Medications To Avoid Or Use With Caution
Sign up for our email list and receive our publication on medications with potential complications you should be aware of.
Before making any decisions about treatment of Parkinsons disease, you will want to learn about the different types of medications available for Parkinsons disease and discuss the pros and cons of each with your physician. It may help to know that there is no right answer, and if you try something that doesnt work for you, you can always adjust your plan.
To learn more about adjusting medication plans, view our webinar on What to Do When Your Medications Stop Working.
What Are Dopaminergic Antiparkinsonism Agents
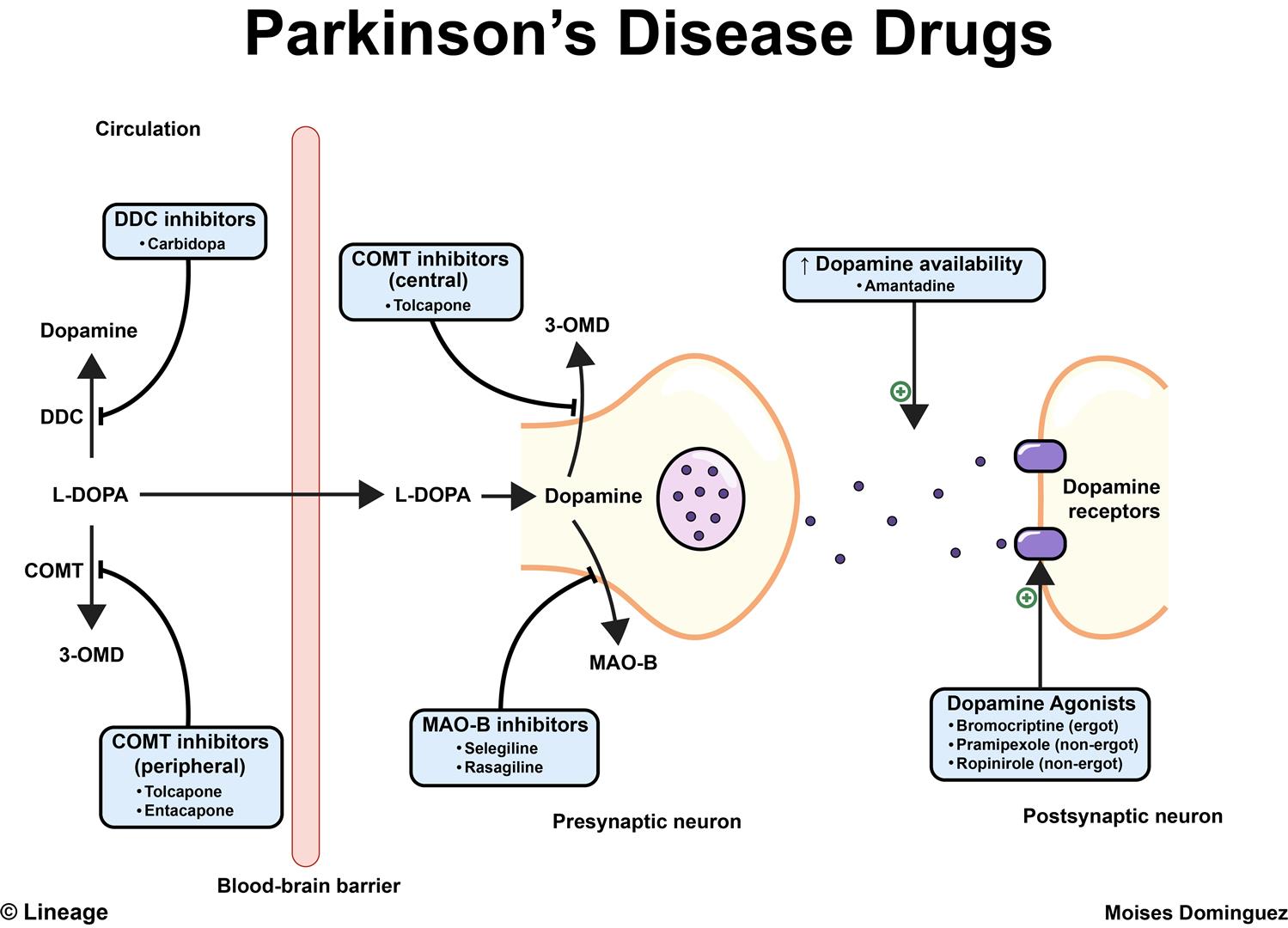
Dopaminergic antiparkinsonism agents aim to replace dopamine or prevent the degradation of dopamine.Antiparkinson drugs that aim to replace dopamine in the central nervous system, either release dopamine or mimic the action of dopamine. Drugs that replace dopamine are generally given with peripherally acting dopa carboxylase inhibitors, to prevent the metabolism of levodopa to dopamine peripherally. Dopamine receptor agonists bind to dopamine receptors and mimic the action of dopamine.Selective monoamine oxidase inhibitors bind to the enzyme MAO-B and prevent dopamine from being broken down. Antiparkinson agents are used to treat Parkinson’s disease, which is a degenerative disorder of movement that occurs due to dopamine deficiency in the brain, particularly in the basal ganglia.
