How It All Fits Together
Diagnosing Parkinsons disease can be tricky. The process relies heavily on your doctors judgment. In addition, the causes and risk factors of Parkinsons are not entirely clear yet, which contributes to the difficulty in diagnosing this condition.
However, there have been efforts to try and detect this disease earlier. For instance, clinicians have started focusing more on prodromal symptoms, which are early symptoms that appear before movement-related difficulties begin.
These symptoms include:
- Loss of smell, which can sometimes occur years before other symptoms
- Chronic constipation, without any other explanation
- Rapid eye movement behavior disorder, which causes sleep disturbances
How Parkinson’s Disease Is Diagnosed
Claudia Chaves, MD, is board-certified in cerebrovascular disease and neurology with a subspecialty certification in vascular neurology.
There’s no “gold standard” test that will diagnose Parkinson’s disease . Instead, a healthcare provider relies on their own clinical observations and judgment, along with a patient’s description of possible signs and symptoms, to make the diagnosis. That, of course, makes a physical examination very important in this process. Much of your healthcare provider’s exam will be aimed at assessing whether you have the so-called cardinal signs of Parkinson’s: resting tremor, rigidity , bradykinesia and postural instability .
What Causes Parkinson’s Disease
Parkinsons disease occurs when nerve cells in the basal ganglia, an area of the brain that controls movement, become impaired and/or die. Normally, these nerve cells, or neurons, produce an important brain chemical known as dopamine. When the neurons die or become impaired, they produce less dopamine, which causes the movement problems of Parkinson’s. Scientists still do not know what causes cells that produce dopamine to die.
People with Parkinson’s also lose the nerve endings that produce norepinephrine, the main chemical messenger of the sympathetic nervous system, which controls many functions of the body, such as heart rate and blood pressure. The loss of norepinephrine might help explain some of the non-movement features of Parkinson’s, such as fatigue, irregular blood pressure, decreased movement of food through the digestive tract, and sudden drop in blood pressure when a person stands up from a sitting or lying-down position.
Many brain cells of people with Parkinson’s contain Lewy bodies, unusual clumps of the protein alpha-synuclein. Scientists are trying to better understand the normal and abnormal functions of alpha-synuclein and its relationship to genetic mutations that impact Parkinsons disease and Lewy body dementia.
Recommended Reading: Parkinson Silverware
Is Early Diagnosis Possible
Experts are becoming more aware of symptoms of Parkinsons that precede physical manifestations. Clues to the disease that sometimes show up before motor symptoms and before a formal diagnosis are called prodromal symptoms. These include the loss of sense of smell, a sleep disturbance called REM behavior disorder, ongoing constipation thats not otherwise explained and mood disorders, such as anxiety and depression.
Research into these and other early symptoms holds promise for even more sensitive testing and diagnosis.
For example, biomarker research is trying to answer the question of who gets Parkinsons disease. Researchers hope that once doctors can predict that a person with very early symptoms will eventually get Parkinsons disease, those patients can be appropriately treated. At the very least, these advances could greatly delay progression.
Parkinson’s Disease and Movement Disorders Center
Our center provides compassionate and timely treatment to patients with movement disorders, such as dystonia, ataxia, essential tremor and similar conditions. But our mission goes beyond patient care excellence. By offering educational events and support groups, we empower patients and caregivers to become better partners in their health.
Network Analysis And Cognition
While the clinical diagnosis of PD rests largely on the motor signs and symptoms , non-motor symptoms can be prominent and even precede the motor symptoms . For example, RBD, as discussed earlier, represents a strong risk factor for PD . Cognitive dysfunction can be substantial in PD, typically appearing later in the disease and progressing slower. Nevertheless, the point prevalence of PD is high , and with time the majority of patients will develop cognitive impairment or dementia .
Neurology87Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Medicine2Neurology87Neuroimage78
The partial relation between PDCP expression and dopaminergic dysfunction may help explain why non-demented PD patients can have different changes in cognition when receiving dopaminergic treatments. Specifically, improvement in verbal learning that some patients exhibit with levodopa treatment, depends on baseline PDCP expression . PD patients with caudate tracer uptake in the 3550% range exhibit modest PDCP elevations and show improved cognitive response with medications. In contrast, those with a relatively intact caudate dopaminergic system exhibit cognitive decline with levodopa, which is in accordance with a dopamine overdose hypothesis . Similarly, patients with advance dopaminergic dysfunction and high PDCP scores lose the cognitive benefit from levodopa, possibly due to advance pathology in key PDPC nodes .
