Monoamine Oxidase B Inhibitors
Other PD medications work by inhibiting the enzymes involved in dopamine metabolism, which preserves the levels of endogenous dopamine. One such class is the MAO-B inhibitors. As is discussed above, MAO-B is one of the main enzymes involved in the breakdown of dopamine, and reducing the activity of this enzyme therefore results in increased dopaminergic activity within the striatum, mediated by endogenous dopamine . Their use relieves motor symptoms in PD patients, and as with dopamine agonists they may be used as an initial treatment option, to delay the need for levodopa therapy, to reduce the risk of levodopa-induced motor complications . While they are sometimes sufficient for control of symptoms in early disease, most patients ultimately require levodopa-based treatment. MAO-B inhibitors may also be used in combination with levodopa-based preparations, to allow for a reduction in the levodopa dose.
How Do I Prevent Falls From Common Hazards
- Floors: Remove all loose wires, cords, and throw rugs. Minimize clutter. Make sure rugs are anchored and smooth. Keep furniture in its usual place.
- Bathroom: Install grab bars and non-skid tape in the tub or shower. Use non-skid bath mats on the floor or install wall-to-wall carpeting.
- Lighting: Make sure halls, stairways, and entrances are well-lit. Install a night light in your bathroom or hallway and staircase. Turn lights on if you get up in the middle of the night. Make sure lamps or light switches are within reach of the bed if you have to get up during the night.
- Kitchen: Install non-skid rubber mats near the sink and stove. Clean spills immediately.
- Stairs: Make sure treads, rails, and rugs are secure. Install a rail on both sides of the stairs. If stairs are a threat, it might be helpful to arrange most of your activities on the lower level to reduce the number of times you must climb the stairs.
- Entrances and doorways: Install metal handles on the walls adjacent to the doorknobs of all doors to make it more secure as you travel through the doorway.
Contact Our Information And Referral Helpline
The Parkinson Canada Information and Referral Helpline is a toll-free Canada-wide number for people living with Parkinsons, their caregivers and health care professionals. We provide free and confidential non-medical information and referral services. When you have questions or need assistance, our information and referral staff help connect you with resources and community programs and services that can help you. We provide help by phone or email, Monday to Friday, 9:00 a.m. 5:00 p.m. ET.
You May Like: Micrographia In Parkinson’s Disease
Editorial Sources And Fact
- Parkinsons Disease: Diagnosis & Treatment. Mayo Clinic. December 8, 2020.
- Pringsheim T, Day GS, Smith DB, et al. Dopaminergic Therapy for Motor Symptoms in Early Parkinson Disease Practice Guideline Summary: A Report of the AAN Guideline Subcommittee. Neurology. November 15, 2021.
- Levodopa and Carbidopa. MedlinePlus. June 15, 2018.
The Clinical Symptoms Of Parkinsons Disease

Department of Neurology, Broomfield Hospital, Chelmsford, Essex, CM1 7ET UK
Queen Mary School of Medicine and Dentistry, University of London, London, UK
Department of Neurology, Broomfield Hospital, Chelmsford, Essex, CM1 7ET UK
Queen Mary School of Medicine and Dentistry, University of London, London, UK
Read Also: How To Support Someone With Parkinson’s Disease
What Are The Side Effects Of Parkinson’s Drugs
The most common reactions include nausea, vomiting, dizziness , sleepiness and visual hallucinations.
In the last few years, levodopa and dopamine agonists in particular have been associated with the emergence of behavioral changes such as impulse control disorders. These are characterized by failure to resist an impulse to perform certain actions.
Impulse control disorders include a range of behaviors such as compulsive gambling or shopping, hypersexuality, binge eating, addiction to the Internet or to other recreational activities. These activities are often pleasant in the moment, but over time may become harmful to you or to others. If you are experiencing these behaviours, tell your neurologist/doctor. Often the medication can be adjusted which can reduce or control the behaviour.
Care partners can play an important role in helping to identify when these behaviours occur. If you are a care partner, tell the person if you have noticed a change in his/her behaviour or personality and encourage him/him/her to speak with the doctor immediately so medication can be adjusted.
Medication Management For Motor Symptoms
Although many symptoms can occur in Parkinsons, the most common motor symptoms are tremor, stiffness, and slowness. In this webinar, movement disorder specialist Dr. Aaron Haug discusses treatment strategies and explains in detail the specific medications used to treat the motor symptoms of Parkinsons.
