Advanced Therapies For Parkinsons Disease
When significant off-time or dyskinesia persists despite optimised oral treatment, advanced therapies should be considered. Apomorphine, a potent dopamine agonist given by continuous subcutaneous infusion, is the least invasive and most straightforward of these. Following on from extensive clinical experience, the recent double-blind TOLEDO study confirmed a significant reduction in off-time and improved on-time with apomorphine versus placebo.
Deep-brain stimulation involves surgical placement of electrodes into brain regions such as the subthalamic nucleus to improve motor fluctuations or refractory tremor. DBS is typically considered in patients without significant axial or neuropsychiatric problems. It improves motor function, off-time and QoL in patients with PD, and provides significant benefits over medical therapy even in patients with an average disease duration of 7 years. The benefits of DBS on motor function, fluctuations and activities of daily living have been demonstrated up to 10 years postoperatively, although axial features continue to progress. Infusion of levodopacarbidopa intestinal gel via jejunostomy has also been shown to improve off-time compared to oral levodopa, and is commissioned in specialist centres where other advanced therapies are ineffective or contraindicated. Further information on the decision-making process for advanced therapies is summarised in a dedicated review.
Dont Miss: Parkinsons Disease And Driving
When Should I See My Healthcare Provider About Lewy Body Dementia
If you or a loved one are experiencing symptoms of Lewy body dementia, talk to your healthcare provider.
If youve been diagnosed with Lewy body dementia, youll need to see your healthcare team regularly to monitor your health and symptoms and to make sure your medications are working.
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Learning early that you have a diagnosis of Lewy body dementia allows you and your family to plan for a meaningful quality of life together and enables you to get your legal, financial and healthcare plans and desires in order. Your healthcare team will be ready to provide education, support and care for you or your loved one. Ask your team for information on local LBD support groups as well. Support groups can be very helpful for sharing care tips and providing comfort in knowing youre not alone.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 08/18/2022.
References
- Genetic and Rare Diseases Information Center. Lewy Body Dementia. Accessed 8/18/2022.
- Haider A, Spurling BC, Sánchez-Manso JC. Lewy Body Dementia. . In: StatPearls . Treasure Island : StatPearls Publishing 2022. Accessed 8/18/2022.
- Merck Manual Professional Version. Lewy Body Dementia and Parkinson Disease Dementia. Accessed 8/18/2022.
- National Institutes of Neurological Disorders and Stroke. Dementia with Lewy Bodies Information Page. Accessed 8/18/2022.
- National Institute on Aging. What Is Lewy Body Dementia? Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments. Accessed 8/18/2022.
Patient Demographics And Clinical Characteristics
One hundred and twenty-one LSPD patients were initially recruited . Following motor assessment but before the proposed NPA, 12 patients died and 16 declined to participate in the NPA . A total of 93 LSPD patients agreed to perform the NPA. However, when patients were visited at home, the neuropsychologist found that it would not be possible to carry out the NPA of eight patients due to their physical/motor disability. Of these eight patients, we only collected information through the neurological and neuropsychiatric evaluation, and through the clinical history that we performed with the help of the caregiver .
Figure 1. Patients and assessments flowchart. MDS PDD, Parkinson’s Disease dementia criteria recommended by Movement Disorder Society Task Force LSPD, Late-stage Parkinson’s Disease patients LSPD-D, Late-stage Parkinson’s Disease dementia patients NPA, Neuropsychological assessment GDS, Geriatric Depression Scale.
Table 2. Demographic and clinical characteristics of LSPD patients.
In total, 85 patients underwent complete NPA . Forty-nine were women, with a mean age of 75.4 years , 6.5 years of education, 16.9 years of disease duration, age at PD onset , a mean H& Y of 4.1 and loss of independence assessed by the S& E corresponding to 36.7% .
