What Are The Early Warning Signs Of Parkinson’s Disease
Parkinsons warning signs can be motor symptoms like slow movements, tremors or stiffness. However, they can also be non-motor symptoms. Many of the possible non-motor symptoms can appear years or even decades ahead of motor symptoms. However, non-motor symptoms can also be vague, making it difficult to connect them to Parkinson’s disease.
Non-motor symptoms that might be early warning signs include:
Parkinsons Disease For Primary Care With Dr Albert Hung
December 5, 2022 By Matthew Watto, MD
Master the ins-and-outs of Parkinsons Disease! Were joined by Dr. Albert Hung, who teaches us pearls for the initial history and physical exam in a patient with undiagnosed Parkinsons, a framework for management of early and advanced motor symptoms, tips for treating autonomic symptoms and cognitive / psychiatric features, and more.
Claim free CME for this episode at curbsiders.vcuhealth.org!
- Producer, Writer, Show Notes, and Infographic: Malini Gandhi
- Cover Art: Kate Grant
- Hosts: Matthew Watto MD, FACP Paul Williams MD, FACP
- Reviewer: Emi Okamoto MD
- Showrunner: Matthew Watto MD, FACP Paul Williams MD, FACP
- Technical Production: PodPaste
Visit betterhelp.com/curb to save 10% off your first month.
Is Surgery An Option
If medicine doesnât work well enough, your doctor may suggest deep brain stimulation . In DBS, your doctor implants electrodes deep in the brain. A device connected to them delivers electrical pulses. Those pulses can help control the tremors caused by Parkinson’s.
In the past, doctors sometimes used other operations to damage the brain in ways to help with movement symptoms. But they rarely use those surgeries now.
Recommended Reading: What Are The Side Effects Of Parkinson’s Disease
How Is Parkinson’s Disease Diagnosed
Diagnosis is difficult at every stage of the disease, but particularly in the early stages. No single test can provide a diagnosis. A diagnosis will likely involve physical and neurological examinations, conducted over time to assess changes in reflexes, coordination, muscle strength, and mental function. Your doctor might also see how you respond to medicine.
You may need to have brain imaging tests to rule out other conditions that might be causing your symptoms. Such tests could include MRI and CT scans and possibly some other types of scans. Blood tests may also be done to exclude other illnesses.
Over The Counter & Complementary Therapies
People with Parkinsons who seek relief from their symptoms may decide to explore complementary therapies, which can support or complement traditional medicine. While there are many kinds of complementary medicine, this section focuses on herbs, vitamins and supplements.
Page reviewed by Dr. Chauncey Spears, Clinical Assistant Professor and Dr. Amelia Heston, Movement Disorders Fellow at the University of Michigan.
Read Also: What Causes Death In Parkinson’s
What Are The Symptoms Of Parkinson’s Disease How Is Parkinson’s Disease Diagnosed
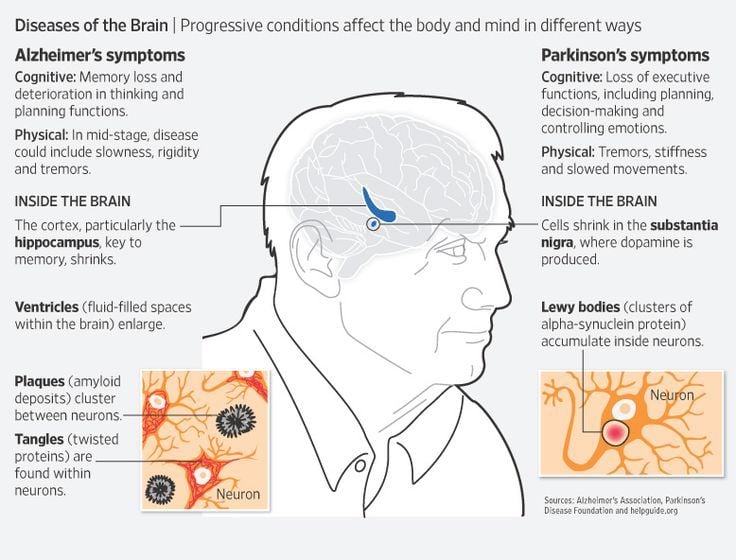
People with Parkinsons disease suffer from motor symptoms as well as non-motor symptoms.
