What To Do If Your Senior Has Parkinsons
If you notice Parkinsons-like symptoms in your older adult, the first thing to do is talk with their doctor. The doctor should review their complete medication history and you should let them know about any other symptoms or changes.
Important: Dont make any changes to medications without doctor approval that could cause serious problems.
Is Parkinsons Disease Inherited
Scientists have discovered gene mutations that are associated with Parkinsons disease.
There is some belief that some cases of early-onset Parkinsons disease disease starting before age 50 may be inherited. Scientists identified a gene mutation in people with Parkinsons disease whose brains contain Lewy bodies, which are clumps of the protein alpha-synuclein. Scientists are trying to understand the function of this protein and its relationship to genetic mutations that are sometimes seen in Parkinsons disease and in people with a type of dementia called Lewy body dementia.
Several other gene mutations have been found to play a role in Parkinsons disease. Mutations in these genes cause abnormal cell functioning, which affects the nerve cells ability to release dopamine and causes nerve cell death. Researchers are still trying to discover what causes these genes to mutate in order to understand how gene mutations influence the development of Parkinsons disease.
Scientists think that about 10% to 15% of persons with Parkinsons disease may have a genetic mutation that predisposes them to development of the disease. There are also environmental factors involved that are not fully understood.
Which Test Can Be Done When The Diagnosis Is In Doubt
I request a small set of tests on almost all patients I diagnose with Parkinsons. These detect some mimics of Parkinsons disease.
Some doctors dont request all these tests. And for a good reason.
The diagnosis of Parkinsons mimics is primarily based on a careful history and examination. Even in my practice, these tests change the diagnosis only in a minority of patients.
I like the additional confirmation provided by these tests. They also have other benefits. For example, they help me determine the proper dosages of medications like Amantadine.
| Simple tests to detect Parkinsons Mimics |
|---|
| 1. MRI-Brain with size measurements of brain parts called the midbrain and pons. I usually also request a unique picture called SWI, which shows iron inside the brain.
2. Blood tests: |
But when the diagnosis s really in doubt, there is another brain scan that can be done.
A Trodat scan. Or even better an F-DOPA scan. Both these scans measure dopamine activity inside the brain.
You can read more about Trodat & F-DOPA scans by clicking here.
These scans are not perfect. Let me tell you why very quickly:
In Parkinsons disease, dopamine activity inside the brain is deficient. This deficiency produces an abnormal scan. If the Trodat/F-DOPA scan is normal, it is unlikely that you have Parkinsons disease.
Recommended Reading: Who Discovered Parkinson’s Disease
Controlled Release Madopar And Sinemet
Controlled release preparations have the letters CR or HBS after the drug name.
These let the levodopa enter your body slowly instead of all at once. They can increase the time between doses.
They may be used when the dose of standard levodopa starts to wear off and the person taking it no longer feels the treatment is effective.
Controlled release options can sometimes reduce involuntary movements .
What Drugs Can Cause Parkinsons Disease
Physiologically, Parkinsons disease is caused due to low levels of dopamine secretion in the body. Thus, any medication that blocks the level of dopamine in the body and cause Parkinsons symptoms. Dopamine is a brain chemical that essentially helps control movement of a person. The various drugs include-
Antipsychotic Drugs- Parkinson symptoms are seen to be common in patients who are prescribed antipsychotic drugs. Parkinsonism as a side effect of chlorpromazine is quite common. Typical antipsychotic drugs include chlorpromazine, promazine, haloperidol, perphenazine, fluphenazine and pimozide. Dopamine receptors are widely distributed in the brain and typical antipsychotics may affect dopamine receptors in the striatum.
GI Motility Drugs- GI prokinetic drugs like metoclopramide, levosulpiride, clebopride, itopride and domperdone may cause side effects thereby making the patient prone to Parkinsonism.
Also Check: Caring For Someone With Parkinson’s
What Treatments Are Available For Parkinsons Psychosis
Your doctor may first reduce or change the PD medication youre taking to see whether that reduces psychosis symptoms. This is about finding a balance.
People with PD may need higher doses of dopamine medication to help manage motor symptoms. But dopamine activity shouldnt be increased so much that it results in hallucinations and delusions. Your doctor will work with you to find that balance.
