What Are The Most Common Medicines Used To Treat Pd
Sinemet®
Levodopa is the most commonly prescribed and most effective medicine for controlling the symptoms of PD, particularly bradykinesia and rigidity.
Levodopa is a chemical found naturally in our brains. When given as a medicine, it is transported to the nerve cells in the brain that produce dopamine. It is then converted into dopamine for the nerve cells to use as a neurotransmitter.
Sinemet is made up of levodopa and another drug called carbidopa. Levodopa enters the brain and is converted to dopamine while carbidopa prevents or lessens many of the side effects of levodopa, such as nausea, vomiting, and occasional heart rhythm disturbances. It is generally recommended that patients take Sinemet on an empty stomach, at least ½ hour before or one hour after meals.
There are two forms of Sinemet: controlled-release or immediate-release Sinemet. Controlled-release Sinemet and immediate-release Sinemet are equally effective in treating the symptoms of PD, but some people prefer the controlled release version. Ask your doctor which approach is best for you.
Dopamine agonists
Dopamine agonists are medicines that activate the dopamine receptor. They mimic or copy the function of dopamine in the brain.
Parlodel®, Requip®, and Mirapex® are all dopamine agonists. These medicines might be taken alone or in combination with Sinemet. Generally, dopamine agonists are prescribed first and levodopa is added if the patient’s symptoms cannot be controlled sufficiently.
Symmetrel®
Risk Of Omitting Or Delaying Pd Medicines
PD medication should not be stopped abruptly and should always be given on time. Late or missed doses may result in patients swallowing, speech and mobility being affected, leading to further difficulties. In addition, delays in the administration of medicines can lead to an increased risk of falls, care needs, pain, and distress, and may lengthen the hospital stay. The following points highlight the seriousness that delaying or omitting a PD medicine may lead to:
Some Disadvantages Of Mao
When selegiline is taken together with levodopa, side effects such as dyskinesias , hallunications or vivid dreaming may sometimes occur or worsen.
When people have taken rasagiline on its own , the most commonly reported side effects have been:
- Headache
- Depression
When taken with levodopa, the most common reports have been of uncontrolled movements and accidental falls.
Many of these side effects may be due to the increase in dopamine caused by rasagiline or selegiline. Your doctor or consultant can alter the dosage to correct these effects.
If youre taking some types of antidepressant, you might not be able to take MAO-B inhibitors, as these drugs can interact with each other to raise blood pressure to a dangerous level.
Your neurologist or pharmacist is the best person to advise on potential interactions with other medications.
Read Also: Are Hallucinations A Symptom Of Parkinson’s
What To Do To Prevent Drug
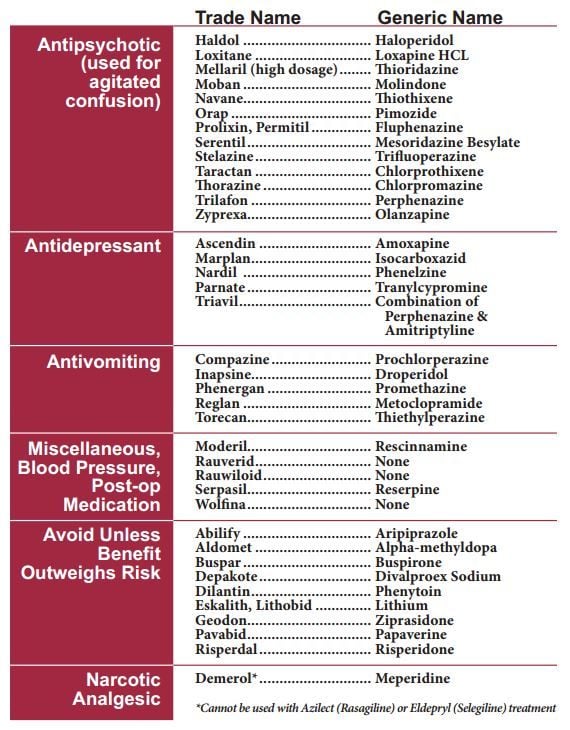
The most common drugs linked to this condition are two used to treat schizophrenia or psychotic symptoms of dementia. They are haloperidol and perphenazine . Ask your doctor about parkinsonism if you or a loved one is concerned about a drug, especially these two drugs.
