Risk Factors For Parkinsons Disease
- Age people over 60 years old are more likely to develop Parkinsons disease, and the risk increases as people age.
- Gender men are more likely to develop Parkinsons disease than women.
- Family history if you have a family history of Parkinsons disease, you are more likely to develop it yourself.
- Exposure to toxins research has linked herbicides or pesticides to an increased risk of developing Parkinsons disease.
- Race Caucasians are more likely to develop Parkinsons disease.
- Living in a rural location people who live in a rural location are more likely to develop Parkinsons.
How Is Parkinsons Disease Tested And Diagnosed
At Banner Health, our neurologists have years of experience in testing and diagnosing Parkinson’s disease. Our team of compassionate experts knows that each patient is different, so we work with you to quickly find the right diagnosis to begin building your treatment plan.
Parkinsons is not simple to diagnose. No test exists to diagnose Parkinsons disease. Doctors test and diagnose Parkinsons based on your medical history, symptoms and neurological and physical exams.
Many times a primary care provider is the first to suspect a Parkinsons diagnosis. If youre experiencing symptoms such as tremors, shaking, slow movement, stiffness and/or trouble with balance, talk to your doctor or seek the opinion of a neurologist. Banner Health neurologists are movement disorder specialists, who have experience and specific training to assess and treat Parkinsons.
How To Diagnose Pd
The diagnosis of PD is still largely a clinical one, as there is no definitive test able to confirm the diagnosis during life, with the exception of gene testing in a reduced number of cases. PD is a disease combining clinically defined parkinsonism with specific pathological findings, namely, dopaminergic neuron loss in the region of substantia nigra pars compacta, as well as the presence of intraneuronal Lewy bodies , although there are a few notable exceptions to this with regard to the pathological diagnosis. From a practical perspective, the first step for the diagnosis of PD is careful history taking. Thorough questioning of the patient and family should be performed, trying to define which symptoms emerged and their sequence, as well as perceived anatomical involvement. Inquiry about the presence of premotor symptoms including sleep-related REM sleep behavior, loss of smell, and constipation can be helpful if present. Drug intake history, both past and present, especially concerning drugs able to cause parkinsonian symptoms, is paramount. Likewise, possible exposure to environmental toxics should also be searched for . Past and present medical disorders should be systematically recorded. Family history is also an important stage, and should include neurological disorders in other family members, as well as inquiry about ethnic ancestry as monogenic forms of PD are more prevalent in some .
Read Also: Treatment Of Anxiety In Parkinson’s Disease
Referral To A Specialist
If your GP suspects Parkinson’s disease, you’ll be referred to a specialist.
This will usually be:
- a neurologist, a specialist in conditions affecting the brain and nervous system
- a geriatrician, a specialist in problems affecting elderly people
The specialist will most likely ask you to perform a number of physical exercises so they can assess whether you have any problems with movement.
A diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease is likely if you have at least 2 of the 3 following symptoms:
- shaking or tremor in a part of your body that usually only occurs at rest
- slowness of movement
- muscle stiffness
If your symptoms improve after taking a medication called levodopa, it’s more likely you have Parkinson’s disease.
Special brain scans, such as a single photon emission computed tomography scan, may also be carried out in some cases to try to rule out other causes of your symptoms.
Causes Of Parkinsons Disease
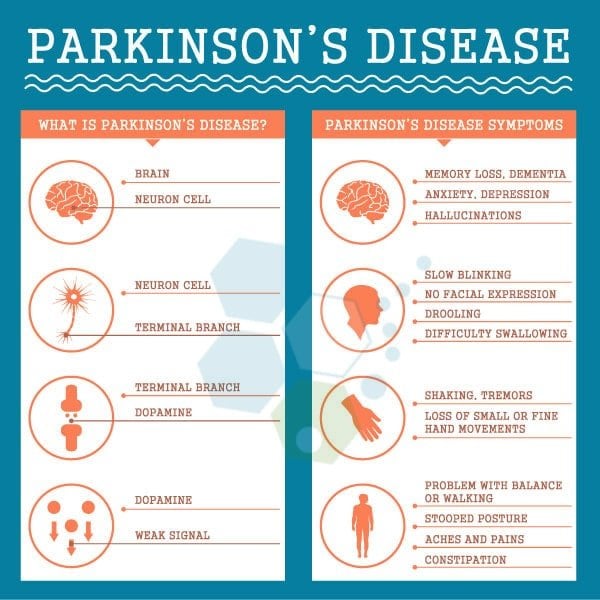
The cause of Parkinsons disease is unknown, but the disease occurs when the dopamine levels in the brain drop. Dopamine is the chemical in the brain that tells other areas of the brain when and how to move. Factors that can play a role in the development of Parkinsons disease include:
- Genes in rare cases where multiple family members have Parkinsons disease, patients may have a genetic mutation that can cause Parkinsons disease. In other cases, there are several genetic mutations that can increase your risk of developing Parkinsons.