You May Like: Masked Face Parkinson’s Disease
Diagnosis Of Parkinsons Disease
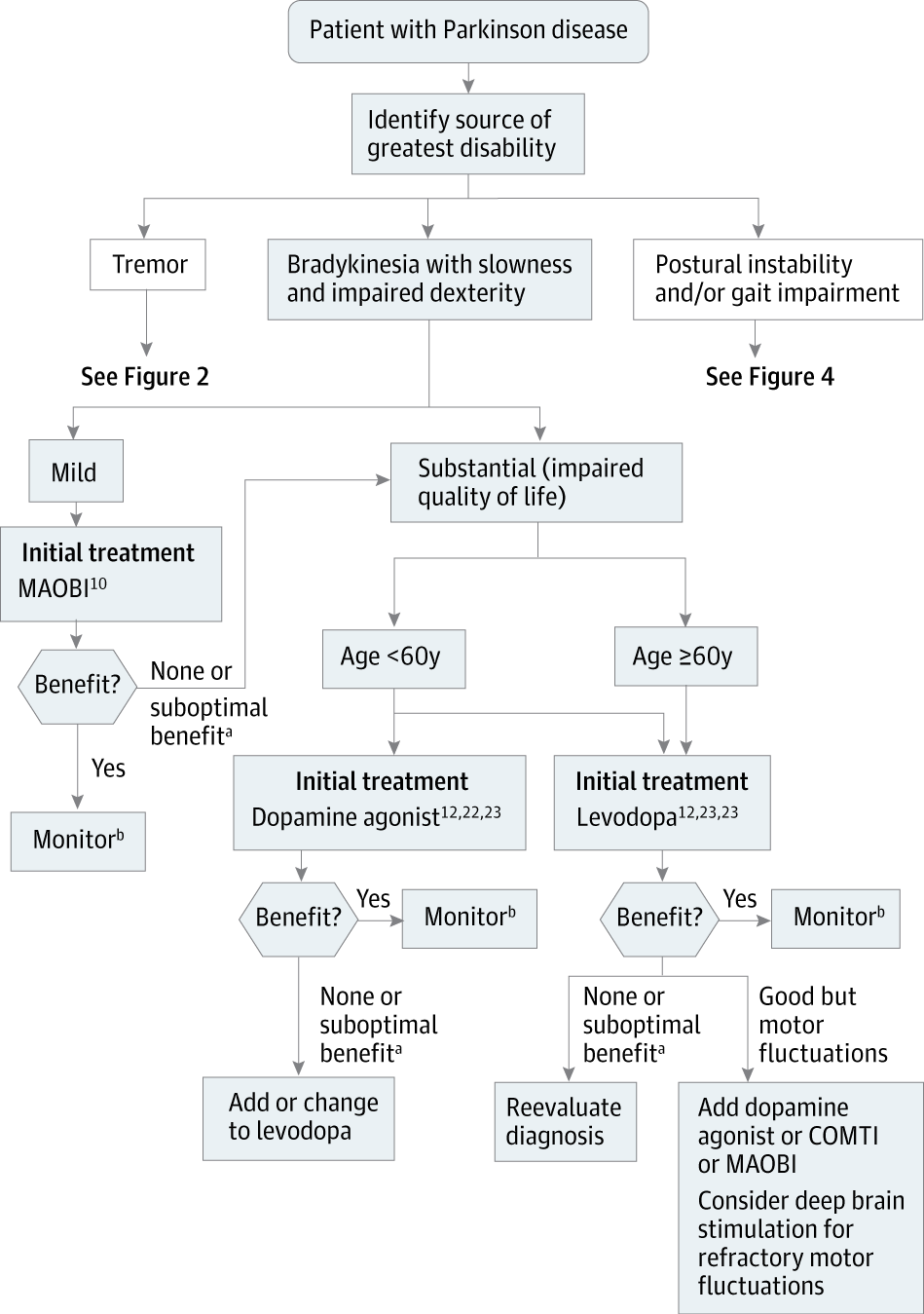
The diagnosis of PD is clinical and requires bradykinesia, defined as slowness of movement and decrement in amplitude or speed, usually assessed using finger tapping, foot tapping or pronationsupination hand movements. In addition, rest tremor or rigidity is required to confirm a parkinsonian syndrome. Tremor was absent at presentation in 30% in one series of pathologically proven PD. Patients with suspected PD should be referred quickly and untreated to a specialist in movement disorders for evaluation. Key points for discussion at diagnosis include the need to inform vehicle licensing agencies and insurers, signposting to written or web-based information on newly diagnosed PD, and provision of contact details for the local PD nurse specialist .
Current International Parkinson and Movement Disorder Society diagnostic criteria for Parkinsons disease adapted from Postuma RB, Berg D, Stern M et al. MDS clinical diagnostic criteria for Parkinsons disease. Mov Disord 2015 30:1591601. At least two supportive criteria and no red flags required for a diagnosis of clinically established Parkinsons disease. Conditions in italics should be considered if the corresponding exclusion criteria or red flags are present.
Recommended Reading: How To Prevent Getting Parkinsons Disease
How Is Parkinson Disease Diagnosed
Parkinson disease can be hard to diagnose. No single test can identify it. Parkinson can be easily mistaken for another health condition. A healthcare provider will usually take a medical history, including a family history to find out if anyone else in your family has Parkinson’s disease. He or she will also do a neurological exam. Sometimes, an MRI or CT scan, or some other imaging scan of the brain can identify other problems or rule out other diseases.
