Obtaining A Parkinson’s Disease Diagnosis
During the exam, the neurologist will look for cardinal symptoms of the disease. Facial expressions and features will be assessed. The doctor will look for signs of tremor while the patient is at rest. The doctor may watch how easily the patient stands up from sitting in a chair. The doctor may also stand behind the patient and gently pull back on the patients shoulders and look for how easily the patient can regain balance. Good responsiveness to levodopa also helps support the diagnosis of PD. However, taking levodopa may exclude patients from clinical studies that need to recruit recently diagnosed patients who have not yet had treatment . Participation in a clinical trial should be discussed with the doctor.
PD can be challenging to accurately diagnose, particularly in early stages of the disease, which is why a neurologist trained in movement disorders is critical. Approximately 5-10% of patients with PD are misdiagnosed, as many of the symptoms of PD are similar to other diseases. If the patient thinks that he or she has been misdiagnosed, a second opinion may help.1,2
Symptoms Of Parkinson’s Disease
The symptoms of Parkinson’s disease usually develop gradually and are mild at first.
There are many different symptoms associated with Parkinson’s disease. Some of the more common symptoms are described below.
However, the order in which these develop and their severity is different for each individual. It’s unlikely that a person with Parkinson’s disease would experience all or most of these.
What Are My Next Steps
If your doctor doesnt diagnose Parkinsons, they can help you find out what the best next step is depending on what condition they suspect. In some cases, treatment may be as simple as changing the dosage of a medication that may be leading to Parkinsons-like symptoms.
Receiving a Parkinsons diagnosis can be overwhelming. If your diagnosis is confirmed, contact a movement disorder specialist as soon as possible. A specialist can help you develop a strategy to delay the onset of more severe disease and manage symptoms youre already experiencing.
You May Like: Parkinson’s Disease And Hallucinations
How Is It Diagnosed
Diagnosing Parkinsons disease is mostly a clinical process, meaning it relies heavily on a healthcare provider examining your symptoms, asking you questions and reviewing your medical history. Some diagnostic and lab tests are possible, but these are usually needed to rule out other conditions or certain causes. However, most lab tests arent necessary unless you dont respond to treatment for Parkinsons disease, which can indicate you have another condition.
You May Like: Parkinsons And Heart Problems
Comparison Of Patients In Whom A Diagnosis Of Parkinsons Disease Was Maintained Or Rejected
Patients in whom a diagnosis of Parkinsons disease was confirmed had more severe disease as measured by the Hoehn and Yahr stage , more often had a tremor at rest or a classical pill rolling tremor , and more often reported a good initial and sustained response to levodopa than those in whom it was rejected.
Patients in whom the diagnosis was changed to non-parkinsonian tremor had no other parkinsonian features such as rigidity, bradykinesia, hypomimia, or monotonous speech. They also reported falls significantly less frequently and had higher mini-mental state scores . Those in whom the diagnosis was changed to atypical parkinsonism had more severe akinesia , rigidity , and postural instability , less commonly reported an initially or currently good response to levodopa , but more often had incontinence and additional features incompatible with Parkinsons disease. Those in whom the diagnosis was changed to vascular parkinsonism were older than those in whom a diagnosis of Parkinsons disease was confirmed , had a larger number of smoking years , more often had gait difficulties as their first complaint , and had more severe postural instability they never had a rest tremor.
Also Check: Can Stress Cause Parkinson’s
Molecular Imaging In Parkinson’s Disease
The diagnosis of PD relies on the clinical manifestation of cardinal motor symptoms, bradykinesia, and tremor at rest or rigidity . A positive response to dopaminergic drugs is supportive of the diagnosis. Single photon emission computed tomography or PET ligands that are specific for dopamine transporters indirectly enable the quantification of the deficit of dopaminergic nigrostriatal projections and can provide further support of diagnosis . Deficiencies of monoamine synthesis can be measured with dihydroxyphenylalanine which is a substrate for the enzyme aromatic amino acid decarboxylase in all monoaminergic neurons including noradrenergic neurons .
The role of deficits of noradrenaline in motor and non-motor symptoms is not clear and research on the noradrenergic system in PD patients has been hindered by lack of specific methods to visualize the noradrenergic neurons and projections in vivo. We have recently carried out PET studies to investigate the role of noradrenaline in non-motor symptoms in PD patients and these studies will form the basis of discussions in the paragraphs below.
Paul Johns BSc BM MSc FRCPath, in, 2014
Is There Anything I Can Do To Slow The Progression Of Parkinsons Symptoms
Treatment for Parkinsons can help you manage your symptoms. Currently, theres no way to cure or stop the progression of Parkinsons. However, medical professionals have found ways to slow the progression of symptoms with therapies such as medications and deep brain therapy.
