What Are The Surgical Treatments For Parkinsons Disease
Most patients with Parkinsons disease can maintain a good quality of life with medications. However, as the disease worsens, medications may no longer be effective in some patients. In these patients, the effectiveness of medications becomes unpredictable reducing symptoms during on periods and no longer controlling symptoms during off periods, which usually occur when the medication is wearing off and just before the next dose is to be taken. Sometimes these variations can be managed with changes in medications. However, sometimes they cant. Based on the type and severity of your symptoms, the failure of adjustments in your medications, the decline in your quality of life and your overall health, your doctor may discuss some of the available surgical options.
Dont Miss: Adaptive Silverware For Parkinsons
Whats Different About Young
The age of diagnosis matters for a variety of reasons, from probable causes of early cases to symptoms and treatment:
- Genetics. As with any case of Parkinsons disease, the exact cause is usually unknown. That said, The young-onset cases of Parkinsons disease are, on average, a bit more likely to be familial or genetic, says Gregory Pontone, M.D., director of the Johns Hopkins Movement Disorders Psychiatry Clinic.
- Symptoms. In many patients with YOPD, dystonia is an early symptom. People with YOPD also report more dyskinesia . They also tend to exhibit cognitive problems, such as dementia and memory issues, less frequently.
- Progression. Patients with young-onset Parkinsons appear to have a slower progression of the disease over time, says Pontone. They tend to have a milder course, staying functional and cognitively intact for much longer.
- Treatment. Most patients with Parkinsons take the medication levodopa. However, other drugs, such as MAO-B inhibitors, anticholinergics, amantadine, and dopamine receptor agonists, may be used before levodopa.
Financial Disclosures For The Previous 12months
N.P.V. has stock ownership in Rosetta Therapeutics and has received grants from the Michael J. Fox Foundation for Parkinson’s disease and philanthropic funding from the Blidner Family Foundation. G.G.K. has served as an advisor for Biogen, and has received grants from Edmond J. Safra Philanthropic Foundation, Rossy Philanthropic Foundation, the Michael J. Fox Foundation, and Parkinson Society Canada. A.E.L. has served as an advisor for Abbvie, Acorda, AFFiRis, Biogen, Denali, Janssen, Intracellular, Kallyope, Lilly, Lundbeck, Paladin, Retrophin, Roche, SPARC, Theravance, and Corticobasal Degeneration Solutions received honoraria from Sun Pharma, Medichem, Medtronic, AbbVie, and Sunovion and received grants from Brain Canada, Canadian Institutes of Health Research, Corticobasal Degeneration Solutions, Edmond J. Safra Philanthropic Foundation, Rossy Philanthropic Foundation, the Michael J. Fox Foundation, the Ontario Brain Institute, Parkinson Foundation, Parkinson Society Canada, and W. Garfield Weston Foundation.
Also Check: Pacemaker In Brain For Parkinson’s
A Recent Study Reveals How Parkinsons Spreads Throughout The Brain
According to a recent study led by Weill Cornell Medicine scientists, aggregates of the protein alpha-synuclein spread in the brains of Parkinsons disease patients through a cellular waste-ejection process.
During the process, known as lysosomal exocytosis, neurons release protein waste that cannot be broken down and recycled. The revelation, which was recently published in the journal Nature Communications, might solve one of Parkinsons diseases mysteries and lead to new techniques for treating or preventing the neurological disease.
Our results also suggest that lysosomal exocytosis could be a general mechanism for the disposal of aggregated and degradation-resistant proteins from neuronsin normal, healthy circumstances and in neurodegenerative diseases, said study senior author Dr. Manu Sharma, an assistant professor of neuroscience in the Feil Family Brain and Mind Research Institute and Appel Alzheimers Disease Research Institute at Weill Cornell Medicine.
Cultures at 14 and 49 days in vitro. Credit: Sharma Lab
In the study, Dr. Sharma and his team, including co-first author Ying Xue Xie, a doctoral candidate in the Weill Cornell Graduate School of Medical Sciences, showed with detailed studies of Parkinsons mouse models that alpha-synuclein aggregatescapable of spreading and causing neurodegenerationoriginated within neurons. These aggregates, they found, then accumulate within capsule-like waste bins in cells called lysosomes.
