Iv Complications Of Therapy
A. DYSKINESIAS
32. Duration: What proportion of the waking day are dyskinesias present?
0 = None.
33. Disability: How disabling are the dyskinesias?
0 = Not disabling.
34. Painful Dyskinesias: How painful are the dyskinesias?
0 = No painful dyskinesias.
35. Presence of Early Morning Dystonia
0 = No
36. Are off periods predictable?
0 = No
37. Are off periods unpredictable?
0 = No
38. Do off periods come on suddenly, within a few seconds?
0 = No
39. What proportion of the waking day is the patient off on average?
0 = None
40. Does the patient have anorexia, nausea, or vomiting?
0 = No
41. Any sleep disturbances, such as insomnia or hypersomnolence?
0 = No 1 = Yes
42. Does the patient have symptomatic orthostasis?
0 = No
Parkinsons Disease Symptom Rating Scale
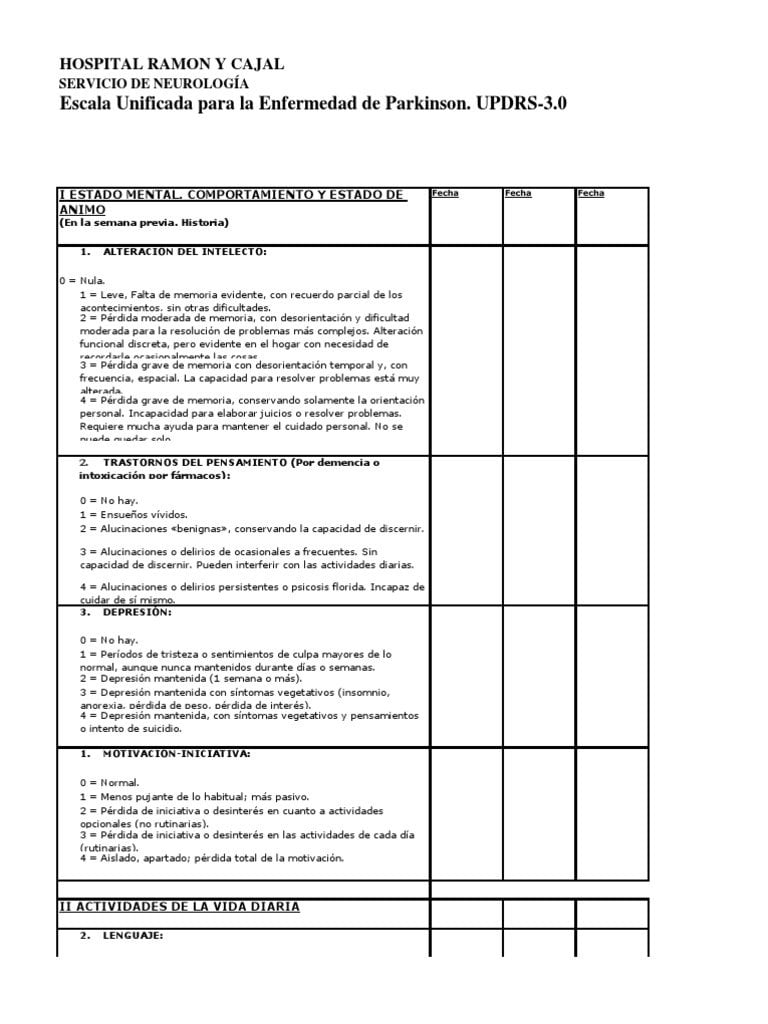
After conducting a neurological examination, the neurologist will enter their observations into a form called the Unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale, a table that neurologists and movement disorder specialists use to track and assess how well the treatments and medications they prescribe are helping the patient, The observations made on the first visit will serve as baseline. Symptoms are rated 1 2 3 4 . If the patient is responding well to medication, the neurologist will continue with the regimen. If they are not, the neurologist will consider that Parkinson’s may not be a correct diagnosis and will conduct further testing.
Unified Parkinsons Disease Rating Scale Evaluation
The UPDRS scale was scored by a single neurologist to avoid the confounding effects of interrater variability. The evaluator is a board-certified neurologist and specialist in PD who is certified in the administration of the UPDRS. The UPDRS Total score was computed as the sum of UPDRS subscales I, II, and III.
Peak Aerobic Capacity
Treadmill testing was always conducted during the early afternoon hours when subjects were on soon after taking medication. Exercise tests were terminated according to American College of Sports Medicine guidelines . Gait belts and other safety precautions protected against falls resulting from loss of balance. There were no falls during the treadmill VO2 peak tests or assessments of ambulatory function. Subjects were instructed to use as little handrail support as possible during the treadmill tests.
Both the treadmill testing and overground ambulatory function testing protocols have been previously described for this study population in articles by Katzel et al. , and those descriptions are provided in the Appendix .
