Can Parkinsons Disease Be Prevented
Unfortunately, no. Parkinsons disease is long-term disease that worsens over time. Although there is no way to prevent or cure the disease , medications may significantly relieve your symptoms. In some patients especially those with later-stage disease, surgery to improve symptoms may be an option.
What Is Parkinson Disease
Parkinson disease is a movement disorder. It can cause the muscles to tighten and become rigid This makes it hard to walk and do other daily activities. People with Parkinsons disease also have tremors and may develop cognitive problems, including memory loss and dementia.
Parkinson disease is most common in people who are older than 50. The average age at which it occurs is 60. But some younger people may also get Parkinson disease. When it affects someone younger than age 50, it’s called early-onset Parkinson disease. You may be more likely to get early-onset Parkinson disease if someone in your family has it. The older you are, the greater your risk of developing Parkinson disease. It’s also much more common in men than in women.
Parkinson disease is a chronic and progressive disease. It doesn’t go away and continues to get worse over time.
The Cerebellum And Parkinsonian Akinesia/rigidity
Parkinsons disease is not a homogenous disease and has two predominant forms: akinesia and rigidity and prominent resting tremor . Akinesia can be defined as a delay or a failure in movement initiation , particularly for self-initiated movements. Functional neuroimaging studies using PET or blood oxygen leveldependent functional MRI frequently demonstrated increased activation in the cerebellum in patients with Parkinsons disease during performance of various upper limb movements . For example, during externally or internally timed simple finger movements , motor timing , complex sequential movements , bimanual two-hand coordinated tasks or two different motor tasks simultaneously , patients with Parkinsons disease OFF medication showed hyperactivation in the cerebellum.
Brain areas more activated in patients with Parkinsons disease than in normal subjects during automatic execution of sequential movements. Modified from, with permission from Oxford University Press.
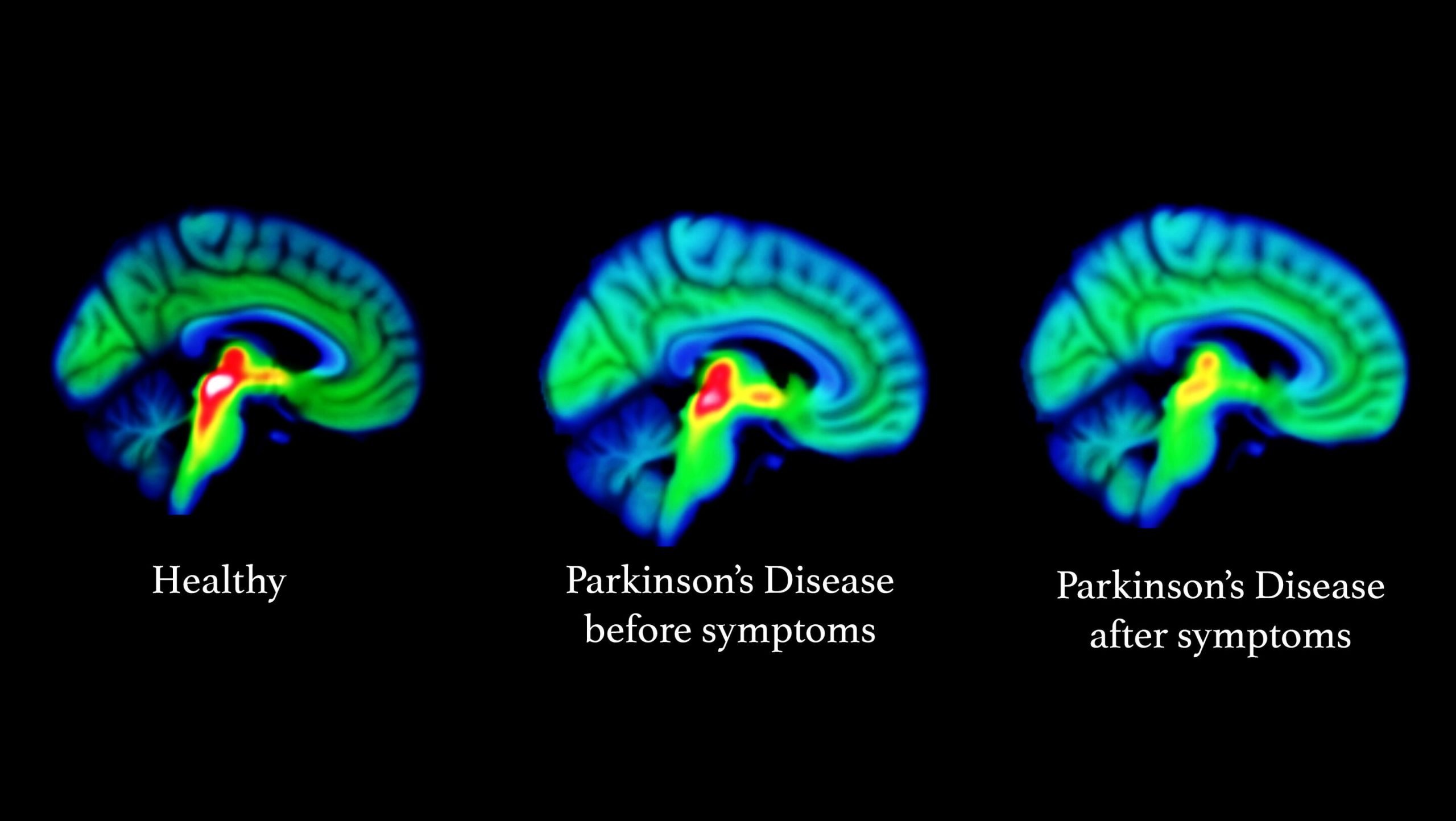
The neurodegenerative process in Parkinsons disease begins several years before the onset of any clinical symptoms . The motor symptoms of Parkinsons disease usually present after 70% of dopaminergic neurons have degenerated . Presumably, the compensatory effect in the cerebellum and other brain regions accounts for delaying the onset of motor symptoms and preserving relatively normal function.
