What Is A Datscan And What Role Does It Play In A Parkinsons Diagnosis
In 2011, the FDA approved the use of a scan called a dopamine transporter scan . A DaTscan is an imaging technology that allows visualization of the dopamine system in the brain. It is similar to an MRI, but looks at the function of the brain rather than the structure.
A DaTscan involves injection of a small amount of a radioactive drug that is then measured by a single-photon emission computed tomography scanner . The SPECT scanner measures the levels and location of the drug in the brain.
It is important to know that a negative DaTscan does not rule out PD, especially early in the disease, but a positive DaTscan can help confirm it. A positive DaTscan can differentiate PD from essential tremor as there is no dopamine deficiency in the latter. However, DaTscan abnormalities can be seen in PD as well as other forms of atypical parkinsonism that cause a loss of dopamine . This means that a positive result does not differentiate Parkinsons disease from other forms of atypical parkinsonism.
Structural And Functional Imaging
Traditional structural imaging modalities, such as X-ray computed tomography and brain MRI using anatomical T1 or T2-weighted sequences, are limited to use for identifying the dopaminergic deficits in the brain of patients with PD. However, MRI can be useful in the identification of structural lesions associated with other forms of parkinsonism, such as those underlined by vascular pathology or neoplasms. Structural MRI can also be useful for measuring the degree and distribution of brain atrophy. With regards to differential diagnosis, it has been shown that abnormal T2 MRI hypo-intensities in the putamen discriminate MSA-P from PD with 88% sensitivity and 89% specificity. Decreased putaminal signal intensities were higher using T2*-weighted gradient echo than T2-weighted fast-spin echo sequences and more useful in differentiating PD from MSA-P. Atrophy of the superior cerebellar peduncles and the frontal cortex also aid in discriminating PSP from PD with 74/94% and 95/91% specificity/sensitivity, respectively .
Diagnostic accuracy of MRI modalities.
You May Like: Does Sam Waterston Have Parkinsons
Regional Cerebral Glucose Metabolism And Pd
18F-FDG PET can be used to assess levels of resting regional cerebral glucose metabolism. Absolute levels in the lentiform nucleus lie within the reference range in PD however, covariance analysis reveals an abnormal profile of relatively raised resting lentiform nucleus and lowered frontal and parietotemporal metabolism . The degree of expression of this PD-related profile correlates with clinical disease severity, thus providing a potential biomarker of disease progression. Successful treatment with levodopa or deep brain stimulation reduces expression of the PD-related profile . Given this, changes in treatment could result in a potential confounding factor if 18F-FDG PET were to be used as a biomarker to follow PD progression.
Eckert et al. performed 18F-FDG PET on 8 patients with suspected early parkinsonism but normal findings on 18F-dopa PET . None of these 8 patients expressed a PD-related profile of glucose metabolism, and over 3 y none of them showed any clinical progression of their disorder. This finding reinforces the viewpoint that normal dopaminergic imaging excludes the presence of a degenerative parkinsonian syndrome.
Recommended Reading: Cure For Parkinson’s Disease Stem Cells
Is An Mri Exam Safe For Parkinson’s Disease
Yes. The MRI exam poses no risk to the average person if appropriate safety guidelines are followed. But, if you have a deep brainstimulator to treat your Parkinson’s disease, talk to your doctor before having an MRI since the stimulator may need to be turned off. It should be evaluated and turned on again after the MRI.
Some conditions may make an MRI exam inadvisable. Others mean that precautions need to be taken. Tell your doctor if you have any of the following conditions:
- Weigh more than 300 pounds
- Not able to lie on back for 30 to 60 minutes
What Should I Expect During The Mri
As the MRI scan begins, you will hear the equipment making a variety of banging, clanging and muffled thumping sound that will last for several minutes. None of them are anything other than annoying. Other than the sound, you should experience no unusual sensations during the scanning.
Certain MRI exams require an injection of a contrast material. This helps identify certain anatomic structures on the scan images.
Please feel free to ask questions. Tell the technologist or the doctor if you have any concerns.
Recommended Reading: Parkinson’s Disease And Occupational Therapy
Differential Diagnosis Of Parkinsonian Syndromes Using Quantitative Biomarkers
Several studies have suggested that the combination of R2* and FA markers may better differentiate people with PD from healthy aged subjects with greater than 95% global accuracy .
In MSA-P, increased diffusivity and reduced anisotropy was found in the putamen, pons and middle cerebellar peduncle and greater iron deposition in the putamen, using phase-contrast susceptibility imaging or relaxometry .