In general:
* Make sure you or a loved one are on the lowest effective dose.* If you already have Parkinsons disease, then tell your doctor if the symptoms appear to be getting worse since starting the drug.* Never stop taking a drug on your own. Talk to your doctor about any concerns.
* Parkinsons Disease Society. Drug-induced parkinsonism.* Albin RL. Parkinsons disease: background, diagnosis, and initial management. Clinics in Geriatric Medicine. 2006 22:735-751.* Alvarez MV, Evidente VG. Understanding drug-induced parkinsonism Separating pearls from oysters. Neurology. 2008 70:e32-e34.
Connies notes: Neuro meds common side effects include dizziness,nausea,headache,vomitting and sleep disorders
Considerations For The Inpatient Management Of Parkinsons Disease
Recognising and managing certain complications of Parkinsons disease can help improve care and reduce the risk of admission for people living with the condition.
Degenerative neurological disorders
Sergio Azenha / Alamy Stock Photo
Parkinsons disease is a neurological disorder in which there is progressive death of dopaminergic neurones in the substantia nigra the part of the mid-brain responsible for managing movement and the dopaminergic system with more than 50% of cell death occurring before symptom manifestation. The subsequent deficiency of dopamine synthesis, owing to this cell death, leads to the progression of motor symptoms including bradykinesia, rigidity, tremor and postural instability,.
Around 137,000 people in the UK have a PD diagnosis. The cause of the disease is yet to be discovered, but a combination of environmental and genetic factors are thought to increase its risk. Despite this, there is a lack of robust, large-scale evidence of a definitive link between any specific environmental risk factors. Around 20% of patients affected by PD have a first-degree relative that is affected by the disease. Prevalence is higher with increasing age and men appear to be at higher risk of developing the disease than women,. Patients with PD have a reduced life expectancy and studies have suggested up to a five-times higher mortality rate than people in the same age group without PD.
Don’t Miss: Drugs That Cause Parkinson Like Symptoms
Delayed Administration And Contraindicated Drugs Place Hospitalized Parkinsons Disease Patients At Risk
Mr. Grissinger, an editorial board member of, is Director of Error Reporting Programs at the Institute for Safe Medication Practices in Horsham, Pennsylvania .
Problem: One-third of all patients with Parkinsons disease visit an emergency department or hospital each year, making it a surprisingly common occurrence. The disease affects about 1 million people and is currently the 14th leading cause of death in the U.S. Hospitalization can be risky for patients with Parkinsons disease when viewed from the perspective of pharmacological management.
Undergoing surgical procedures can be particularly risky for patients with Parkinsons disease. Antiparkinsonian agents have been inappropriately withheld because patients were to receive nothing by mouth prior to surgery, and surgical patients have been given a contraindicated anesthetic agent or a centrally acting antidopaminergic drug such as haloperidol, metoclopramide, or prochlorperazine postoperatively. One in three patients with Parkinsons disease has been prescribed contraindicated drugs during hospitalization. Serious complications, mostly neuropsychiatric, have occurred in more than half of these patients.,
Withdrawal Syndrome With Levodopa
Research has shown that withdrawal symptoms can happen when someone very suddenly stops taking levodopa, perhaps because they are experiencing impulsive and compulsive behaviour. It can lead to symptoms such as depression, anxiety and pain. Any withdrawal from Parkinsons medications needs to be done gradually, under the supervision of a health professional, to avoid the risk of developing this syndrome.
Don’t Miss: Tell Me About Parkinson’s
They Despise What They Do Not Know
Many patients complain of the disdainful reaction they encounter when they ask their doctors about adding mucuna to their treatment regimen.
