What Lifestyle Changes Can I Make To Ease Parkinsons Symptoms
Exercise: Exercise helps improve muscle strength, balance, coordination, flexibility, and tremor. It is also strongly believed to improve memory, thinking and reduce the risk of falls and decrease anxiety and depression. One study in persons with Parkinsons disease showed that 2.5 hours of exercise per week resulted in improved ability to move and a slower decline in quality of life compared to those who didnt exercise or didnt start until later in the course of their disease. Some exercises to consider include strengthening or resistance training, stretching exercises or aerobics . All types of exercise are helpful.
Eat a healthy, balanced diet: This is not only good for your general health but can ease some of the non-movement related symptoms of Parkinsons, such as constipation. Eating foods high in fiber in particular can relieve constipation. The Mediterranean diet is one example of a healthy diet.
Preventing falls and maintaining balance: Falls are a frequent complication of Parkinsons. While you can do many things to reduce your risk of falling, the two most important are: 1) to work with your doctor to ensure that your treatments whether medicines or deep brain stimulation are optimal and 2) to consult with a physical therapist who can assess your walking and balance. The physical therapist is the expert when it comes to recommending assistive devices or exercise to improve safety and preventing falls.
Read Also: Is Parkinsons A Form Of Cancer
Correlation Of Clinical Rigidity Scores And Damping Ratio
The damping ratios of PD subjects had a linear relationship with clinical rigidity scores .3). No other model parameters significantly correlated with rigidity, including natural frequency and peak time.
There is a linear relationship between clinical rigidity scores and damping ratio . This relationship could be utilized to predict rigidity scores, which significantly correlate with actual recorded rigidity scores.
What Causes Rigidity In Parkinsons Disease
The exact cause of rigidity in people suffering from Parkinson is not precisely known. It is believed that the reduction in dopamine , also called as a neurotransmitter relays the message to some areas of the brain for producing smooth and purposeful movement. These some areas of the brain are put together in a circuit called basal ganglia. When Parkinson damages these dopamine producing neurons, the communication between them is disrupted and rigidity is caused.
Also Check: Parkinson’s And Stiff Neck
Correspondence Between Connectivity And Clinical Rigidity Scores
We used multivariate linear regression to determine whether or not clinical rigidity scores could be predicted from the connectivity patterns in PD subjects . Specifically, we modeled the rigidity scores as:
where Y was a vector of rigidity scores of dimensions 10 by 1, X was 10 by n and is a 10 by 1 vector of residuals. Since, in this case, the number of potential regressors exceeds the number of examples , we utilized LASSO regression . Unlike other methods such as ridge regression or ordinary least squares, LASSO regression puts a sparsity constraint on so that most values are zero and attempts to find the most informative connections to predict clinical scores . The number of regressors selected by the LASSO operator was to give the least predictive error based on a 10-fold cross-validation. Once the regressors were selected, we used robust regression to estimate the significance of the individual regressors.
Data Extraction And Analysis
A systematic review was conducted by two independent authors. We used a standardized data extraction protocol, collecting information about population, intervention, methods, results, and outcome measures. For each study we defined the design, sample size, joint explored, type of system used for the quantification of rigidity, evaluation protocol, rigidity outcome measures, and other clinical variables related to PD severity, functional independence, quality of life, and results. Finally, both authors reached an agreement about each extracted data item. Studies employing objective assessment methods of muscle rigidity in PD patients were selected.