- Environment environmental factors such as extended exposure to Agent Orange, herbicides, pesticides, fungicides and metals or leads used in factories could also play a role in causing Parkinsons disease.
Don’t Miss: Parkinson’s Disease Therapeutic Regimen
The Path Towards Early Accurate Diagnosis Of Parkinsons Disease
Like Alzheimers disease and many other neurological diseases, Parkinsons disease begins long before symptoms arise. The benefits of early diagnosis of such diseases are immense and not only affect patients and their families but also the wider society and research community.
Research efforts surrounding Parkinsons disease risk factors, early symptoms, traditional biomarkers, and digital biomarkers will pave the way for an earlier, more accurate diagnosis. Our growing understanding of the factors involved in Parkinsons disease risk, development, and progression opens the door to more robust and sensitive testing and diagnostic approaches.
What Is A Neurological Exam
A neurological exam, also called a neuro exam, is an evaluation of a person’s nervous system that can be done in the healthcare provider’s office. It may be done with instruments, such as lights and reflex hammers. It usually does not cause any pain to the patient. The nervous system consists of the brain, the spinal cord, and the nerves from these areas. There are many aspects of this exam, including an assessment of motor and sensory skills, balance and coordination, mental status , reflexes, and functioning of the nerves. The extent of the exam depends on many factors, including the initial problem that the patient is experiencing, the age of the patient, and the condition of the patient.
Don’t Miss: Michael J Fox Parkinson’s Foundation Address
Arm Swing During Gait
Among the three measurements that were considered for measuring gait impairment, arm swing acceleration was selected. While it was not the best outcome measure across any of the criteria, it showed solid performance across all of them. Results for the measures that were not selected are included in Supplementary Table .
The Spearman rank correlation between the arm swing acceleration during the gait task and expert consensus rating of MDS-UPDRS task 3.10 was =0.46 , N=164 . A small effect was observed comparing the on and off state. The mean difference in the measure was 0.8 ms2. Test-retest ICC was 0.43 week-on-week , and 0.75 for monthly-averaged measures . The in-clinic PD-VME measure was between the 25th and the 75th percentiles of the remote PD-VME measures for 39% of the participants.
Fig. 4: Gait.
Is There A Test For Parkinsons Disease
Currently, there is no single test for Parkinsons diseaseno brain scan or lab test can provide a definitive diagnosis of Parkinsons disease. Instead, doctors diagnose Parkinsons disease clinically, meaning a diagnosis is dependent on medical history, answers to certain questions, a physical examination, and the presence of specific physical symptoms.
Typically, the process for diagnosing Parkinsons disease follows these general steps:
Clinical diagnosis of Parkinsons disease, or any disease for that matter, relies heavily on the doctors judgment and expertise. Oftentimes, the patients symptoms, along with the neurological examination, are sufficient for determining the correct diagnosis, particularly for patients in the later stages of the disease. However, doctors may suggest further testing, such as brain imaging, to rule out any conditions that mimic the symptoms of Parkinsons disease .
Also Check: Parkinson’s Long Term Prognosis
Other Tests Used To Diagnose Parkinsons Disease
Diagnosis of PD is generally made using a medical history and a physical/neurological exam. Imaging tests, such as MRI , PET scans, or DaTscans are expensive and are not routinely used.1,7
An active area of research is the development of biomarkers which are molecules in the blood, urine, or cerebrospinal fluid that can reliably indicate PD. Imaging tests that can detect aggregates of a molecule called synuclein, which is linked to PD, are also being actively researched.
