What Risks Come Along With Doing Deep Brain Stimulation
DBS is a surgical procedure. As with any surgery there are some risks associated with it. Some of the risks of DBS include infection and bleeding. Your neurosurgeon may discuss some additional risks with you. Studies have shown that any risks are relatively small, but they should be kept in mind when considering DBS.
How Does It Work
DBS changes brain activity in a controlled way, and its effects are reversible.
DBS may help the brain to release more adenosine triphosphate , an energy-carrying molecule that occurs in the cells of all living things. This release of ATP leads to a buildup of adenosine.
Activating the adenosine A1 receptor triggers a process that reduces both tremor and any adverse effects that DBS may cause. This works because the process dampens excitatory transmission in the thalamus.
The DBS procedure does not destroy any nerve cells or healthy brain tissue, but there can be some adverse effects.
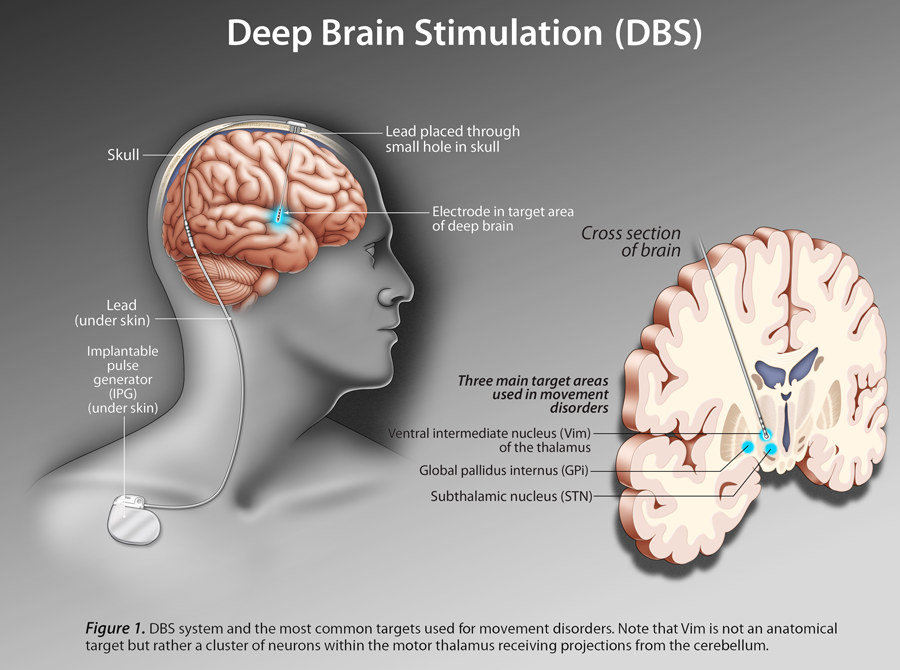
Surgery To Implant The Deep Brain Stimulation Device
Deep brain stimulation requires the surgical implantation of an electrical device into the brain. A neurosurgeon uses imaging scans to pinpoint the right spot in the brain for implanting the electrode.
When surgeons have determined the correct location, they create a small opening in the skull and insert a thin, insulated wire, through which they insert the electrode. Surgery to implant the electrode takes about four hours and requires general anesthesia. You may then stay overnight in the hospital for observation.
The next day, doctors perform the second part of the surgery, which involves connecting the insulated wire to a battery-operated pulse generator that is implanted under the skin near the collarbone. Most people can return home after this procedure.
Several days after the surgery, you meet with your neurologist, who programs the pulse generator. Pushing a button on an external remote control sends electrical impulses from the pulse generator to the electrode in the brain.
People who use deep brain stimulation work closely with their neurologist to find the combination of settings that best controls their symptoms. After several visits, they are able to control the strength of the electrical impulses on their own. Following this adjustment period, most people require only occasional maintenance visits.