You May Like: Parkinson’s Disease Experimental Treatment
Core Features Of Probable Pdd
The primary defining feature of PDD is dementia that develops in the setting of established PD . Therefore, the critical first step in the diagnosis process is to identify idiopathic PD, prior to the development of dementia. For a diagnosis of PDD, two core features must be present: a diagnosis of PD according to the Queen Square Brain Bank criteria and PD developed prior to the onset of dementia .
In this case, a dementia syndrome is defined as impairment in at least two cognitive domains and cognitive deficiency severe enough to impair daily life that must be independent of impairment because of PD motor symptoms. The MDS Task Force recommended that the Mini-Mental State Examination may be useful as a screening instrument for identifying cognitive impairment in PDD patients the MMSE is a simple and universally applied scale that can be easily and quickly performed in the clinical setting . An MMSE score of 25 or below is proposed as the cut-off for identifying clinically significant cognitive impairment in this population .
What Causes Parkinsons Disease Dementia
A chemical messenger in the brain called dopamine helps control and coordinate muscle movement. Over time, Parkinsons disease destroys the nerve cells that make dopamine.
Without this chemical messenger, the nerve cells cant properly relay instructions to the body. This causes a loss of muscle function and coordination. Researchers dont know why these brain cells disappear.
Parkinsons disease also causes dramatic changes in a part of your brain that controls movement.
Those with Parkinsons disease often experience motor symptoms as a preliminary sign of the condition. Tremors are one of the most common first symptoms of Parkinsons disease.
As the disease progresses and spreads in your brain, it can affect the parts of your brain responsible for mental functions, memory, and judgment.
Over time, your brain may not be able to use these areas as efficiently as it once did. As a result, you may begin experiencing symptoms of Parkinsons disease dementia.
You have an increased risk of developing Parkinsons disease dementia if:
Read Also: Parkinson’s Education For Nurses
What Are The Symptoms Of Parkinson Disease
Parkinson disease symptoms usually start out mild, and then progressively get much worse. The first signs are often so subtle that many people don’t seek medical attention at first. These are common symptoms of Parkinson disease:
- Tremors that affect the face and jaw, legs, arms, and hands
- Slow, stiff walking
What Can I Expect If A Loved One Or I Have Lewy Body Dementia
Each persons experience with Lewy body dementia is unique to them. How slowly or quickly the disease progresses is impossible to know, but may be influenced by your general health and any existing conditions you may have.
Because LBD is a progressive disease, difficulties with mind and body functions get worse over time. Currently, theres no known way to stop the progression of the disease.
However, theres always hope. Research on dementia with Lewy bodies, Alzheimers disease and Parkinsons disease with dementia are ongoing. New medications are being developed and new treatment approaches are being investigated.
You May Like: Delusions In Parkinson’s Disease
Motor Fluctuations And Dyskinesia
For the treatment of motor features of tremor, bradykinesia, and rigidity associated with Parkinson’s disease, dopaminergic therapies are initially effective however, motor fluctuations eventually complicate therapy and can cause significant disability and impair quality of life. Sustained-release carbidopa/levodopa and bromocriptine have not been found to reduce off time.
Risk factors for motor complications include disease severity, younger age at onset of Parkinson’s disease, high levodopa dosage, and longer disease duration. The motor fluctuations usually are addressed with levodopa adjustments as well as adjunctive medications or surgery as discussed below.
What Are The Complications Of Parkinson Disease
Parkinson disease causes physical symptoms at first. Problems with cognitive function, including forgetfulness and trouble with concentration, may arise later. As the disease gets worse with time, many people develop dementia. This can cause profound memory loss and makes it hard to maintain relationships.
Parkinson disease dementia can cause problems with:
- Speaking and communicating with others
- Problem solving
- Paying attention
If you have Parkinson disease and dementia, in time, you likely won’t be able to live by yourself. Dementia affects your ability to care of yourself, even if you can still physically do daily tasks.
Experts don’t understand how or why dementia often occurs with Parkinson disease. Its clear, though, that dementia and problems with cognitive function are linked to changes in the brain that cause problems with movement. As with Parkinson disease, dementia occurs when nerve cells degenerate, leading to chemical changes in the brain. Parkinson disease dementia may be treated with medicines also used to treat Alzheimer’s disease, another type of dementia.
Recommended Reading: Cbd And Parkinson’s Disease
A Review On Parkinsons Disease Treatment
5214526Tori K. Lee Eva L. Yankee
Department of Biology, Angwin, CA 94508, USA .