As it is an unorthodox therapy, it is perfectly understandable that the physician does not want to prescribe mucuna: it is not part of the generally accepted body of treatments they are trained to manage..
When a doctor decides to incorporate mucuna, he faces new difficulties, particularly with patients treated with other drugs. This requires the additional effort of studying the situation and designing a strategy for each individual case.
On the other hand, we cannot allow patients to treat themselves in hiding. Therefore, it is desirable that as doctors, we have to educate ourselves about mucuna so that we can choose to use it or not in a particular type of patient.
One should never despise the unfamiliar. After studying the properties of mucuna and weighing its advantages and disadvantages, we should decide on a rational basis, whether it is beneficial, neutral, or inadvisable for a specific case.
If the patient perceives that we master the subject, he will entrusted his care to us, rather than attempting to treat himself. That way, he will cooperate if we ban the mucuna or recommend a gradual dosage pattern. We earn their trust when we have enough information and credibility.
Serotonin Reuptake Blocking Antidepressants Fluoxetine Sertraline And Paroxetine
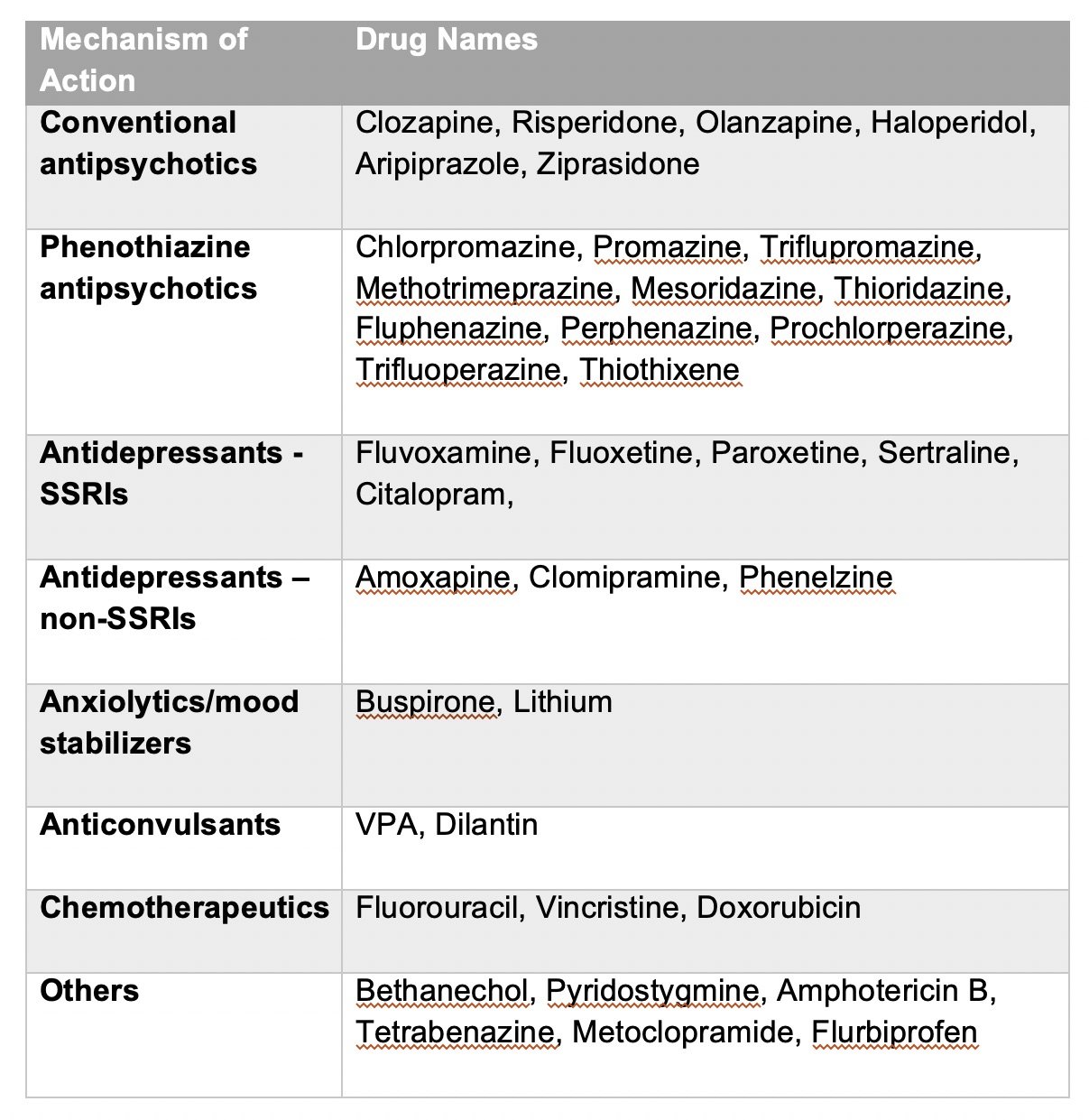
Several other medications have been reported to cause drug-induced parkinsonism and to worsen parkinsonism in people with Parkinson disease, including the serotonin reuptake blocking antidepressants fluoxetine, sertraline, and paroxetine. Two calcium channel blockers available in Europe and South America , which are piperazine derivatives, are thought to cause drug-induced parkinsonism by blocking dopamine receptors. Reports of parkinsonism induced by other drugs, such as lithium and amiodarone, are so rare that only after parkinsonism has developed should the possible drug effect be taken into account. Because lithium is not known to block dopamine receptors, another mechanism is likely. Some animal data implicate an effect of lithium on intercellular signalling via G-protein coupled receptors . One antidepressant, amoxapine, has dopamine receptor-blocking properties and, therefore, may induce parkinsonism. Parkinsonism as a transient side effect of alcohol withdrawal has been reported without later development of Parkinson disease, but it is unknown how common this is .
