Rna Interference And Gene Of Snca Pink And Parkin
Scientists have done a lot of experiments on RNA interference of SNCA . In vitro, they use polyethylene glycol-polyethyleneimine as a vector for α-synuclein siRNA delivery to PC12 cell. The polyethylene glycol-polyethyleneimine siSNCA complex were well developed and with low cytotoxicity. It shows high transfection efficiency, suppressing the SNCA mRNA expression and preventing cell from death via apoptosis induced by 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridine . In vivo, down-regulations of α-synuclein shows a promising future for synucleinopathies in PD. Human SNCA gene silencing with AAV-micro30-hSNCA in rat substantia nigra could have benefits on forelimb behavior and substantia nigra dopaminergic neuron loss, but these positive effects was compromised by the inflammation which was triggered by the co-expression of either silencing vector and the reduced Tyrosin hydrocylase-immunoreactive expression . Table 2b is the sum of In vivo and In vitro study of RNA interference therapy for PD.
Table 2B. In vivo and In vitro study of RNA interference therapy for PD.
New Medications For Off Time
A number of new medications approved recently are designed to reduce OFF time. These medications fall into two major categories:
- Medications that lengthen the effect of a carbidopa/levodopa dose
- Medications that are used as needed if medication effects wear off
Well give specific examples below. In general, new medications that extend the length of a carbidopa/levodopa dose are used if OFF time is somewhat predictable and occurs prior to next dose. New medications that are used as needed are most beneficial when OFF time is not predictable.
New medications that lengthen the effect of a dose of carbidopa/levodopa
- Istradefylline is an adenosine A2A receptor antagonist which was approved in the US in 2019 as an add-on therapy to levodopa for treatment of OFF time in PD. Unlike many of the other medications, it has a novel mechanism of action and is the first medication in its class to be approved for PD. It acts on the adenosine receptor, which modulates the dopaminergic system, but is not directly dopaminergic. The drug was developed in Japan and underwent clinical trials both in Japan and in the US.
- Opicapone is a catechol-O-methyltransferase inhibitor that is taken once a day. It was approved in the US in 2020 as an add-on therapy to levodopa for motor fluctuations.
New formulations of levodopa designed to be used as needed if medication effects wear off
Other medications used as needed if medication effects wear off
What Kinds Of Genetic Research Is Being Done
Researchers are investigating genes that code proteins responsible for producing dopamine. By increasing the amount of dopamine in the brain, Parkinson’s symptoms can be minimized if not prevented.
What other treatments are being researched?
- Drug treatments. Researchers are investigating drugs that block the action of glutamate, an amino acid that destroys nerve cells, as well as the role of the antioxidant coenzyme Q-10 in slowing the progression of Parkinson’s disease.
- Neural growth factor. Preliminary studies have shown that neural growth factor revives the dormant cells needed to produce dopamine, dramatically improving symptoms.
- Deep brain stimulation. Research is underway to better understand how deep brain stimulation works in Parkinson’s disease. Researchers are also studying improved ways of stimulating the brain.
Show Sources
Don’t Miss: How Do You Know If You Have Parkinson’s
How Soon After Treatment Will I Feel Better And How Long Will It Take To Recover
The time it takes to recover and see the effects of Parkinson’s disease treatments depends strongly on the type of treatments, the severity of the condition and other factors. Your healthcare provider is the best person to offer more information about what you can expect from treatment. The information they give you can consider any unique factors that might affect what you experience.
Who Does It Affect
The risk of developing Parkinsons disease naturally increases with age, and the average age at which it starts is 60 years old. Its slightly more common in men or people designated male at birth than in women or people designated female at birth .
While Parkinsons disease is usually age-related, it can happen in adults as young as 20 .
Don’t Miss: Can Parkinson’s Disease Be Treated
The Next Generation Of Trials
Studer was part of the initial studies involving fetal tissue in the 1980s and 1990s, and knew from the start that the work was more of a proof of principle than a solution for people with Parkinsons. For me it was clear that a fetal transplant isnt a long-term solution because of ethical, legal and practical issues. Because this procedure requires 4 to 12 fetuses per patient, there was no way they could treat thousands, let alone tens of thousands, of people that way. Instead, Studer turned to stem cells.