Statistical Methods
Also Check: Parkinson’s Disease Stages Dementia
How Is Parkinsons Disease Diagnosed
A clinical diagnosis by a neurologist is the most common way of trying to determine whether a person has Parkinson’s disease. Trying is the definitive word here because as of now, there are no blood tests that are effective in diagnosing the disease. Neurologists may order Brain MRI or CT scans to rule out other possible disorders. For some patients, neurologists will order a DaTscan, which is a dopamine transporter imaging study. An abnormal DaTscan may be helpful to confirm a suspected diagnosis of Parkinsons, but a normal DaTscan result does not rule out the possibility that a patient may still have Parkinsons disease. Most often, in order to arrive at a diagnosis, neurologists will take the patient’s medical and family history, listen to the symptoms they report experiencing, and perform a detailed neurological examination to determine the agility of the limbs and neck, note any gait and balance problems and observe facial animation and tremors.
If their suspicions weigh out, the neurologist will prescribe a treatment plan using medication and other therapies. If these ameliorate the patient’s symptoms, they will consider the diagnosis to be adequate. If they don’t, they will look for another possible cause.
In order to place the patient at the correct stage of Parkinson’s and judge the efficacy of treatment, neurologists use two rating systems the Hoehn and Yahr Scale and the Parkinson’s Disease Symptom Rating Scale.
Regression Models For Updrs

In our preliminary work, we explored two different architectures based on a single-channel and dual-channel LSTM of hand-crafted features and showed that the latter provides superior performance . In this section, we first describe an extension to that model by applying transfer learning using PAMAP2 dataset. Next, we develop a new 1D and 2D CNN-LSTM models using raw motion signals and their timefrequency representations, respectively. The proposed ensemble model is described next. Lastly, Gradient Tree Boosting is described as a traditional machine learning method for comparison purposes.
Dual-channel LSTM network with transfer learning
LSTM is a special type of Recurrent Neural Networks to overcome the vanishing gradient problem when training using gradient descent with backpropagation through time. LSTM can efficiently learn the temporal dependencies and has been successfully used in applications involving signals with temporal memory. In this work, LSTM architecture proposed by is used.
LSTM unit consists of input gate , input modulation gate , forget gate , output gate , and memory cell at time step t). Before applying the operations in these gates, current feature vector ) at time t in round r is linearly transformed using the following equation:
Recommended Reading: Do Parkinson Patients Shake During Sleep
How Do People Act When They Have Parkinsons Disease
People with Parkinsons disease will first develop tremors in the hand on one side of the body, and as the disease progresses, it will spread to the limbs on both sides. The tremor may appear as pill-rolling, or rubbing together of the forefinger and thumb. Their movements may slow and they may have trouble getting up from a chair. Their posture will often be stooped, and when they walk, they may shuffle or drag their feet andhold their arms stiffly at their sides. Other changes include smaller handwriting and a softer speaking voice.
The Advantage Of Deep Learning
The dual-channel LSTM developed in our preliminary work provides only slightly higher performance than Gradient Tree Boosting with a 0.62 correlation vs. 0.61. However, transfer learning from the activity recognition dataset improves performance by providing a 10% higher correlation and 13% lower MAE when compared to Gradient Tree Boosting. This behavior indicates that temporal dependencies captured by the first two LSTM layers using hand-crafted features extracted from healthy subjects are beneficial to UPDRS-III estimation.
Another observation is that both the 1D and 2D CNN-LSTM networks outperform Gradient Tree with 0.70 and 0.67 correlation, respectively with greater than 10% increase in correlation, and 6.93 and 7.11 MAE, respectively, with a decrease of greater than 9% in MAE. These networks achieve comparable performance to the dual-channel LSTM with hand-crafted features, which means CNN could extract relevant data-driven features.
We also observe that the ensemble of the models based on hand-crafted and data-driven features improves the performance. The ensemble of multiple models is known to improve the regression results if the models solve different aspects of the given problem . Hence, we can conclude that the trained deep models are diverse and learn different views of the motion signals , and therefore, are necessary for successful UPDRS-III estimation.
Recommended Reading: What Age Do You Develop Parkinson’s
Is Theracycle Safe To Use
The Theracycle is designed specifically for users with movement disorders and has many safety features. Its motion can be stopped instantly using either a push of a button or a pull of the safety cord. The structural steel frame can support up to 350lbs and cast iron parts are extremely durable and built to last. The seat is extra large for added comfort, safety and stability.
What Is A Rating Scale
A rating scale is a means of providing information on a particular feature by assigning a value to it. In Parkinsons, rating scales require the rater to put a value to the feature or symptom in question, according to a set scale. The rater may be the person with Parkinsons or a healthcare professional.
