Delusions From Parkinsons Disease
Delusions affect only about 8 percent of people living with PD. Delusions can be more complex than hallucinations. They may be more difficult to treat.
Delusions often start as confusion that develops into clear ideas that arent based on reality. Examples of the types of delusions people with PD experience include:
- Jealousy or possessiveness. The person believes someone in their life is being unfaithful or disloyal.
- Persecutory. They believe that someone is out to get them or harm them in some way.
- Somatic. They believe they have an injury or other medical problem.
- Guilt. The person with PD has feelings of guilt not based in real behaviors or actions.
- Mixed delusions. They experience multiple types of delusions.
Paranoia, jealousy, and persecution are the most commonly reported delusions. They can pose a safety risk to caregivers and to the person with PD themselves.
PD isnt fatal, though complications from the disease can contribute to a shorter expected life span.
Dementia and other psychosis symptoms like hallucinations and delusions do contribute to increased hospitalizations and increased rates of death .
One study from 2010 found that people with PD who experienced delusions, hallucinations, or other psychosis symptoms were about 50 percent more likely to die early than those without these symptoms.
But early prevention of the development of psychosis symptoms may help increase life expectancy in people with PD.
Clinical Presentation And Cases
The National Institute of Mental Health and the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke sponsored a workshop on PDP, and provisional diagnostic criteria were published in 2007 .9 It is important for providers to recognize the clinical spectrum of symptoms associated with PDP. Symptoms will range from mild visual distortions and the sense of a presence to fully formed, complex hallucinations to delusions . The most common type of complex hallucinations is visual, although other sensory modalities may be affected. Auditory hallucinations have been reported in 8% of patients with PDP, but predominant auditory symptoms are uncommon.10 Hallucinations may initially be nondisruptive, such as seeing ants on the floor or hearing music. Patients may report such hallucinations are not disturbing and may be interesting or even entertaining. Because these types of hallucinations are not disruptive, patients may not be as likely to report their occurrence to caregivers or clinicians. Over time, and with the progression of PD, the nondisruptive quality of hallucinations tends to diminish and is replaced by an alarming or more malignant quality that disrupts daily activities.11
Thanks For Signing Up
We are proud to have you as a part of our community. To ensure you receive the latest Parkinsons news, research updates and more, please check your email for a message from us. If you do not see our email, it may be in your spam folder. Just mark as not spam and you should receive our emails as expected.