Don’t Miss: Parkinson’s Disease And Eating Problems
Parkinsons Medication And Alcohol: The Final Word
Whether or not you should drink alcohol while being treated for Parkinson’s disease will depend on the medication you’re taking. It is worth discussing this issue with your doctor, especially if you have concerns about alcohol dependence or addiction.
General health guidelines state that you should avoid drinking alcohol with any medication that makes you drowsy, sleepy or impairs your concentration. That said, many people with Parkinsons disease find that the occasional glass of wine is not harmful, as long as their doctor has agreed that they can drink in moderation.
You should always speak to your doctor before you mix Parkinson’s disease medication and alcohol for the first time. You should never drive or operate heavy machinery when you have been drinking alcohol, and you should make sure you are in safe surroundings to minimize the risk of falls or injury.
APA ReferenceSmith, E. . Can You Drink Alcohol with Parkinsons Disease Medication?, HealthyPlace. Retrieved on 2021, August 28 from https://www.healthyplace.com/parkinsons-disease/treatment/can-you-drink-alcohol-with-parkinsons-disease-medication
How Dopamine Agonists Are Used
Dopamine agonists are used at all stages of Parkinsons. You might take them alone when treatment is being started, or alongside levodopa to provide a more effective treatment with fewer side effects.
Treatment with dopamine agonists has to be started carefully to minimise the risk of side effects, with the dose gradually increasing until you and your specialist or Parkinsons nurse are happy that your symptoms are under control. Some dopamine agonists are available as one a day tablets. These can be a better option for the body and may help both movement and other symptoms of Parkinsons.
Read Also: Gene Therapy For Parkinson’s Disease An Update
Side Effects With Levodopa
To avoid use in individuals with known allergy or hypersensitivity to Mucuna pruriens or components.
There have been some side effects of mucuna. In a study of patients with Parkinsons disease, a derivative of Mucuna pruriens caused minor adverse effects, which were mainly gastrointestinal in nature.