Key Aspects Of Drug Induced Parkinsonism
- Drug induced Parkinsonism is relatively less likely to produce the problem of tremor than its counterpart idiopathic Parkinsons disease.
- DIP is highly symmetric, but doctors usually fail to distinguish the 2 syndromes in case of an individual therapy.
- The problem of DIP persists in patients for a few weeks to up to many months even when a patient stops the consumption of respective offending drug.
- Drug induced Parkinsonism has a longstanding and a significant effect on the daily lives of a patient. Hence, doctors should essentially stay cautious while prescribing the drugs of depaminergic receptor blockers to their patients.
Also Read:
You May Like: Medications For Parkinson’s Patients
Any Medication That Blocks Dopamine In The Body Can Cause Parkinsons Symptoms
You may have heard of Parkinsons disease , a movement disorder. Someone with it may have characteristic signs, such as a pill-rolling tremor in the fingers or a hunched forward posture. You may recognize someone with this disease from the faltering, tiny steps they take when they walk or by their rigidly emotionless face.
The cause of Parkinsons disease is mostly unknown. Some people develop Parkinsons-like symptoms after treatment with certain medications. This is called drug-induced parkinsonism or secondary parkinsonism. Certain medications can also worsen symptoms in someone who already has Parkinsons disease.
Any medication that blocks dopamine in the body can cause Parkinsons symptoms. Dopamine is a brain chemical that helps control movement. Common dopamine-blocking drugs are antipsychotics. They are used to treat certain mental illnesses or severe nausea. Less commonly, certain types of calcium channel blockers cause drug-induced parkinsonism. These drugs may be used to treat chest pain and high blood pressure, or irregular heart rate.
Conditions That Can Cause Tremors Besides Parkinsons:
The tremor of Parkinsons disease occurs even at rest. Hence it is called a rest tremor. Very few other conditions produce rest tremor.
But, many other diseases produce a tremor which is seen only when moving, for example when writing. This is called an Action tremor or posturokinetic tremor. Even these diseases are sometimes misdiagnosed as Parkinsons disease.
| Causes of Rest Tremor |
|---|
|
2. Excessive stress, coffee or smoking 3. Medications such as bronchodilators, valproate and lamotrigine 4. Chromosomal problems such as Fragile-X syndrome 5. Parkinsons disease itself! And many others |
Also Check: Signs Of Parkinson’s Disease
Delayed Administration And Contraindicated Drugs Place Hospitalized Parkinsons Disease Patients At Risk