Arguments For Early Use
Levodopa is the most effective medication there is to treat Parkinson’s symptoms. That said, it’s not without side effects.
One of the fears of levodopa use is that it can cause excessive movement called dyskinesia. People with dyskinesia have a writhing movement that is out of their control. While it looks uncomfortable, however, most with dyskinesia prefer it to parkinsonism, and studies suggest that dyskinesia ultimately doesn’t have much an impact on quality of life.
Some researchers have suggested that dopamine may actually accelerate the disease course while patching over the symptoms. More research has not supported this view, however.
Symptoms may fluctuate while on dopamine, meaning there may be times of the day when tremor, rigidity, and slow movements are less well-controlled than others. On the other hand, it’s unclear how those fluctuations actually impact quality of life. Furthermore, people on other medications like dopamine agonists may also eventually have fluctuations.
Other arguments in support of the early use of levodopa say that it will improve the quality of life early in the disease’s course, the importance of which has not been given sufficient attention. Levodopa is also considerably less expensive than dopamine agonists.
Read Also: Yopd Life Expectancy
Common Drugs For Parkinson’s Disease
Levodopa and carbidopa . Levodopa is the most commonly prescribed medicine for Parkinsonâs. Itâs also the best at controlling the symptoms of the condition, particularly slow movements and stiff, rigid body parts.
Levodopa works when your brain cells change it into dopamine. Thatâs a chemical the brain uses to send signals that help you move your body. People with Parkinsonâs donât have enough dopamine in their brains to control their movements.
Sinemet is a mix of levodopa and another drug called carbidopa. Carbidopa makes the levodopa work better, so you can take less of it. That prevents many common side effects of levodopa, such as nausea, vomiting, and irregular heart rhythms.
Sinemet has the fewest short-term side effects, compared with other Parkinsonâs medications. But it does raise your odds for some long-term problems, such as involuntary movements. An inhalable powder form of levodopa and the tablet istradefylline have been approved for those experiencing OFF periods, OFF periods can happen when Parkinsonâs symptoms return during periods between scheduled doses of levodopa/carbidopa.
People who take levodopa for 3-5 years may eventually have restlessness, confusion, or unusual movements within a few hours of taking the medicine. Changes in the amount or timing of your dose will usually prevent these side effects.
Dopamine agonists. These drugs act like dopamine in the brain. They include pramipexole , rotigotine , and ropinirole , .