Diet and exercise are also known to slow down Parkinsons. Studies have shown that eating a nutritious diet, such as the Mediterranean diet, can help slow down the progression of Parkinsons disease.
Additionally, getting regular exercise has been shown to slow down symptom progression. People with Parkinsons should try to get at least 2.5 hours of exercise each week. A physical therapist or another medical professional can help you develop an exercise routine that meets your needs.
Dont Miss: Parkinsons Disease Trial News
Recommended Reading: What Causes Parkinson’s Syndrome
Ruling Out Other Conditions
The process of ruling out similar conditions is referred to as differential diagnosis. Parkinsons has symptoms in common with Alzheimers disease, frontotemporal dementia, and Huntington disease. Parkinsons symptoms can be caused by medications such as antipsychotics that may be taken for depression or schizophrenia. Parkinsonism can also be caused by another disease this is known as secondary parkinsonism. Conditions that can cause secondary Parkinsonism include hydrocephalus , some types of brain tumors, Wilsons disease, problems with the parathyroid gland, chronic liver failure, issues with the blood supply to the brain, and infections such as HIV, neurosyphilis, toxoplasmosis, and progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy .
Your doctor may be able to quickly rule many of these conditions based on your medical and family history or simple blood tests. Other disorders may require time and repeated tests before they can be confirmed or ruled out. The presence of other diseases in addition to Parkinsons may complicate the differential diagnosis and eventually result in multiple diagnoses.
Condition Guide
Symptoms And Risk Factors
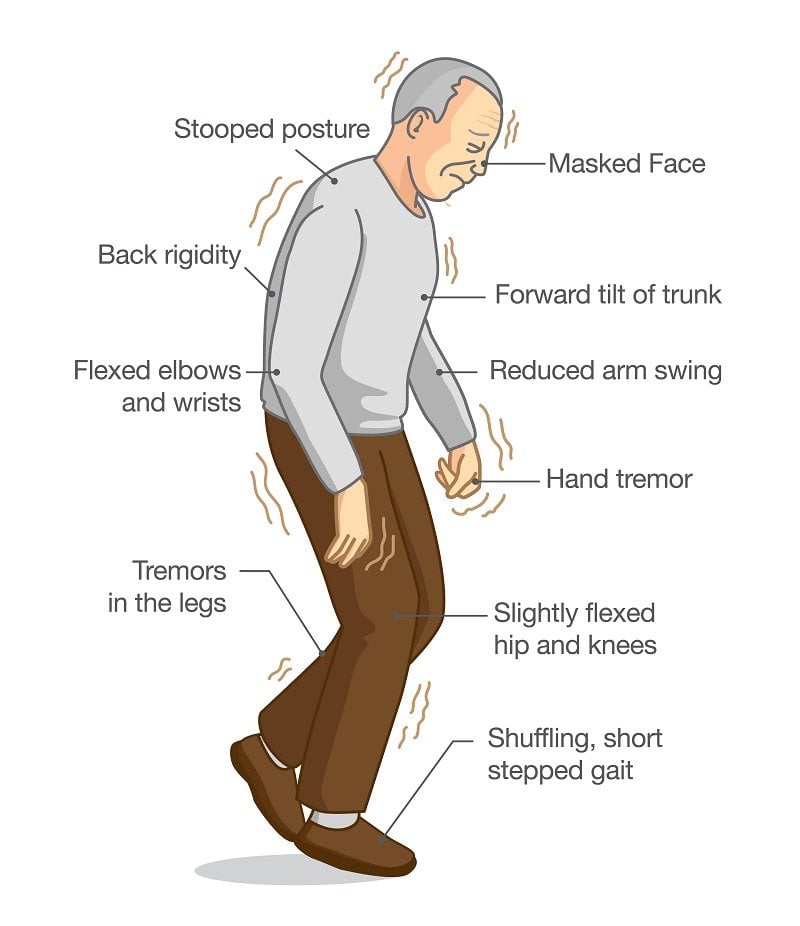
Motor, or movement-related, symptoms of Parkinsons disease may include shaking in the arms, legs, hands, and face. Stiffness, slow movements, and trouble with coordination and balance are also associated with this condition.
People with Parkinsons disease may also have difficulty with speech. For example, a person with Parkinsons disease may speak in a monotone or quiet voice.
Other symptoms can include fewer facial expressions, also known as facial masking, and difficulty with writing, buttoning, or other fine motor tasks. Later in the course of this condition, a person may have trouble swallowing and experience worsening balance and frequent falls.
Even early on, Parkinsons disease can cause nonmotor symptoms, including anxiety, depression, constipation, a reduced sense of smell, urinary incontinence, dizziness when standing, fatigue, and sleep disorders. As the disease progresses, a person may experience hallucinations or cognitive impairment.