Also Check: Weighted Silverware
Parkinsons Disease And Initial Motor Symptoms
What has been assumed to be primarily a dopamine deficiency in PD is better viewed as a disruption of multiple monoaminergic systems, with dopamine disruption dominating the motor symptoms and serotonin taking a dominant position in Parkinsons disease psychosis .
The classic tale of neurodegeneration in Parkinsons begins with the loss of 50% to 80% of nigral neurons. This stage is when the first traditional motor symptoms appear .
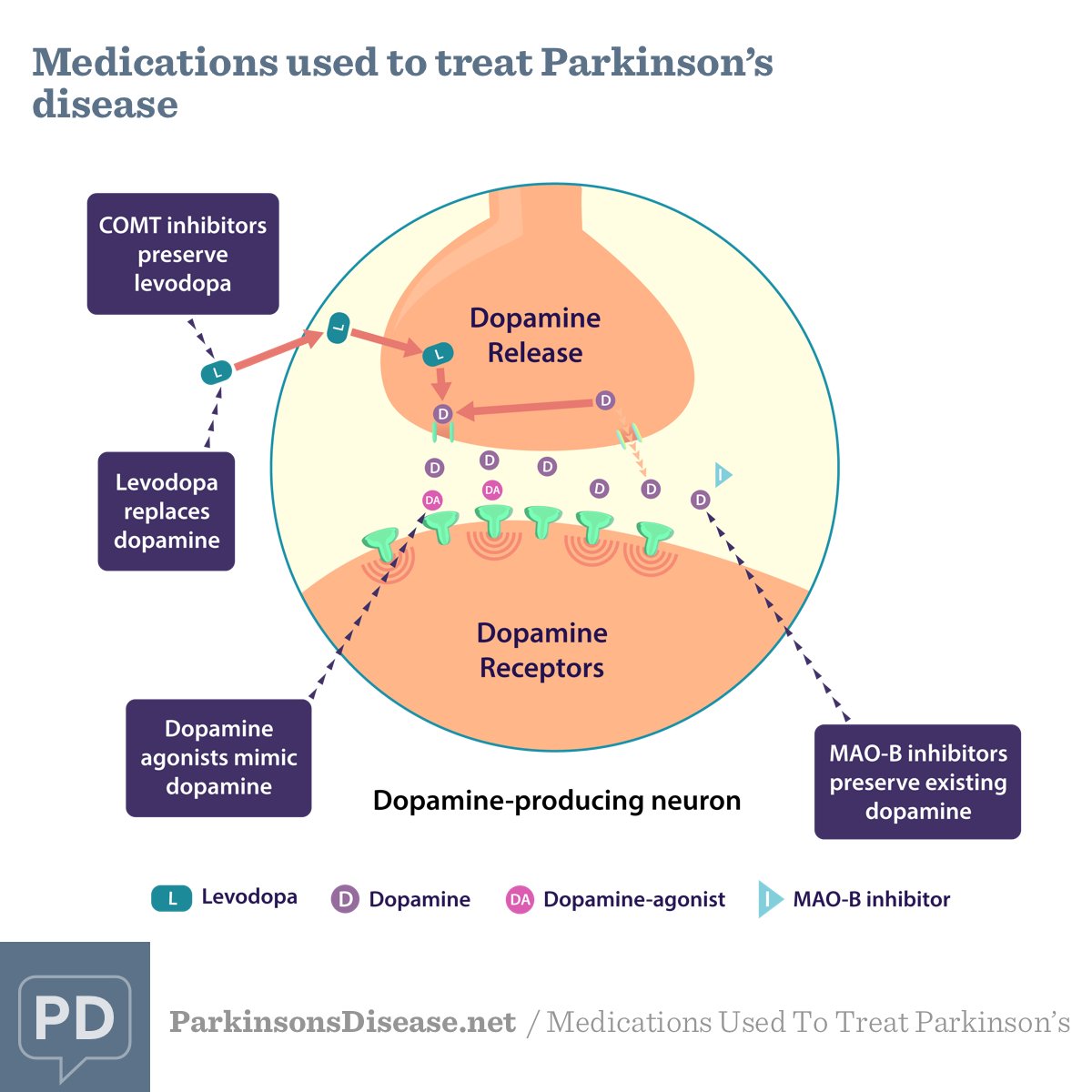
As early motor symptoms become unmanageable, patients are often prescribed levodopa and carbidopa to help restore the dopaminergic tone of the nigrostriatal pathway.
- Levodopa is a dopamine precursor, as likely to be metabolized outside the brain as inside.
- Carbidopa, and other enzyme inhibitors , delay the conversion of levodopa, allowing more of it to pass the blood-brain-barrier for conversion in the brain.
Once in the brain, the exogenous dopamine is used just like the endogenous neurotransmitter, not only resupplying the nigrostriatal pathway and reducing motor symptoms but affecting other residential monoaminergic systems, especially those involved in PDP.
While individuals with late-onset Parkinsons are more susceptible to developing psychotic symptoms, PDP in younger patients can emerge acutely and is associated with concurrent Lewy body dementia.2
Nonpharmacological Approaches To Pdp

Recent small retrospective and open-label studies have revealed significant improvements on psychiatric measurements and short-term improvements on motor symptoms of PD with the use of Electroconvulsive Therapy for PDP . Although it could be used as a last resource, larger prospective clinical trials will be needed to confirm these results before widely recommending this therapy for cases of PDP. There are several anecdotal observations from expert groups for the use of Electroconvulsive Therapy in very severe PDP cases where all pharmacological approaches have failed.
Psychotherapeutic treatments and educational approaches have been emerging as potential adjunctive methods for the treatment of PD psychosis. Although studies have not confirmed results, these approaches should not prevent the clinician providing psychosocial care . These neuropsychological approaches include educating the patient and caregiver with information on psychiatric symptoms with a special emphasis on training sessions, which focus on medication management and more specific coping strategies .
Recommended Reading: Prayers For Parkinson’s Disease
What Are The Types Of Parkinsons Hallucinations
Hallucinations can affect any of the five senses:
- Sight . Seeing something that isnt there, such as insects crawling on the walls or a deceased relative.
- Hearing . Hearing voices or sounds that arent real.
- Smell . Smelling an odor that isnt there, like cookies baking or a skunks spray.
- Feeling . Feeling imaginary things, like bugs crawling on your skin.