Don’t Miss: Voice Amplifiers For Parkinson’s
Is There A Parkinson’s Disease Brain Scan
MRI brain scans and single photon emission computed tomography scans are often performed to rule out other causes of your symptoms, including strokes or a brain tumor. However, neither of these scans are diagnostic of Lewy bodies. There is no Parkinson’s disease brain scan, and no tests can conclusively show that you have Parkinson’s disease.
APA ReferenceSmith, E. . How Parkinsons Disease Affects the Brain, HealthyPlace. Retrieved on 2021, December 23 from https://www.healthyplace.com/parkinsons-disease/effects/how-parkinsons-disease-affects-the-brain
Is Parkinsons Diagnosed In The Brain
Parkinsons disease is one of the most challenging neurological disorders to diagnose and treat. If your doctor suspects you have Parkinsons disease, you will usually be referred to a neurologist for further tests. These tests will involve certain movements and exercises to check your symptoms.
A neurologist will look for motor symptoms such as:
- A tremor that occurs at rest
- Slowed movement
- Muscle stiffness
If you have two or more of these symptoms and your doctor has taken blood tests to rule out other causes, its likely you will be diagnosed with Parkinsons disease. Your symptoms will be closely monitored to see any progression of Parkinsons disease, which can take years.
Recommended Reading: Cleveland Clinic Parkinson’s Bicycle Study 2017
Medicines For Parkinson’s Disease
Medicines prescribed for Parkinson’s include:
- Drugs that increase the level of dopamine in the brain
- Drugs that affect other brain chemicals in the body
- Drugs that help control nonmotor symptoms
The main therapy for Parkinson’s is levodopa, also called L-dopa. Nerve cells use levodopa to make dopamine to replenish the brain’s dwindling supply. Usually, people take levodopa along with another medication called carbidopa. Carbidopa prevents or reduces some of the side effects of levodopa therapysuch as nausea, vomiting, low blood pressure, and restlessnessand reduces the amount of levodopa needed to improve symptoms.
People with Parkinson’s should never stop taking levodopa without telling their doctor. Suddenly stopping the drug may have serious side effects, such as being unable to move or having difficulty breathing.