What Are The Risk Factors For Parkinsons
There are a few known risk factors for Parkinsons. These include:
- having a family history of Parkinsons
- being over 60 years
- having been exposed to herbicides, pesticides, and other toxins
Its important to note that these risk factors only cause a slight increase in risk. Having one or more risk factors isnt an indicator youll develop Parkinsons. However, if youre concerned about your risk for Parkinsons, talk with a doctor.
Don’t Miss: Can Head Injury Cause Parkinson’s
What Doctor Treats Tremors
Baltuch: Neurologists are generally the first specialists you’ll see for essential tremor treatment. This is because treatment typically involves medications, such as a series of pills. However, some people try several different medications and still have a disabling tremor that interferes with daily living.
What Is Parkinsons And How Can Mri Help
More than ten million people are living with Parkinsons disease worldwide, with about one million cases expected to be in the United States by 2020.1 This is more than the number of people with multiple sclerosis, muscular dystrophy and Lou Gehrigs disease combined.1 With the rising prevalence of Parkinsons disease, its important to understand the signs and symptoms of the disease. Likewise, physicians and radiology departments may need to know what role magnetic resonance imaging may play.
Dont Miss: Prayer For Parkinsons Disease
Also Check: Does Parkinson’s Cause Incontinence
Imaging The Pharmacology Of Depression In Pd
The prevalence of depression in PD has been reported to range from 10% to 45% . Because Lewy body pathology is known to affect serotonergic and noradrenergic as well as dopaminergic neurotransmission, dysfunction of any or all of these systems would seem to be a reasonable candidate for the functional substrate of depression . To date, functional imaging has failed to demonstrate a correlation between serotonergic dysfunction and depression in PD.
123ICIT binds with nanomolar affinity to dopamine, noradrenaline, and serotonin transporters. Although striatal uptake of 123ICIT 24 h after intravenous injection primarily reflects DAT binding, midbrain uptake 1 h after administration reflects serotonin transporter availability . Kim et al. have reported normal brain stem 123ICIT uptake in PD. They found no difference between uptake in depressed and nondepressed patients and no correlation between radiotracer uptake and Hamilton Depression Rating Scale scores .
Recommended Reading: Does Parkinsons Cause Hair Loss
Dark Pigment In Brain Cells
The brain cells affected by Parkinsons contain a pigment called neuromelanin. This pigment gives the cells a characteristic dark colouring.
The technique may be sensitive enough to monitor the progression of Parkinsons.
As these cells are lost in Parkinsons, this pigmentation is reduced. Recent research has suggested MRI may be sensitive enough to detect this change.
However, there are many different machines and methods for taking MRI brain scans, which could affect how accurate the technique is at detecting Parkinsons.
The team developed ways to standardise results from different types of machine to increase the accuracy of the technique as a diagnostic tool.
They also discovered that the technique may be sensitive enough to monitor the progression of Parkinsons.
Read Also: On Off Phenomenon
Read Also: New Parkinson’s Medication For Hallucinations
The Role Of Magnetic Resonance Imaging For The Diagnosis Of Atypical Parkinsonism
- 1Institut du Cerveau et de la Moelle épinièreICM, INSERM U 1127, CNRS UMR 7225, Sorbonne Université, UPMC Univ Paris 06, UMRS 1127, CNRS UMR 7225, Paris, France
- 2ICM, Movement Investigations and Therapeutics Team , Paris, France
- 3ICM, Centre de NeuroImagerie de RechercheCENIR, Paris, France
- 4Service de Neuroradiologie, Hôpital Pitié-Salpêtrière, APHP, Paris, France
- 5Dynamics and Pathophysiology of Neuronal Networks Team, Center for Interdisciplinary Research in Biology, Collège de France, CNRS UMR7241/INSERM U1050, MemoLife Labex, Paris, France
- 6Department of Neurology, Avicenne University Hospital, Sorbonne Paris Nord University, Bobigny, France
- 7Département des Maladies du Système Nerveux, Hôpital Pitié-Salpêtrière, APHP, Paris, France
Is The Imaging Metric Appropriate For The Question Being Asked
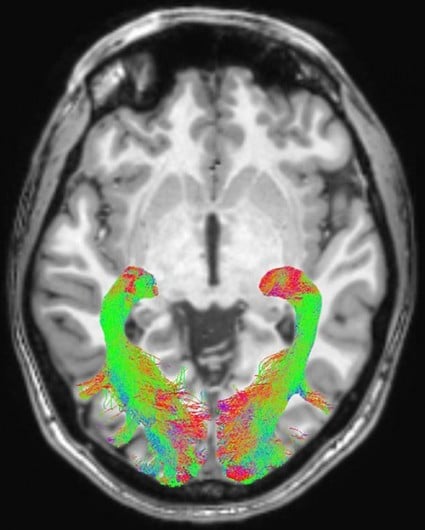
Neuroanatomy Relevant to Parkinsons Disease