Immunosuppression is a particularly important element of BlueRocks approach, because it relies on a single cell line that cannot be adjusted to more closely resemble the recipients own tissues. A group led by stem-cell scientist and neurosurgeon Jun Takahashi at Kyoto University in Japan is attempting to provoke a lesser immune response by pairing transplant recipients with cells that are less likely to be rejected. The researchers are using cell-surface proteins, called major histocompatibility complexes , that are recognized by the adaptive immune system and can have varying levels of compatibility from one person to another. Rather than using frozen cell lines, Takahashi and his colleagues are creating a fresh batch of MHC-matched cells for each transplant.
Designer Neurons Offer New Hope For Treatment Of Parkinson’s Disease
- Date:
- Arizona State University
- Summary:
- Scientists describe a process for converting non-neuronal cells into functioning neurons able to take up residence in the brain, send out their fibrous branches across neural tissue, form synapses, dispense dopamine and restore capacities undermined by Parkinson’s destruction of dopaminergic cells.
Neurodegenerative diseases damage and destroy neurons, ravaging both mental and physical health. Parkinson’s disease, which affects over 10 million people worldwide, is no exception. The most obvious symptoms of Parkinson’s disease arise after the illness damages a specific class of neuron located in the midbrain. The effect is to rob the brain of dopamine — a key neurotransmitter produced by the affected neurons.
In new research, Jeffrey Kordower and his colleagues describe a process for converting non-neuronal cells into functioning neurons able to take up residence in the brain, send out their fibrous branches across neural tissue, form synapses, dispense dopamine and restore capacities undermined by Parkinson’s destruction of dopaminergic cells.
The current proof-of-concept study reveals that one group of experimentally engineered cells performs optimally in terms of survival, growth, neural connectivity, and dopamine production, when implanted in the brains of rats. The study demonstrates that the result of such neural grafts is to effectively reverse motor symptoms due to Parkinson’s disease.
New perspectives on Parkinson’s disease
Read Also: Best Books On Parkinson’s Disease
What Are The Early Warning Signs Of Parkinson’s Disease
Parkinsons warning signs can be motor symptoms like slow movements, tremors or stiffness. However, they can also be non-motor symptoms. Many of the possible non-motor symptoms can appear years or even decades ahead of motor symptoms. However, non-motor symptoms can also be vague, making it difficult to connect them to Parkinson’s disease.
Non-motor symptoms that might be early warning signs include:
- Sleep problems such as periodic limb movement disorder , rapid eye movement behavior disorder and restless legs syndrome.
Experimental Drug Stops Parkinsons Disease Progression In Mice
Researchers say they have developed an experimental drug that slows the progression of Parkinsons disease itself
Johns Hopkins researchers say they have developed an experimental drug, similar to compounds used to treat diabetes, that slows the progression of Parkinsons disease itself as well as its symptoms in mice. In experiments performed with cultures of human brain cells and live mouse models, they report the drug blocked the degradation of brain cells that is the hallmark of Parkinsons disease. The drug is expected to move to clinical trials this year.
It is amazingly protective of target nerve cells, says Ted Dawson, M.D., Ph.D., director of the Institute for Cell Engineering and professor of neurology at the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine.
A report of the studys results was published June 11 in Nature Medicine.
According to the investigators, NLY01 works by binding to so-called glucagon-like peptide-1 receptors on the surface of certain cells. Similar drugs are used widely in the treatment of type 2 diabetes to increase insulin levels in the blood. Though past studies in animals suggested the neuroprotective potential of this class of drugs, researchers had not shown directly how it operated in the brain.
They explored this hypothesis by testing the drugs effectiveness in mice engineered to have a rodent version of Parkinsons disease.
Read Also: Support Services For Parkinson’s Disease
Surgery For Parkinsons Disease
Based on the severity of the condition and the medical profile, the doctor may recommend surgery as one treatment option for Parkinson’s disease.