Other medicines used to treat Parkinsons symptoms include:
- Dopamine agonists to mimic the role of dopamine in the brain
- MAO-B inhibitors to slow down an enzyme that breaks down dopamine in the brain
- COMT inhibitors to help break down dopamine
- Amantadine, an old antiviral drug, to reduce involuntary movements
- Anticholinergic drugs to reduce tremors and muscle rigidity
So What Do We Know So Far
Location of the substantia nigra. FrozenManCC BY-SA 4.0
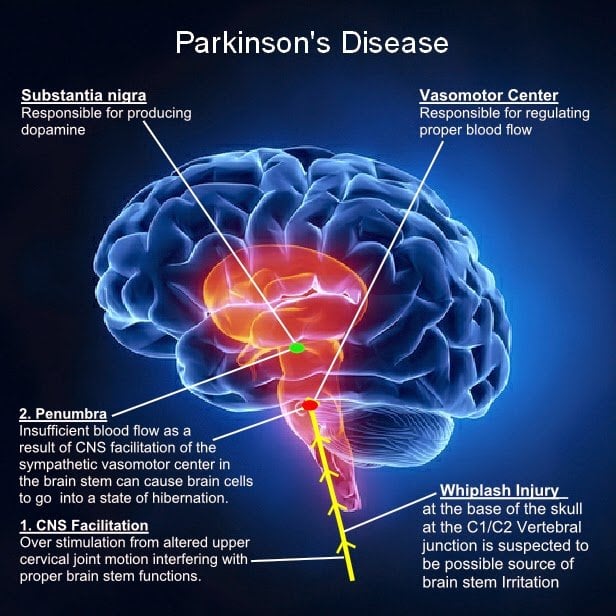
The substantia nigra is an area of the mid brain located at the top of the spinal cord, which has been the focus of much work into how Parkinsons affects the brain.
There are a right and a left substantia nigra, and often one side is affected before the other. Because of this, people with Parkinsons often experience symptoms primarily on one side of their body, particularly in the early stages. Indeed, this common feature of the condition often helps to distinguish Parkinsons from other similar conditions.
When it comes to confirming a diagnosis, it is the substantia nigra where pathologists look for changes at the end of life in brain tissue that has been donated to research. And the loss of the dopamine-producing cells in this area of the brain, accompanied by the presence of clumps of alpha-synuclein protein , has been the hallmark of Parkinsons for decades.
You can read more about the alpha-synuclein protein, and how it plays a role in the spread of Parkinsons, in a previous blog post:
Don’t Miss: What Foods Should Be Avoided When Taking Levodopa
Locating The Basal Ganglia
|
The basal ganglia are collections of nerve cells located deep within the brain. They include the following:
The basal ganglia help initiate and smooth out muscle movements, suppress involuntary movements, and coordinate changes in posture. |
What Are The Symptoms Of Parkinson Disease
Parkinson disease symptoms usually start out mild, and then progressively get much worse. The first signs are often so subtle that many people don’t seek medical attention at first. These are common symptoms of Parkinson disease:
- Tremors that affect the face and jaw, legs, arms, and hands
- Slow, stiff walking
Also Check: Prayers For Parkinson’s Disease
What Lifestyle Changes Can I Make To Ease Parkinsons Symptoms
Exercise: Exercise helps improve muscle strength, balance, coordination, flexibility, and tremor. It is also strongly believed to improve memory, thinking and reduce the risk of falls and decrease anxiety and depression. One study in persons with Parkinsons disease showed that 2.5 hours of exercise per week resulted in improved ability to move and a slower decline in quality of life compared to those who didnt exercise or didnt start until later in the course of their disease. Some exercises to consider include strengthening or resistance training, stretching exercises or aerobics . All types of exercise are helpful.
Eat a healthy, balanced diet: This is not only good for your general health but can ease some of the non-movement related symptoms of Parkinsons, such as constipation. Eating foods high in fiber in particular can relieve constipation. The Mediterranean diet is one example of a healthy diet.
Preventing falls and maintaining balance: Falls are a frequent complication of Parkinson’s. While you can do many things to reduce your risk of falling, the two most important are: 1) to work with your doctor to ensure that your treatments whether medicines or deep brain stimulation are optimal and 2) to consult with a physical therapist who can assess your walking and balance. The physical therapist is the expert when it comes to recommending assistive devices or exercise to improve safety and preventing falls.