Dopaminergic Input And Organizational Features Of The Dorsal And Lateral Striatum
As reviewed above, it is generally accepted that dysfunction in PD stems from the degeneration of SNc neurons , which leads to motor dysfunction and the loss of VTA neurons , which leads to behavioral dysregulation, including demotivation, anhedonia, and depression within PD . While both pathways have been studied extensively across an array of conditions and pathologies, the modulatory mechanisms of the nigrostriatal pathway neurons have been fairly well described while the varied mechanisms and roles of VTA efferents continue to be elucidated. Within the nigrostriatal pathway, GABAergic medium spiny neurons of the dorsal/lateral striatum receive excitatory glutamatergic signals that can be modulated via dopaminergic inputs originating from the SNc. MSNs are moderately sized cells with large, multi-structured dendritic arbors that constitute a staggering 95% of all postsynaptic nigrostriatal neurons . Local circuit interneurons of the dorsal striatum are also actively involved in regulating MSN activity and can be subdivided into cholinergic interneurons and aspiny GABAergic interneurons known as low-threshold, fast-spiking neurons . Striatal cholinergic and MSNs express several neurotransmitter receptors including the -aminobutyric acid , glutamate, DA, adenosine, serotonin, opioids, and substance P receptors .
Recommended Reading: Similar To Parkinsons
What Are Common Dopamine Agonists And What Do They Treat
There are two main categories of DA medications, ergoline and non-ergoline.
The first generation are ergoline type and are used less often today since they have some serious heart- and lung-related risks linked with their use. This is mainly because the older medications attach to any available dopamine receptors in the body and are not selective.
Experimental Models Of Parkinsonism In Laboratory Animals
The DA deficiency observed in the mesostriatal system in Parkinson’s disease is the main event underlying the pathophysiology of the motoric symptomatology. Accordingly, appropriate experimental models in laboratory animals should feature the typical loss of DA neurons in the substantia nigra and an associated DA reduction in the corpus striatum in order to be useful in investigating ways of therapeutic intervention.
Typically, three main experimental models have been used in the laboratory as dopaminergic phenocopies of Parkinson’s disease to address cellular mechanisms of DA deficiency and restoration. Two of those models rely on selective neurotoxins to chemically destroy dopaminergic nigral neurons. The third model is the weaver mutant mouse , which has a genetic mutation that leads to mesencephalic DA neuron degeneration.
Unilateral destruction of the substantia nigra in the laboratory mouse through local stereotactic injection of 6-hydroxydopamine. Micrographs from upper to lower correspond to coronal levels from rostral to caudal. Immunocytochemistry with antityrosine
You May Like: Judy Woodruff Parkinson’s
What Should I Know About Parkinsons Disease And Medications
There have been rapid and remarkable changes over the past decade in treating Parkinsons disease . The development of new medicines and the understanding of how best to use them and the older drugs have significantly improved the quality of life for people with the disease.
There is currently no treatment that has been proven to affect the disease progression or development of medication that can slow the disease process. There are two general approaches to the treatment of PD improve the symptoms with medications and engage in physical therapy. Most patients with PD can be adequately treated with medicines that alleviate their symptoms. For the approximately 15% of patients for whom medicines are not sufficiently effective, new, highly effective, and safe surgical treatments are available.
Choices about medicines made early in the course of the disease have a strong impact on the long-term course of the illness. Therefore, you should seek the advice of doctors specially trained in treating PD even when the illness is only suspected. Movement disorders specialists are neurologists who have completed their training in neurology and have received special advanced training in treating PD and other related diseases.
Treatment Of Parkinsons Symptoms With The Dopamine Precursor L
Based on Carlssons discoveries, Hornykiewicz and colleagues developed the treatment of PD with the DA precursor, L-DOPA . This approach compensates for decreased DA by promoting DA synthesis in midbrain DA neurons. As evidenced in several pop-culture pieces, such as the award-winning motion picture Awakenings starring Robin Williams and Robert De Niro and based on the novel of the same name written by Oliver Sacks, the success of this approach in patients with PD was dramatic and often quite rapid . Despite these dramatic effects, it was reported that L-DOPAs effects were often inconsistent, even within the same patients, and often eventually induced profound and intolerable side effects such as dyskinesia, motor fluctuations, and various emotional disturbances and psychiatric problems . Furthermore, all the clinical benefits of the treatment are eventually reverted with a continuation of dopaminergic neuronal death, as L-DOPA administration does not halt disease progression . However, despite these limitations, the improvement seen in some patients is so pronounced that these downsides do not prevent its use. Indeed, after almost 60 years, L-DOPA remains the gold-standard medication for PD .