Read Also: Does Vitamin B12 Help Parkinson’s
How Is Parkinsons Disease Treated
There is no cure for Parkinsons disease. However, medications and other treatments can help relieve some of your symptoms. Exercise can help your Parkinsons symptoms significantly. In addition, physical therapy, occupational therapy and speech-language therapy can help with walking and balance problems, eating and swallowing challenges and speech problems. Surgery is an option for some patients.
Who Should Consider A Genetic Test For Parkinsons
There are two groups of people who might consider getting genetic testing and we will discuss each group separately.
Genetic testing for PD is a common request and a number of commercial labs perform panels of genetic testing for PD. You may ask: How can I test myself for Parksinons? Whether youre considering getting a genetic test through your doctor, or performing one at home, its important to note that at-home test dont map the entire gene for mutations. Genetic testing through your doctor will test for GBA, PARK7, SNCA, LRRK2, parkin and PINK1.
Both groups are faced with two questions: Should I get genetic testing? And if so, what should I do with the results? Before we address these two questions, we need to learn more about the complexity of genetic testing in PD.
Recommended Reading: Prayers For Parkinson’s Disease
Physical And Neurological Examination
Your doctor will conduct a physical and neurological examination. This can involve observing your behavior, movements, and mental state and conducting tests or asking you to perform certain exercises.
These are some of the symptoms of Parkinsons your doctor can determine visually:
- Fewer spontaneous movements or hand gestures
- Reduced frequency of blinking
- Tremors in your hands while they are at rest, often only in one hand
- Hunched posture or forward lean while walking
- Stiff movements
These are some of the exercises your doctor may ask you to do to evaluate your movements, balance, and coordination:
- Opening and closing your fist
- Tapping your fingers, toes, and heels
- Holding your arms out in front of you
- Moving your finger from one point to another
- Rotating your wrists or ankles
- Standing from a chair
Thanks For Signing Up
We are proud to have you as a part of our community. To ensure you receive the latest Parkinsons news, research updates and more, please check your email for a message from us. If you do not see our email, it may be in your spam folder. Just mark as not spam and you should receive our emails as expected.
Recommended Reading: Cleveland Clinic Parkinson’s Bicycle Study 2017
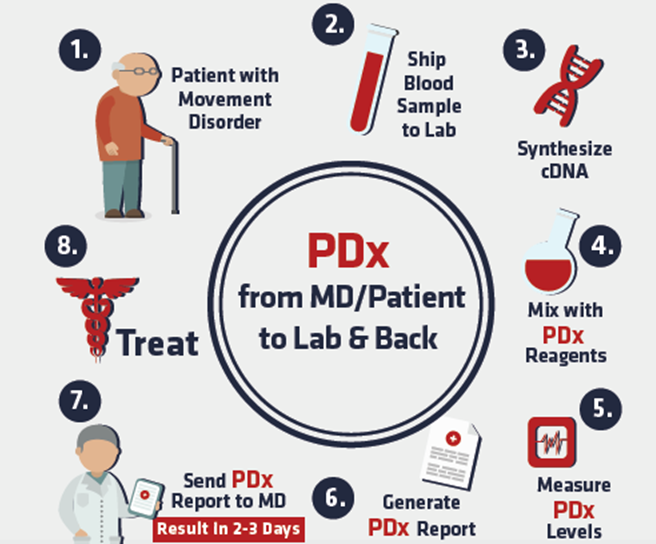
Testing For Parkinsons Disease
There is no lab or imaging test that is recommended or definitive for Parkinsons disease. However, in 2011, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved an imaging scan called the DaTscan. This technique allows doctors to see detailed pictures of the brains dopamine system.
A DaTscan involves an injection of a small amount of a radioactive drug and a machine called a single-photon emission computed tomography scanner, similar to an MRI.
The drug binds to dopamine transmitters in the brain, showing where in the brain dopaminergic neurons are.
The results of a DaTscan cant show that you have Parkinsons, but they can help your doctor confirm a diagnosis or rule out a Parkinsons mimic.