Changes In Brain Volume In Parkinsons Disease
Strong correlation exists between brain size and cognitive functions. In PD patients, atrophy of the brain was observed in many cortical and subcortical areas, which contributes in decrease in the volume of the brain. Interestingly, it was reported that volume of the frontal lobe, temporoparietal junction, parietal lobe, insula, anterior cingulate cortex, basal ganglia, and thalamus increased in PD patients. Prefrontal lobe plays a crucial role in cognitive functions and in PD patients loss of gray matter has been reported.
Read Also: Sam Waterston Tremor
What Part Of The Brain Is Affected By Parkinson Disease
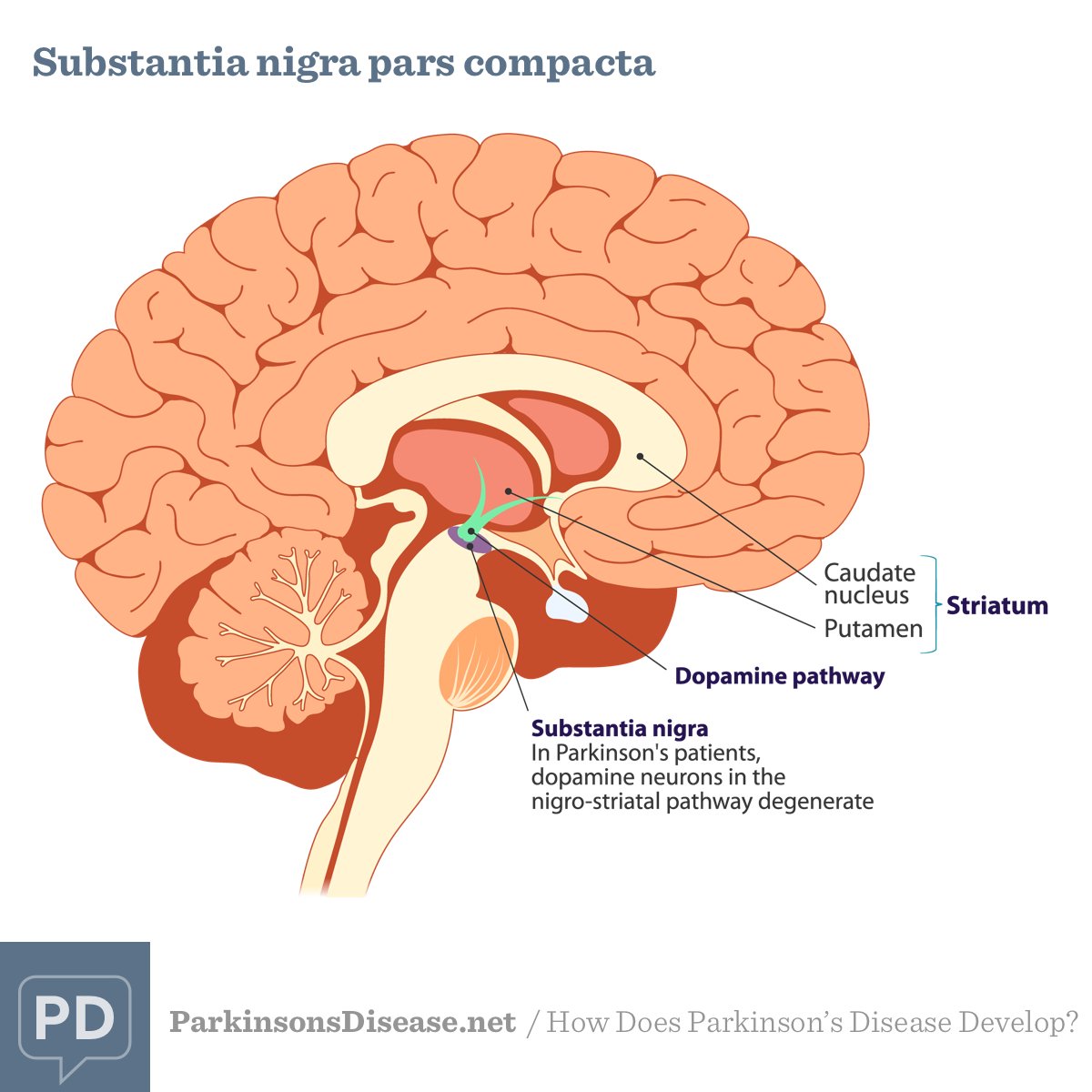
Parkinson disease is predominantly a disorder of the basal ganglia, which are a group of nuclei situated at the base of the forebrain. The striatum, composed of the caudate and putamen, is the largest nuclear complex of the basal ganglia. The striatum receives excitatory input from several areas of the cerebral cortex, as well as inhibitory and excitatory input from the dopaminergic cells of the substantia nigra pars compacta . These cortical and nigral inputs are received by the spiny projection neurons, which are of 2 types: those that project directly to the internal segment of the globus pallidus , the major output site of the basal ganglia and those that project to the external segment of the globus pallidus , establishing an indirect pathway to the GPi via the subthalamic nucleus .