Problem: One-third of all patients with Parkinsons disease visit an emergency department or hospital each year, making it a surprisingly common occurrence.1 The disease affects about 1 million people and is currently the fourteenth leading cause of death in the US. Hospitalization can be risky for patients with Parkinsons disease when viewed from the perspective of pharmacological management.
Patients with Parkinsons disease require strict adherence to an individualized, timed medication regimen of antiparkinsonian agents. Dosing intervals are specific to each individual patient because of the complexity of the disease. It is not unusual for patients being treated with carbidopa/levodopa to require a dose every 1 to 2 hours. When medications are not administered on time, according to the patients unique schedule, patients may experience an immediate increase in symptoms.2,3 Delaying medications by more than 1 hour, for example, can cause patients with Parkinsons disease to experience worsening tremors, increased rigidity, loss of balance, confusion, agitation, and difficulty communicating.2 Studies show that three out of four hospitalized patients with Parkinsons disease do not receive their medications on time, or have had doses entirely omitted.4 According to the National Parkinson Foundation, 70% of neurologists report that their patients do not get the medications they need when hospitalized.2
Two case examples
Other medication safety concerns
References
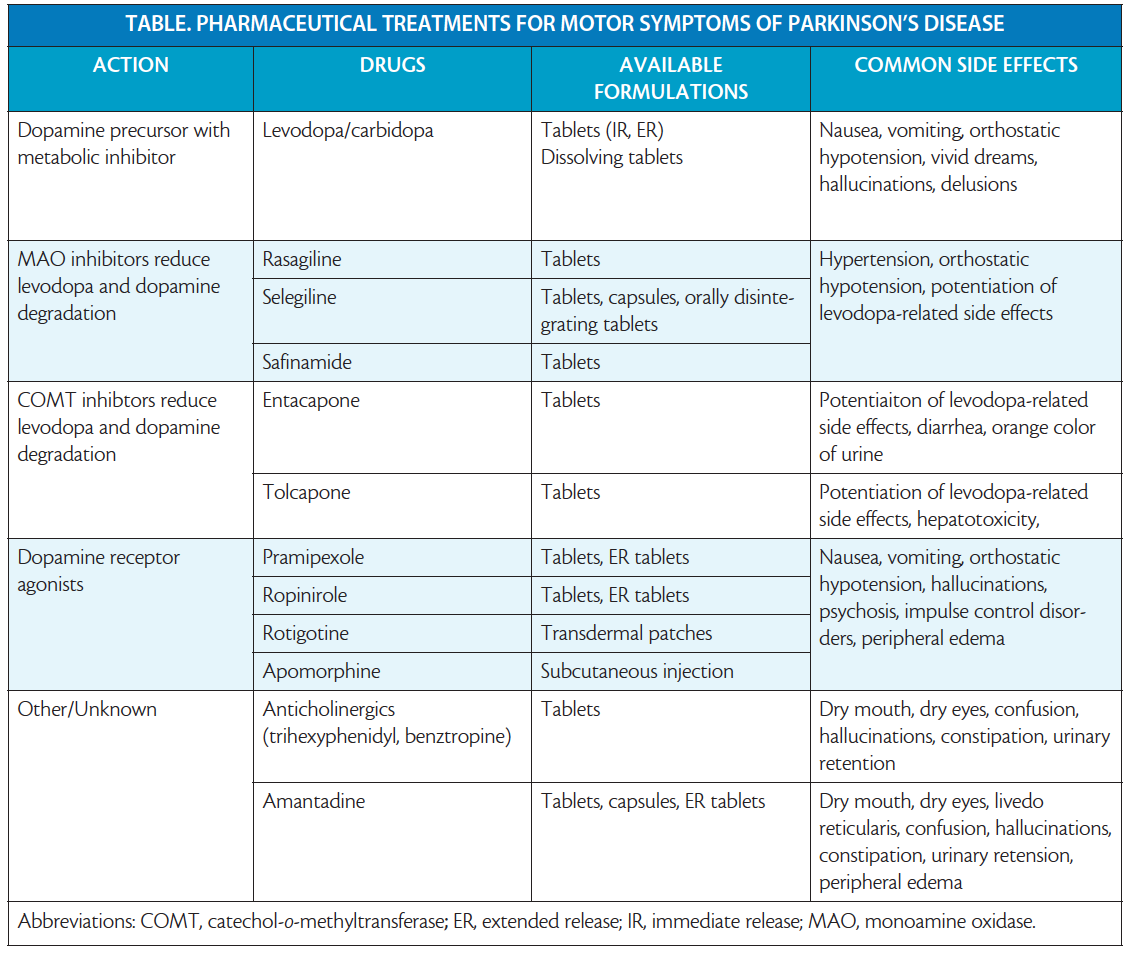
What Medications Are Used To Treat Parkinsons Disease
Medications are the main treatment method for patients with Parkinsons disease. Your doctor will work closely with you to develop a treatment plan best suited for you based on the severity of your disease at the time of diagnosis, side effects of the drug class and success or failure of symptom control of the medications you try.
Medications combat Parkinsons disease by:
- Helping nerve cells in the brain make dopamine.
- Mimicking the effects of dopamine in the brain.
- Blocking an enzyme that breaks down dopamine in the brain.
- Reducing some specific symptoms of Parkinsons disease.
Levodopa: Levodopa is a main treatment for the slowness of movement, tremor, and stiffness symptoms of Parkinsons disease. Nerve cells use levodopa to make dopamine, which replenishes the low amount found in the brain of persons with Parkinsons disease. Levodopa is usually taken with carbidopa to allow more levodopa to reach the brain and to prevent or reduce the nausea and vomiting, low blood pressure and other side effects of levodopa. Sinemet® is available in an immediate release formula and a long-acting, controlled release formula. Rytary® is a newer version of levodopa/carbidopa that is a longer-acting capsule. The newest addition is Inbrija®, which is inhaled levodopa. It is used by people already taking regular carbidopa/levodopa for when they have off episodes .