- Taste . Having a strange taste in your mouth that isnt from something youve eaten or a medical condition.
Some people sense the presence of a person or an animal nearby. Others see real objects transform into other things for example, a vase changes into a dog.
Its more common to have hallucinations at night, when the darkness creates shadows. Hallucinations can last anywhere from a few seconds to a few minutes.
Early in the disease, most people with Parkinsons psychosis have insight, which means they understand that what theyre experiencing isnt real. Later in the disease, often people lose insight and believe that what they see, hear, or feel is real.
What Are The Symptoms Of Psychosis
Two of the most prominent symptoms are hallucinations and delusions.7 Hallucinations involve seeing, hearing, experiencing or sensing things that are not really there. Delusions are false beliefs that are not based in reality. In describing symptoms of Parkinsons disease psychosis, patients may use such common terms as: seeing things, paranoia, flashbacks, nightmares, false beliefs, or not being in touch with reality.8
Don’t Miss: On And Off Phenomenon
Current Pharmacologic Therapies For Dementia
Three drugs clozapine, quetiapine, and pimavanserin are currently available to treat dementia symptoms in individuals with Parkinsons, with varying side effects and efficacy profiles. In a review published earlier this year, Kevin Kyle, MBBCh, and Jeff M. Bronstein, MD, PhD, of the David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA, discussed the benefits and risks of each of these drugs.1 Below are the highlights.
Symptoms in the context of PDD and LBD present a substantial burden to patients and caregivers, with increased morbidity and mortality risk, they wrote. These symptoms present a major therapeutic challenge in terms of balancing risk to benefit ratio in this fragile population.
Definition Risk Factors & Clinical Course Of Psychosis
PD-psychosis is defined as the presence of at least one of the following: illusions, false sense of presence, hallucinations or delusions that occurred after PD onset have been recurrent or continuous for 1 month and are not more reasonably accounted for by another cause . In clinical practice, anticipating patients who will develop psychosis is a challenge. Clinical characteristics that have been reported as risk factors for developing psychosis in PD include: other medical conditions , long-term dopaminergic therapy, longer disease duration and development of cognitive impairment, specifically executive dysfunctions. Memory deficits and frontal lobe atrophy have been associated with hallucinations . Genetic factors should also be considered as an associated risk factor for developing psychosis in PD. Recently, genetic polymorphisms have shown a significant association with the presence of hallucinations and PD patients with glucocerebrosidase gene mutations have been shown to develop psychosis earlier than patients without mutations . Premorbid psychiatric symptoms and/or neuropsychological symptoms such as vivid dreams and anxiety also have been associated with development of psychosis. A recent neuropsychological PD study showed that hallucinations with loss of insight were associated with impairment in cognitive tasks localized to posterior cortical dysfunction , suggesting a progression from frontal to posterior cortical areas as psychosis progresses .
Also Check: Sam Waterston Tremor
Who Is At Risk For Psychosis
Theres no predicting with certainty which patients with Parkinsons disease will go on to develop symptoms like hallucinations or delusions. A number of risk factors both internal and external- are associated with the condition.Some of these risk factors include: age, duration and severity of Parkinsons disease and the taking of dopamine therapy.3-6
Fda Approval: What It Means
FDA approval of a drug means that data on the drugs effects have been reviewed by CDER, and the drug is determined to provide benefits that outweigh its known and potential risks for the intended population. The drug approval process takes place within a structured framework that includes:
Although many of the FDAs risk-benefit assessments and decisions are straightforward, sometimes the benefits and risks are uncertain and may be difficult to interpret or predict. The agency and the drug maker may reach different conclusions after analyzing the same data, or there may be differences of opinion among members of the FDAs review team. As a science-led organization, FDA uses the best scientific and technological information available to make decisions through a deliberative process.
Accelerated Approval
Since the Accelerated Approval pathway was established in 1992, many drugs that treat life-threatening diseases have successfully been brought to market this way and have made a significant impact on disease course. For example, many antiretroviral drugs used to treat HIV/AIDS entered the market via accelerated approval, and subsequently altered the treatment paradigm. A number of targeted cancer-fighting drugs also have come onto the market through this pathway.
More information on Accelerated Approval is here.
You May Like: Prayer For Parkinson’s Disease
What Treatments Are Available For Parkinsons Psychosis
Your doctor may first reduce or change the PD medication youre taking to see whether that reduces psychosis symptoms. This is about finding a balance.