Isolated cases of acute toxic psychosis have been reported1, probably due to levodopa content. Therefore, as with Sinemet and Madopar, its use should be avoided in patients with psychosis or schizophrenia
Mao Type B Inhibition
Monoamine oxidase is a naturally occurring enzyme which is responsible for the breakdown of dopamine. MAO Type B inhibitors are reputed to scavenge free radicals formed by oxidative metabolism of dopamine hence the unproven theory that they may have a neuro protective effect.
Currently, in Australia, the available MAO Type B inhibitors are:
- Azilect®
- Selgene®
Azilect® taken once a day.
Eldepryl® taken twice a day with the second dose no later than noon, otherwise sleep disturbances may occur.
Selgene® as above
Drug interactions may occur with these medications. Pethidine® and some forms of antidepressants should be treated with caution. It is essential to discuss this with your treating specialist.
Also Check: Parkinson’s Foundation Miami Florida
Contraindicated Drugs For Parkinson’s Patients
More than two dozen drugs should not be taken by Parkinsons patients because they alter the brains dopamine system. Always let your neurologist know before you have surgery, so he or she can work with your medical team to keep your Parkinsons in control. View a list of drugs that Parkinsons patients should not take.
Practice Quiz: Antiparkinsonism Agents
Lets evaluate what youve learned in this nursing pharmacology study guide for antiparkinsonian agents.
1. What is the goal of therapy for Parkinsons disease?
A. To decrease dopamine and to increase cholinergic neuronsB. To balance dopamine and cholinergic neuronsC. To excite neurons moreD. To inhibit neurons more
2. What is the mainstay of treatment for Parkinsons?
A. Symmetrel
4. Which can decrease efficacy of levodopa?
A. PhenytoinC. NiacinD. Both A and B
5. A construction worker for 10 years is about to receive anticholinergics. What should the nurse consider in handling this patient?
A. Do not give the drug to the patient.B. Administer it with caution.C. Discuss it with the doctor and have the order changed.D. Arrange for a possible increase in the dose.
6. Which of the following is a contraindication for the use of anticholinergic agents?
A. Heart rate of 120 beats per minuteB. Myasthenia gravisD. All of the above.
Answers and Rationale
1. Answer: B. To balance dopamine and cholinergic neurons .
2. Answer: B. levodopa.
Levodopa, the precursor of dopamine is the gold standard of treatment for Parkinsons. It crosses the blood-brain barrier and is converted into dopamine. When combined with carbidopa, the enzyme dopa decarboxylase is inhibited from metabolizing levodopa, leading to higher levels that can cross the barrier.
3. Answer: C. Benadryl.
4. Answer: D. Both A and B.
Both phenytoin and pyridoxine or Vitamin B6 can decrease the effectiveness of levodopa.
Recommended Reading: Is Rigidity A Symptom Of Parkinson’s
Antagonists Of At1 Receptor For Angiotensin Ii
The mechanism behind the hypotensive effect of antagonists of AT1 receptor for angiotensin II is associated with the binding of the drug to AT1 receptor for angiotensin II in adrenal glands and smooth muscles of the blood vessels. This prevents the vasoconstrictive effect of angiotensin II and aldosterone release. Of note, the antagonists of AT1 receptor for angiotensin II do not modulate the metabolism of bradykinin, noradrenalin and substance P .
Data from the Polish ministerial database suggest that the antagonists of AT1 receptor for angiotensin II do not interact with anti-parkinsonian agents, apart from an insignificant interaction between sartans and bromocriptine or cabergoline, which is associated with the enhancement of their hypotensive effect . In contrast, Lexicomp® and Stockleys® include significant interactions between MAO-B inhibitors and antagonists of AT1 receptor.
Table presents the interactions between the antagonists of AT1 receptor for angiotensin II most frequently used in the treatment of arterial hypertension and anti-parkinsonian agents, stratified according to their significance.
Cholinesterase Inhibitors Widely Used To Treat Dementia
Cholinesterase inhibitors, widely used to treat dementia, may cause worsened parkinsonism, primarily increased tremor . Large double-blind trials of rivastigmine, a cholinesterase-inhibiting drug, in both dementia with Lewy bodies and Parkinson disease dementia have demonstrated that rivastigmine is well tolerated without significant worsening of motor function overall, although tremor may increase . The other cholinesterase inhibitors have been less well studied but appear to have similar benefits and side effects.