Parkinsons disease can occur at any age, but it most commonly affects people older than age 50. The condition is likely caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Pesticide exposure and drinking well water, for example, have been associated with an increased risk of Parkinsons disease.
3.9/5useddisordersfollowdisordersdiagnose Parkinsons diseaserelated to it here
what are the four cardinal signs of Parkinsons disease?
How does Parkinsons start?
Don’t Miss: Best Anxiety Medication For Parkinson’s
What Are The Treatments
Currently there is no cure for Parkinsons disease.
Symptoms can be mild in the early stages of the condition and people might not need immediate treatment. Your doctor and specialist will monitor your situation.
There are several different types of drugs used to treat Parkinsons disease. Drug treatments are tailored to each individuals needs and are likely to involve a combination of different drugs. Your medication should be reviewed regularly. It is likely that, over time, changes will be made to the types of drugs you take and the doses you take each day.
The main types of drug treatment for Parkinsons disease are:
- drugs which replace dopamine
- drugs which mimic the role of dopamine
- drugs which inhibit the activity of acetylcholine
- drugs which prevent the body breaking down dopamine
- other drugs such as anti-sickness medication
Everybody is affected differently by medication. The possible side effects of Parkinsons disease drugs include nausea , vomiting , tiredness and dizziness. Some people might experience confusion, nightmares and hallucinations. For some people, dopamine agonists have been linked to compulsive behaviour such as addictive gambling or hypersexuality .
The effectiveness of the main drug treatment levodopa can wear off over time and its long-term use can cause some people to develop involuntary twisting or writhing movements of the arms, legs or face . To reduce the risk, doctors might delay the use of levodopa for younger people.
How Is Parkinson’s Disease Diagnosed
Your doctor will ask questions about your symptoms and your past health and will do a neurological exam. This exam includes questions and tests that show how well your nerves are working. For example, your doctor will watch how you move. He or she will check your muscle strength and reflexes and will check your vision.
Your doctor also may check your sense of smell and ask you questions about your mood.
In some cases, your doctor will have you try a medicine for Parkinson’s disease. If that medicine helps your symptoms, it may help the doctor find out if you have the disease.
Tests
There are no lab or blood tests that can help your doctor know whether you have Parkinson’s. But you may have tests to help your doctor rule out other diseases that could be causing your symptoms. For example:
- An MRI or CT scan is used to look for signs of a stroke or brain tumor.
- Blood tests check for abnormal thyroid hormone levels or liver damage.
Another type of imaging test, called PET, sometimes may detect low levels of dopamine in the brain. These low levels are a key feature of Parkinson’s. But PET scanning isn’t commonly used to evaluate Parkinson’s. That’s because it’s very expensive, not available in many hospitals, and only used experimentally.
Don’t Miss: Lewy Body Parkinson’s Disease Symptoms
How Can Mris Be Used To Detect Early Onset Parkinsons
MRIs use magnets to create detailed images of the inside of the body. Brain MRIs can help doctors spot tumors, brain bleeding, and other brain health conditions. Recently, medical researchers have discovered that MRIs can also spot small changes in the brain that can indicate Parkinsons disease.
A 2019 study on MRIs and Parkinsons found that people with Parkinsons often have visibly damaged brain neurons. The damage to neurons is present before any brain atrophy begins, and before symptoms are present.
Using this information, doctors can prescribe appropriate treatments, such as Deep Brain Stimulation therapy, that can slow down decline and improve the quality of life for people with Parkinsons.
Complementary And Alternative Therapies
Some people with Parkinson’s disease find complementary therapies help them feel better. Many complementary treatments and therapies claim to ease the symptoms of Parkinson’s disease.
However, there’s no clinical evidence they’re effective in controlling the symptoms of Parkinson’s disease.
Most people think complementary treatments have no harmful effects. However, some can be harmful and they shouldn’t be used instead of the medicines prescribed by your doctor.
Some types of herbal remedies, such as St John’s wort, can interact unpredictably if taken with some types of medication used to treat Parkinson’s disease.
If you’re considering using an alternative treatment along with your prescribed medicines, check with your care team first.
Don’t Miss: What Kills A Person With Parkinson’s Disease
Definition And Differential Diagnosis
There are many manifestations of but the classical diagnostic symptoms are:
- slowness and poverty of movement
The physical signs of include:
- slowness of movement
At diagnosis, these signs are usually unilateral, but they become bilateral as the disease progresses. Later in the disease additional signs may be present including postural instability , cognitive impairment and orthostatic hypotension .