A. Braak staging of -synuclein pathology. At death, PD patients exhibit the following stages of -Syn pathology: stage I olfactory bulb only , Stage IIa brainstem predominant , stage IIb limbic predominant , stage III brainstem and limbic and stage IV neocortical . While not all patients with pathology will exhibit clinical symptoms , the progression of neuropathology generally corresponds to the progression of both motor and non-motor symptoms . B. The SN is subdivided into the ventral pars reticulata and the dorsal pars compacta , the latter is composed of dopaminergic neurons. The SNc is further divided into the dorsal and ventral tier, with the loss of dopaminergic neurons occurring first in the caudal and ventrolateral tier . Within A9, there are five nigrosomes , with N1 exhibiting the earliest loss of dopaminergic neurons . Dopaminergic neuronal loss typically spreads to neighboring groups from the N1 in PD . C. Fronto-subcortical loops comprise the motor, associative, and limbic domains, which respectively transit through the posterior, anterior, and ventral striatum, thus segregated functionally and anatomically. GPe = globus pallidus externa. GPi = globus pallidus interna. STN = subthalamic nucleus. SNc = substantia nigra pars compacta. SNr = substantia nigra pars reticulata. Adapted with permission from: .
Also Check: How Long Does Parkinsons Last
Don’t Miss: Medication For Parkinson’s And Restless Leg Syndrome
Further Testing In Parkinson’s
In other situations, where perhaps the diagnosis is not as clear, younger individuals are affected, or there are atypical symptoms such as tremor affecting both hands or perhaps no tremor at all, further testing may help. For example, imaging can play a role in differentiating between essential tremor and Parkinsons. It can also be important to confirm what is initially a clinical diagnosis of Parkinsons prior to an invasive treatment procedure such as surgical DBS
Mri In Parkinson’s Testing
One of the more common tests done during a neurologic workup is an MRI scan and one may think that in the investigation of a disease that affects the brain such as Parkinsons, this imaging test would be a necessity. In the context of Parkinsons disease, however, an MRI is not particularly helpful. It looks at the structure of the brain which, for all intents and purposes, appears normal in this disease. An MRI may, however, be indicated when symptoms appear in younger people or if the clinical picture or the progression of symptoms is not typical for Parkinsons. In these situations, MRI can be used to rule out other disorders such as stroke, tumors, hydrocephalus , and Wilsons Disease .
Read Also: How To Care For Parkinson’s At Home
Diagnosis Of Parkinson Disease: Motor Symptoms
The clinical diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease is based on the presence of characteristic motor symptoms: bradykinesia, rigidity, postural instability, and resting tremor but neuropathology is still considered the gold standard for definite diagnosis. Differentiating PD from other movement disorders can be challenging throughout the disease course, because signs and symptoms often overlap. Indeed, neuropathology studies reveal that clinical diagnosis of PD can be confirmed with an accuracy of about 75%. Good response to levodopa is often used to support the diagnosis of PD. However, cases of pathologically proven PD with poor response to levodopa have also been reported.
Misdiagnosis of PD can occur for several reasons. In a community-based study of patients taking antiparkinsonian medication, the most common misdiagnosis were essential tremor, Alzheimer’s disease, and vascular parkinsonism. In addition, many of the prominent features of PD may also occur as a result of normal aging or from comorbid and multifactorial medical conditions .
R. Savica, … G. Logroscino, in, 2016
Response To Parkinsons Drugs
After examining you, and depending on the severity of your symptoms, your specialist may suggest you take medication for Parkinsons. If your symptoms improve after taking Parkinsons medication for a few weeks or months, your specialist may confirm a Parkinsons diagnosis. However, some people with other forms of parkinsonism will also respond well to these drugs.
Your specialist may suggest you have a scan to help make a diagnosis. However, scans alone cant make a definite diagnosis of Parkinsons, so they are not commonly used.