Recommended Reading: Alternative Treatment For Parkinson’s Disease
What Happens During Deep Brain Stimulation Surgery
Patients are awake under light sedation during the deep brain stimulation surgery for two important reasons. It allows your neurosurgeon to monitor electrical activity in the brain during the procedure and to test to make sure the wires are in the right place. Deep Brain Stimulation surgery is usually performed in two stages:
- Stage 1: Your neurosurgeon makes a very precise roadmap of your brain with images obtained through an MRI or CT scan. A stereotactic frame – which keeps your head in a fixed position – is a three-dimensional guidance system that helps your surgeon pinpoint areas deep inside your brain. Once the target areas are located, your surgeon implants the wires, or electrodes, in your brain. Patients usually stay in the hospital for 1-2 days after this surgery.
- Stage 2: Your neurosurgeon implants the battery pack and connecting wires in the chest 10 to 14 days after Stage 1. Patients are usually awake under general anesthesia and can go home the same day.
The generator that controls the electrical impulses in your brain is turned on two weeks after the implantation. Some patients are concerned about being awake during surgery. If you are concerned, we invite you to speak to and connect with prior patients to learn more about the experience. The surgery can be done asleep using our advanced imaging capabilities for patients who do not want to be awake.
You Are About To Exit The Abbott Family Of Websites For A 3rd Party Website
Links which take you out of Abbott worldwide websites are not under the control of Abbott, and Abbott is not responsible for the contents of any such site or any further links from such site. Abbott is providing these links to you only as a convenience, and the inclusion of any link does not imply endorsement of the linked site by Abbott.The website that you have requested also may not be optimized for your screen size.
Read Also: Microbiome Diet For Parkinson’s Disease
What Is Deep Brain Stimulation
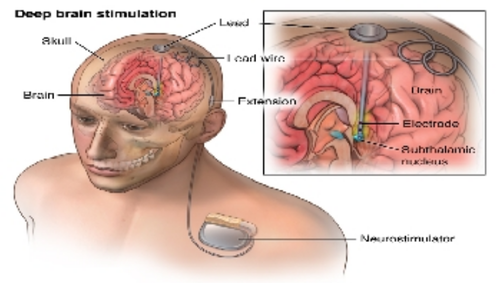
DBS is a surgical procedure in which thin electrodes are implanted into parts of the brain that control movement. The electrodes deliver tiny electrical pulses to these brain regions. This allows the brain to maintain normal movement activity with a lower dose of levodopa. The electrodes are connected by a wire to a pulse generator that is implanted under the skin in the chest. The electrodes and the wire are also under the skin, so that no part is visible externally.
Quality Care From A Team Of Medical Professionals
Doctors Michael Okun and Kelly Foote like to joke that theyre an unlikely pair because, in the medical world, surgeons and non-surgeons dont usually mix. However unusual their partnership, the co-founders of the University of Florida Center for Movement Disorders make an excellent team.
According to Drs. Okun and Foote, a patient receives the best care when a team of medical practitioners from different disciplines gets together to talk behind the patients back. At the Center for Movement Disorders, Okun and Foote have designed a model that allows patients to come to one place and see every type of doctor they need.
This model is not only more convenient for patients, but it also enables a uniquely powerful collaboration of minds. A team comprised of a neurologist, neurosurgeon, psychiatrist, neuropsychologist, physical therapist, occupational therapist, speech and swallowing expert, and social worker meet with the patient and then come together to discuss the individual case.
This interdisciplinary model facilitates a thorough pre-surgery workup, adequately prepares the patient for the procedure, and leads to a more accurate understanding of the patients brain.
Ultimately, Drs. Foote and Okun strive to achieve a treatment model that leads to the best possible patient outcomes.
Read Also: Is Memory Loss A Symptom Of Parkinson’s
Thanks For Signing Up
We are proud to have you as a part of our community. To ensure you receive the latest Parkinsons news, research updates and more, please check your email for a message from us. If you do not see our email, it may be in your spam folder. Just mark as not spam and you should receive our emails as expected.
Deep Brain Stimulation For Parkinsons Disease
For people with severe motor symptoms of Parkinsons disease that are not adequately controlled by medication, a treatment called deep brain stimulation may offer some relief.
Deep brain stimulation requires the surgical placement of a small conductor called an electrode in the brain. The electrode delivers electrical stimulation that blocks the nerve signals that cause tremors.