Motor symptoms include intermittent tremors, slow and rigid movements. Non-motor symptoms include loss of smell, pain and even dementia.
In the initial stages of Parkinsons disease a person may experience symptoms such as:
- Slight rigidity in the arms and legs
- unable to change facial expressions according to emotions spontaneously
- Slight back pain due to which the posture of the person may be slightly stooped
- Sudden stiffness in the body at times
- Tremor on one arm on one side of the body
- The symptoms may be experienced only on one side of the body
- Handwriting may get messier and smaller
In the intermediate stage of Parkinsons disease a person may experience symptoms such as:
- Slower movements and therefore takes longer to do the daily work such as combing, dressing etc
- Loss of balance
- Sudden falls due to frequent loss of balance
- Slurring of speech
- Inability to speak loudly and clearly
- Erratic footwork, as the person is unable to start walking immediately after getting up as if the feet are stuck to the ground, or change direction quickly while walking
- Taking smaller steps than normal while walking
- Trouble swallowing food
- May require aids while walking such as a walker
In the advanced stage of Parkinsons disease the symptoms include:
Changes In Cognition And Parkinsons Disease
Some people with Parkinsons may experience changes in their cognitive function, including problems with memory, attention, and the ability to plan and accomplish tasks. Stress, depression, and some medications may also contribute to these changes in cognition.
Over time, as the disease progresses, some people may develop dementia and be diagnosed with Parkinsons dementia, a type of Lewy body dementia. People with Parkinsons dementia may have severe memory and thinking problems that affect daily living.
Talk with your doctor if you or a loved one is diagnosed with Parkinsons disease and is experiencing problems with thinking or memory.
Recommended Reading: What Causes Pain In Parkinson’s Patients
What Can I Expect If I Have This Condition
Parkinsons disease is a degenerative condition, meaning the effects on your brain get worse over time. However, this condition usually takes time to get worse. Most people have a normal life span with this condition.
You’ll need little to no help in the earlier stages and can keep living independently. As the effects worsen, youll need medication to limit how the symptoms affect you. Most medications, especially levodopa, are moderately or even very effective once your provider finds the minimum dose you need to treat your symptoms.
Most of the effects and symptoms are manageable with treatment, but the treatments become less effective and more complicated over time. Living independently will also become more and more difficult as the disease worsens.
How long does Parkinsons disease last?
Parkinsons disease isnt curable, which means its a permanent, life-long condition.
Whats the outlook for Parkinsons disease?
Parkinson’s disease isn’t fatal, but the symptoms and effects are often contributing factors to death. The average life expectancy for Parkinson’s disease in 1967 was a little under 10 years. Since then, the average life expectancy has increased by about 55%, rising to more than 14.5 years. That, combined with the fact that Parkinson’s diagnosis is much more likely after age 60, means this condition doesn’t often affect your life expectancy by more than a few years .
Parkinson’s Disease And Movement Disorders Center
Our center provides compassionate and timely treatment to patients with movement disorders, such as dystonia, ataxia, essential tremor and similar conditions. But our mission goes beyond patient care excellence. By offering educational events and support groups, we empower patients and caregivers to become better partners in their health.
Read Also: Shadow Boxing For Parkinson’s
What Are The Causes Of Parkinson’s Disease
The causes of Parkinsons disease include:
- Genetics and family history
- Frequent exposure to pesticides such as insecticides, herbicides, and fungicides
- Lewy bodies that are abnormal clumps of proteins found in the brain stem of people with Parkinsons disease which affect brain functions
- Loss of dopamine production in the brain when cells that produce dopamine are damaged
New Diagnostic Standards For Parkinsons
Until recently, the gold-standard checklist for diagnosis came from the U.K.s Parkinsons Disease Society Brain Bank. It was a checklist that doctors followed to determine if the symptoms they saw fit the disease. But thats now considered outdated. Recently, new criteria from the International Parkinson and Movement Disorder Society have come into use. This list reflects the most current understanding of the condition. It allows doctors to reach a more accurate diagnosis so patients can begin treatment at earlier stages.