Also Check: Sam Waterston Parkinson’s
How Dopamine Agonists Work
Dopamine agonists work by mimicking the action of dopamine. They bind to dopamine receptors found on the nerve cells that regulate motor function and body movement. There are five types of dopamine receptors belonging to two dopaminergic subfamilies . The dopaminergic receptor subfamily D1 consists of D1 and D5 receptors, generally associated with dyskinesia. The dopaminergic receptor subfamily D2 includes D2, D3, and D4 receptors, which are related to symptoms of movement disorders. Dopamine agonists primarily target agonist activity specific to D2 subfamily receptors.
Side Effects Of Dopamine Agonists
The side effects of using dopamine agonists include nausea, headaches, constipation, hallucinations, orthostatic hypotension , swelling of legs, sleepiness, dizziness, fainting, sleep attacks, and impulsive-compulsive behaviors such as over-shopping, over-eating, gambling, or hypersexuality.
When the dopamine agonist dose is lowered or stopped, some patients experience symptoms of withdrawal such as anxiety, pain, depression, and suicidal tendencies. Therefore, caution is necessary during the use as well as discontinuation of dopamine agonists.
Parkinsons News Today is strictly a news and information website about the disease. It does not provide medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. This content is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health providers with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read on this website.
Read Also: Cleveland Clinic Parkinson’s Bicycle Study 2017
What Future Medications May Be Available For Parkinsons
There are numerous studies investigating new treatments for Parkinsons disease.
There has been new information about the role of autoimmunity and T-cells in the development of Parkinsons disease, possibly opening the door to a role for biologics.
Stem cells are also being investigated as a treatment option for Parkinsons disease.
Background Of The Disease
About 250,000 people suffer on Parkinsons disease in Germany. Another 100,000 can be assumed as not detected. Up to 180 patients per 100,000 habitants are estimated. About 1% of the 60-years old people and 3% of the 80-years old people have Parkinsons disease. 10% of the patients are younger than 40 years, 30% younger than 50 years. 40% get the disease between 50 and 60 years. Men have a double risk to get the disease then women. Incidence is increasing with age.
The clinical symptoms or Morbus Parkinson is mainly the bradykinesis, tremor , and rigor .
Don’t Miss: Prayers For Parkinson’s Disease
Mitochondrial Dysfunction: A Pivotal Pathological Mechanism Of Parkinsons Disease
Mitochondria are complex cytosolic organelles of eukaryotic cells whose primary function is the generation of cellular energy in the form of ATP by oxidative phosphorylation. Mammalian mitochondria contain between 2 and 10 mitochondrial DNA molecules encoding 22 transfer RNAs, two ribosomal RNAs, and 13 polypeptides, each of which is part of the respiratory chain and the oxidative phosphorylation system . The mitochondrial respiratory chain contains four protein complexes that form the site of oxidative phosphorylation. This site is responsible for NADH and FADH2 oxidation, co-occurring with the movement of protons from the matrix into the intermembrane space. This movement produces an electrochemical gradient denoted as mitochondrial membrane potential . This gradient stimulates the ATP synthase to reduce molecular oxygen and synthesize ATP. This step is fundamental in aerobic metabolism and constitutes the primary provider of ATP at the final stage of cellular respiration . Nevertheless, the biological function of mitochondria goes far beyond energy production and includes the metabolism of lipids and amino acids and the support of intermediate metabolic pathways, such as the Krebs cycle.
How Does Pd Affect Dopamine
Doctors believe that PD affects the brains ability to create dopamine.7 Since the brain cannot produce the dopamine it needs, a persons movement begins to be affected. PD can also cause other symptoms as the brain begins to create less dopamine.8
People with PD can have issues with sleep, depression, and blood pressure. Younger people with PD can also have issues with impulse control.9 As you can see, these are all related to the parts of the brain that create dopamine. Doctors are not sure why this happens, or what causes PD.
PD causes the neuron cells in the substantia nigra to break down and die. People with PD have 80 percent fewer dopamine-producing cells in their substantia nigra than people without PD have.7
Doctors are not sure why this happens. If doctors can figure out why PD causes the brain to stop producing dopamine, they think they may be able to find a better treatment for PD.