Recommended Reading: Nursing Diagnosis For Parkinson’s Disease
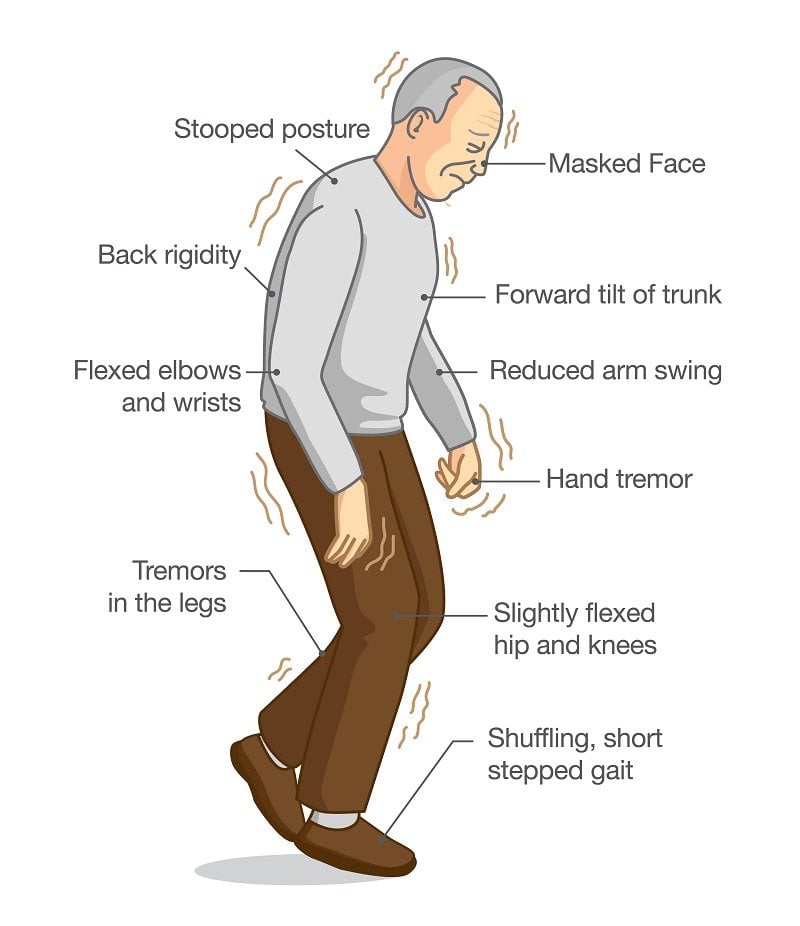
Every Person With Parkinsons May Experience Different Movements
There are multiple types of movements that a person with Parkinsons disease can experience. Some people may have just one or two of these symptoms, while another may experience all of them. Likewise, the degree of severity can vary from person to person, and symptoms that may bother some people may not bother others at all.
Its important to note that theres not a single answer that works for every person with Parkinsons, says Todd Herrington, MD, PhD, a neurologist at Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston and an instructor in neurology at Harvard Medical School in Cambridge, Massachusetts. You have to ask the person, What bothers you, and how much does it affect you? What the caregiver or the even the physician observes as the most severe symptoms may not feel that way to the person with Parkinsons.
Here are eight types of movements that people with Parkinsons may experience. Learn more about what these symptoms are and what can be done to prevent them.
Dopaminergic Medication And Rigidity
Some authors have studied the reliability of their instruments by examining whether they are able to detect the âoffâ vs. âonâ change produced by the administration of levodopa and other antiparkinsonian drugs . Theoretically, the rigidity responds well to medication , but frequently the outcome measures used in clinical trials seem to suffer from an obvious subjectivity, poor sensitivity to change, and variable inter- or intra-examiner reliability . On the other hand, the use of instrumentalized methods could provide greater assurance regarding the efficacy of pharmacotherapy , since they offer quantitative information. With the current data, we can conclude that there are sensors and servomotors capable of detecting the âoffâ vs. âonâ change in terms of objective muscle stiffness, while other instruments do not find statistically significant differences after the administration of medication in rigidity values . More research is required through instrumentalized methods to know the degree of effectiveness of medication on rigidity.
You May Like: Does Parkinson’s Cause Pain In Legs
Is Parkinsons Disease Inherited
Scientists have discovered gene mutations that are associated with Parkinsons disease.
There is some belief that some cases of early-onset Parkinsons disease disease starting before age 50 may be inherited. Scientists identified a gene mutation in people with Parkinsons disease whose brains contain Lewy bodies, which are clumps of the protein alpha-synuclein. Scientists are trying to understand the function of this protein and its relationship to genetic mutations that are sometimes seen in Parkinsons disease and in people with a type of dementia called Lewy body dementia.
Several other gene mutations have been found to play a role in Parkinsons disease. Mutations in these genes cause abnormal cell functioning, which affects the nerve cells ability to release dopamine and causes nerve cell death. Researchers are still trying to discover what causes these genes to mutate in order to understand how gene mutations influence the development of Parkinsons disease.
Scientists think that about 10% to 15% of persons with Parkinsons disease may have a genetic mutation that predisposes them to development of the disease. There are also environmental factors involved that are not fully understood.