What Is Parkinsons Disease
Parkinsons disease is a nervous system disease that affects your ability to control movement. The disease usually starts out slowly and worsens over time. If you have Parkinsons disease, you may shake, have muscle stiffness, and have trouble walking and maintaining your balance and coordination. As the disease worsens, you may have trouble talking, sleeping, have mental and memory problems, experience behavioral changes and have other symptoms.
Read Also: Judy Woodruff Health Problems
What Medications Are Used To Treat Parkinsons Disease
Medications are the main treatment method for patients with Parkinsons disease. Your doctor will work closely with you to develop a treatment plan best suited for you based on the severity of your disease at the time of diagnosis, side effects of the drug class and success or failure of symptom control of the medications you try.
Medications combat Parkinsons disease by:
- Helping nerve cells in the brain make dopamine.
- Mimicking the effects of dopamine in the brain.
- Blocking an enzyme that breaks down dopamine in the brain.
- Reducing some specific symptoms of Parkinsons disease.
Levodopa: Levodopa is a main treatment for the slowness of movement, tremor, and stiffness symptoms of Parkinsons disease. Nerve cells use levodopa to make dopamine, which replenishes the low amount found in the brain of persons with Parkinsons disease. Levodopa is usually taken with carbidopa to allow more levodopa to reach the brain and to prevent or reduce the nausea and vomiting, low blood pressure and other side effects of levodopa. Sinemet® is available in an immediate release formula and a long-acting, controlled release formula. Rytary® is a newer version of levodopa/carbidopa that is a longer-acting capsule. The newest addition is Inbrija®, which is inhaled levodopa. It is used by people already taking regular carbidopa/levodopa for when they have off episodes .
What Are The Symptoms Of Parkinsons Disease
Symptoms of Parkinsons disease and the rate of decline vary widely from person to person. The most common symptoms include:
Other symptoms include:
- Speech/vocal changes: Speech may be quick, become slurred or be soft in tone. You may hesitate before speaking. The pitch of your voice may become unchanged .
- Handwriting changes: You handwriting may become smaller and more difficult to read.
- Depression and anxiety.
- Sleeping disturbances including disrupted sleep, acting out your dreams, and restless leg syndrome.
- Pain, lack of interest , fatigue, change in weight, vision changes.
- Low blood pressure.
You May Like: On And Off Phenomenon
What Causes Parkinsons Disease
Parkinsons disease occurs when nerve cells in an area of the brain called the substantia nigra become impaired or die. These cells normally produce dopamine, a chemical that helps the cells of the brain communicate . When these nerve cells become impaired or die, they produce less dopamine. Dopamine is especially important for the operation of another area of the brain called the basal ganglia. This area of the brain is responsible for organizing the brains commands for body movement. The loss of dopamine causes the movement symptoms seen in people with Parkinsons disease.
People with Parkinsons disease also lose another neurotransmitter called norepinephrine. This chemical is needed for proper functioning of the sympathetic nervous system. This system controls some of the bodys autonomic functions such as digestion, heart rate, blood pressure and breathing. Loss of norepinephrine causes some of the non-movement-related symptoms of Parkinsons disease.
Scientists arent sure what causes the neurons that produce these neurotransmitter chemicals to die.
Mayo Clinic Q And A: Diagnosing Parkinsons Disease
DEAR MAYO CLINIC: My mother was recently diagnosed with Parkinsons, but she doesnt have many symptoms. I would like her to get a second opinion. Is there a blood test that can determine if the diagnosis is accurate?
ANSWER: Theres no one test that can be used to diagnose Parkinsons disease. Instead, the diagnosis is based on a persons medical history and symptoms, along with a neurological and physical exam. If your mother has doubts about her Parkinsons diagnosis, getting a second opinion from a neurologist who specializes in the disease would be reasonable.
Parkinsons disease is a progressive disorder of the nervous system that affects movement. In people who have this disease, certain nerve cells in the brain, called neurons, gradually die.
Many Parkinsons symptoms are related to the loss of brain neurons that produce a chemical messenger called dopamine. Loss of dopamine can lead to a variety of symptoms. Those symptoms can vary widely from person to person. Parkinsons develops slowly over time. In the diseases early stages, symptoms may be very mild and barely noticeable.
Parkinsons typically impairs a persons normal spontaneous body movements, such as blinking, smiling or swinging the arms while walking. The loss of dopamine that happens in Parkinsons may sometimes trigger sleep disorders, panic attacks, anxiety or insomnia.