Recommended Reading: Parkinson’s Double Vision
How Dopamine Travels
The electrical circuits in your brain move at lightning speed faster, even. They send information and data through your brain and out into your central nervous system rapidly so you can move and react. However, when these transmitters are interrupted or redirected, symptoms and signs of potential problems can become apparent.
Dopamine is transported through your brain along specific pathways. These are called dopaminergic pathways or dopamine pathways. In people with Parkinsons disease, two significant dopamine pathways the mesolimbic pathway and the nigrostriatal pathway stop communicating with other neurons and parts of the brain.
Typically, these pathways are responsible for moving dopamine from specific parts of the brain. In the brains of people with Parkinsons disease, these pathways are no longer connected. With no dopamine to move, levels of the neurotransmitter begin to fall.
A blood test can be used to measure the level of dopamine transporters in the body. Research suggests a lower level of the dopamine transporter density is implicated in Parkinsons disease development.
What Does It Do
Dopamine has many functions in the body. It is an important part of motor function, which is how the body moves correctly. It is also an important part of how the brain understands reward and reinforcement.2
It works to make you feel good when you do something correctly. Finally, it is one of the chemicals in the brain that is responsible for sexual arousal.3
Read Also: Does Vitamin B12 Help Parkinson’s
How Does Treatment Work
Currently most of the drugs that treat PD work to either replace or mimic dopamine in a persons brain.7 A few drugs work by keeping the body from breaking down dopamine, so it can stay in a persons system longer.
Doctors also think that there are other neurotransmitters that affect and are affected by PD.10 They are currently doing research to find out what these neurotransmitters are and how drugs affecting them may help with better PD treatment in the future. Hopefully, these studies will lead to better outcomes for all people with PD.
Things To Know About Dopamine Agonists
It is important for people with PD to see a movement disorders specialist who is trained in the use of these drugs for PD. They understand the interactions of these drug and how some medicines may make symptoms worse.
It is important to know that delaying or stopping PD medicines will affect symptoms and can also be dangerous. For example, missing a dose of a dopamine agonist may lead to withdrawal symptoms like anxiety or pain.3
Before beginning treatment for Parkinson’s disease, tell your doctor about all your health conditions and any other drugs, vitamins, or supplements you are taking. This includes over-the-counter drugs.
Read Also: Parkinson’s Hallucinations Commercial
Preventative Approaches: Targeting The Causes Of Parkinsons Disease
Unfortunately, although some therapies for PD produce a period of recovery for about 5 years, there is a sharp decrease in the beneficial effects of treatments thereafter . Indeed, the best approach would be to understand the relevant triggers of the disease in order to target the physiopathological mechanisms causing the death of dopaminergic neurons. Epidemiological studies have shown that less than 10% of PD cases have a strict familial etiology, while most of them are sporadic and appear to be caused by other factors associated with susceptibility genes . Although these factors are not fully understood, there is a consensus that PD is induced by a combination of age, gender, genetic background, and environmental factors. However, neither of these has, alone, been identified as a leading cause of PD . While the cellular and neurochemical mechanisms underlying PD have remained incompletely understood, what data have been collected point to heavily to mitochondrial dysfunction, oxidative stress, inflammation, and excitotoxicity in the pathogenesis of both familial and sporadic cases of PD .
This evidence suggests that preventing mitochondrial dysfunction can be a key therapeutic goal to achieve as stand-alone or adjunctive therapy against PD.