Google Cofounder Sergey Brin Reportedly Has Quietly Donated More Than $1 Billion Toward Parkinsons Disease
That makes him one of just a few people alive today to have donated more than $1 billion toward a specific disease.
American business magnate, computer scientist, and internet entrepreneur, who co-founded Google with Larry Page. Brin was the president of Google’s parent company, Alphabet Inc., until stepping down from the role on December 3, 2019, Sergey Brin disclosed in a rare interview that he has a much higher chance of getting Parkinsons disease than the general population, due to a genetic mutation. Since then, without fanfare, Brinnow the worlds 12th-richest person, worth $78 billion, per Forbeshas quietly become the largest individual donor to Parkinsons research, with a heavy emphasis on advancing basic science.
RELATED:
According to Forbes, Brin has funneled $1.1 billion to fund research of the disease, according to people familiar with his philanthropic giving. That makes him one of just a few people alive today to have donated more than $1 billion toward a specific disease.
Despite these advances, many key facts about Parkinsons are still a mystery. We dont know what causes the disease, we dont know why it progresses, we dont know how to measure it, and we dont know how to stop it, laments Dr. James Beck, the chief scientific officer of the Parkinsons Foundation. We dont understand the biology of the disease. Without such knowledge, its far more difficult to develop drugs that will meaningfully slow or cure it.
Recommended Reading: Parkinson’s Wearing Off Symptoms
The Future: Parkinsons Clinical Trials
Researchers are continuously working on ways to slow the progression of Parkinsons disease, restore lost functioning, and help prevent the disease from developing in the first place. You can find out if you or a loved one is right for one of hundreds of clinical trials for Parkinsons Disease at the Fox Trial Finder.
Read Also: Does Sam Waterston Have Parkinsons
Discovery Of Effective Treatments
In 1958, Carlsson found that levodopa , a treatment still widely used today, was effective in treating the symptoms of Parkinsonism. His work demonstrated that the motor symptoms in Parkinsons disease are related to a decrease in dopamine in the striatum following the degeneration of dopaminergic neurons of the nigrostriatal pathway. This discovery rapidly advanced hypotheses surrounding the role of dopamine loss in the pathogenesis of Parkinsons disease.
Read Also: Brain Chip For Parkinson’s Disease
Michael J Fox Broke His Arm And Lost His Optimism
It was the summer of 2018 and the year had already been rough for Michael J. Fox. Now, in addition to managing a progressive disease, he was recovering from spinal surgery and starving for a little time to himself, according to the CBC. But no sooner did he get his wish when he slipped on a tile in his kitchen and fell on his arm, shattering it. Alone and unable to get help, Fox remembered at that moment, he was tired of his when life hands you lemons, make lemonade attitude about his condition. That was the point where I went Im out of the freakin lemonade business,’ he told the CBC. I cant put a shiny face on this. This sucks, and who am I to tell people to be optimistic?’
Fractures are not uncommon among people with Parkinsons. According to the Parkinsons Foundation, the disease can cause changes to a persons skeleton, including lower bone density. In fact, if a person with Parkinsons does less walking and other exercises in which their skeleton needs to support their weight, they run the risk of weaker bones, increasing their chances of bone fractures if they fall. In Foxs case, as he detailed to the CBC. his arm was so badly broken that it needed to be rebuilt. And what about his optimism? That too would need some rebuilding.
Also Check: Parkinsons And Marriage Breakdown
What Are The Different Stages Of Parkinsons Disease
Each person with Parkinsons disease experiences symptoms in in their own unique way. Not everyone experiences all symptoms of Parkinsons disease. You may not experience symptoms in the same order as others. Some people may have mild symptoms others may have intense symptoms. How quickly symptoms worsen also varies from individual to individual and is difficult to impossible to predict at the outset.
In general, the disease progresses from early stage to mid-stage to mid-late-stage to advanced stage. This is what typically occurs during each of these stages:
Early stage
Early symptoms of Parkinsons disease are usually mild and typically occur slowly and do not interfere with daily activities. Sometimes early symptoms are not easy to detect or you may think early symptoms are simply normal signs of aging. You may have fatigue or a general sense of uneasiness. You may feel a slight tremor or have difficulty standing.