Passive Manipulation Of Limbs
To test for the presence of rigidity, we need to passively manipulate the limbs of the patient. However, If the disease is in its early stage or the symptoms are well controlled with medications, we may not be able to see rigidity. We will need to use some activation maneuvers, that basically consist in performing repetitive movements with the limb contralateral to the one that is being tested.
Also, there are two types of rigidity:
– Lead-pipe rigidity: where the tone is uniformly and smoothly increased throughout the entire range of movement
– Cogwheel rigidity: where a tremor is superimposed on the hypertonia, making the movement irregular due to intermittent increase and reduction of tone
Upper Extremity Testing
For the upper extremity the most sensitive joint where to check for rigidity is the wrist. To uncover rigidity, passively rotate the wrist and feel for a resistance to the movement. It is very important that the arm of the patient is fully relaxed when rotating the wrist. To do this, place your proximal hand under the patients forearm, while your distal hand grabs and rotates the wrist of the patient. When rigidity is present, the range of motion will be preserved but you will feel a resistance in performing the movement.
Wrist rotation with activation maneuver.
It is also possible to test for rigidity in the elbow by passively flexing and extending the forearm.
Elbow flexion-extension with activation maneuver.
Lower Extremity Testing
Read Also: Parkinson’s And Massage Therapy
Determining Diagnosis Through Response To Parkinsons Medication
If a persons symptoms and neurologic examination are only suggestive of Parkinsons disease or if the diagnosis is otherwise in doubt, the physician may, nevertheless, prescribe a medication intended for Parkinsons disease to provide additional information. In the case of idiopathic Parkinsons, there is typically a positive, predictable response to Parkinsons disease medication in the case of some related Parkinsonian syndromes, the response to medication may not be particularly robust, or it may be absent entirely.
Unfortunately, there are no standard biological tests for the disease, such as a blood test. However, researchers are actively trying to find biomarkers in blood and other bodily fluids that could help confirm the diagnosis.
Ruling Out Other Conditions
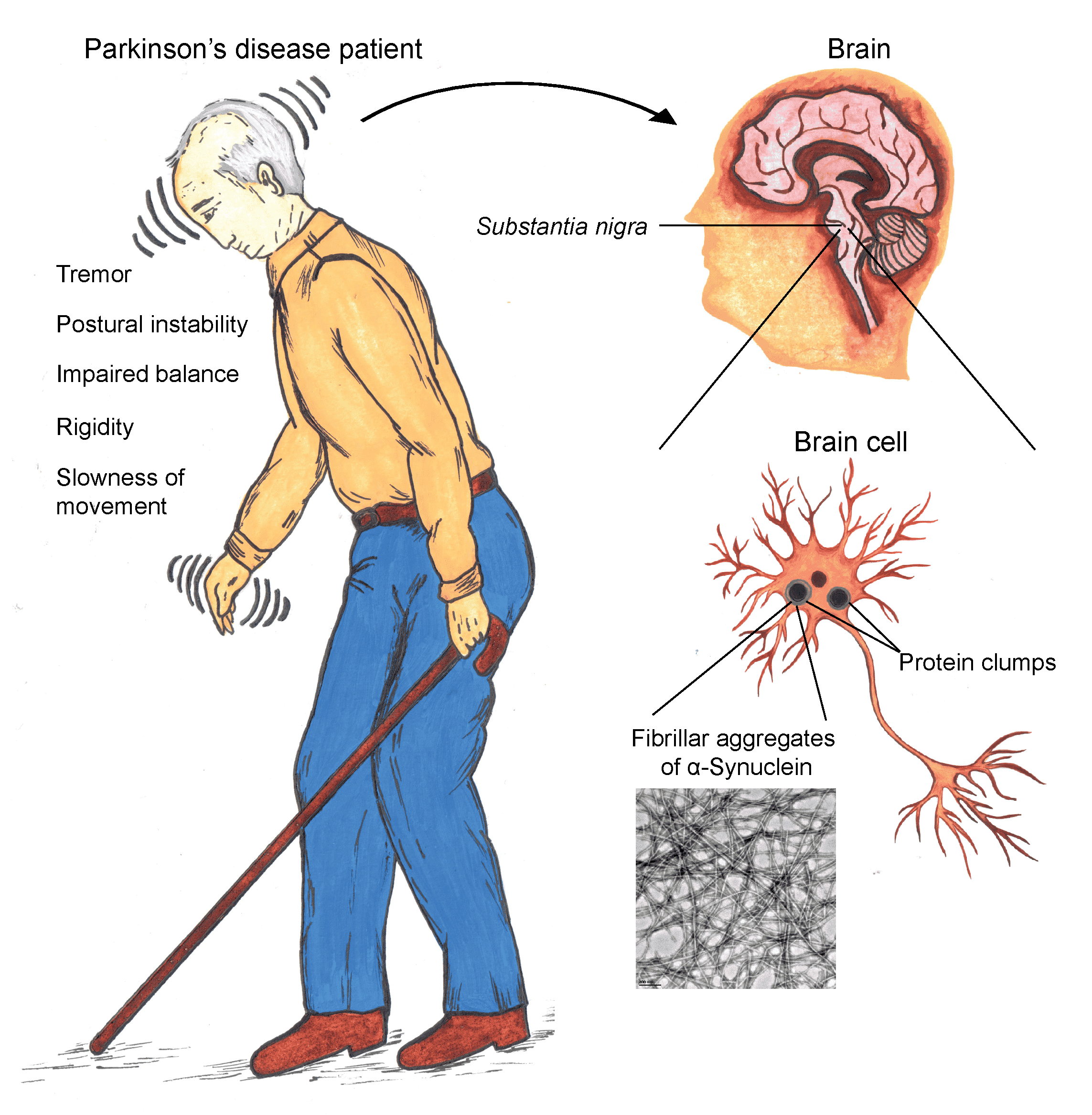
The symptoms of PD are similar to symptoms caused by other conditions, and an important part of the diagnosis process is excluding other diseases that may be the source of the patients symptoms. Other diseases that could cause similar symptoms include stroke, hydrocephalus, or other neurodegenerative disorders. Some medications can also cause Parkinsons like symptoms, and the doctor will assess these. Good responsiveness to levodopa for the motor symptoms is indicative of PD. However, many clinical trials need patients newly diagnosed with PD that have never taken levodopa. So, it may be worthwhile discussing participation in clinical trials with the doctor first.1