You May Like: Boxing And Parkinson’s Disease
Tips For Living With Hallucinations
It is important for people with PD to talk about hallucinations with their family and care team, because they are manageable and can be troublesome if not treated. Discuss all possible symptoms with your doctor, no matter how minor, rare or bizarre you may think they are.
- Good lighting and stimulating activities in the evening can help keep hallucinations at bay.
- While a hallucination is occurring, caregivers can help their loved one by reassuring them that they will be safe and validating their partners experience. For example, say, Ill take the cat outside instead of arguing that there is no cat.
Examples Of Delusions In Pd

- Jealousy
- Belief: Your partner is being unfaithful.
- Behavior: Paranoia, agitation, suspiciousness, aggression.
Read Also: Does Parkinson’s Cause Neuropathy
Study Population And Protocol
All study-related procedures were approved by the Regional and Institutional Ethical Committee and performed in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki.
The present study included a consecutive series of 42 patients with the clinical diagnosis of PD based on the UK Brain Bank criteria, and concomitant TMZ treatment who presented at the Department of Neurology, University of Pécs, Hungary between 2014 and 2018. TMZ treatment had been applied independently of the authors. The University of Pécs is a tertiary movement disorders center, and many of the participants were referred for further treatment. Each patient was examined immediately after learning the concomitant use of TMZ .
After obtaining an individual written informed consent for participating in the study, all enrolled patients underwent detailed neurological and neuropsychological assessments at BL. None of the enrolled subjects was treated with other medications which could have worsened the symptoms of PD. Subsequently, TMZ treatment was discontinued, and patients were reevaluated 3 months after the withdrawal of the drug based on the recommendation given by the EMA. Oral antiparkinsonian treatment remained stable in all subjects in the interval between the BL and 3-month FU visits. The included patients were followed for at least a 12-month period after the withdrawal of TMZ.
How Can You Improve Aggressiveness And Hallucinations In Parkinsons
Hallucinations may spark anger or aggression in a person with Parkinsons disease. Some ways to help include:
- Reassure them, tell them they are safe.
- Speak slowly and calmly.
- Ask questions about the persons feelings.
- Listen to the person, dont interrupt.
- Avoid sudden movements.
- Give the person space and a way out, so they dont feel cornered or threatened.
- Make an emergency plan ahead of time for what you and others in the house will do if the person experiencing hallucinations becomes a danger to themselves, you, or anyone else.
- When it is safe, help the person speak with their healthcare provider about making a plan to address the hallucinations.
You May Like: Drugs To Treat Parkinson’s
Medication Guidelines For Parkinson’s Disease
There is no one best mix of Parkinsonâs medicines. You and your doctor will have to try a few treatment approaches to figure out the best one for you.
But there are some general guidelines for taking your medication. Be sure to ask your doctor or pharmacist for any specific tips for your treatment.
Not All Drugs In These Classes Will Cause Symptoms Of Parkinsonism
Whats the difference?
Drug-induced parkinsonism usually develops on both sides of the body, while typical Parkinsons disease does not. Also, drug-induced parkinsonism usually does not progress like typical Parkinsons.
Unlike Parkinsons, drug-induced symptoms usually go away after the drug is stopped. It may take several months, though, for the symptoms to completely stop. If the symptoms remain, then it is possible that the drug may have unmaskedunderlying Parkinsons disease.
Who is at risk?
- Female: Women are twice as much at risk as men.
- Elderly: Older people are more likely to be on multiple medications or to have underlying Parkinsons disease.
- Those with a family history of Parkinsons disease.
- People with AIDS.
Also Check: What Are The Complications Of Parkinson’s Disease
The Cause Of Parkinsons Delusions And Hallucinations
Some risk factors associated with the development of psychosis in Parkinsons disease include:
- Age: Parkinsons disease usually occurs in people over age 60.
- Duration and severity of Parkinsons disease: Psychosis is more common in advanced or late-stage Parkinsons disease.
- Later onset: Occurring later in life
- Hyposmia: A decreased sense of smell
- Cognitive impairment: Problems with thinking, including trouble remembering, difficulty learning new things, difficulty concentrating, problems making decisions that affect everyday life
- Depression: People who have both depression and Parkinsons disease are at a greater risk of developing psychosis.