Often, a family member or friend notices some of the subtle signs before you do. They may notice things like body stiffness or lack of normal movement slow or small handwriting, lack of expression in your face, or difficulty getting out of a chair.
Mid stage
Mid-late stage
Standing and walking are becoming more difficult and may require assistance with a walker. You may need full time help to continue to live at home.
Advanced stage
Recommended Reading: Are You Allowed To Drive If You Have Parkinson’s
Diagnosis And Clinical Assessment Devices
The use of new technology-based tools allows quantitative assessment of the motor function of PD patients. Sensors, video-assessment methods or mobile phone applications are some of the techniques that improve the sensitivity, accuracy and reproducibility of the evaluation of PD patients . Portable devices that include inertial measurement units measure the orientation, amplitude and frequency of movement, as well as the speed of the part of the body where they are located. IMUs are usually made up of accelerometers and gyroscopes, and occasionally magnetometers. IMUs situated in different parts of the patients body make a precise record of tremor, bradykinesia, dyskinesias and even gait patterns . On the other hand, continual monitoring of the motor status in the domestic environment is also possible by using these technology-based tools . These new technology-based systems open up an unexpected range of specific and real-time data, thereby resulting in the prospect of better diagnostic accuracy, more sensitive monitoring of the motor and non-motor symptoms, and more precise adjustments of medical therapies. However, their use is limited in routine clinical practice due to the heterogeneity of the studies, which limit the extrapolation of results, and the high cost of the devices .
Read Also: Weighted Silverware
Thanks For Signing Up
We are proud to have you as a part of our community. To ensure you receive the latest Parkinsons news, research updates and more, please check your email for a message from us. If you do not see our email, it may be in your spam folder. Just mark as not spam and you should receive our emails as expected.
Also Check: Does Parkinson’s Affect Your Speech
A Little Bit Of History
A new important breakthrough took place in 1983 when Langston and colleagues reported a group of drug users who developed acute parkinsonism after MPTP exposure . These patients developed an acute syndrome indistinguishable from PD. This is due because the MPTP metabolite, MPP+, destroys the dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra after a series of alterations in the mitochondrial matrix and the electron transport chain. The SNc of Parkinson patients was also described as exhibiting a marked decrease in complex I activity . The fact that some PD patients have certain polymorphisms in genes that express subunits of complex I suggests that this could be a vulnerability factor in PD . New models based on MPTP intoxication allowed researchers to ascertain PD hallmarks both in vitro and in vivo . Due to the achievements of pharmacological DA treatments, search of cell-based DA replacement approaches were initiated with largely disappointing results . From the surgical and therapeutic point of view, discrete lesions of the BG improved parkinsonism . A monkey model of PD showed motor signs improvement as a result of the chemical destruction of the subthalamic nucleus , with evidence of reversal of experimental parkinsonism by STN lesions. This same year deep brain stimulation of the STN became effective for PD treatment .