Also Check: Parkinson’s And Marriage Breakdown
Parkinson’s Disease: Diagnosis And Treatments
01 April, 2021
Parkinsons disease is the second most common neurodegenerative disease among people over 65. In fact, between two to three percent of this particular population suffers from the illness. Consequently, Parkinsons presents a challenge for researchers. Its clinical diagnosis is based on the presence of bradykinesia and other motor symptoms.
However, the disease also causes other symptoms. Its also associated with a number of non-motor symptoms. Naturally, these increase the sufferers overall level of disability. Therefore, research tends to focus on early detection of Parkinsons.
Recent research regarding diagnostic biomarkers has used neuroimaging techniques for the early detection of this disease. Generally, the treatment of Parkinsons is based on the pharmacological substitution of striatum dopamine.
Parkinsons disease is clinically defined by the presence of bradykinesia . In addition, at least one other cardinal motor symptom will be present. For example, stiffness or tremor at rest.
However, as well as cardinal motor symptoms, most Parkinsons patients also experience non-motor symptoms, which adds to their suffering.
The most commonly used scale for monitoring motor disability related to Parkinsons disease is the Unified Parkinsons Disease Rating Scale .
Diagnosis Of Parkinsons Disease
There are currently no blood or laboratory tests to diagnose non-genetic cases of Parkinsons. Doctors usually diagnose the disease by taking a persons medical history and performing a neurological examination. If symptoms improve after starting to take medication, its another indicator that the person has Parkinsons.
A number of disorders can cause symptoms similar to those of Parkinsons disease. People with Parkinsons-like symptoms that result from other causes, such as multiple system atrophy and dementia with Lewy bodies, are sometimes said to have parkinsonism. While these disorders initially may be misdiagnosed as Parkinsons, certain medical tests, as well as response to drug treatment, may help to better evaluate the cause. Many other diseases have similar features but require different treatments, so it is important to get an accurate diagnosis as soon as possible.
Don’t Miss: Boxing And Parkinson’s Disease
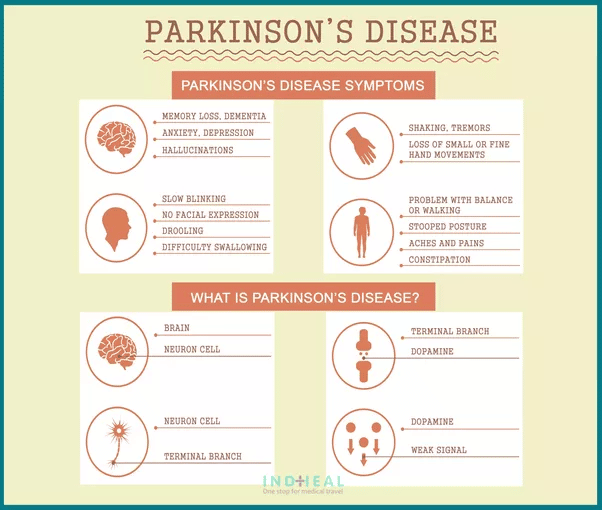
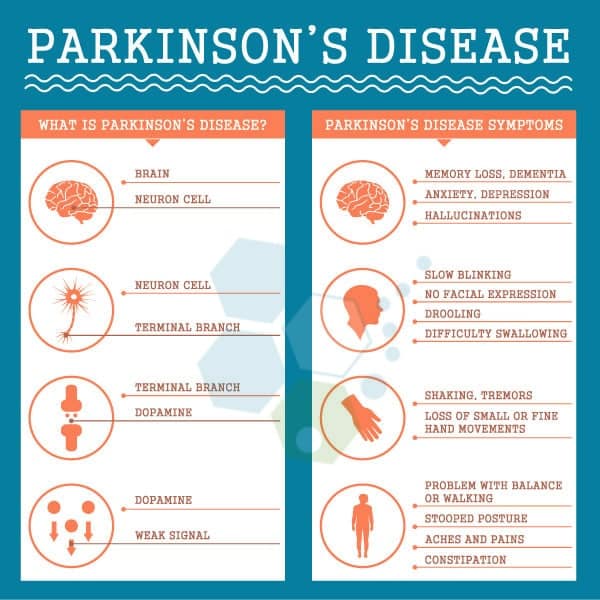
Symptoms Of Parkinsons Disease
Parkinsons has four main symptoms:
- Tremor in hands, arms, legs, jaw, or head
- Muscle stiffness, where muscle remains contracted for a long time
- Slowness of movement
- Impaired balance and coordination, sometimes leading to falls
Other symptoms may include:
The symptoms of Parkinsons and the rate of progression differ among individuals. Early symptoms of this disease are subtle and occur gradually. For example, people may feel mild tremors or have difficulty getting out of a chair. They may notice that they speak too softly, or that their handwriting is slow and looks cramped or small. Friends or family members may be the first to notice changes in someone with early Parkinsons. They may see that the persons face lacks expression and animation, or that the person does not move an arm or leg normally.
