewer movement-related side effects compared to levodopa for Parkinsons treatment
- newer DA medications bind more selectively to dopamine receptors and have less heart-related side effects
- extended release formulations of newer DA medications lower the burden of taking multiple doses throughout the day
- manipulation of dopamine can cause serious side effects including compulsive behavior and other mental health problems
- can cause dizziness, fainting, or sudden sleepiness which is dangerous for tasks that require alertness like driving
- can cause withdrawal syndrome including sudden high fever, muscle stiffness, kidney failure, and other problems with sleep, mood, and pain if stopped abruptly
indicates there are two major groups of dopamine receptors, D1 and D2, with subgroups under them which are responsible for many behavioral, hormonal, and muscle related effects in our body.
The D1 group includes D1 and D5 receptors, and the D2 group includes D2, 3, and 4.
Each is found in different areas throughout our body and responsible for important actions from how we move to how we learn. Lack of dopamine in our cells affects our bodies in many negative ways.
Summing Upthe Best Dopamine Supplements Of 2021
Dopamine is a critical neurotransmitter that plays an essential role in our mental health as well as our physical health. When you have low levels of dopamine, you may experience a loss of motivation, symptoms of depression, and an inability to focus. It can also lead to low libido.
As with any supplement, speak to your doctor before you try any dopamine supplements listed above.
Don’t Miss: Parkinson’s And Memory Loss
Possible Neuroprotective Mechanisms Of Vitamin D In Pd
VDR belongs to the intranuclear receptor superfamily, composing of eight coding exons and three alternative 5 noncoding exons, spanning over 105kb, on chromosome 12 . The most widely studied biallelic polymorphic sites are BsmI, TaqI, ApaI, and FokI. Substantial researches have been carried out to explore the relationship between these allelic variations and PD. Kim et al. detected VDR gene BsmI polymorphisms in over 300 Korean individuals . The frequency of VDR genotype bb was significantly increased in the PD patients than that in the controls . The bb genotype was more common in PD patients with postural instability and gait difficulty than in the PD patients with tremor . A meta-analysis showed that VDR BsmI and FokI polymorphisms were associated with the risk of PD , and VDR FokI genotype was associated with the severity and cognitive decline of PD . Muscular and motor impairments, which can seriously affect the motor behaviour, were found in the VDR-knockout mice , indicating that vitamin D may be involved in the pathogenesis of PD.
Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor is a protein that is essential for the maintenance and survival of dopaminergic neurons and can inhibit microglial activation . Many animal studies showed that 1,25-2-D3 could enhance the endogenous GDNF expression in vitro and in vivo and inhibit the glial cell activation to protect dopaminergic neurons from immune inflammation .
Also Check: What Are The Complications Of Parkinsons Disease
Possible Neuroprotective Mechanisms Of Vitamin C In Pd
There is evidence that ascorbic acid can protect against both levodopa toxicity and the MPTP neurotoxicity . Vitamin C can increase the production of dihydroxyphenylalanine . Seitz et al. noted overproduction of DOPA in a dose-dependent manner after incubation of the human neuroblastoma cell line SK-N-SH with ascorbic acid for 2 hours. Additionally, the gene expression of tyrosine hydroxylase increased threefold after incubation with ascorbic acid for 5days. The scholars speculated that ascorbic acid may be effective in the treatment of early-stage PD .
Vitamin C can improve the absorption of levodopa in elderly PD patients with a poor levodopa bioavailability . Previous studies showed that ascorbic acid can reduce the levodopa dosage under the premise of equal efficacy . Combination of anti-PD drugs and vitamin C may be more effective for alleviating the symptoms of PD.
Recommended Reading: Beginning Symptoms Of Parkinson’s
Taking Dopamine Agonist Drugs: Pramipexole And Ropinirole
Below we have included the different forms of pramipexole medication and an overview of how to take them.
The most recent and complete information on your specific drug will be on your patient information leaflet that comes with your medication packet. Always read it carefully before you start your treatment.
For detailed information you should follow the advice of your specialist or Parkinsons nurse about how to take pramipexole so that it works well for your Parkinsons.
Pramipexole drugs are also used to help your symptoms when your levodopa medication causes you to experience wearing off and dyskinesia. This could be motor fluctuations, or wearing off before your next dose of levodopa is due.