People with PD may need higher doses of dopamine medication to help manage motor symptoms. But dopamine activity shouldnt be increased so much that it results in hallucinations and delusions. Your doctor will work with you to find that balance.
Parkinsons Disease Psychosis: Hallucinations Delusions And Paranoia
As part of Parkinsons Disease and its treatment, hallucinations, illusions, delusions, suspiciousness and paranoid behaviors occur in over 50% of patients. In this 1-hour webinar Dr. Christopher Goetz suggests lifestyle changes, medication adjustments and a recently FDA approved drug to specifically treat psychosis in Parkinsons Disease.
Recommended Reading: Yopd Life Expectancy
Etiology Of Psychotic Symptoms
PD is characterized by the loss of dopaminergic neurons with cell bodies residing in the substantia nigra pars compacta with resultant decreased dopamine release in the basal ganglia. The etiology of psychosis is less understood and may involve dysfunctional dopaminergic and serotonergic, and possibly cholinergic, pathways. Indeed, drugs that block dopaminergic receptors can cause extrapyramidal symptoms.
Risk factors for PDP include: exposure to dopaminergic medications, advancing age, increasing impairment in executive function, dementia, increasing severity and duration of PD, comorbid psychiatric symptoms such as depression and anxiety, daytime fatigue, sleep disorders, visual impairment, and polypharmacy . The presence of psychosis in patients with PD is a strong predictor of institutionalization. A study comparing PD patients still living at home with those in nursing care facilities found a 16-fold higher likelihood of hallucinations in the institutionalized group . Another review of a population of PD patients with psychosis found that after 2 years, hallucinations were linked to dementia , nursing home placement or death .
Conflict Of Interest Statement
All of the authors were involved in a randomized controlled trial of quetiapine in Parkinsons disease psychosis, which is now complete. This was a noncommercial trial funded by the Parkinsons Disease Society. Dr Michael Samuel has received honoraria for lectures/educational material from UCB, GSK, Medtronic and Orion. He has received unrestricted educational grants from Britannia, Solvay, GSK, Teva, Ipsen, Boehringer-Ingelheim and Medtronic. He has received funding for educational trips from Teva, Ipsen, Pfizer, Medtronic, UCB and Boehringer-Ingelheim.
Read Also: Similar To Parkinsons
Beyond Parkinsons Dopamine Theory: Other Medications
There are some arguments against the dopamine theory of PDP. For example, in individuals with PD who undergo deep brain stimulation , some studies have demonstrated that psychosis emerges at similar rates in these PD patients as levodopa-treated PD patients.9,10 The most convincing arguments, however, come from the actions of atypical, or second-generation, antipsychotics currently used to treat primary psychosis.
How Commonly Do Parkinsons Disease Patients Develop Psychosis
Psychosis in Parkinsons disease generally comes in two forms: hallucinations or delusions . When hallucinations occur, they are mostly visual . Sometimes, they can be threatening, but this is less common. Auditory hallucinations are rare in Parkinsons disease and if they do occur, they are usually accompanied by visual hallucinations.
Delusions are usually of a common theme, typically of spousal infidelity. Other themes are often paranoid in nature Because they are paranoid in nature, they can be more threatening and more immediate action is often necessary, compared to visual hallucinations . It is not uncommon that patients actually call 9-1-1 or the police to report a burglary or a plot to hurt them.
Unfortunately, psychosis occurs in up to 40% of Parkinsons disease patients . In the early stage of Parkinsons disease psychosis, the patient often still has a clear understanding and retains their insight, but this tends to worsen over time and insight may eventually be lost. At later stages, patients may be confused and have impaired reality testing that is, they are unable to distinguish personal, subjective experiences from the reality of the external world. Psychosis in Parkinsons disease patients frequently occurs initially in the evening, then later on spills into the rest of the day.
Don’t Miss: Cleveland Clinic Parkinson’s Bicycle Study 2017
Features Of Parkinson’s Disease Psychosis
PDP typically arises later in the course of the disease, approximately 10 years after initial diagnosis of PD. Symptoms typically arise in the context of retained insight and clear sensorium . Over time, symptoms such as visual hallucinations or delusions tend to recur and progress and insight is lost. Prominent hallucinations early in the course of the disease may suggest Lewy body dementia, Alzheimer’s disease, or a preexisting psychiatric disorder .