There are several types of surgery that may be performed that can help patients with Parkinson’s disease. Most of the treatments are aimed at helping the tremor or rigidity that comes with the disease. In some patients, surgery may decrease the amount of medication that is needed to control the symptoms.
There are three types of surgeries that may be performed for Parkinson’s disease, including the following:
It is important to remember that surgery may help with symptoms of Parkinson’s disease, but does not cure the disease or stop the progression of the disease.
Treatments In Phase 1 And 2 Clinical Trial
In these phases, the drugs are being studied to evaluate their effectiveness and safety.
- Tasigna is being investigated to treat cognitive changes in Parkinsons disease. The drug is usually administered when patients fail to improve with other medications and can target both motor and cognitive problems.
- Mavoglurant is being studied as an add-on therapy to improve dyskinesia associated with long-term use of levodopa in Parkinosns disease patients.
You May Like: Glutathione Supplements For Parkinson’s
What Can Be Done About These Unpleasant Gi Problems
Unfortunately, research studies on GI problems related to PD have been few and far between, so doctors do not have any tried and true methods to deal with them. Some of the drugs to treat GI problems in people without PD cannot be used for those with PD because these drugs negatively impact dopamine systems in the brain.
If you have PD and experience constipation, it makes sense to try to use safe and simple methods to address this issue before you add new drugs to your daily regimen. Increasing dietary fiber and drinking lots of water and other fluids is a reasonable first step in treatment. If your doctor approves it, you might also consider taking fiber supplements, such as psyllium or methylcellulose. If these simple methods dont work, your doctor might consider giving you a stool softener or a laxative.
Dont Miss: Michael J Fox Living With Parkinsons
How Could Stem Cells Help People With Parkinson’s
Stem cells are the parent cells of all tissues in the body. This means they can turn into any type of cell. The hope is that they will eventually be able to make these cells into specific types of cells, like dopamine-producing neurons, that can be used to treat Parkinson’s disease. However, there are concerns that patients may have the same risk of increased involuntary movements as those who undergo fetal cell transplantation. And, like fetal cell transplantation, stem cell therapy is surrounded by moral and ethical controversy.
Also Check: Gene Therapy For Parkinson’s Disease An Update
How Are Clinical Trials Conducted
Clinical trials that test drugs or interventions are conducted in a series of carefully monitored phases designed to answer specific questions.
Phase I trial: researchers test a new drug or treatment in people for the first time. A small group of people, typically fewer than 100, are monitored to evaluate the drug or treatment’s safety, determine a safe dosage range, and identify side-effects.
Phase II trial: study the effectiveness of a drug or treatment in a larger group of people.
Phase III trial: the study drug or treatment is given to a large group of several hundred to several thousand people. This large-scale testing gives more detailed information about the drug’s benefits, effectiveness, range of possible side effects, and compare it with standard treatment or placebo.
Phase IV trial: usually conducted on treatments that have already been Food and Drug Administration approved and is available to the general population. These trials help monitor the safety of the intervention in a larger population and obtain additional information about the benefits and use of the intervention.