Received:First Decision:Revised:Accepted:Available online:Academic Editors:Copy Editor:Production Editor:
© The Author 2021. Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, for any purpose, even commercially, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
Lewy Body Dementia Vs Parkinsons Disease Dementia
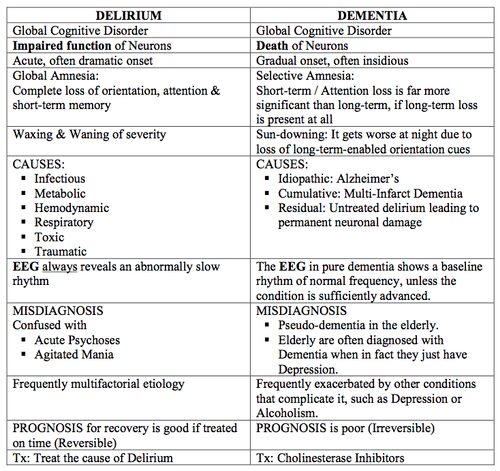
Diagnoses of Lewy body dementia include dementia with Lewy bodies and Parkinsons disease dementia. Symptoms in both of these diagnoses can be similar.
Lewy body dementia is a progressive dementia caused by abnormal deposits of a protein called alpha-synuclein in the brain. Lewy bodies are also seen in Parkinsons disease.
The overlap in symptoms between Lewy body dementia and Parkinsons disease dementia include movement symptoms, rigid muscles, and problems with thinking and reasoning.
This seems to indicate that they could be linked to the same abnormalities, though more research is needed to confirm that.
The later stages of Parkinsons disease have more severe symptoms that may require help moving around, around-the-clock care, or a wheelchair. Quality of life can decline rapidly.
Risks of infection, incontinence, pneumonia, falls, insomnia, and choking increase.
Hospice care, memory care, home health aides, social workers, and support counselors can be a help in later stages.
Parkinsons disease itself isnt fatal, but complications can be.
Research has shown a median survival rate of about
You May Like: What Is Lewy Body Parkinson’s Disease
Over The Counter & Complementary Therapies
People with Parkinsons who seek relief from their symptoms may decide to explore complementary therapies, which can support or complement traditional medicine. While there are many kinds of complementary medicine, this section focuses on herbs, vitamins and supplements.
Page reviewed by Dr. Chauncey Spears, Clinical Assistant Professor and Dr. Amelia Heston, Movement Disorders Fellow at the University of Michigan.
Behaviors Seen In Parkinsons Disease Dementia
As dementia progresses, managing disorientation, confusion, agitation, and impulsivity can be a key component of care.
Some patients experience hallucinations or delusions as a complication of Parkinsons disease. These may be frightening and debilitating. Approximately 50 percent of those with the disease may experience them.
The best thing to do when giving care to someone experiencing hallucinations or delusions from Parkinsons disease dementia is to keep them calm and reduce their stress.
Take note of their symptoms and what they were doing before they exhibited signs of hallucinating and then let their doctor know.
This element of the disease can be particularly challenging for caregivers. Patients may become unable to care for themselves or be left alone.
Some ways to make caregiving easier include:
- sticking to a normal routine whenever possible
- being extra comforting after any medical procedures
- limiting distractions
- using curtains, nightlights, and clocks to help stick to a regular sleep schedule
- remembering that the behaviors are a factor of the disease and not the person
Read Also: Exercise And Parkinson’s Questions And Answers From The Experts
What Is Parkinson Disease
Parkinson disease is a movement disorder. It can cause the muscles to tighten and become rigid This makes it hard to walk and do other daily activities. People with Parkinsons disease also have tremors and may develop cognitive problems, including memory loss and dementia.
Parkinson disease is most common in people who are older than 50. The average age at which it occurs is 60. But some younger people may also get Parkinson disease. When it affects someone younger than age 50, it’s called early-onset Parkinson disease. You may be more likely to get early-onset Parkinson disease if someone in your family has it. The older you are, the greater your risk of developing Parkinson disease. It’s also much more common in men than in women.
Parkinson disease is a chronic and progressive disease. It doesn’t go away and continues to get worse over time.
Continuous Care Of Concurrent Medical Conditions
Maintenance care for chronic illnesses, like hypertension, dyslipidemia, COPD, diabetes mellitus, depression, and chronic pain syndrome, should be routinely monitored. Relevant examination and adjustment of medications should be done as needed on an individual basis. The following should be considered accordingly: RetinaVue and urine microalbumin assay for diabetic retinopathy and nephropathy screening, spirometry for COPD evaluation, office-based tonometry for glaucoma screening, bone density measurement for females aged 65 and above and for males 70 years and above, or for those who have a history of a fracture before the ages specified in the guidelines above .