You May Like: Any New Treatments For Parkinson’s
Rehabilitation For Parkinsons Patients
Parkinsons disease patients may find that rehabilitation services, including physical therapy, ease symptoms. Therapy focuses on helping patients build strength and move more easily. Goals may include improving walking, balance and overall movement.
Ask your doctor or specialist about getting a referral for rehabilitation with a therapist. Often rehabilitation services are close to home, in your community.
MaineHealth has home care services that support patients in their homes. Services may include:
- Help with laundry and household chores
- Counseling and emotional support
- Personal care help with daily activities
Testing For Parkinsons Disease
There is no lab or imaging test that is recommended or definitive for Parkinsons disease. However, in 2011, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved an imaging scan called the DaTscan. This technique allows doctors to see detailed pictures of the brains dopamine system.
A DaTscan involves an injection of a small amount of a radioactive drug and a machine called a single-photon emission computed tomography scanner, similar to an MRI.
The drug binds to dopamine transmitters in the brain, showing where in the brain dopaminergic neurons are.
The results of a DaTscan cant show that you have Parkinsons, but they can help your doctor confirm a diagnosis or rule out a Parkinsons mimic.
Also Check: Parkinson’s Disease Continuing Education Physical Therapy
Why Is A Neurological Exam Done
A complete and thorough evaluation of a person’s nervous system is important if there is any reason to think there may be an underlying problem, or during a complete physical. Damage to the nervous system can cause problems in daily functioning. Early identification may help to find the cause and decrease long-term complications. A complete neurological exam may be done:
-
During a routine physical
New Diagnostic Standards For Parkinsons
Until recently, the gold-standard checklist for diagnosis came from the U.K.s Parkinsons Disease Society Brain Bank. It was a checklist that doctors followed to determine if the symptoms they saw fit the disease. But thats now considered outdated. Recently, new criteria from the International Parkinson and Movement Disorder Society have come into use. This list reflects the most current understanding of the condition. It allows doctors to reach a more accurate diagnosis so patients can begin treatment at earlier stages.