Specialists at NYU Langones Center for Neuromodulation perform more than 100 deep brain stimulation procedures each year. Our neurologists, neurosurgeons, and psychiatrists provide a thorough evaluation to ensure youre a good candidate for the procedure.
You May Like: Medications For Parkinson’s Patients
Featured In This Video
The Froedtert & the Medical College of Wisconsin regional health network is a partnership between Froedtert Health and the Medical College of Wisconsin supporting a shared mission of patient care, innovation, medical research and education. Our health network operates eastern Wisconsin’s only academic medical center and adult Level I Trauma Center at Froedtert Hospital, Milwaukee, an internationally recognized training and research center engaged in thousands of clinical trials and studies.
ATTENTION: If you speak another language, assistance services, free of charge, are available to you. Call: 414-805-3000
What To Think About
A neurologist with special training in Parkinson’s disease is most often the best kind of doctor to make a decision about deep brain stimulation. If you might benefit from the operation, your neurologist can refer you to a brain surgeon with experience doing the surgery.
Deep brain stimulation may be considered as an addition to levodopa therapy, not a replacement for it. It does not cure Parkinson’s disease and does not eliminate the need for medicine. The surgery can help maintain and extend the benefits of levodopa therapy. But it should not be considered for people with Parkinson’s disease who also respond poorly to levodopa therapy.
Because of an increased risk of falling in people who have DBS, it’s a good idea to understand the ways you can prevent falls after the surgery.
One of the possible advantages of deep brain stimulation over “lesional” surgery for Parkinson’s disease is that it can be changed or reversed. The effects of lesional surgery, which involves creating a lesion or intentionally destroying a small portion of the brain, are permanent, but the electrodes used in deep brain stimulation can be adjusted, turned off, or removed if they cause problems.
Deep brain stimulation for tremor caused by multiple sclerosis is still experimental, expensive, and not widely available.
Don’t Miss: Parkinson’s Disease Causes Death
What Are The Benefits Of Deep Brain Stimulation Therapy
There are various benefits of the Deep Brain Stimulation procedure. These are:
- Regulatory approved procedure: The Deep Brain Stimulation procedure is approved by various regulatory authorities such as USFDA. Apart from Parkinsons, DBS is authorized to treat essential tremor, dystonia, obsessive-compulsive disorder, and epilepsy.
- Advanced procedure: DBS procedure is an advanced treatment option that improves the overall quality of life of the patient.
- Effective: DBS procedure is quite effective. Approximately 85% of people experience a significant reduction in their Parkinsons symptoms.
- Improves quality of life: DBS improves the quality of life. People began to experience confidence in the public after undergoing DBS. Further, they are less dependent on others for performing daily activities.
- Reduce the dose of medications: The initial treatment of Parkinsons disease is medications. As the conditions progress, the doctor either adds the medications or increases the dose of current medications. However, these medications have side effects. DBS helps in reducing the dose of medications and lowers side effects.
- Adjustable: The DBS is adjustable. As the disease progresses, the surgeon can adjust the strength of impulse without the need for further surgery.
- Reversible: DBS procedure is reversible. If the patient does not require DBS, the surgeon can either cut-off the impulse or remove the complete device.
What To Expect After Deep Brain Stimulation
Patients considering deep brain stimulation should have realistic expectations for results. The surgery relieves symptoms, but it is not a cure. It can also take up to six months of adjustments after surgery for some patients to achieve optimal results.
- More than 70 percent of patients with Parkinson’s Disease experience significant improvements to their motor function, or how they control their body movements. They may gain up to 4.5 hours of good “on time.”
- Results can be dramatic in patients with dystonia. Some improvement occurs in 50 to 70 percent of patients.
- In patients with essential tremor, 72 to 85 percent of patients see improvement.
You May Like: Games For Parkinson’s Patients
How Deep Brain Stimulation Therapy Works
Doctors recommend Deep Brain Stimulation in conditions such as Parkinsons disease, dystonia, essential tremor, epilepsy, and obsessive-compulsive disorder. The procedure is complex and carries risks. The risks are bleeding, stroke, infection, headache, seizures, and pain and swelling at the implantation site.