You May Like: Does Jesse Jackson Have Parkinsons
Basics Of Parkinsons Disease
Parkinsons disease , or paralysis agitans, is a common neurodegenerative condition, which typically develops between the ages of 55 and 65 years. This disease was first named and described by James Parkinson in 1817. The progression of this disease is gradual and prolonged. It has a plausible familial incidence, although the estimates of these occurrences are low and usually sporadic. This disease is organized into two classifications: genetic and sporadic. Genetic PD follows Mendelian inheritance. Sporadic PD, which accounts for about 90% of all Parkinsons cases, is a more complex category in which the pathogenic mechanisms that underlie it are not yet fully understood. Nonetheless, it is known that the byzantine interactions of genetic and environmental influences play roles in the determination of sporadic PD. Several subtypes of PD exist. Each has its own set of causative factors and susceptibilities, pathology, and treatment courses. General risk factors, symptoms, and pathology will be discussed first, before addressing some of the subtypes.
Pharmacological Treatment Of Parkinsons Disease
There is currently no proven disease-modifying or neuroprotective therapy for PD. A summary of previous neuroprotection trials is given in a recent review article. Current evidence-based treatment for PD is symptomatic and mainly based around dopaminergic replacement or modulation . The evidence base is summarised in recent guidelines from the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence and the International Parkinson and Movement Disorder Society. Levodopa, dopamine agonists and monoamine oxidase B inhibitors are all licensed for use as initial therapy in PD. Anticholinergics are no longer routinely used due to the risk of cognitive decompensation.
Pharmacological therapies currently used for initial and adjunctive treatment of motor symptoms in Parkinsons disease
Also Check: Parkinsons Age Of Onset
You May Like: Parkinson’s And Violent Behavior
Pharmacological Management Of Motor Symptoms
1.3.1 Before starting treatment for people with Parkinson’s disease, discuss:
-
the person’s individual clinical circumstances, for example, their symptoms, comorbidities and risks from polypharmacy
-
the person’s individual lifestyle circumstances, preferences, needs and goals
-
the potential benefits and harms of the different drug classes .
Table 1 Potential benefits and harms of dopamine agonists, levodopa and MAOB inhibitors
1.3.13 If dyskinesia is not adequately managed by modifying existing therapy, consider amantadine.
1.3.14 Do not offer anticholinergics to people with Parkinson’s disease who have developed dyskinesia and/or motor fluctuations.
Treatment Guidelines For Pdd
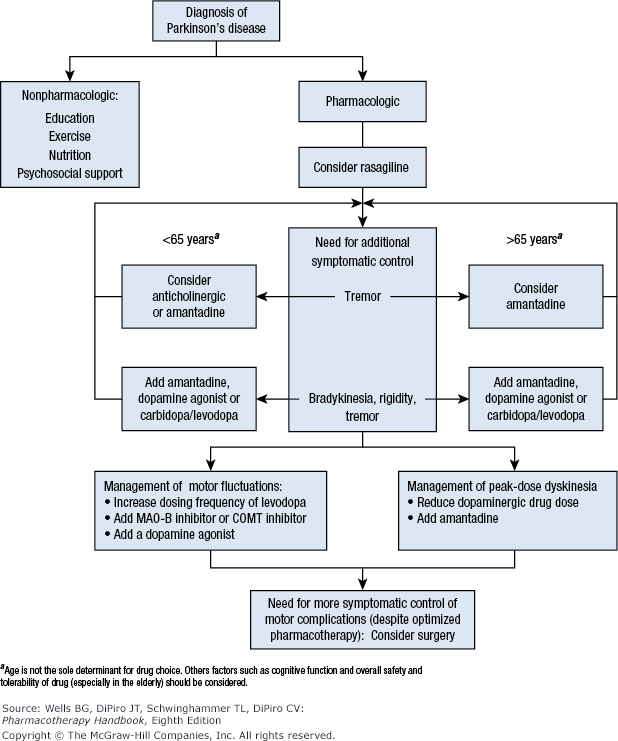
The fundamental goals of treatment for PPD patients are to reduce suffering caused by the cognitive and accompanying symptoms, while delaying progressive cognitive and physical decline. How to reach these goals is a challenge to medical providers, patients, and families because the severity of PD, mood disorders, hearing defects, and mental function declining can overlap and affect each other. That needs comprehensive evaluation, planning, and cooperation/coordination with neurologists. An algorithm shown in Figure 2 will help PCPs to orchestrate the treatment plan with patients and their families.
Figure 2.
Algorithm workflow for management of PDD patient.
Also Check: Hormone Therapy For Parkinson’s