Also Check: Parkinson’s Phlegm At Night
Impulsive And Compulsive Behaviour
A small number of people taking levodopa have problems with impulsive or compulsive behaviour. This can also be called impulse control disorder. It affects a much smaller percentage of people taking levodopa than those taking dopamine agonists, but it is still a possible side effect. Further information is available at Compulsive and impulsive behaviour.
Another potential problem is dopamine dysregulation syndrome, where someone with Parkinsons might be tempted to take more of their Parkinsons medication than they are prescribed. If you think this is happening to you or the person you are caring for, tell your GP, specialist or Parkinsons nurse right away.
It is important that all people with Parkinsons are monitored for any potential risk of impulsive and compulsive behaviour while being treated with levodopa.
People with Parkinsons, their carers, friends and family members should work with healthcare professionals to monitor any changes in behaviour. If you start to experience these symptoms, you should discuss it with your specialist or Parkinsons nurse immediately. You should not stop taking the medication.
Read Also: Can A Blood Test Detect Parkinsons
How Is Parkinsons Disease Diagnosed
Diagnosing Parkinsons disease is sometimes difficult, since early symptoms can mimic other disorders and there are no specific blood or other laboratory tests to diagnose the disease. Imaging tests, such as CT or MRI scans, may be used to rule out other disorders that cause similar symptoms.
To diagnose Parkinsons disease, you will be asked about your medical history and family history of neurologic disorders as well as your current symptoms, medications and possible exposure to toxins. Your doctor will look for signs of tremor and muscle rigidity, watch you walk, check your posture and coordination and look for slowness of movement.
If you think you may have Parkinsons disease, you should probably see a neurologist, preferably a movement disorders-trained neurologist. The treatment decisions made early in the illness can affect the long-term success of the treatment.
Also Check: How To Get Checked For Parkinson’s Disease
Iidopamine Receptor Supersensitivity In Parkinsons Disease
Treatment of Parkinsons disease with L-DOPA remains the primary therapy. While a very effective therapy, long-term treatment invariably leads to the development of dyskinesias . We have proposed that L-DOPA-induced dyskinesia in the treatment of Parkinsons disease results from an aberrant switch in the linkage of the D1 receptor to signal transduction systems that activate the protein kinase, extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase . As discussed, dopamine depletion of the striatum results in opposite effects on the function of D2-indirect and D1-direct pathway neurons evidenced by changes in gene expression . While, either L-DOPA or selective D2 and D1 receptor agonist treatments reverse some of the gene expression changes, the response of D1 receptor-expressing direct pathway neurons is supersensitive to these treatments, which is evident by the induction of a large number of so called immediate-early genes .
E. Cubo, CG. Goetz, in, 2014
Recommended Reading: Drugs That Cause Parkinson Like Symptoms
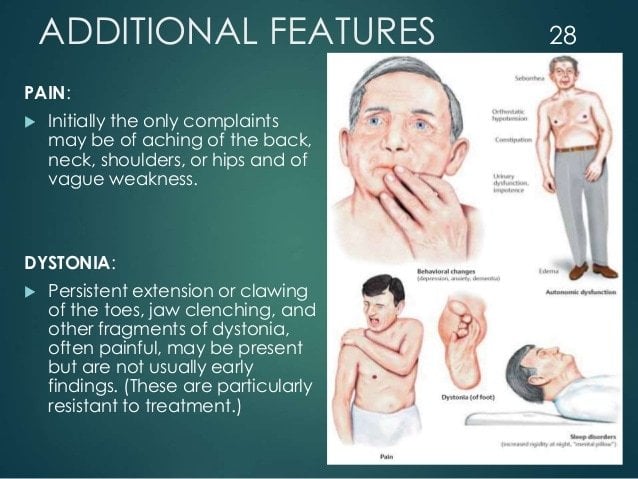
Symptoms Of Parkinsons Disease
The type, number, severity and progression of Parkinsons disease symptoms vary greatly. Every person is affected differently they may not get every symptom.
Some of the more common symptoms are:
- resting tremor
- blood pressure fluctuation
- constipation.
People living with Parkinsons for some time may experience hallucinations , paranoia and delusions . These symptoms are able to be treated so have a talk with your doctor.