Gene Therapy For Modulating The Synthesis Of Neurotransmitter
Adeno-Associated Virus -Glutamate Decarboxylase
Aromatic Amino Acid Decarboxylase and Tyrosine Hydroxylase/Aromatic Amino Acid Decarboxylase/Guanosine Triphosphate Cyclohydrolase Gene Therapy
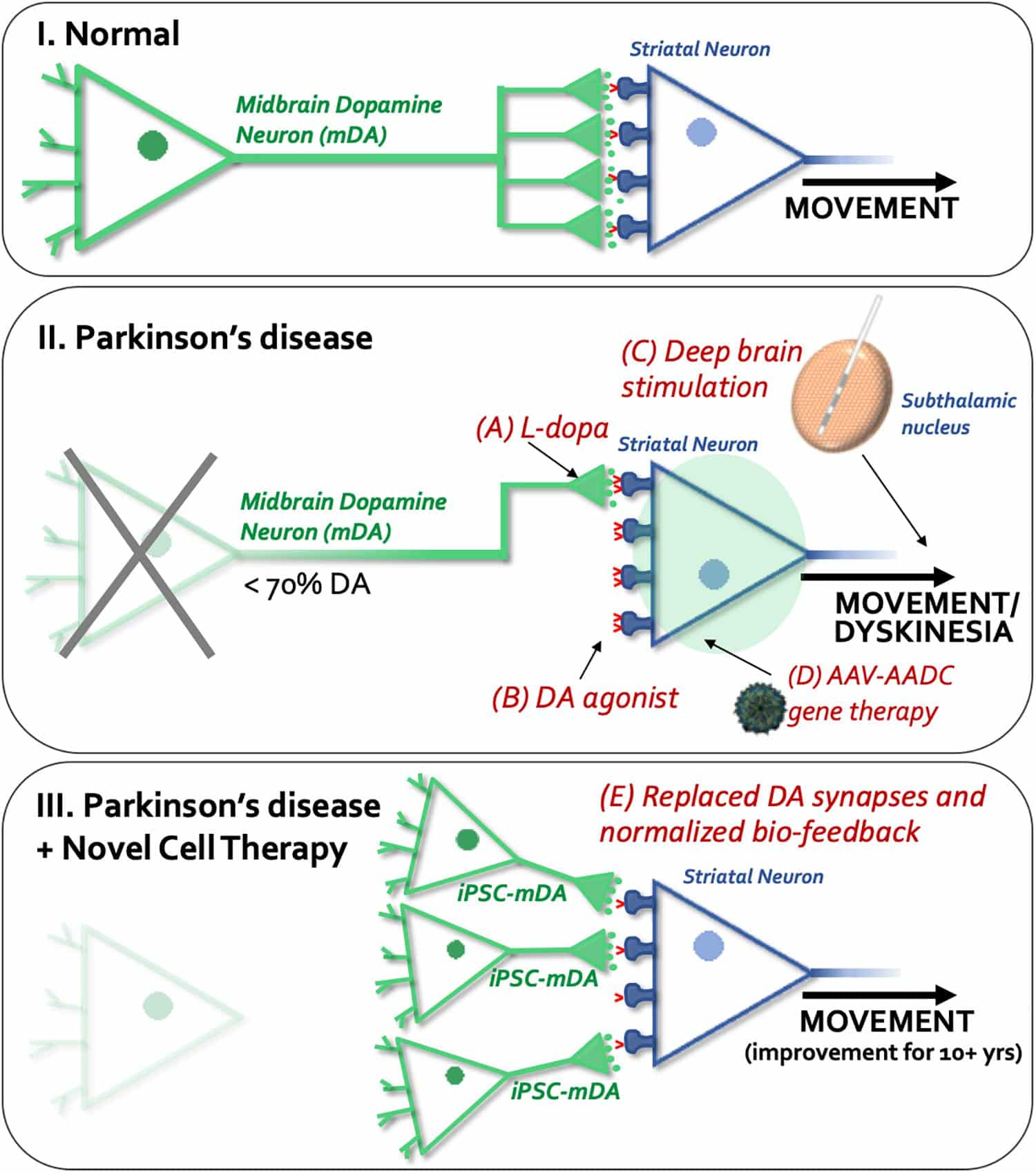
The beneficial effect of oral administration of L-dopa will soon be complicated by motor symptoms. Olanow et al. find that continuous dopamine stimulation might counter balance these long-term effects of drug . Based on these theories, researchers focused on increasing dopamine level through enhancing the chemical synthesis of dopamine from levodopa. The conversion of levodopa to dopamine needs the enzyme acromatic L-amino acid decarbocylase . With the PD advancing, activities of AADC diminished, this further limiting dopamine level and resulted a larger need for the dosage of levodopa . The transduction of AADC gene to intrinsic striatal neurons could enhance the synthesis of dopamine and might improve the dopamine level in brain. The continuous existence of DA might reduce the need of levodopa in advancing PD , and with the reduction of levodopa, the side effect like LIDs might be alleviated. A phase I clinical trial of gene transfer of AAV mediated gene delivery of AADC into putamen of 6 PD patients was launched. using multiple measures, including UPDRS, motor state diaries and PET trace for AADC, 6 months after surgery, the off-state of motor function was improved by 46% based on UPDRS scores, PET shows a 56% increase in FMT activities, both effect last 96 weeks .