- Diurnal somnolence: Daytime sleepiness
- REM sleep behavior disorder: A sleep disorder in which you physically act out dreams involves making vocal sounds and sudden, often extreme, arm and leg movements during REM sleep
- Visual disorders: Impaired vision
- Severe axial impairment: Speech, swallowing, balance, freezing of gait
- Autonomic dysfunction: Impairment of the autonomic nervous system , which controls involuntary or unconscious actions such as heart rate, breathing, body temperature, blood pressure, digestion, and sexual function
- High medical comorbidity: The existence of more than one condition or illness in the same person at the same time with Parkinsons disease, may include conditions such as dementia, depression, and sleep disorders
How Is Parkinsons Disease Diagnosed
Diagnosing Parkinsons disease is sometimes difficult, since early symptoms can mimic other disorders and there are no specific blood or other laboratory tests to diagnose the disease. Imaging tests, such as CT or MRI scans, may be used to rule out other disorders that cause similar symptoms.
To diagnose Parkinsons disease, you will be asked about your medical history and family history of neurologic disorders as well as your current symptoms, medications and possible exposure to toxins. Your doctor will look for signs of tremor and muscle rigidity, watch you walk, check your posture and coordination and look for slowness of movement.
If you think you may have Parkinsons disease, you should probably see a neurologist, preferably a movement disorders-trained neurologist. The treatment decisions made early in the illness can affect the long-term success of the treatment.
Recommended Reading: Parkinson’s Disease Environmental Factors
Drugs For Parkinsons: The Shocking Side Effects
There are 2 main categories of drugs for Parkinsons Disease, and both have powerful side effects: levodopa, which makes many patients shaky with dyskinesia, and dopamine agonists, which can make turn people into gamblers, sex addicts or hit them with sleep attacks including when theyre driving. This is the story of DA.
At least 1 million people in the US and an estimated 10 million worldwide live with Parkinsons, making it the second most common neurodegenerative disorder . Parkinsons disease, a disorder of the central nervous system, is caused by a degeneration of nerve cells in certain parts of the brain that produce a neurotransmitter called dopamine. Dopamine, commonly known for its role in controlling the brains reward and pleasure center, is partly responsible for starting a circuit of messages that coordinate normal movement.
In the absence of dopamine, the neurons called dopamine receptors in the brains striatum are not adequately stimulated. In simple language, as a persons brain slowly stops producing dopamine, a person has less and less ability to regulate his or her movements, body, and emotions. The result is impaired movement with tremors, slowness, stiffness or balance problems. Lesser known symptoms include depression, apathy and dementia.
Article continues below
Serotonin Reuptake Blocking Antidepressants Fluoxetine Sertraline And Paroxetine
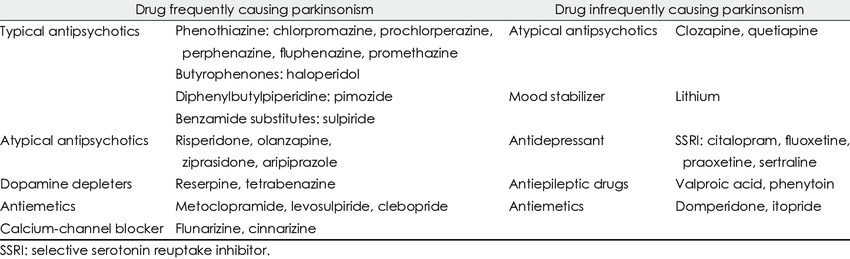
Several other medications have been reported to cause drug-induced parkinsonism and to worsen parkinsonism in people with Parkinson disease, including the serotonin reuptake blocking antidepressants fluoxetine, sertraline, and paroxetine. Two calcium channel blockers available in Europe and South America , which are piperazine derivatives, are thought to cause drug-induced parkinsonism by blocking dopamine receptors. Reports of parkinsonism induced by other drugs, such as lithium and amiodarone, are so rare that only after parkinsonism has developed should the possible drug effect be taken into account. Because lithium is not known to block dopamine receptors, another mechanism is likely. Some animal data implicate an effect of lithium on intercellular signalling via G-protein coupled receptors . One antidepressant, amoxapine, has dopamine receptor-blocking properties and, therefore, may induce parkinsonism. Parkinsonism as a transient side effect of alcohol withdrawal has been reported without later development of Parkinson disease, but it is unknown how common this is .
Also Check: Parkinson’s Disease Mouse Model