Figure 1. Breakthroughs in Parkinsons disease history.
Changes To Your Walking
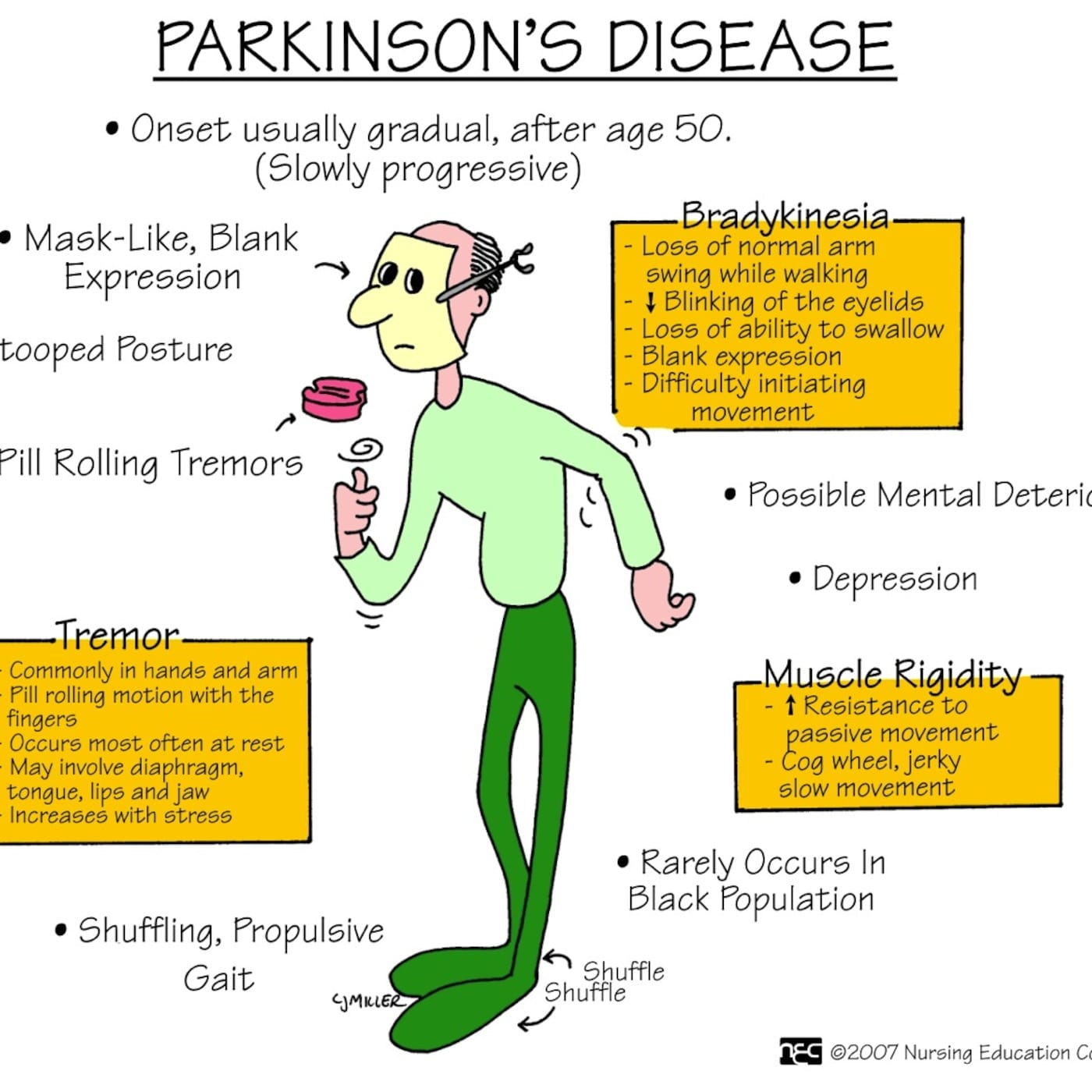
- Not swinging your arms while walking
- Multiple steps required to turn around when walking, possibly tripping up the feet
- One foot turning inward or outward a bit, causing tripping
- One arm could also be bent inward
The turning of the arm or foot, called dystonia, is often one of the first signs we see, so were always on the lookout for it, Dr. Joseph says.
Don’t Miss: Difference Between Tremors And Parkinson’s
Scientists Take The Next Step In Unraveling The Relationship The Protein Plays In The Disease
minute read
An international team of scientists is advancing research in Parkinson’s disease. Today, the team released a new study outlining research that could potentially change the future of treating patients.
Currently, there are no disease-modifying therapies for Parkinsons disease that can change the progression of the disease. An international team of scientists led by faculty at the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus is hoping to change that.
Today, the team published new research in the journal Brain that takes scientists one step closer to understanding -synuclein , a key protein that they found links inflammation and Parkinsons disease.
The protein Syn is predominantly expressed in neurons and is associated with neurodegenerative diseases, such as Parkinsons disease and dementia with Lewy bodies. This new study identifies the novel mechanism that links interferon activation and Syn function in neurons as a potential trigger for developing Parkinsons disease.
What Would Parkinson The Social Reformer Think
Parkinson was a social reformer writing under the nom de plume Old Herbit he campaigned for the rights of lunatics, children, and older people. Age is the strongest risk factor for PD. Worldwide prevalence of PD per 100,000 is 41 at 4049 years compared to 428 at 6069 years and 1,903 in those older than 80 years . 200 Years ago, when Parkinson wrote the Shaking Palsy, average life expectancy at birth in the UK was less than 45 years. For a women born in the UK 2010, this is now 82 years. In recent years life expectancy has also begun to increase in the developing world resulting in an increased burden of chronic disease. Traditionally healthcare systems in the developing world have been focused on managing communicable disease in younger populations. As their populations age the need to manage chronic disease in an ageing population will present an increasing challenge. Dorsey et al. have projected that the number of individuals living with PD will more than double between 2005 and 2030, and that the population of PD patients is set to become increasingly concentrated in the developing world .