People with Parkinson’s disease often develop a parkinsonian gait that includes a tendency to lean forward take small, quick steps and reduce swinging their arms. They also may have trouble initiating or continuing movement.
Symptoms often begin on one side of the body or even in one limb on one side of the body. As the disease progresses, it eventually affects both sides. However, the symptoms may still be more severe on one side than on the other.
Determining Diagnosis Through Response To Parkinsons Medication
If a persons symptoms and neurologic examination are only suggestive of Parkinsons disease or if the diagnosis is otherwise in doubt, the physician may, nevertheless, prescribe a medication intended for Parkinsons disease to provide additional information. In the case of idiopathic Parkinsons, there is typically a positive, predictable response to Parkinsons disease medication in the case of some related Parkinsonian syndromes, the response to medication may not be particularly robust, or it may be absent entirely.
Unfortunately, there are no standard biological tests for the disease, such as a blood test. However, researchers are actively trying to find biomarkers in blood and other bodily fluids that could help confirm the diagnosis.
Also Check: Mri Brain Scan For Parkinson’s Disease
Basics Of Parkinsons Disease
Parkinsons disease , or paralysis agitans, is a common neurodegenerative condition, which typically develops between the ages of 55 and 65 years. This disease was first named and described by James Parkinson in 1817. The progression of this disease is gradual and prolonged. It has a plausible familial incidence, although the estimates of these occurrences are low and usually sporadic. This disease is organized into two classifications: genetic and sporadic. Genetic PD follows Mendelian inheritance. Sporadic PD, which accounts for about 90% of all Parkinsons cases, is a more complex category in which the pathogenic mechanisms that underlie it are not yet fully understood. Nonetheless, it is known that the byzantine interactions of genetic and environmental influences play roles in the determination of sporadic PD. Several subtypes of PD exist. Each has its own set of causative factors and susceptibilities, pathology, and treatment courses. General risk factors, symptoms, and pathology will be discussed first, before addressing some of the subtypes.
Parkinsons Foundation Center Of Excellence
Mount Sinai Beth Israel is designated as a Center of Excellence by the Parkinsons Foundation, specialized team of neurologists, movement disorder specialists, physical and occupational therapists, mental health professionals and others who are up-to-date on the latest Parkinson’s disease medications, therapies, and research to provide the best care.
Read Also: Parkinson’s Disease And Urinary Incontinence Treatment
How Parkinsons Disease Is Diagnosed
Parkinsons disease is usually diagnosed clinically, meaning that a physician looks for the presence or absence of the possible symptoms of Parkinsons disease by interviewing the patient and performing a detailed neurologic examination.
While there is presently no definitive test for Parkinsons, it can often be identified by a general neurologist, who is trained to diagnose and treat neurologic disorders. To avoid misdiagnosis, consultation with a movement disorder specialist is recommended. A movement disorder specialist is a physician who has undergone additional, subspecialty training in the diagnosis and treatment of movement disorders, such as Parkinsons, after training in general neurology.