Behavioral And Clinical Data
Each patients overall motor impairment was indexed using the total score of the Unified Parkinsons Disease Rating Scale part III, where higher scores indicate more severe overall motor symptoms. While some previous studies have examined motor subtypes by classifying patients into AR or tremor-dominant groups, we chose to examine individual differences in these two domains of motor symptoms. Each individuals AR score was calculated as a sum of UPDRS III ratings on rigidity, finger tapping, hand movements, arising from chair, posture, gait, and body bradykinesia, and the tremor scores as a sum of ratings on resting tremor of the arms and legs and action tremor of the arms . To determine if motor impairments became more severe over time we evaluated motor domain scores in 274 patients who had behavioral data collected at all four time points. Baseline demographic information regarding these participants can be found in Table .
You May Like: Parkinson’s And Hearing Loss
Diagnosis Of Parkinsons Disease
There are currently no blood or laboratory tests to diagnose non-genetic cases of Parkinsons. Doctors usually diagnose the disease by taking a persons medical history and performing a neurological examination. If symptoms improve after starting to take medication, its another indicator that the person has Parkinsons.
A number of disorders can cause symptoms similar to those of Parkinsons disease. People with Parkinsons-like symptoms that result from other causes, such as multiple system atrophy and dementia with Lewy bodies, are sometimes said to have parkinsonism. While these disorders initially may be misdiagnosed as Parkinsons, certain medical tests, as well as response to drug treatment, may help to better evaluate the cause. Many other diseases have similar features but require different treatments, so it is important to get an accurate diagnosis as soon as possible.
Depression May Be An Early Symptom Of Parkinsons
Depression is one of the most common, and most disabling, non-motor symptoms of Parkinsons disease. As many as 50 per cent of people with Parkinsons experience the symptoms of clinical depression at some stage of the disease. Some people experience depression up to a decade or more before experiencing any motor symptoms of Parkinsons.
Clinical depression and anxiety are underdiagnosed symptoms of Parkinsons. Researchers believe that depression and anxiety in Parkinsons disease may be due to chemical and physical changes in the area of the brain that affect mood as well as movement. These changes are caused by the disease itself.
Here are some suggestions to help identify depression in Parkinsons:
- Mention changes in mood to your physician if they do not ask you about these conditions.
- Complete our Geriatric Depression Scale-15 to record your feelings so you can discuss symptoms with your doctor. Download the answer key and compare your responses.
- delusions and impulse control disorders
Don’t Miss: What Mattress Is Best For Parkinson Patients
Neurophysiological Mechanisms Of Rigidity
The neurophysiological mechanisms underlying rigidity in PD are still a matter of debate. In global terms, there are currently two hypotheses that partially explain the physiopathology. One of them focuses on changes produced at the spinal level, mainly of the Ia and Ib interneurons, as a consequence of an altered input by the reticulospinal tract . The high fusimotor activity from neuromuscular spindles has also been proposed as a contributor to this alteration .
In any case, the modification at the medullary level would produce changes that generate two parallel and partially related phenomena: tonic increase in the stretch reflex and increase in the shortening reaction . The shortening reaction is an abnormal response of a muscle that has been shortened and responds with a contraction to the change in length. This is a paradoxical response and has been observed prominently in people with PD in the âoffâ state using EMG data during a servomotor analysis .
Clinical Diagnosis Of Rigidity
A doctor will test for rigidity by flexing and extending the patients relaxed wrist and elbow joint, and look for sustained rigidity or intermittent rigidity if tremors are associated with it.
Clinically, Parkinsons rigidity is characterized by increased muscle tone during examination using passive movement of the affected body parts. Parkinsons rigidity is more marked in flexor muscles than extensor muscles . Rigidity may be enhanced by voluntary movement of other body parts and is more pronounced during slow stretching rather than fast stretching. These features help to differentiate Parkinsons rigidity from spasticity, which becomes worse during fast movements.