Examples Of Ergoline Da
Bromocriptine . Approved to treat Parkinsons disease and dopamine-related hormonal conditions like hyperprolactinemia and related conditions, Bromocriptine is a prescription drug, available as a tablet or capsule, that comes in both generic and brand versions. Its rarely used today.
Cabergoline.This prescription medication is available as a tablet used to treat hyperprolactinemia, a condition in which high levels of the hormone prolactin are produced by the pituitary gland. Increased prolactin levels can interfere with womens menstrual cycle, ovulation, and milk production. In men, it can cause reproductive and sexual problems.
Read Also: Best Walking Cane For Parkinson’s
Dopamine Agonist Withdrawal Syndrome
Patients on dopamine agonists frequently experience side effects such as hallucinations, cognitive dysfunction, and impulse control disorders. If these side effects become debilitating, it may be necessary to taper patients off their dopamine agonists. However, it has been observed that a subset of patients who undergo tapering of dopamine agonists develop anxiety, diaphoresis, agitation, and a craving for the dopamine agonists. This putative withdrawal syndrome has been termed dopamine agonist withdrawal syndrome . Other symptoms include psychiatric symptoms, insomnia, daytime fatigue, autonomic symptoms, and generalized pain. DAWS was first described in 2010 in the course of a prospective study looking at the motor and nonmotor symptoms of patients with Parkinson’s disease . Out of the 93 patients studied, 26 underwent dopamine agonist taper and 5 of these patients developed a constellation of symptoms felt to comprise DAWS. The onset of the symptoms in all patients correlated with the withdrawal of dopamine agonists, which is why it was felt less likely to be simply a nonmotor symptom of PD itself. The patients who developed DAWS could not be treated with benzodiazepines, antidepressants, or cognitive behavioral therapy.
Philippe Chanson, Dominique Maiter, in, 2017
Effects Of Bbr And Dhbbr On Dopamine Levels In Mouse Dopamine Neurons
After the mouse dopamine neuron cells were cultured to stability , trypsin was added for digestion. Then, the cells were counted and plated in 48-well microplates. Next, the cells were incubated in a 5% CO2 and 37°C cell incubator for 24h, with the addition of BBR or dhBBR as the treatment group . After 6h of culture, the cells were removed for disruption, and the LC-MS/MS method was used for detection of dopamine levels .
You May Like: Do You Get Pain With Parkinson’s
Compulsive Behaviors And Gambling