What to expect during your visit with a physician
Typically, a trained physician will only consider the diagnosis of Parkinsons disease if the person being examined has at least two of the core motor symptoms of Parkinsons, including tremor, the characteristic bradykinesia , or rigidity. At the end of your visit, the physician should discuss with you why you may or may not have Parkinsons disease and the level of certainty about the diagnosis. This determination is based on your medical history and examination at this visit.
Brain imaging and other tools to aid diagnosis of Parkinsons
How Soon After Treatment Will I Feel Better And How Long Will It Take To Recover
The time it takes to recover and see the effects of Parkinson’s disease treatments depends strongly on the type of treatments, the severity of the condition and other factors. Your healthcare provider is the best person to offer more information about what you can expect from treatment. The information they give you can consider any unique factors that might affect what you experience.
Also Check: Does David Brooks Have Parkinson’s
Proteins Tied To Parkinsons And Alzheimers Jointly Involved In Cognitive Change
A significantly lower alpha-synuclein to pTau181 ratio was seen in Parkinsons patients than in controls, and among patients with cognitive impairment relative to those without such problems.
This ratio is a metric that merits further exploration in Parkinsons disease, with the potential for biomarker use similar to the protein ratio of in Alzheimers disease, the researchers wrote.
The amount of EVs containing the beta-amyloid protein did not differ among any of the groups.
These novel findings support the view that aggregating proteins typically associated with Parkinsons disease and Alzheimers disease are jointly involved in the of cognitive impairment in Parkinsons disease, the team wrote.
Further, diminished insulin signaling propagation reflected in lower availability seems to characterize cognitive impairment in Parkinsons disease and may broadly contribute to disease progression and severity, the researchers added.
Elevated levels of alpha-synuclein-containing EVs were significantly associated with shorter disease duration in Parkinsons patients. Fewer EVs with alpha-synuclein and IRS-1 also linked to more severe motor disease as measured by MDS-UPDRS part 3, as did higher levels of EVs carrying phosphorylated tau.
No EV biomarkers were linked to the daily levodopa equivalent dose, the combined total of Parkinsons medications.
Treatment Of Advanced Motor Symptoms
In more advanced Parkinsons disease, patients will often experience a shorter window of time in which levodopa / carbidopa is effective, and tend to develop on / off fluctuations in which they experience wearing off of the medication towards the end of the dose . This is because levodopa has a short half life in the blood while in earlier stages of Parkinsons disease the body can accommodate this, in later stages the accommodation is less robust, and wearing off will occur. Additionally, when patients do take enough medication to achieve an on state, they may exhibit too much movement, known as levodopa-induced dyskinesias , which can include writhing, swaying, and bobbing. Thus, the challenge in managing motor symptoms in advanced Parkinsons disease is trying to strike a balance between wearing off and levodopa-induced dyskinesias When patients reach this point, a movement disorder specialist should be involved in management.
In thinking about management of advanced motor symptoms, Dr. Hung notes that thinking about pharmacokinetics is key: essentially, considering how to stretch out the duration of action of levodopa to prevent so many highs and lows. There are several strategies in treating motor symptoms in advanced Parkinsons disease:
Read Also: Vacations For Parkinson’s Patients
What Doctors Look For When Diagnosing Parkinsons
Certain physical signs and symptoms noticed by the patient or his or her loved ones are usually what prompt a person to see the doctor. These are the symptoms most often noticed by patients or their families:
-
Shaking or tremor: Called resting tremor, a trembling of a hand or foot that happens when the patient is at rest and typically stops when he or she is active or moving
-
Bradykinesia: Slowness of movement in the limbs, face, walking or overall body
-
Rigidity: Stiffness in the arms, legs or trunk
-
Posture instability: Trouble with balance and possible falls
Once the patient is at the doctors office, the physician:
-
Takes a medical history and does a physical examination.
-
Asks about current and past medications. Some medications may cause symptoms that mimic Parkinsons disease.
-
Performs a neurological examination, testing agility, muscle tone, gait and balance.