Read Also: When A Person Is Suffering With Parkinson’s Disease
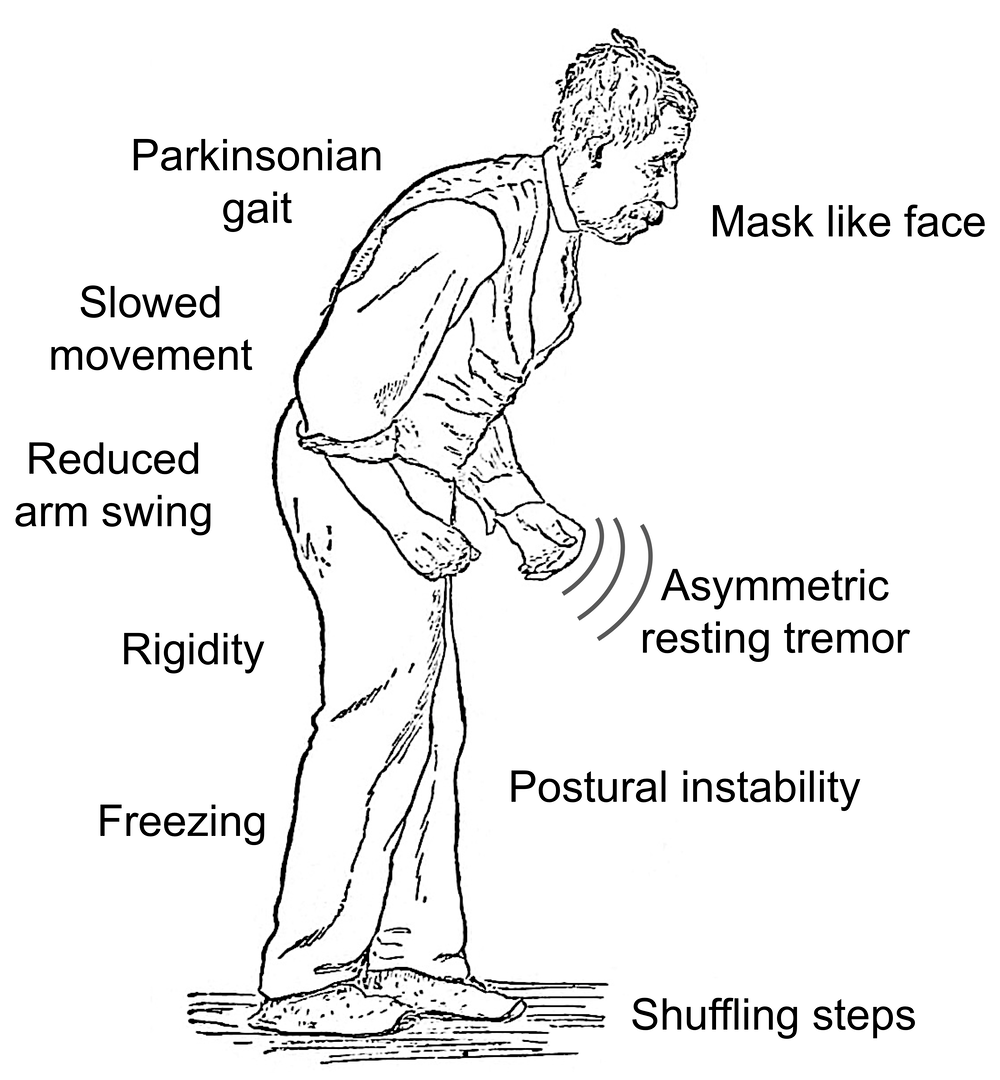
The Four Cardinal Symptoms Of Parkinson’s Disease
The hands and legs quiver and shake when seated and while sleeping. When movement is initiated, the shaking often stops. This is the most typical symptom of Parkinson’s disease.
The muscles become stiff and the body no longer moves smoothly. When movement becomes jerky, it is called cogwheel rigidity, and when stiffness continues, it is called lead-pipe rigidity.
Quick movements can no longer be performed. Movements become small and the arms hardly swing while walking. Movement becomes even slower when attempting multiple movements simultaneously.
A loss of balance occurs easily when pushed gently while standing. Balance and posture are difficult to regain and falls often result. These symptoms appear when the disease has progressed . At this stage, medical care becomes subsidized by the Japanese government.
What Does Cogwheeling Look Like
In cogwheel rigidity, your muscle will be stiff, like in other forms of rigidity. But you might also have tremors in the same muscle when its at rest.
Cogwheel rigidity can affect any limb, but its most common in the arms. It can affect one or both arms.
With any type of muscle rigidity, your muscle might feel tight. You might not be able to move the muscle fully. This can be painful and uncomfortable.
Rigidity of any kind is one of the three main types of symptoms of Parkinsons disease. The other two are tremors and slowed movement called bradykinesia. Therefore, cogwheel rigidity can help doctors diagnose Parkinsons disease.
To test you for cogwheel rigidity, your doctor will have you relax the muscles in your limb. Theyll then flex and extend your limb. Theyre looking to see if:
- your muscle is stiff and inflexible when they try to move it
- your limb moves with small, jerky motions
Ratcheting motions are the hallmark of cogwheel rigidity. For you, this might feel like a click or catch in your muscle as you move your arm.