Parkinsons rating scales are a means of assessing the symptoms of the condition. They provide information on the course of the condition and/or assess quality of life. They may also help to evaluate treatment and management strategies, which can be useful to researchers as well as to people with Parkinsons, their carers and medical team.
Motor scales are the best-known and most widely used, but non-motor symptom scales are equally important. Combined with a motor scale, these give a more balanced picture of how a person is affected by the condition. A low motor score may suggest that a person has mild Parkinsons but, at the same time, the person may have disabling non-motor symptoms, which impact on quality of life.
Also Check: Symptoms Of Lewy Body Parkinson’s
Vi Schwab And England Activities Of Daily Living Scale
100% = Completely independent. Able to do all chores without slowness, difficulty or impairment. Essentially normal. Unaware of any difficulty. 90% = Completely independent. Able to do all chores with some degree of slowness, difficulty and impairment. Might take twice as long. Beginning to be aware of difficulty. 80% = Completely independent in most chores. Takes twice as long. Conscious of difficulty and slowness. 70% = Not completely independent. More difficulty with some chores. Three to four times as long in some. Must spend a large part of the day with chores. 60% = Some dependency. Can do most chores, but exceedingly slowly and with much effort. Errors some impossible. 50% = More dependent. Help with half, slower, etc. Difficulty with everything. 40% = Very dependent. Can assist with all chores, but few alone. 30% = With effort, now and then does a few chores alone or begins alone. Much help needed. 20% = Nothing alone. Can be a slight help with some chores. Severe invalid. 10% = Totally dependent, helpless. Complete invalid. 0% = Vegetative functions such as swallowing, bladder and bowel functions are not functioning. Bedridden.
Therapeutic Role Of Rtms In Parkinson Disease
Early studies suggested an improvement in pointing performance and on the Unified Parkinson Disease Rating Scale after rTMS to the motor cortex.101 Subthreshold rTMS applied to the motor cortex at both 0.5 Hz and 10 Hz improved motor performance.102 However, such changes lasted only for minutes. A long-lasting effect of rTMS may be obtained with repeated application over a period of days. In a randomized study, patients receiving 5-Hz rTMS to the motor cortex experienced improvements in the UPDRS motor scores, walking speed, and a self-assessment scale that persisted for over 1 month.103 In a double-blind, placebo-controlled study, rTMS over 4 weeks using four cortical targets in each session showed a therapeutic effect that lasted for at least 1 month after treatment ended.104
Low-frequency rTMS studies, by contrast, showed no significant reduction in motor UPDRS but may be a potential treatment for levodopa-induced dyskinesias.106 A single session of rTMS at 1 Hz to the supplementary motor area bilaterally lowered the severity of dyskinesias for 30 minutes after stimulation.108Repeated administration of 1-Hz rTMS of the motor cortex109,110 and cTBS to the cerebellum111 have shown promise also as potential treatment for levodopa-induced dyskinesias.
Recommended Reading: What Causes Pain In Parkinson’s Patients
I Have A Movement Disorder Which Precludes Me From Traditional Type Of Exercise Will The Theracycle Really Allow Me To Exercise
Yes. The Theracycles motor assists you in attaining continuous exercise for longer periods that, due to lack of strength and endurance, would otherwise not be possible on traditional exercise equipment for users with movement disorders. We are so convinced the Theracycle will work for you, we offer a money-back guarantee within 30-days of delivery if you are not completely satisfied.
How Do You Get Parkinsons Disease
Parkinson’s is a complex, neurodegenerative disease that affects no two people the same way. It stems from the brain losing the ability to produce dopamine, a neurotransmitting hormone that plays a role in movement, memory, motivation, and the ability to experience pleasure. In rare cases, Parkinson’s may occur in successive generations of a family, but 10 to 15% of cases result from changes in the genes. One school of thought is that Parkinson’s Disease results from a perfect storm of environmental factors, genetic changes, and lifestyle.
Read Also: Exercise Class For Parkinson’s Disease
Why Does The Theracycle Cost More Than A Basic Exercise Bike
The Theracycle is not a simple or traditional exercise bike. The biggest difference is the unique motorized technology and the 15-speed variable gearbox, which allows you to attain and maintain a significantly faster cadence for a longer period than you can achieve using a traditional stationary or road bike. A Theracycle has been proven to reduce neurological symptoms and improve motor function and mobility.
Additionally, the bike is custom engineered for the specific needs of people with movement disorders, not only in its open walk-though design, but also when it comes to durability and, most importantly, stability. The Theracycle is built on a very sturdy, heavy structural steel frame. It has a low center of gravity by design, which is ideal for those with balance, dexterity or gait issues providing a safe and secure exercise option in the comfort of your own home. Also important is the motor-assisted handlebar which provides both core and upper body exercise with a repetitive rowing motion for a full-body workout. A Theracycle provides a meditative and relaxing option for both mental and physical therapy that is low impact to your joints and muscles.