What Are Some Possible Side Effects Of The Dopamine Receptor Agonists
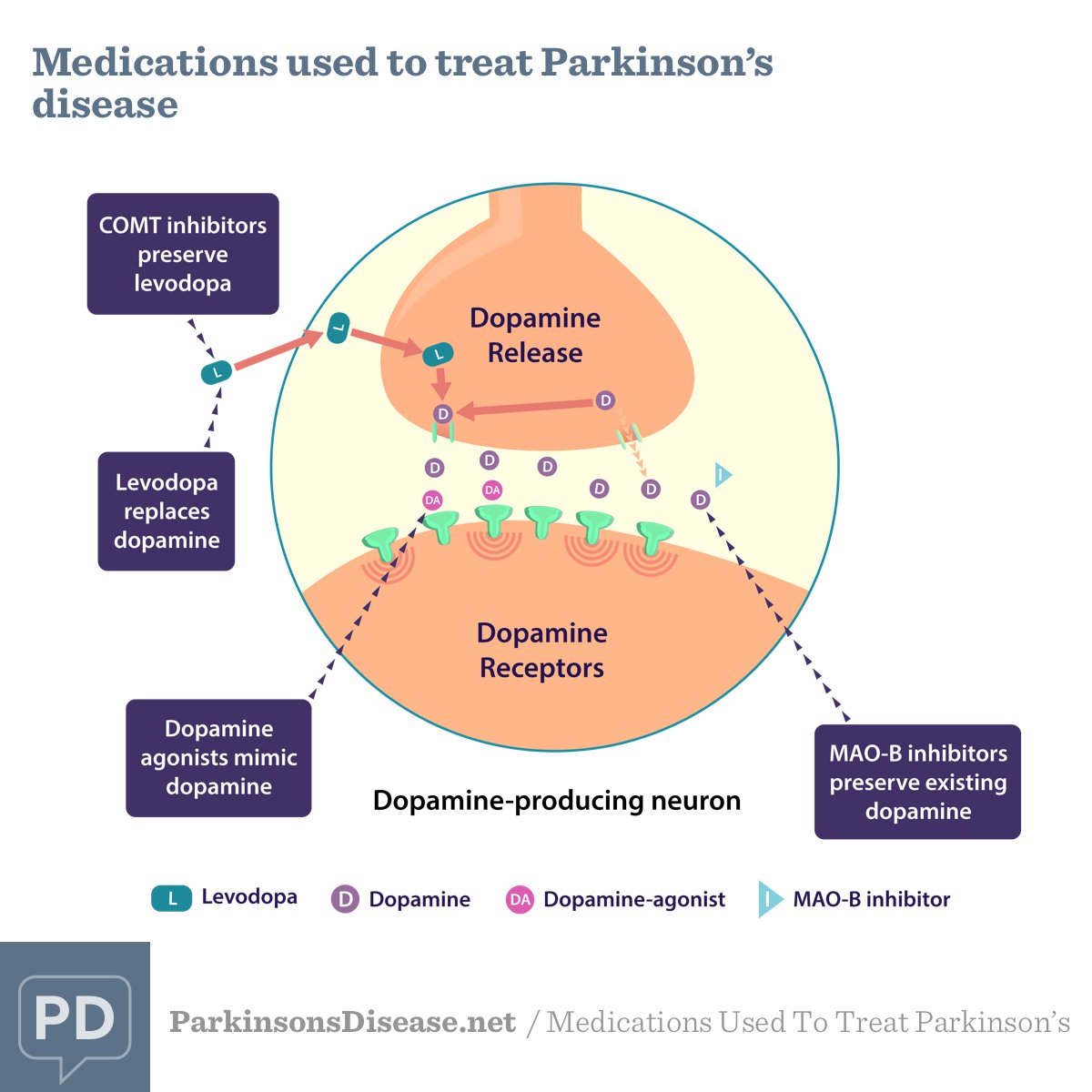
Dopamine agonists have many of the side effects of other dopaminergic agents. These include hallucinations and orthostatic hypotension . Leg swelling can also occur. Dopamine agonists can induce sleepiness as well as sleep attacks and must be used with great caution in those patients who are driving. Compulsive behavior is a well described side effect and could take the form of over-shopping, over-eating, gambling or hyper-sexuality.
In some patients, a withdrawal syndrome can be experienced as the dopamine agonist is lowered and stopped. Symptoms of the withdrawal syndrome can include anxiety, pain, depression, and even suicidality. Patients should be warned about the possibility of experiencing withdrawal when a dopamine agonist is tapered so if they experience these symptoms, they can modify how the medication is weaned off.
Also Check: Diseases Similar To Parkinsons