Also Check: Parkinson’s Big Movement Exercises
What Should I Know About Parkinsons Disease And Medications
There have been rapid and remarkable changes over the past decade in treating Parkinsons disease . The development of new medicines and the understanding of how best to use them and the older drugs have significantly improved the quality of life for people with the disease.
There is currently no treatment that has been proven to affect the disease progression or development of medication that can slow the disease process. There are two general approaches to the treatment of PD improve the symptoms with medications and engage in physical therapy. Most patients with PD can be adequately treated with medicines that alleviate their symptoms. For the approximately 15% of patients for whom medicines are not sufficiently effective, new, highly effective, and safe surgical treatments are available.
Choices about medicines made early in the course of the disease have a strong impact on the long-term course of the illness. Therefore, you should seek the advice of doctors specially trained in treating PD even when the illness is only suspected. Movement disorders specialists are neurologists who have completed their training in neurology and have received special advanced training in treating PD and other related diseases.
Treatments For Parkinsons Disease

Mount Sinai specialists are skilled in providing the full range of therapies for Parkinsons disease. While your treatment plan may include medications, and possibly surgery, we also believe in the importance of maintaining a regular exercise regimen and eating a healthy, balanced diet.
Medications: The most common treatment for Parkinsons disease is dopamine replacement therapy, usually levodopa, which generally produces significant improvements in walking and movement, as well as reductions in stiffness and tremors. We also use other medications that target either the synthesis or breakdown of dopamine in the body.
Deep Brain Stimulation: Mount Sinais Center for Neuromodulation is recognized for its excellence in performing deep brain stimulation surgery for selected patients with Parkinsons disease. In deep brain stimulation, electrodes are placed in the areas of the brain responsible for symptoms. We connect these electrodes through a wire to a neurostimulator, also called a battery pack, which delivers electrical stimulation to the brain and can modulate the symptoms of PD. We can adjust the electrical parameters of the device to obtain very good control over symptoms. Most patients experience dramatic improvement.
Read Also: Do You Have Pain With Parkinson’s Disease
Dopamine Agonist Withdrawal Syndrome
If you suddenly stop taking dopamine agonists, this can lead to dopamine agonist withdrawal syndrome, which can cause symptoms such as depression, anxiety or pain.
Any withdrawal from Parkinsons drugs needs to be done in a tapered way, under the supervision of a health professional.
Speak to your specialist for advice.
Meditation And Relaxation Techniques
Meditation and relaxation techniques can take many forms. Listening to relaxing music is the most basic form. Mindful meditation can be used to relax and focus on breathing or negative emotions and thoughts. It can also be used to help a person become more aware of their surroundings or body movements. Several studies have shown a connection between Parkinsons disease symptoms and mindful meditation.
You May Like: Parkinson’s Disease Resting Tremor
How Is Parkinsons Treated In The Early Stages
Three main groups of medication are used to treat Parkinsons in the early stages:
- Levodopa : is converted into dopamine in the brain.
- Dopamine agonists: stimulate the nerve receptors responsible for the uptake of dopamine.
- MAO-B inhibitors : block the breakdown of dopamine in the brain.
The medications are usually taken in tablet form. Some dopamine agonists are also available as patches.
In the early stages, some people with mild symptoms cope just fine without medication. If at some stage the symptoms become too much of a problem, levodopa and dopamine agonists are the main medication options. They work slightly differently to each other, and some products may cause side effects more often or have worse side effects than others. But both are very effective in the early stages of the illness. That helps many people with Parkinsons to live a fairly symptom-free life for at least a few years.
What Future Medications May Be Available For Parkinsons
There are numerous studies investigating new treatments for Parkinsons disease.
There has been new information about the role of autoimmunity and T-cells in the development of Parkinsons disease, possibly opening the door to a role for biologics.
Stem cells are also being investigated as a treatment option for Parkinsons disease.
Recommended Reading: Can Parkinson’s Disease Cause Dementia
Medication Guidelines For Parkinson’s Disease
There is no one best mix of Parkinsonâs medicines. You and your doctor will have to try a few treatment approaches to figure out the best one for you.
But there are some general guidelines for taking your medication. Be sure to ask your doctor or pharmacist for any specific tips for your treatment.