Also Check: Can Parkinson’s Stay Mild
What Is A Datscan
A DaTscan is an imaging drug, also called Ioflupane I 123 or phenyltropane, that acts as a radioactive tracer for dopamine transporters within the brain. This drug was approved by the FDA in 2011. It may help distinguish the diagnosis of essential tremor from Parkinsons syndromes, like Parkinsons disease or Parkinsons disease dementia.
The drug is administered during the SPECT scan. This scanning technique gathers images of a particular area in the brain called the striatum, a cluster of neurons in the subcortical basal ganglia of the forebrain. The striatum helps facilitate the transportation of dopamine.
DaTscan is injected into the patients bloodstream and eventually circulates to the brain. The tracer attaches itself to a molecule found on dopamine neurons in the striatum called the dopamine transporter . The patient then undergoes a SPECT scan which will produce an image of the dopaminergic neuron terminals that remain available in the striatum.
In patients with a diagnosis of Parkinsons disease, or parkinsonism , this area of the brain will show dark. This indicates the loss of dopamine-containing nerve cells within the brain, a hallmark of the disease.
How Parkinsons Disease Is Diagnosed
Parkinsons disease is usually diagnosed clinically, meaning that a physician looks for the presence or absence of the possible symptoms of Parkinsons disease by interviewing the patient and performing a detailed neurologic examination.
While there is presently no definitive test for Parkinsons, it can often be identified by a general neurologist, who is trained to diagnose and treat neurologic disorders. To avoid misdiagnosis, consultation with a movement disorder specialist is recommended. A movement disorder specialist is a physician who has undergone additional, subspecialty training in the diagnosis and treatment of movement disorders, such as Parkinsons, after training in general neurology.
What to expect during your visit with a physician
Typically, a trained physician will only consider the diagnosis of Parkinsons disease if the person being examined has at least two of the core motor symptoms of Parkinsons, including tremor, the characteristic bradykinesia , or rigidity. At the end of your visit, the physician should discuss with you why you may or may not have Parkinsons disease and the level of certainty about the diagnosis. This determination is based on your medical history and examination at this visit.
Brain imaging and other tools to aid diagnosis of Parkinsons
Don’t Miss: Parkinson’s Foundation Kansas City
How Do You Treat Body Tremors Naturally
Lifestyle and home remedies
The Mediterranean diet may lower risk of essential tremor.
- Vegetable, legumes, fruits.
- Low levels of dairy, meat and poultry.
- Low to moderate alcohol consumption.
Determining Diagnosis Through Response To Parkinsons Medication
If a persons symptoms and neurologic examination are only suggestive of Parkinsons disease or if the diagnosis is otherwise in doubt, the physician may, nevertheless, prescribe a medication intended for Parkinsons disease to provide additional information. In the case of idiopathic Parkinsons, there is typically a positive, predictable response to Parkinsons disease medication in the case of some related Parkinsonian syndromes, the response to medication may not be particularly robust, or it may be absent entirely.
Unfortunately, there are no standard biological tests for the disease, such as a blood test. However, researchers are actively trying to find biomarkers in blood and other bodily fluids that could help confirm the diagnosis.
You May Like: Toxins That Cause Parkinson’s
What Is Parkinsons Disease
Parkinsons disease is a chronic neurological condition. It is progressive and symptoms worsen over time. It is named after Dr James Parkinson who first described the condition in 1817.
People with Parkinsons disease experience a loss of nerve cells in the part of their brains responsible for controlling voluntary movements. This part of the brain is called the substantia nigra . The nerve cells in the substantia nigra usually produce a chemical called dopamine which helps transmit messages from the brain to the rest of the body via the central nervous system . As these cells are lost, people with Parkinsons disease experience a loss of dopamine and the messages controlling movement stop being transmitted efficiently.
Parkinsons disease is more common as people get older but it can affect younger adults. Men tend to be affected in slightly higher numbers than women.
Description Of The Test
A routine brain MRI study, at 1.5T or 3T magnetic field strength, takes about 30 minutes and includes different acquisitions, also referred to as sequences. We recommend to include T1-weighted and T2 FLAIR, either as 2D or 3D acquisitions. Both transversal and sagittal planes should be available. Furthermore, the protocol should include diffusion-weighted imaging and a susceptibility sensitive sequence, either T2* or susceptibility weighted imaging . For a more detailed evaluation of the basal ganglia and small areas of tissue loss, it is advisable to also include a T2-weighted sequence. The purpose and limitations of these various sequences are described in Table 1.
Read Also: Physical Therapy For Parkinson’s Disease