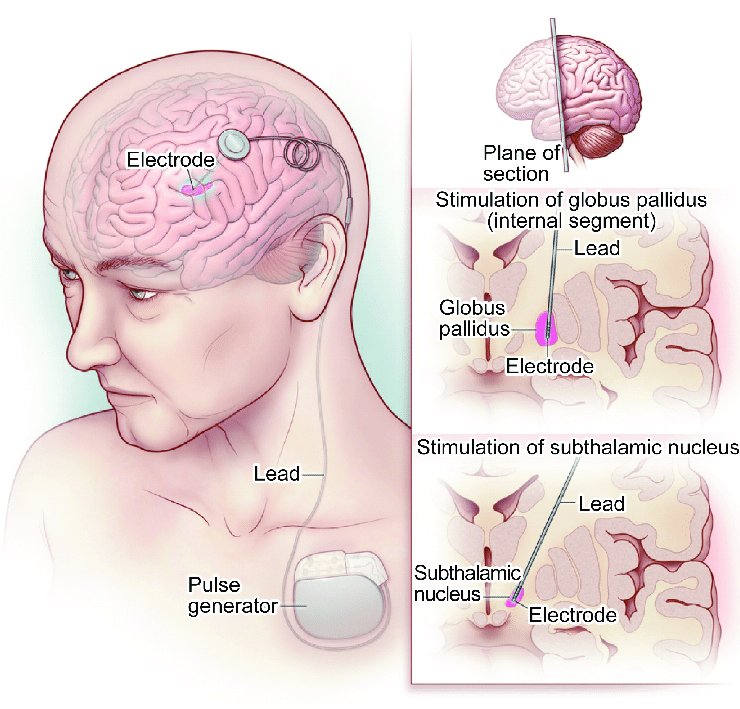
There are three parts of a deep brain stimulator. These are the pulse generator, the extension, and the lead. The surgeon fits the pulse generator near the clavicle bone. The pulse generator generates the electrical impulses that reach the electrodes through the wire. These impulses control the activity of the brain.
Surgeons implants the leads along with the electrodes at the target areas of the brain. The wire connects the electrodes with the pulse generator. Deep Brain Stimulation functions like the pacemaker of the heart.
People who are unable to have relief from the medications or who cannot tolerate the medications are the right candidates for this procedure.
Risks Of Deep Brain Stimulation
Older patients, men and patients with high blood pressure are most at risk for:
- Bleeding: Symptomatic bleeding occurs in less than 2 percent of patients and may manifest as weakness, language difficulty, or confusion. Symptoms are permanent in less than 1 percent of all patients operated on.
- Infection: The implanted devices become infected in approximately 5 percent of patients, often requiring surgical removal.
- Seizures: Occurs in less than 1 percent of patients
Recommended Reading: Stage 2 Parkinson’s Disease
How Effective Is Dbs For Parkinson’s And Tremors What Are The Benefits Of Dbs For Parkinson’s And Tremor
Since DBS mimics the effect of high-dose medication, DBS surgery effectively stops Parkinson’s patients’ tremors and partially responds to the medication.
However, in patients whose tremor does not stop from the beginning despite a high dose of medication, with DBS focused on the tremor center in the brain, it is possible to stop both Parkinson’s tremor and other tremors with a success rate of 85-90%.
What Happens During The Dbs Procedure
Most DBS procedures are performed with the patient awake under local anesthesia, with their head immobilized in a rigid frame, so that the surgical team can monitor patient response to the electrode placement as it occurs. A few centers are now offering image-guided placement, in which the surgery is performed under general anesthesia without the frame. The pulse generator is usually implanted during a second surgery, scheduled about a week after the first.
Don’t Miss: Natural Supplements For Parkinson’s Disease
Am I A Candidate For Deep Brain Stimulation At Ucla
Deep brain stimulation is not a first-line therapy. That means before considering this surgery, patients must have tried medications and other therapies and not responded well. At the UCLA Neuromodulation for Movement Disorders and Pain Program, we offer deep brain stimulation to treat the following:
- Idiopathic Parkinson’s disease: Patients with atypical parkinsonism are not candidates
- Dystonia: Primary, generalized and segmental dystonias respond best
- Obsessive Compulsive Disorder
Deep brain stimulation is an off-label procedure for Tourette’s syndrome, cluster headaches and chronic pain. That means it is not yet an FDA-approved treatment for these conditions. Deep brain stimulation may not be right for everyone. Our multidisciplinary team considers the history, needs, and expectations of each patient before recommending surgery.