Don’t Miss: New Medicine For Parkinson’s Disease
If Its Not Parkinsons Disease What Else Could It Be
There are several other conditions that might produce symptoms that can be mistaken for Parkinsons disease. Here are some possibilities:
- Medication side effects: Certain drugs can produce or exacerbate symptoms.
- Essential, or familial, tremor: This is a relatively common and benign cause of recurrent tremor and is often confused with the tremor of idiopathic Parkinsons. A general neurologist or movement disorder specialist is the best physician to help differentiate between these two conditions.
- A Parkinsonian syndrome: The symptoms of several neurologic conditions are similar to those of idiopathic Parkinsons, but they are often managed differently and often do not respond to the typical medications.
Remember: Only a general neurologist or movement disorder specialist can tell you with reasonable certainty if you have idiopathic Parkinsons. If for some reason you are not comfortable with the results of your first physician visit, getting a second opinion from another general neurologist or movement disorder specialist is always an option. It is important that you feel comfortable with your physician to ensure the best possible outcome for you.
Once you or your loved one has a diagnosis of Parkinsons disease, it is time to discuss treatment options with your physician.
Pattern Of Symptoms In Parkinsons Disease
While the motor symptoms are the current standard for diagnosing PD, research has shown that PD non-motor symptoms, particularly gastrointestinal symptoms and the reduced sense of smell, may begin years before the motor symptoms appear. When the motor symptoms show up in the body, they generally begin on one side of the body. This is called unilateral presentation. As the disease progresses, the symptoms may spread to the other side of the body as well.3,6
PD is a progressive disease, and the symptoms worsen over time. This progression of symptoms is also noteworthy when considering a diagnosis of PD.3
Read Also: My Life With Parkinson’s
How Is Parkinson’s Disease Diagnosed
Your doctor will ask questions about your symptoms and your past health and will do a neurological exam. This exam includes questions and tests that show how well your nerves are working. For example, your doctor will watch how you move. He or she will check your muscle strength and reflexes and will check your vision.
Your doctor also may check your sense of smell and ask you questions about your mood.
In some cases, your doctor will have you try a medicine for Parkinson’s disease. If that medicine helps your symptoms, it may help the doctor find out if you have the disease.
Tests
There are no lab or blood tests that can help your doctor know whether you have Parkinson’s. But you may have tests to help your doctor rule out other diseases that could be causing your symptoms. For example:
- An MRI or CT scan is used to look for signs of a stroke or brain tumor.
- Blood tests check for abnormal thyroid hormone levels or liver damage.
Another type of imaging test, called PET, sometimes may detect low levels of dopamine in the brain. These low levels are a key feature of Parkinson’s. But PET scanning isn’t commonly used to evaluate Parkinson’s. That’s because it’s very expensive, not available in many hospitals, and only used experimentally.
Physical Exam For Parkinson’s

During a physical exam, the doctor examines the patients body for signs of disease. The doctor will include a visual inspection , palpation , ascultation , and percussion . The physical exam for PD is generally conducted by a neurologist and may also be called a neurological exam. It is recommended that a patient see a neurologist with special training in movement disorders as these specialists have the most knowledge about the symptoms and medications. During a neurological exam, the patient may be asked to sit, stand, walk, and extend their arms as the doctor evaluates balance and coordination. Most neurologists recommend a spouse or caregiver attend the exam with the patient to help with answering important questions.1,2
Don’t Miss: Parkinson’s Disease And Nutrition
I Have Pd And Several Symptoms Should I Get A Datscan
Likely no. There is no need for DaTscan when your history and exam suggest Parkinsons disease and you meet the diagnostic criteria. Occasionally, if signs and symptoms are mild or you dont meet the diagnostic criteria, your doctor will refer you for a DaT scan. Keep in mind that ultimately the diagnosis is based on your history and physical exam. The DaT scan is most commonly used to complete the picture and is not a test for a diagnosis.