For an illustration of the subthalamic nucleus, see the image below.
References
Hauser RA, Grosset DG. FP-CIT SPECT Brain Imaging in Patients with Suspected Parkinsonian Syndromes. J Neuroimaging. 2011 Mar 16. .
Wirdefeldt K, Adami HO, Cole P, Trichopoulos D, Mandel J. Epidemiology and etiology of Parkinson’s disease: a review of the evidence. Eur J Epidemiol. 2011 Jun. 26 Suppl 1:S1-58. .
Anderson P. More Evidence Links Pesticides, Solvents, With Parkinson’s. Medscape Medical News. Available at . Accessed: June 11, 2013.
Grimes DA, Lang AE. Treatment of early Parkinsons disease. Can J Neurol Sci. 1999 Aug. 26 Suppl 2:S39-44. .
Who Gets Parkinsons Disease
Estimates vary, but about 1 million people are living with Parkinsons disease in the U.S. Doctors diagnose about 60,000 cases a year, most in people over age 60. Younger people can also get Parkinsons. About 5-10% of patients have young-onset Parkinsons disease, diagnosed before age 50.
About 15% of patients have Parkinsons-plus syndromes, also known as atypical Parkinsons. Medications may be less effective for these syndromes, which can lead to disability sooner.
Risk factors for Parkinsons disease include:
- Age: Risk increases with age. Average age at diagnosis is 65.
- Gender: Men are at higher risk.
- Environmental exposure: Lifetime exposure to well water, which may contain pesticide runoff, can increase risk. So can exposure to air particles containing heavy metals, such as in industrial areas.
- Family history: Having a close relative with the disease could increase your risk. Researchers have identified a dozen genes that may be linked to Parkinsons disease.
- Sleep disorder: People who act out their dreams are up to 12 times more likely to develop Parkinsons disease. Its not clear whether this condition, called REM sleep behavior disorder or RBD, is a cause or symptom of Parkinsons disease.
- Head trauma: Traumatic brain injury increases risk of Parkinsons, even years later.
Don’t Miss: Parkinson’s Hallucinations Commercial
Who Gets Parkinson’s Disease
About 1 million people in the United States have Parkinson’s disease, and both men and women can get it. Symptoms usually appear when someone is older than 50 and it becomes more common as people get older.
Many people wonder if you’re more likely to get Parkinson’s disease if you have a relative who has it. Although the role that heredity plays isn’t completely understood, we do know that if a close relative like a parent, brother, or sister has Parkinson’s, there is a greater chance of developing the disease. But Parkinson’s disease is not contagious. You can’t get it by simply being around someone who has it.
How Is Parkinsons Disease Treated
There is no cure for Parkinsons disease. However, medications and other treatments can help relieve some of your symptoms. Exercise can help your Parkinsons symptoms significantly. In addition, physical therapy, occupational therapy and speech-language therapy can help with walking and balance problems, eating and swallowing challenges and speech problems. Surgery is an option for some patients.
Recommended Reading: Adaptive Silverware For Parkinson’s
Structural And Functional Brain Patterns Of Non
- Department of Neurology, Jena University Hospital, Jena, Germany
Parkinsons disease is a common, progressive and multisystem neurodegenerative disorder characterized by motor and non-motor symptoms. Advanced magnetic resonance imaging, positron emission tomography, and functional magnetic resonance imaging can render the view toward understanding the neural basis of these non-motor syndromes, as they help to understand the underlying pathophysiological abnormalities. This review provides an up-to-date description of structural and functional brain alterations in patients with PD with cognitive deficits, visual hallucinations, fatigue, impulsive behavior disorders, sleep disorders, and pain.