You May Like: Latest Medication For Parkinson’s Disease
Group Singing May Be Therapy For Walking Problems Tremor
Ample evidence supports the benefits of physical activity for people with neurodegenerative diseases, including Parkinsons disease. The cellular underpinnings of these benefits are not well-established and have been of recent interest in the research community.
Irisin is released from skeletal muscles and other tissues into the bloodstream during exercise, and has emerged as one molecule that might underlie some of these benefits, raising the possibility that irisin could be a therapeutic molecule for neurodegenerative diseases.
Researchers previously found that increases in irisins precursor, FNDC5, led to exercise-like genetic changes in the brain and was linked to cognitive improvements in mice. Irisin itself led to improved cognitive function and lower inflammation in a mouse model of Alzheimers disease, another neurodegenerative condition.
Motivated by the knowledge of exercises benefits in Parkinsons, the researchers investigated the effects of the hormone in models of the neurodegenerative disease.
Parkinsons is characterized by the toxic accumulation of a misfolded alpha-synuclein protein in nerve cells, leading to their dysfunction and eventual death. The nerve cells most vulnerable to this accumulation are dopamine-producing cells.
To model the condition in cultured nerve cells, the researchers administered preformed fibrils of the alpha-synuclein protein. This prompts naturally occurring alpha-synuclein in the cells to misfold and accumulate.
Advances In Deep Brain Stimulation
Deep brain stimulation is another established treatment for PD that is useful in treating dopamine-dependent motor symptoms when levodopa-induced side effects become particularly problematic. DBS involves the surgical implantation of electrodes that stimulate subcortical structures including the subthalamic nucleus and globus pallidus internus9194. DBS offers significant improvements in motor symptoms and fluctuations in comparison to best medical therapy in some advanced PD patients, but dopamine-resistant symptoms other than tremor respond poorly95. It has also been suggested in an open-label trial that DBS is beneficial in early PD patients, with improved tremor scores and reduced development ofde novo tremor96. In addition to surgical complications, DBS strategies may cause cognitive and neuropsychiatric adverse effects as well as speech dysfunction. Novel DBS approaches, including adaptive DBS, targeting different regions, and refined intra-operative imaging techniques promise to offer improved clinical applicability and reduce the impact of adverse effects97.
Also Check: Is Parkinsonism The Same As Parkinson’s Disease
Risk Of Omitting Or Delaying Pd Medicines
PD medication should not be stopped abruptly and should always be given on time. Late or missed doses may result in patients swallowing, speech and mobility being affected, leading to further difficulties. In addition, delays in the administration of medicines can lead to an increased risk of falls, care needs, pain, and distress, and may lengthen the hospital stay. The following points highlight the seriousness that delaying or omitting a PD medicine may lead to:
You May Like: Parkinsons And Violent Behavior
Why Are Clinical Studies Important
All types of research are critical for improving care. Basic science research tests done in a laboratory can help us learn more about the human body and the causes of PD. Basic research can also point scientists in promising directions as they develop and refine treatments.
Clinical studies are essential because through them, discoveries made in the laboratory can help people with PD today and in the future. The Parkinsons Foundation is at the forefront of PD research and clinical studies are central to our vision. The Foundations Parkinsons Outcomes Project was the first study of its kind and continues to be the largest clinical study. Every year, insights from the study help optimize PD care, leading to better quality of life for people with PD today and better health for people with PD tomorrow.
Also Check: Seizures Associated With Parkinson’s Disease
How Is It Diagnosed
Diagnosing Parkinson’s disease is mostly a clinical process, meaning it relies heavily on a healthcare provider examining your symptoms, asking you questions and reviewing your medical history. Some diagnostic and lab tests are possible, but these are usually needed to rule out other conditions or certain causes. However, most lab tests aren’t necessary unless you don’t respond to treatment for Parkinson’s disease, which can indicate you have another condition.