You may be a candidate for deep brain stimulation if:
- Your cognitive function is still intact. If it’s not, the surgery can worsen cognitive decline.
- Your brain MRI that does not show signs of significant cerebrovascular disease or other neurodegenerative disease
- You are medically fit for 3-6 hours of awake surgery
What Is The Dbs Surgery Process
Patients suitable for this surgery will be brought to the hospital and taken through the necessary preoperative evaluations. They will undergo DBS surgery on the second day, where the actual brain surgery part of the intervention is. The patients are awake, able to talk with us and communicate their experiences during the surgery.
During this approximate 2.5-hour process, the medical team creates the physiological map of the brain using the Microelectrode Recording and Stimulation technique and by establishing cooperation with the patient. The surgeon places DBS electrodes by locating the brain cells responsible for the disease with an error margin of fewer than 80 microns.
Afterward, within half an hour, when the patient is anesthetized, the surgeon places the neurostimulator in the chest area and connects it to the DSB electrodes with extension cables. After the operation, the treating doctor provides neurostimulator programming, reduces and adjusts the patient’s medications within 2-3 weeks of outpatient clinic control.
Read Also: Idiopathic Parkinson’s Disease Life Expectancy
You Are About To Exit For Another Abbott Country Or Region Specific Website
Please be aware that the website you have requested is intended for the residents of a particular country or region, as noted on that site. As a result, the site may contain information on pharmaceuticals, medical devices and other products or uses of those products that are not approved in other countries or regions.The website you have requested also may not be optimized for your specific screen size.
What Benefits Does The Procedure Offer
DBS is not a cure for Parkinsons, but it may help control motor symptoms while allowing a reduction in levodopa dose. This can help reduce dyskinesias and reduce off time. DBS does not usually increase the peak benefits derived from a dose of levodopa the best levodopa response before DBS is a good indicator of the best response after DBS. But it can help extend the amount of on time without dyskinesias, which may significantly increase quality of life.
DBS does not provide most patients benefit for their non-motor symptoms, such as depression, sleep disturbance, or anxiety. DBS also does not usually improve postural instability or walking problems. If a symptom you have does not respond to levodopa, it is not likely to respond to DBS.
Don’t Miss: How To Cure Parkinson’s Naturally
Improving Quality Of Life For Patients With Movement Disorders Through Deep Brain Stimulation
MUSC Health neurosurgeon Istvan Takacs, M.D., co-director of the Gamma Knife Center, describes how deep brain stimulation works, the advantages of performing it awake and how it can dramatically affect the quality of life of patients with movement disorders such as Parkinsons disease, essential tremor and dystonia. At MUSC Healths Movement Disorders Program, neurosurgeons and neurologists and other members of the care team collaborate closely to provide patients seamless, comprehensive care.
- |
- 171 Ashley Avenue, Charleston SC 29425
- |
- Contact Us
*DISCLAIMER
Why It Is Done
Deep brain stimulation may be used to relieve symptoms of Parkinson’s disease, especially tremor, when they cannot be controlled with medicine. It is considered the surgical treatment of choice for Parkinson’s disease, because it is more effective, safer, and less destructive to brain tissue than other surgical methods.
Deep brain stimulation of the thalamus is done to treat both disabling tremor caused by Parkinson’s disease and essential tremor.
Procedures that stimulate the subthalamic nucleus and the globus pallidus are done to help control a wider range of symptoms and are used more often than stimulation of the thalamus. Symptoms that are most often helped include problems with changes between “on” and “off” time and dyskinesia. Symptoms that are less likely to get better include problems with walking, balance, and speech. In some cases, DBS can make these problems worse.
Deep brain stimulation may also be used to treat severe tremor related to multiple sclerosis . Deep brain stimulation usually is a last resort after all other options have been tried without success to treat MS tremor. Only people with severe tremor are candidates.
You May Like: Restore Gold Parkinson’s Reviews