Read Also: Parkinson’s Disease Hallucinations Commercial
Antipsychotic Drugs Called Neuroleptics
Drug-induced parkinsonism is due primarily to drugs that block dopamine receptors, particularly the D2 receptors . These drugs are most often the antipsychotic drugs, called neuroleptics, such as haloperidol, chlorpromazine, and trifluoperazine, but include metoclopramide, a gastrointestinal motility enhancer, and the antiemetics prochlorperazine and droperidol. In addition, medications that block synthesis of dopamine, such as alpha-methyl para-tyrosine and alpha-methyl dopa or deplete dopamine also induce parkinsonism. In these cases the pathophysiology is presumably due to diminished dopamine receptor stimulation, resulting in a pharmacologic state closely resembling Parkinson disease.
However, the atypical antipsychotics also block D2 receptors. Yet there is no apparent correlation between the degree of this blockade and the risk for inducing parkinsonism. The explanation for this is uncertain. One current hypothesis is the fast off theory, postulating that the duration of the D2 blockade, rather than the percentage of receptors blocked, determines the likelihood of parkinsonism . A competing theory is that the ratio of 5 HT-2a receptor blockade versus the dopamine D2 receptor blockade is critical because of the interplay between the serotonin and dopamine systems in the brain. An older theory relating extrapyramidal side effects to anticholinergic activity is considered untenable because the concomitant use of anticholinergics does not eliminate the problem.
Specific Warning About Mucuna
We assume that all contraindications, interactions, precautions and side effects that we know about synthetic levodopa should be considered when taking levodopa from mucuna.
Specific contraindications include thinning of the blood , and care should be taken with antiplatelet and anti-inflammatory drugs because mucuna increases clotting time.
Mucuna should not merge with anticoagulants or with antiplatelet drugs such as clopidogrel. Caution should be exercised and the additive effect should be taken into account if it is associated with acetylsalicylic and NSAIDs .
We should also be careful with antidiabetic medicines: mucuna lows glycemic index, and thus is to be considered a potential additive effect. Other interactions are possible, so always consult your regular doctor.
On the one hand, it can be argued that mucuna has been used for many centuries in India and has been available for several years online without a prescription, and yet serious problems have not been revealed. But that is just an observation.
Regarding Sinemet and Madopar, we have thousands of controlled studies, while publications on mucuna are still scarce. One must therefore use greater caution when choosing mucuna. While the future appears to be positive, we need the confirmation of more scientific studies.
Also Check: Can You Be Tested For Parkinson’s
Mechanism Of Action Of Available Drugs
The major classes of drugs currently available for the treatment of idiopathic Parkinson’s disease are shown in Table 1. Many aim to increase dopamine in the brain, by increasing its production or altering its metabolism .
|
Table 1 |
Drugs with alter metabolism in boxed red italics
Levodopa
Levodopa is absorbed from the small intestine and transported into the brain where it is converted to dopamine. Levodopa has a short plasma half-life of about one hour. Early in Parkinson’s disease, levodopa has a long duration of action which is independent of plasma concentration, but as the disease progresses, the duration of the effect reduces. The short-duration effect is strongly linked to plasma concentration and lasts, at most, hours.
Slow-release preparations are gradually absorbed, resulting in more sustained plasma concentrations. They have reduced bioavailability higher doses are required to match the benefit of an equivalent strength of a standard preparation. Rapid release preparations are taken in liquid form to enhance passage through the stomach and absorption from the small intestine.
Dopamine agonists
Apomorphine is a potent emetic so patients must be pre-treated with domperidone 20 mg three times daily orally for at least 48 hours before the first injection. Domperidone should be continued for at least a few weeks once regular intermittent treatment has commenced. The dose can then be tapered slowly as tolerance to the emetic effects of apomorphine usually develops.