There is no single way to define Parkinsons disease or what is often called idiopathic Parkinsons disease in order to differentiate it from other causes of parkinsonism, such as multiple system atrophy and progressive supranuclear palsy .
is traditionally defined, pathologically, by the finding of Lewy bodies and degeneration of catecholaminergic neurones at post-mortem. Using a pathological definition of PD is problematic for a number of reasons:
- A pathological diagnosis is not practical in life.
- Lewy body inclusions in catecholaminergic neurones are seen in individuals without clinical evidence of it is presumed that these are pre-clinical cases.
- Lewy bodies have not been found in otherwise typical individuals with with Parkin mutations, although such rare young-onset genetic cases of PD might be said not to have idiopathic PD.
In recent years, attempts to define genetically have become possible with the discovery of monogenic forms of the disease. However, such families account for a very small proportion of cases.
Common causes of tremor.
What Are The Risk Factors For Parkinsons
There are a few known risk factors for Parkinsons. These include:
- having a family history of Parkinsons
- being over 60 years
- having been exposed to herbicides, pesticides, and other toxins
Its important to note that these risk factors only cause a slight increase in risk. Having one or more risk factors isnt an indicator youll develop Parkinsons. However, if youre concerned about your risk for Parkinsons, talk with a doctor.
Recommended Reading: Cluster Headaches Parkinson’s Disease
Is Early Diagnosis Possible
Experts are becoming more aware of symptoms of Parkinsons that precede physical manifestations. Clues to the disease that sometimes show up before motor symptoms and before a formal diagnosis are called prodromal symptoms. These include the loss of sense of smell, a sleep disturbance called REM behavior disorder, ongoing constipation thats not otherwise explained and mood disorders, such as anxiety and depression.
Research into these and other early symptoms holds promise for even more sensitive testing and diagnosis.
For example, biomarker research is trying to answer the question of who gets Parkinsons disease. Researchers hope that once doctors can predict that a person with very early symptoms will eventually get Parkinsons disease, those patients can be appropriately treated. At the very least, these advances could greatly delay progression.
Symptoms Of Parkinsons Disease
Parkinsons has four main symptoms:
- Tremor in hands, arms, legs, jaw, or head
- Muscle stiffness, where muscle remains contracted for a long time
- Slowness of movement
- Impaired balance and coordination, sometimes leading to falls
Other symptoms may include:
The symptoms of Parkinsons and the rate of progression differ among individuals. Early symptoms of this disease are subtle and occur gradually. For example, people may feel mild tremors or have difficulty getting out of a chair. They may notice that they speak too softly, or that their handwriting is slow and looks cramped or small. Friends or family members may be the first to notice changes in someone with early Parkinsons. They may see that the persons face lacks expression and animation, or that the person does not move an arm or leg normally.
People with Parkinson’s disease often develop a parkinsonian gait that includes a tendency to lean forward take small, quick steps and reduce swinging their arms. They also may have trouble initiating or continuing movement.
Symptoms often begin on one side of the body or even in one limb on one side of the body. As the disease progresses, it eventually affects both sides. However, the symptoms may still be more severe on one side than on the other.
Don’t Miss: How To Support Someone With Parkinson’s Disease
Physical And Neurological Examination
Your doctor will conduct a physical and neurological examination. This can involve observing your behavior, movements, and mental state and conducting tests or asking you to perform certain exercises.
These are some of the symptoms of Parkinsons your doctor can determine visually:
- Fewer spontaneous movements or hand gestures
- Reduced frequency of blinking
- Tremors in your hands while they are at rest, often only in one hand
- Hunched posture or forward lean while walking
- Stiff movements
These are some of the exercises your doctor may ask you to do to evaluate your movements, balance, and coordination:
- Opening and closing your fist
- Tapping your fingers, toes, and heels
- Holding your arms out in front of you
- Moving your finger from one point to another
- Rotating your wrists or ankles
- Standing from a chair
Parkinsons Q& a: How Do I Manage My Time And Mental Health
Navigating Parkinsons disease can feel like a never-ending learning curve. PD Conversations is a place to ask your Parkinsons questions and connect with others living with the disease. In this blog series, we highlight a high-interest question answered by the Parkinsons Foundation Helpline on PD Conversations.
Question: With Parkinsons, how do you find enough time in the day to get everything done and not feel completely overwhelmed? I’m trying to find enough hours in the day to get in the exercise, the cognitive activity, my daily household chores, eating right and taking meds. Any tips?
A Parkinsons disease diagnosis changes many areas of your life. You may have to readjust the way you work, rest and live. The changes that come with PD can cause emotional distress. Common PD symptoms may also include anxiety, apathy and depression. It is normal to have overwhelming feelings through all the changes of living with Parkinsons, but there are resources to support your mental health and help you live well with PD.
Don’t Miss: What Kind Of Doctor Treats Parkinson’s Disease