Anticholinergics For Early On
The first pharmacological agents used in PD therapy were anticholinergic drugs. They reduce the activity of acetylcholine by acting as antagonists at choline receptors, hoping to restore the balance between dopamine and acetylcholine levels that was disturbed by PD. These drugs have largely been replaced by L-DOPA and other centrally acting dopaminergic agonists, but they still remain available for use in the treatment of PD. Benztropine, biperiden, diphenhydramine, ethopropazine, orphenadrine, procyclidine, and trihexyphenidyl are included in this therapeutic class of drugs, though there is little pharmacokinetic information available on them because of their low plasma drug concentrations. Typically, anticholinergic drugs have a greater role in tremor-predominant PD and can be a monotherapy in early stages, but are usually done in adjunct with L-DOPA or other prescribed medications.
Recommended Reading: Psychotherapy For Parkinson’s Disease
Adjust Your Drug Dose
Side effects like dyskinesia might be due to the amount of levodopa youre taking. Ask your doctor whether you can lower your dose enough to prevent side effects while still managing your Parkinsons symptoms. It might take some trial and error to get the dose just right.
Another option is to switch to an extended-release form of dopamine. Because the drug releases more slowly into your blood, it prevents the dopamine spikes and valleys that can trigger dyskinesia.
You might also need to add more of a drug. For example, adding extra carbidopa to levodopa can cut down on nausea.
Ask Your Doctor If You Can Change The Time At Which You Take Your Meds
Dont experiment with the timing of your Parkinsons disease drugs yourself, because this can result in a variety of complications. You can, on the other hand, ask your doctor whether it is possible to take your medications at a different time of day. Meds that induce sleepiness may be better taken before bedtime, for instance, while those drugs that have insomnia as a side effect may be better taken earlier in the day. Your doctor will have had more experience in prescribing the medications you take, and will have helpful tips to share.
You May Like: What Is The First Symptoms Of Parkinson’s Disease
Medications To Avoid Or Use With Caution
Sign up for our email list and receive our publication on medications with potential complications you should be aware of.
Before making any decisions about treatment of Parkinsons disease, you will want to learn about the different types of medications available for Parkinsons disease and discuss the pros and cons of each with your physician. It may help to know that there is no right answer, and if you try something that doesnt work for you, you can always adjust your plan.
To learn more about adjusting medication plans, view our webinar on What to Do When Your Medications Stop Working.
Drug And Medication Therapies
The purpose of treating Parkinsons is to reduce the effect of symptoms on your daily life. Without treatment, you will eventually find that the symptoms make it hard to perform daily activities. Symptoms, such as shaking and stiffness, may cause discomfort the risk of injury from falls may increase, and swallowing may become more difficult. People are encouraged to maintain open and ongoing discussions with their Parkinsons healthcare team when exploring treatment options.
Medication will help you function, but may cause side effects. It is important to find the right balance between the medications benefits and side effects. Everyone with Parkinsons is unique and will experience different symptoms, which means the treatment you receive will be geared to your specific needs. Drugs for Parkinsons work on the brains complex chemistry and may need to be taken several times a day. Use them as prescribed and do not alter your doses without consulting your doctor. Current treatment neither cures Parkinsons nor stops it from advancing.
Recommended Reading: Essential Tremor Vs Parkinson’s Disease
Mechanism Of Action Of Available Drugs
The major classes of drugs currently available for the treatment of idiopathic Parkinsons disease are shown in Table 1. Many aim to increase dopamine in the brain, by increasing its production or altering its metabolism .
|
Table 1 |
Drugs with alter metabolism in boxed red italics
Levodopa
Levodopa is absorbed from the small intestine and transported into the brain where it is converted to dopamine. Levodopa has a short plasma half-life of about one hour. Early in Parkinsons disease, levodopa has a long duration of action which is independent of plasma concentration, but as the disease progresses, the duration of the effect reduces. The short-duration effect is strongly linked to plasma concentration and lasts, at most, hours.
Slow-release preparations are gradually absorbed, resulting in more sustained plasma concentrations. They have reduced bioavailability higher doses are required to match the benefit of an equivalent strength of a standard preparation. Rapid release preparations are taken in liquid form to enhance passage through the stomach and absorption from the small intestine.
Dopamine agonists
Apomorphine is a potent emetic so patients must be pre-treated with domperidone 20 mg three times daily orally for at least 48 hours before the first injection. Domperidone should be continued for at least a few weeks once regular intermittent treatment has commenced. The dose can then be tapered slowly as tolerance to the emetic effects of apomorphine usually develops.