From Cell Replacement To Circuits
A key requirement for cell-replacement therapy to work is that engrafted neurons connect to resident neuronal networks, thereby reconstructing damaged circuits or establishing alternative circuitries that can compensate for the functional deficits elicited by neurodegeneration.
Studies in rodents using allografted fetal VM demonstrate synapse formation from host to graft and from graft to host,. Novel technologies have made the assessment of synaptic integration of hPSC-derived neurons more accessible. For example, retrograde tracing based on modified rabies virus has allowed monosynaptic connections of afferent neurons to and from the graft to be mapped in the 6-hydroxydopamine rat model of PD, and revealed that the host circuitry, specifically nuclei of the intact mesDA system, formed appropriate synaptic contacts with grafted hPSC-derived neurons,. Using the same experimental design, another study demonstrated that grafted neurons also formed synaptic contacts with host circuitry, namely with surrounding striatal medium spiny neurons and neurons of the medial prefrontal cortex that are normally targeted by A10 DA neurons. These studies demonstrate that synaptic integration between host and transplanted neurons is a dynamic process, starting as early as 6 weeks after transplantation and maintained for at least 6 months, that occurs between reconstructed physiologically relevant circuits.
Read Also: Prayer For Parkinsons Disease
Is There Any Guarantee That A Stem Cell
There is no therapy, be it an experimental or established treatment, for which your treating physician can promise or even guarantee a therapeutic success. In the case of innovative and experimental therapies such as stem cell therapy, doctors must perform a benefit-to-risk-analysis for each individual case and ensure that the therapy is beneficial to the patient and these benefits outweigh the risks. Only when this is the case, your doctor will suggest treatment with stem cells.
How Are Stem Cells From Stem Cell Supplement Administered For Parkinsons Disease
Unlike traditional Stem Cell Therapy which can only be applied via injection in the selective hospitals/ clinics, Stem Cell Supplement delivers stem cells through high-tech bio-active softgel capsules which can be shipped in secure packages and delivered right to your home. The lyophilized method employed in Able softgel capsules produces stem cells which remain biologically active without damaging the effectiveness of the valuable, big, bio-active matter. Being enteric coated, Able softgel capsules by-pass the stomach and dissolve in the small intestine whereby the stem cells and other active ingredients are fully absorbed by the body. Therefore, to receive the results and benefits of Stem Cell Supplement, all you need to do is to take 1 3 softgel capsules a day at the comfort of your own home.
Also Check: Parkinson’s Disease Medications Carbidopa Levodopa
Are There Stem Cell Therapies For Parkinsons
Researchers are working on it. Stem cells, often derived from a patient with Parkinsons disease, are currently being studied extensively in the laboratory, both to further our understanding of the molecular mechanisms that cause cell death in PD, and also as a test environment for new medications. However, there are currently no stem cell treatments for Parkinsons disease that have been developed and tested to the point that we are sure that they help and do not cause harm. Researchers however, are furiously underway to develop such a treatment. The research is focused on deciphering the best source of stem cells to use, the best ways to turn the stem cells into dopaminergic neurons and the best ways to introduce the cells into the brain for maximal effect and minimal harm.
Does It Work Efficacy Of Commercial Stem Cell Clinics
Commercial clinics do not as a rule publish their results in peer-reviewed journals to demonstrate to the scientific community that the treatments work. Rather, they usually rely on anecdotes from patients as proof of efficacy. Some clinics are tracking their results by measuring variables such as quality of life before or after the procedure. However, without comparing the patients to a similar group who does not receive the treatment, it is hard to know whether any improvement is due to placebo effect or to the treatment itself.
Don’t Miss: Parkinson’s Disease And Back Pain
The Promise And Potential Of Stem Cells In Parkinsons Disease
Neurosurgeon Viviane Tabar is co-leading a trial to inject stem cells into the brains of people with Parkinsons disease to restore dopamine levels.Credit: Courtesy of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center
Neurosurgeon Viviane Tabar has scrubbed in. In front of her is the first participant in a clinical trial to determine whether stem cells can be safely injected into the brains of people with Parkinsons disease. The cells had been frozen, but they are now thawed and sitting on ice, waiting for their moment.
Tabar, a physician-scientist at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York City, makes an incision in her patients scalp and drills a small hole in their skull. She then uses a brain scan almost like a GPS, she says, to guide her to the putamen a part of the brain in which levels of the neurotransmitter dopamine are unusually low in people with Parkinsons. Once she has confirmed that shes reached the right spot, she injects the stem cells, then repeats the process on the other side of the brain. She hopes these cells will take hold and eventually begin to produce dopamine where otherwise there would be little or none. The surgery itself is minor enough that the patient can go home the next day.