V Modified Hoehn And Yahr Staging
STAGE 0 = No signs of disease. STAGE 1 = Unilateral disease. STAGE 1.5 = Unilateral plus axial involvement. STAGE 2 = Bilateral disease, without impairment of balance. STAGE 2.5 = Mild bilateral disease, with recovery on pull test. STAGE 3 = Mild to moderate bilateral disease some postural instability physically independent. STAGE 4 = Severe disability still able to walk or stand unassisted. STAGE 5 = Wheelchair bound or bedridden unless aided.
Recommended Reading: What Are The Signs Of Parkinson’s Disease
Scales And Questionnaires For Assessment Of Fluctuations
An MDS Task Force reviewed wearing off scales in PD in 2011 according to the methodology described previously. Wearing off symptoms are defined as symptoms that appear prior to the next levodopa dose and respond to levodopa treatment. Two questionnaires reached the standards to be recommended for screening of wearing off symptoms: the Wearing Off Questionnaire -19 or QUICK and the WOQ-9 . These two surveys are shortened versions of the WOQ-32 , a 32-item questionnaire including the most common motor and NMS . This original questionnaire was designed for use in clinical trials and takes the patient about 2530 min to complete. It is only suggested by the MDS Task Force since clinimetric data are insufficient. Based on the results derived from the use of the WOQ-32, the authors identified the most common wearing off symptoms and designed two shorter versions of the original questionnaire for routine clinical use.
The WOQ-19 or QUICK takes about 15 min to complete, has been validated , and has been used by other groups . The WOQ-9 takes about 6 min and has also undergone some clinimetric testing, showing high sensitivity but low specificity . Since then, the Q10 has been proposed as a shorter form of the WOQ-19. This version gives more weight to motor symptoms than the previous two and, therefore, is less appropriate for assessment of nonmotor fluctuations . The four questionnaires are of public domain.
8.1Multidomain Instruments
P. Mazzone, E. Scarnati, in, 2009
Using Cognitive Pretesting In Scale Development For Parkinson’s Disease: The Movement Disorder Society Unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale Example
Article type: Research Article
Authors: Tilley, Barbara C. | LaPelle, Nancy R. | Goetz, Christopher G. | Stebbins, Glenn T. | on behalf of the MDS-UPDRS Task Force
Affiliations: Division of Biostatistics, University of Texas School of Public Health at Houston, Houston, TX, USA | Division of Preventive and Behavioral Medicine, University of Massachusetts, Worcester, Massachusetts, USA | Department of Neurological Sciences, Rush University Medical Center, Chicago, Illinois, USA
Note: Correspondence to: Barbara C. Tilley, Ph.D., Division of Biostatistics, University of Texas School of Public Health at Houston, 1200 Pressler Drive, RAS 833E, Houston, TX 77030, USA. Tel.: +1 713 500 9564 Fax: +1 713 500 9525 E-mail:
Keywords: Cognitive pretesting, Parkinson’s disease, scale development, Modified Unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale
DOI: 10.3233/JPD-130310
Journal: Journal of Parkinson’s Disease, vol. 4, no. 3, pp. 395-404, 2014
Don’t Miss: Does Acupuncture Help Parkinson’s Disease
Thanks For Signing Up
We are proud to have you as a part of our community. To ensure you receive the latest Parkinsons news, research updates and more, please check your email for a message from us. If you do not see our email, it may be in your spam folder. Just mark as not spam and you should receive our emails as expected.
Schwab And England Activites Of Daily Living Scale
The Schwab and England ADL Scale is a means of measuring a persons ability to perform daily activities in terms of speed and independence through a percentage figure. The rating may be made by a professional or by the person being tested. High percentages indicate a high level of independence while low percentages indicate dependence:
- 100% – Completely independent. Able to do all activities without slowness, difficulty or impairment
- 90% – Completely independent. Able to do all activities with some slowness, difficulty or impairment. Activities may take twice as long to complete
- 80% – Independent in most activities, but activities take twice as long. Conscious of difficulty and slowing
- 70% – Not completely independent. More difficulty with activities, which may take three to four times as long. May take large part of day for chores
- 60% – Some dependency. Can do most activities, but very slowly and with much effort, but some chores are impossible
- 50% – More dependent. Help required with half of chores. Difficulty with everything
- 40% – Very dependent. Can assist with all chores but can manage few alone
- 30% – With effort, now and then does a few chores alone or begins alone. Much help needed
- 20% – Cannot do anything alone. Can give some slight help with some chores. Severe invalid
- 10% – Totally dependent, helpless
- 0% – Vegetative functions such as swallowing
You May Like: When Was Parkinson’s Disease Discovered