Also Check: Parkinson’s Disease And Boxing Therapy
What Is The Outlook For Persons With Parkinsons Disease
Although there is no cure or absolute evidence of ways to prevent Parkinsons disease, scientists are working hard to learn more about the disease and find innovative ways to better manage it, prevent it from progressing and ultimately curing it.
Currently, you and your healthcare teams efforts are focused on medical management of your symptoms along with general health and lifestyle improvement recommendations . By identifying individual symptoms and adjusting the course of action based on changes in symptoms, most people with Parkinsons disease can live fulfilling lives.
The future is hopeful. Some of the research underway includes:
- Using stem cells to produce new neurons, which would produce dopamine.
- Producing a dopamine-producing enzyme that is delivered to a gene in the brain that controls movement.
- Using a naturally occurring human protein glial cell-line derived neurotrophic factor, GDNF to protect dopamine-releasing nerve cells.
Many other investigations are underway too. Much has been learned, much progress has been made and additional discoveries are likely to come.
Patient And Public Involvement
The OPDC Discovery Cohort is designed by and for patients and is closely linked with the Parkinsons UK local support group. Patient representatives are also involved in the funding/renewal and strategic oversight processes, and sit on the data access panel with casting votes. Results are disseminated to the study participants through annual newsletters, the OPDC website, and series of talks at participants open days.
Recommended Reading: Parkinson’s Disease Masked Face
Researchers Polled 4324 People With Parkinsons Disease
Researchers polled 4,324 people with Parkinsons disease and significant gait deficits for the study. Problems including unbalance, stumbling, falling, staggering, and freezing are among them. 35% of the participants said their walking issues made it difficult for them to do their normal daily activities, and 52% said they had fallen in the previous year.
The survey clarified the seven basic compensation strategy groups. Internal cueing, such as walking to a count in your head. External cueing, such as walking in rhythm to a metronome. Changing the balance requirement, such as making wider turns. Altering mental state, such as relaxation techniques. Action observation and motor imagery, such as watching another person walk. Adapting a new walking pattern, such as jumping or walking backwards and other techniques. Each category was described and participants were asked if they were familiar with it, and if so, how it worked for them in various situations.
Researchers discovered that people with Parkinsons disease frequently employ walking compensatory measures, but are unaware of all seven. For instance, 17% of people had never heard of any of these tactics, and 23% had never attempted any of them. Only 4% of respondents were aware of all compensation strategy categories.
Discovery Illuminates How Parkinsons Disease Spreads In The Brain
A person with Parkinson’s disease visiting the doctor. Credit: Shutterstock
Aggregates of the protein alpha-synuclein spread in the brains of people with Parkinsons disease through a cellular waste-ejection process, suggests a new study led by Weill Cornell Medicine researchers.
During the process, called lysosomal exocytosis, neurons eject protein waste they cannot break down and recycle. The discovery, published Aug. 22 in Nature Communications, could resolve one of the mysteries of Parkinsons disease and lead to new strategies for treating or preventing the neurological disorder.
Our results also suggest that lysosomal exocytosis could be a general mechanism for the disposal of aggregated and degradation-resistant proteins from neuronsin normal, healthy circumstances and in neurodegenerative diseases, said study senior author Dr. Manu Sharma, an assistant professor of neuroscience in the Feil Family Brain and Mind Research Institute and Appel Alzheimers Disease Research Institute at Weill Cornell Medicine.
In the study, Dr. Sharma and his team, including co-first author Ying Xue Xie, a doctoral candidate in the Weill Cornell Graduate School of Medical Sciences, showed with detailed studies of Parkinsons mouse models that alpha synuclein aggregatescapable of spreading and causing neurodegenerationoriginated within neurons. These aggregates, they found, then accumulate within capsule-like waste bins in cells called lysosomes.
Read Also: Dating Someone With Parkinson’s Disease