Part of Nature Outlook: Stem cells
Parkinsons Disease Stem Cell Therapy Research Update
When I first started The Niche more than a dozen years ago, I hoped wed see a Parkinsons disease stem cell therapyby now. A proven one.
I was a little too optimistic back then. Now in 2022, I know much better how hard translation to the bedside can be in general. Still, Im hopeful. Its just that the timeline is always much longer than you think.
In this post, I give an update on this research area and explain why I am optimistic in the long run.
Read Also: What Medication Does Michael J Fox Take For Parkinson’s
Stem Cells And Parkinsons Disease
In many of my previous posts, I have mentioned that one of the reasons that I am so passionate about stem cell research is the possibility that terminal or debilitating diseases can be cured. One of the diseases that scientists are trying to cure with stem cells is Parkinsons Disease which is a disease that progressively attacks the nervous system. One of the main issues with the disease is that the symptoms appear gradually and then worsen as the disease progresses. There is no cure for Parkinsons Disease, but patients have the choice to take medication to control the symptoms of the disease.
However, a study posted on Monday revealed that a specific stem cell technique has cured Parkinsons disease when tested in mice. This technique involves the implantation of stem cells into the dead nerve or brain cells. The mice tested in the laboratory setting had the version of Parkinsons Disease that is exhibited in mice and had only a few more weeks before the disease would completely inhibit their motor skills. However using methods used in stem cell research, the researchers were able to restore the brain cells that were dying and causing the onset of Parkinsons Disease. The mice even began to regain motor functions that were lost before the treatment.
The picture below shows the effect that Parkinsons disease has on the dopamine receptors in the human brain.
Stem Cell Therapy For Parkinsons Disease
Parkinsons disease is a progressive disorder of the nervous system affecting movements. It develops gradually, starting with the barely noticeable tremors but in the later stages, it is associated with frequent body stiffness and slowing-down or complete loss of movement. People with Parkinsons disease may experience muscular tremors, stiff muscles, delayed muscular movements and issues with locomotor actions such as balance, walking, etc. With recent technological advancements in stem cells, it is possible to proactively alter the effects of the disease and live a full, happy, healthy life. Having the potential to significantly impact the development of diseased state, stem cell treatment for Parkinsons can create dopamine-producing cells which enhance normal communication between neurons and provide a vastly improved quality of life.
You May Like: What Test Is Done For Parkinson’s
What Will The Next Generation Of Clinical Trials Focus On
There are many symptoms of Parkinsons disease. Theyre often rated using the Unified Parkinsons Disease Rating Scale or the Movement Disorder Societys updated revision of that scale, the MDS-UPDRS.
Clinical trials today are generally looking to significantly improve UPDRS or MDS-UPDRS scores for people with Parkinsons disease.
Some trials are testing new delivery methods, such as intravenous infusion or topical applications. Others are looking to determine the safest number of effective doses. And other trials are measuring overall safety while using new medical devices in stem cell therapy.
This is an active area of research. Future trials will help narrow down the most safe and effective approach to stem cell therapy for Parkinsons disease.
Each phase adds more participants, with the first phase usually limited to a few dozen people and several thousand in the third phase. The purpose is to test the treatments safety and effectiveness.
Clinical trials testing stem cell therapy for Parkinsons disease are still in the early phases. If the current trials are successful, it will likely still be 4 to 8 years before this treatment is widely available.
Human Tissue Specimens And Patient Information
We used the small intestine wall and nodose ganglion from a donor with sporadic PD who had nigral Lewy body pathology on neuropathological examination. The body was obtained from the Body Organ Donation Center of Dalian Medical University. The patient signed the consensual document for body and organ donation , and the medical history was provided by her next of kin.
Recommended Reading: How Long Does Parkinson’s Last
Radical New Therapy For Parkinsons Will Use Stem Cell Transplants
Lab-grown nerve cells will replace those destroyed by disease scientists hope treatment may be available in five years
Early next year, a radical new treatment for Parkinsons disease involving tissue transplants will receive its first trial with patients including a group from the UK.
Stem cells grown in the laboratory and transformed into nerve cells will be used to replace those destroyed by the disease. It is hoped that these will stop the spread of debilitating symptoms.
It has taken a long time to get to this stage but hopefully results from these trials will mean that, in a few years, we might be able to offer tissue transplants as standard treatments for Parkinsons, said Prof Roger Barker, of Cambridge University. It is certainly a promising approach.