Parkinsons Disease Psychosis: A Little
One of the lesser-known symptoms of Parkinsons Disease is Parkinsons psychosis. This webpage explains the prevalence, causes and symptoms, treatment options of PD psychosis. More useful to caregivers are sections on potential triggers of psychotic episodes and what caregivers can do about PD psychosis.
Recommended Reading: What Foods Should Be Avoided When Taking Levodopa
Etiology Risk Factors Or Correlates
The exact pathoetiology of PDP has not been identified. Nonpharmacologic risk factors and correlates for the development of PDP include advanced age, comorbid medical conditions , and PD severity and duration.12 The complexity of PDP pathoetiology is apparent from a number of recent reviews and studies suggesting multifactorial abnormalities, including metabolic, neurotransmitter, sensory pathway, and structural brain alterations, as well as changes in visual processing and sleep disorders.12–14 Although exposure to PD medications is not a requirement for development of PDP, multiple medication classes, such as amantadine, anticholinergics, catechol-O-methyltransferase inhibitors, dopamine agonists, levodopa, and monoamine oxidase type B inhibitors, have all been associated with triggering PDP.13 In particular, up to one third of patients exposed to chronic dopaminergic therapy will experience visual hallucinations.15 Other pharmacy elements, such as polypharmacy burden, levodopa-equivalent doses, and use of certain medications , are also associated with the development of PDP symptoms.
Hallucinations And Delusions In Parkinsons Disease
This blog post is based on the latest research and a Parkinsons Foundation Expert Briefing about hallucinations and delusions in Parkinsons. After an explanation of what hallucinations and delusions are, there are tips for what to do, how to minimize these behaviors through lifestyle changes, and medication treatment options.
Don’t Miss: Judy Woodruff Health Problems
Practical Tips For Caregivers Of People With Parkinson’s Psychosis
This 2-page tip sheet has bullet point suggestions for what to do if the person you care for experiences hallucination, delusions or confusion, or becomes agitated or aggressive. In addition, there are tips for how to best be prepared for a doctors appointment when you bring this behavior to the attention of your medical team.
A Caregivers Guide To Parkinsons Disease Psychosis
While more than 50% of those taking carbidopa-levodopa may experience psychosis , medication management of these symptoms is a balancing act. First, families must bring psychotic behavior to the attention of your medical team. Medical causes of the behavior, like infection must be ruled out, followed by a review of medications and possible medication adjustments before a lifestyle changes and possible medications for treatment are added.
Recommended Reading: Fitflop Shoes For Parkinson’s
What Is Parkinsonism Is It Different From Parkinsons
Parkinsons disease is the most common cause of parkinsonism, a category of neurological diseases that cause slowed movement.
No quick or easy diagnostic tests exist for Parkinsons disease, so a patient may receive an initial diagnosis of parkinsonism without a more specific condition being confirmed.
Classic Parkinsons disease referred to as idiopathic because it has no known cause is the most common and most treatable parkinsonism.
About 15 percent of people with parkinsonism have atypical variants, which are also known as Parkinsons-plus syndromes.
How Can I Get Help
First and most importantly, if you find yourself experiencing symptoms such as hallucinations or delusions, speak out. It is essential to talk about your full range of Parkinsons disease symptoms with your treatment team. A dialogue among patients, care partners, and physicians is a critical component of the effective management of your condition.
References: 1. Forsaa EB, Larsen JP, Wentzel-Larsen T, et al. A 12-year population-based study of psychosis in Parkinsons disease. Arch Neurol. 2010 67:996-1001. 2. Ravina B, Marder I Neural Neursurg Psychiatry. 2011 70:734-738. 4. Fenelon G, Mahieux F, Huon M, Ziegler M. Hallucinations in Parkinsons disease: prevalence, phenomenology and risk factors. Brain. 2000 123:733-745. 5. Wolters ECh. PD- related psychosis: pathophysiology with therapeutical strategies. J Neural Transm. 2006 71:31-37. 6. Goldman JG, Holden S. Treatment of psychosis and dementia in Parkinsons disease. Curr Treat Options Neurol. 2014 16: 281. 7. Goldman JG, Vaughan C, Goetz CG. An update expert opinion on management and researcl, strategies in Parkinsons disease psychosis. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2011 12:2009-2024. 8. Data on file, ACADIA Pharmaceuticals Inc. 9. Fenelon G, Alves G. Epidemiology of psychosis in Parkinsons disease. } Neurol Sci. 2010 289:12-17.
Also Check: Pfnca Wellness Programs