Recommended Reading: Zhichan Capsule
Referral To A Specialist
If your GP suspects Parkinson’s disease, you’ll be referred to a specialist.
This will usually be:
- a neurologist, a specialist in conditions affecting the brain and nervous system
- a geriatrician, a specialist in problems affecting elderly people
The specialist will most likely ask you to perform a number of physical exercises so they can assess whether you have any problems with movement.
A diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease is likely if you have at least 2 of the 3 following symptoms:
- shaking or tremor in a part of your body that usually only occurs at rest
- slowness of movement
- muscle stiffness
If your symptoms improve after taking a medication called levodopa, it’s more likely you have Parkinson’s disease.
Special brain scans, such as a single photon emission computed tomography scan, may also be carried out in some cases to try to rule out other causes of your symptoms.
Tests To Rule Out Other Conditions
Blood tests can help rule out other possible causes of the symptoms, such as abnormal thyroid hormone levels or liver damage.
An MRI or CT scan can check for signs of a stroke or brain tumor, which may cause similar symptoms.
Hydrocephalus due to atrophy can occur with some types of dementia and would be visible with one of these imaging tests. If the person has neurologic symptoms but a normal scan result, Parkinsons disease may be present.
The doctor a lumbar puncture to rule out inflammation or a brain infection.
Also Check: On Off Phenomenon
Genetic Testing For Parkinsons Disease
Similar to other complex diseases, the reason a particular person develops Parkinsons disease is likely a combination of genetic makeup and environment. In most people, the genetic contribution to disease development may be due to a number of different genes and the interactions between them. For only a very small percentage of people with PD, about 10%, the disease can be attributed to a single abnormal gene. Figuring out the identity and contributions of all the different genes that play a role in disease development is a very hot topic in PD research today.
Protein Test Could Lead To Earlier And Better Diagnosis Of Parkinsons
Scientists at the Oxford Parkinson’s Disease Centre have been able to use a highly-sensitive method called -synuclein real-time quaking-induced conversion to observe the clumping of alpha-synuclein in the cerebrospinal fluid taken from people with Parkinsons. The findings offer hope that a pioneering new clinical test could be developed to diagnose Parkinsons correctly in its early stages.
Alpha-synuclein is a protein known to form sticky clumps, known as Lewy bodies, in the brain cells of people with Parkinsons and some types of dementia. These clumps are associated with the death of dopamine producing nerve cells which causes the motor symptoms associated with Parkinsons, including freezing, tremors and slowness of movement along with the hidden symptoms such as anxiety and memory problems.
Funded by the charity Parkinsons UK, the study investigated whether the Syn-RT-QuIC method could be used as an early diagnostic test or measure of progression for Parkinsons. The study was carried out in people with Parkinsons taking part in the Discovery study of the OPDC, which is collecting a wealth of data from a specific group of people over time to better understand Parkinson’s. Previous studies have shown potential for this test as a way to identify people with the conditions.¹
The full paper, ‘Diagnostic value of cerebrospinal fluid alpha-synuclein seed quantification in synucleinopathies’, can be read in the journal Brain.
Recommended Reading: Pfnca Wellness Programs
Primary Symptoms Of Parkinsons
The symptoms someone has and how quickly the condition develops will differ from one person to the next. Always consult your doctor to determine if the symptoms youre experiencing may be a sign of Parkinsons disease or a sign of other health issues.
Slowness of Movement
Individuals with Parkinsons disease experience a change in spontaneous movement that causes them to move or respond slowly. The face may lack changing facial expressions .
Tremor
Tremors occur in about 70% of those living with Parkinsons. Typically, the tremor appears on one side of the body in the hand or foot while relaxed or at rest.
Rigidity
Muscles may fail to relax like normal muscles causing the individual to appear rigid and have a decreased range of motion. Rigidity can cause posture changes. Tightness of the muscles of the body may be painful.
Postural Instability
Loss of some reflexes needed to maintain an upright posture may cause individuals to be unstable when standing. The presence of postural instability increases the likelihood of falling.
Secondary motor symptoms include:
Non-motor symptoms of PD include:
- Constipation
- Oily skin, flaky red patches near hairline, nose
- Variable blood pressure
- Mood changes anxiety and depression
- Cognitive changes
- Excessive or low sex drive
- Excessive sweating especially of hands and feet
- Frequent urination and incontinence