Brain Regional Specific Metabolic Disturbance Was Involved In Parkinsons Disease
To further explore discriminating features and potential biomarkers in brain function and disease, the supervised PLS-DA analyses were applied for six different brain regions from three groups . Moreover, a mixed-model analysis was applied to evaluate the effects of dopamine loss and L-dopa replacement on metabolite alterations in the PD and LID rats and the detailed results were shown in Figure 5 and listed in Supplementary Tables S1S6. As predicted, a clear separation between control and PD rats was observed in the midbrain and striatum . Accordingly, using hierarchical clustering on the profile of the identified 21 metabolites, the metabolic profile of midbrain and striatum was strictly separated between control and PD rats, several interesting metabolite clusters became apparent as well . One of these clusters contained glutamate and glutamine, and this alteration in the glutamate metabolism pathway reflected neurotransmitter homeostasis in the brain . In addition, various products of energy metabolism pathways in the striatum were altered in PD rats .
Figure 4. PLS-DA score plots of Con, PD and LID groups in the different brain regions: Mid, midbrain Rstr, right striatum Rcor, right cortex Rhip, right hippocampus Rcer, right cerebellum Hyp, hypothalamus.
Recommended Reading: Similar To Parkinsons
What Are The Causes
The cause of Parkinson’s is largely unknown. Scientists are currently investigating the role that genetics, environmental factors, and the natural process of aging have on cell death and PD.
There are also secondary forms of PD that are caused by medications such as haloperidol , reserpine , and metoclopramide .
New Approaches For Monitoring And Treating Pd
The system-level view of PD features has a high potential for the development of innovative procedures for monitoring and treating PD. We show this by illustrating some of these possibilities. Regarding monitoring, one of the biggest future challenges for imaging techniques applied to PD is to integrate their results to identify the mechanisms that might be targeted with drugs and other interventions.,,
By disentangling the multifaceted mechanisms underlying PD symptoms, the system view of PD proposed here, operationalized into dynamical system-level models integrating multi-source data, could lead to a systematic data-driven improvement of therapies., We support this possibility by referring to some relevant treatment techniques. DBS and transcranial magnetic stimulation have been used with various brain targets, in particular sites involving areas of the BGCtxCer system and not only BG. Indeed, several experiments support the idea that DBS preferentially modulates remote structures rather than local circuits since fibers of passage are more excitable than local cell bodies at the site of stimulation. The analysis of the corticalsubcortical circuits discussed above, possibly supported by computational models integrating multiple data sources, could represent a necessary step to better understand the mechanisms underlying DBS/TMS effects and so to identify possible new targets within the BGCtxCer system.
You May Like: Yopd Life Expectancy
Parkinsons Disease Risk Factors
There are a variety of risk factors for Parkinsons, including those related to your age and environment.
Your risk of developing Parkinsons disease increases with age, and about 1% of people over 60 years old have Parkinsons disease. Although it more commonly affects older people, about 10% of cases are considered early onset, meaning symptoms begin before age 50.
Parkinsons affects more men than women, and having a relative with Parkinsons disease might mean you may have a slightly higher risk of developing it. However, your risk is still low unless you have many relatives with the disease. Environmental toxins, such as ongoing exposure to pesticides and herbicides, may also be a risk factor.
What Is The Outlook For Persons With Parkinsons Disease
Although there is no cure or absolute evidence of ways to prevent Parkinsons disease, scientists are working hard to learn more about the disease and find innovative ways to better manage it, prevent it from progressing and ultimately curing it.
Currently, you and your healthcare teams efforts are focused on medical management of your symptoms along with general health and lifestyle improvement recommendations . By identifying individual symptoms and adjusting the course of action based on changes in symptoms, most people with Parkinsons disease can live fulfilling lives.
The future is hopeful. Some of the research underway includes:
- Using stem cells to produce new neurons, which would produce dopamine.
- Producing a dopamine-producing enzyme that is delivered to a gene in the brain that controls movement.
- Using a naturally occurring human protein glial cell-line derived neurotrophic factor, GDNF to protect dopamine-releasing nerve cells.
Many other investigations are underway too. Much has been learned, much progress has been made and additional discoveries are likely to come.
Read Also: On-off Phenomenon