Another hallmark of cogwheel rigidity is that the jerky movements happen even when the doctor moves your limb slowly. This distinguishes it from spasticity, another potential symptom of Parkinsons disease.
Don’t Miss: What Not To Eat With Parkinson’s
Managing Depression In Parkinsons Disease
People with Parkinsons, family members and caregivers may not always recognize the signs of depression and anxiety. If you are experiencing depression as a symptom of Parkinsons, it is important to know it can be treated.
Here are some suggestions:
- For information and support on living well with Parkinsons disease, contact our Information and Referral line.
- As much as possible, remain socially engaged and physically active. Resist the urge to isolate yourself.
- You may want to consult a psychologist and there are medications that help relieve depression in people with Parkinsons, including nortriptyline and citalopram .
Read Also: Tai Chi For Parkinsons
Make Commercial Breaks Movement Breaks
If youre watching TV, stand up and march while you swing your arms during the commercials. To increase your muscular strength, lift soup cans or a do a few downward dogs.
Moving more every day is easier said than done. Remember, even small changes can make a big difference. Pat yourself on the back for all of the movement activities you do each day. Every victory counts!
Recommended Reading: Are Hallucinations A Symptom Of Parkinson’s
Muscle Rigidity: Lead Pipe And Cogwheel Rigidity
Muscle rigidity due to Parkinsonâs disease can be misdiagnosed as arthritis or general tightness from aging. Rigidity can affect your legs, arms, torso, and face. â
What rigidity feels like. Your muscles may feel tight and difficult to move. They may also stiffen involuntarily like a muscle spasm. This stiffness can also cause joint and muscle pain.
Rigidity and everyday life. This type of stiffness can start impacting your normal functions. Simple tasks like cleaning, exercise, and fulfilling hobbies can become difficult because of rigidity. You may also experience:
- Stiffness in your facial muscles that make it difficult to express yourself
- Stiffness while sleeping that make it difficult to get comfortable and sleep well
- Constant tension in your muscles that leads to muscle fatigue and a lack of energy
- Difficulty with certain motor skills, like writing or getting dressed
- Stiffness in your arms that make it harder to maintain balance while walking
Lead pipe rigidity. This type of stiffness is characterized by a feeling of frozen muscles. The muscles feel stuck and unable to move. â
Attempts to move those limbs are met with resistance throughout the motion. They feel stiff and heavy like a âlead pipeâ for sustained periods of time.
Cogwheel rigidity. This type of rigidity is similar to muscle spasms. The limbs experiencing the stiffness can move in small jerking motions, like a ratchet. You may even feel small clicking sensations when moving your arm. â
What Causes Parkinsons Disease
The most prominent signs and symptoms of Parkinsons disease occur when nerve cells in the basal ganglia, an area of the brain that controls movement, become impaired and/or die. Normally, these nerve cells, or neurons, produce an important brain chemical known as dopamine. When the neurons die or become impaired, they produce less dopamine, which causes the movement problems associated with the disease. Scientists still do not know what causes the neurons to die.
People with Parkinsons disease also lose the nerve endings that produce norepinephrine, the main chemical messenger of the sympathetic nervous system, which controls many functions of the body, such as heart rate and blood pressure. The loss of norepinephrine might help explain some of the non-movement features of Parkinsons, such as fatigue, irregular blood pressure, decreased movement of food through the digestive tract, and sudden drop in blood pressure when a person stands up from a sitting or lying position.
Many brain cells of people with Parkinsons disease contain Lewy bodies, unusual clumps of the protein alpha-synuclein. Scientists are trying to better understand the normal and abnormal functions of alpha-synuclein and its relationship to genetic mutations that impact Parkinsons andLewy body dementia.
Recommended Reading: Do You Have Pain With Parkinson’s Disease
Examining Muscle Weakness And Rigidity In Parkinsons Disease
The sun peeks over the horizon, and before long Dad is up and at it. Its a boxing day, and he wants to time his medications to optimize control over his Parkinsons symptoms.
The other part of his routine revolves around his morning stretches. Muscle rigidity is the first obstacle that he faces when he wakes, and he chooses to confront it with a stretching practice.
Parkinsons disease claims multiple functions as it progresses. Understanding how the disease affects the patient may help to inform treatment decisions. Im a curious person, and Dads stretching routine makes me wonder if Parkinsons disease directly affects the way muscles work. I think about how muscle rigidity and weakness are linked and how others handle these symptoms.
Recommended Reading: Parkinsons Donations In Memory Of