Dopamine agonist treatment of Parkinson’s disease patients has been linked to compulsive eating,102 excessive gambling,103 compulsive shopping, and pathologic hypersexuality,104 with resolution of these problems associated with reduction of the dose of dopamine agonists. In one study, the lifetime prevalence of pathologic gambling in Parkinson’s disease patients was 3.4% and the current prevalence 1.7%.104 Seven percent of patients on pramipexole and 12% of patients on ropinirole were affected. In a similar study, the lifetime prevalence of pathologic hypersexuality in Parkinson’s disease was 2.4% and the current prevalence of 2.0%.105 The current prevalence of compulsive shopping was 0.7%. Thus, the total lifetime prevalence for any impulse control disorder developing in Parkinson’s disease patients on dopamine agonists was as high as 13.7%.
How Dopamine Agonists Work
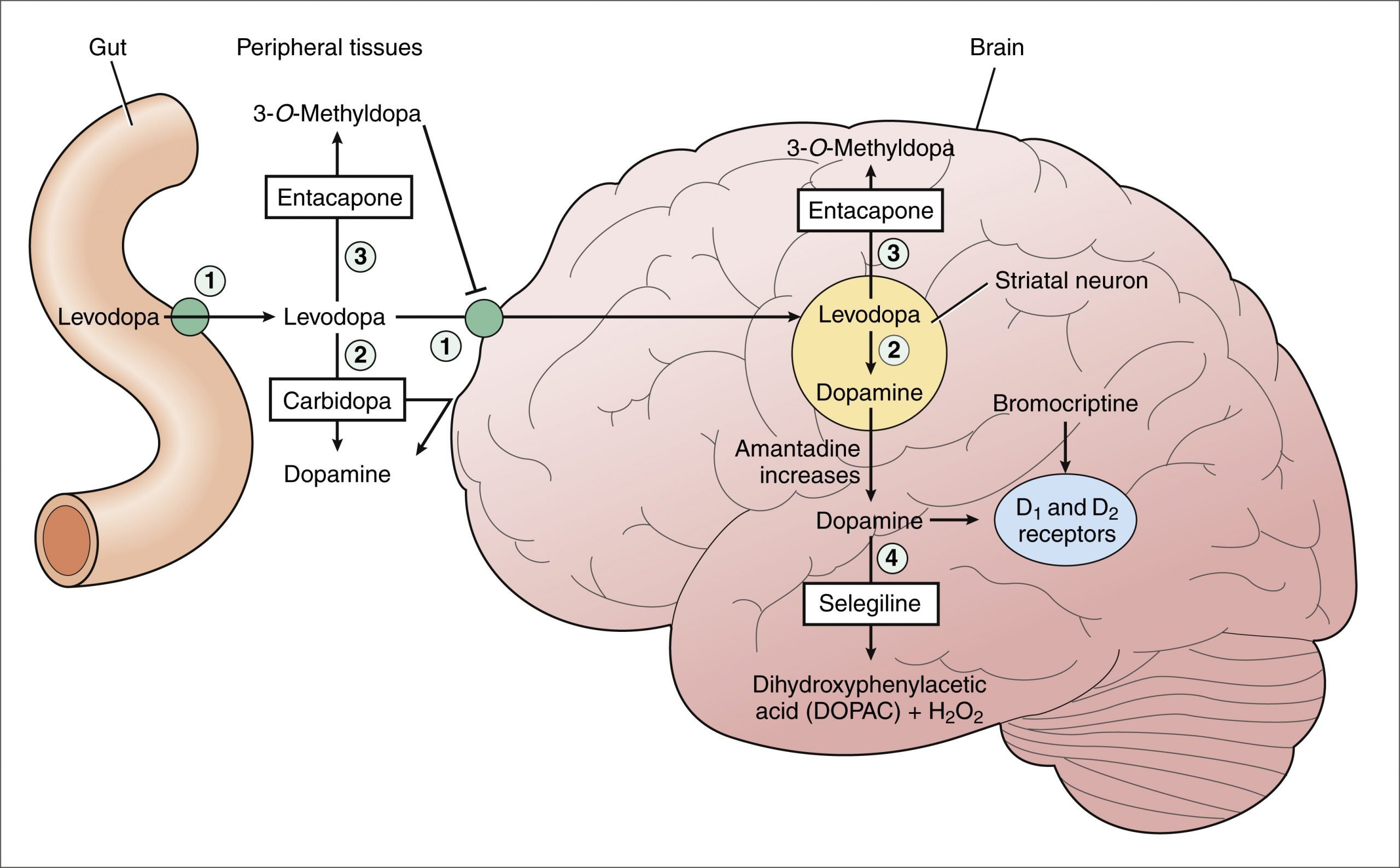
Dopamine agonists work by mimicking the action of dopamine. They bind to dopamine receptors found on the nerve cells that regulate motor function and body movement. There are five types of dopamine receptors belonging to two dopaminergic subfamilies . The dopaminergic receptor subfamily D1 consists of D1 and D5 receptors, generally associated with dyskinesia. The dopaminergic receptor subfamily D2 includes D2, D3, and D4 receptors, which are related to symptoms of movement disorders. Dopamine agonists primarily target agonist activity specific to D2 subfamily receptors.
Also Check: Does Parkinson’s Disease Cause Dizziness
A Quarter Of A Century
The first paper on this issue was Vogel and Schiffter in the journal Pharmacopsychiatria entitled Hypersexuality a complication of dopaminergic therapy in Parkinsons disease.
Publications describing incidences of pathological gambling appeared in the peer reviewed academic literature in 2000 . This reported that 5% of patients treated with l-dopa suffered from pathological gambling. Many neurologists reading this dismissed the data on the basis that this behaviour would have been noticed in the 20 years or more that l-dopa had been used as the mainstay of treatment for Parkinsons disease.
In 2000, Seedat et al. published Pathological gambling behaviour: emergence secondary to treatment of Parkinsons disease with dopaminergic agents in Depression and Anxiety.
Gschwandtner et al. published Pathologic gambling in patients with Parkinsons disease which reported gambling occurring in response to 2 patients becoming addicted to their dopaminergic medication. Two further articles were published in 2002 in little known journals with one paper suggesting that the patients pre-morbid personality may have been a risk factor for treatment to amplify sexual compulsions and gambling.
Several papers published in 2004 reporting impulse control disorders being experienced in response to Parkinsonian treatment but none appeared in mainstream journals.
In March 2006, the BNF reported an increase in libido as a side effect of pramipexole.