In the UK, about 145,000 people live with Parkinsons and about 18,000 new cases are diagnosed every year. The disease is triggered when nerve cells that supply dopamine to the brain start to die due to a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
Dopamine helps a person control movement. When supplies drop, the result is shaking, stiffness, depression and other symptoms that can end with patients using a wheelchair or being bed-ridden. The diseases progress can be slowed by the drug L-dopa, which replaces some of the lost function of dopamine cells. Treatments become less effective over the years. Scientists have been searching for years for new approaches.
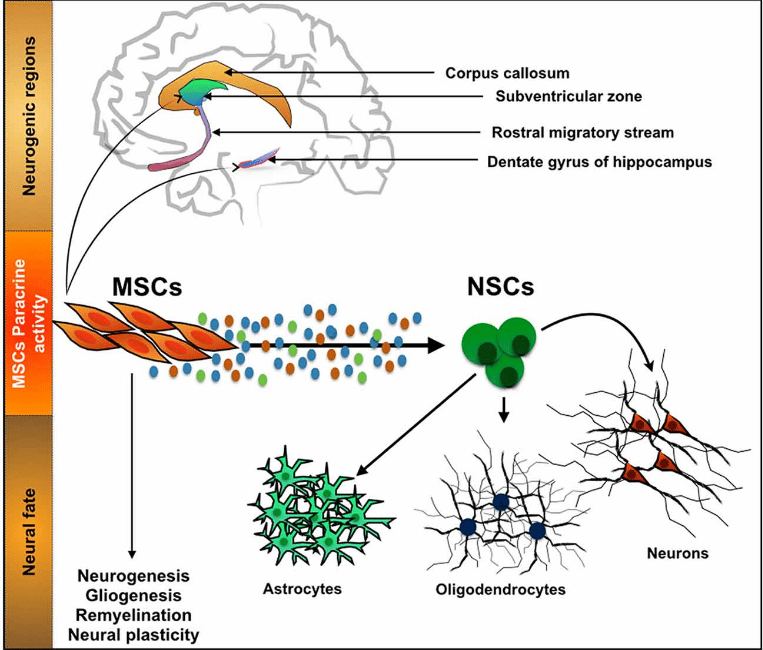
Modulatory Effects Of Mscs On Pd
Recently, dysregulation of the autophagy system has been identified in the brains of PD patients and animal models of the condition, suggesting a potential role for autophagy in PD . In PD models, MSCs have been demonstrated to improve a-syn clearance and regulate autophagy-lysosomal activity . MSCs may activate autophagy signaling through upregulation of Beclin-1 , a key positive regulator of mammalian autophagy. The secretome of MSCs has been found to contain numerous components associated with autophagy signaling in cell-based experiments through induction of autophagy-related genes, including beclin-1 , Gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor-associated protein-like 1 and Autophagy related 12 . The secretome of MSCs drives PI3K/Akt activation and modulates different signaling pathways to improve nutrient absorption, cell growth, metabolism, and proliferation .
According to several investigations, MSCs exhibit immunomodulatory effects after infiltrating to injury sites in response to particular chemotactic recruitment and releasing numerous growth and immunoregulatory factors, so they can alleviate inflammation and improve tissue healing . Therefore, MSC-based cell therapy has been used to modulate inflammation and accommodate tissue regeneration in treating many neuroinflammatory and neurodegenerative illnesses such as Parkinson’s disease .
Also Check: Light Therapy For Parkinson’s Disease
How Is Parkinsons Disease Currently Treated
Since many of the major features of PD are caused by the loss of neurons that release dopamine, treatment focuses on replacing dopamine or imitating its effects with drugs that mimic its actions that have produced great clinical benefit since the 1960s. However, over time these drugs create significant side effects of their own, including erratic motor responses and involuntary movements as well as neuropsychiatric problems. Thus, these drugs, which need to be consistently taken, create problems that ultimately may be as problematic as the disease they are being used to treat.
For later, more advanced stages of the disease, invasive deep brain surgical stimulation may also be used, but is not without risks, and, like the pharmaceutical options, may offer only temporary symptomatic relief.
What Is Parkinsons Disease
Parkinsons Disease is a chronic and progressive movement disorder, meaning that symptoms continue and worsen over time. Nearly one million people in the US are living with Parkinsons disease. The cause is unknown, and although there is presently no cure, there are treatment options such as medication and surgery to manage its symptoms.
Parkinsons involves the malfunction and death of vital nerve cells in the brain, called neurons. Parkinsons primarily affects neurons in an area of the brain called the substantia nigra. Some of these dying neurons produce dopamine, a chemical that sends messages to the part of the brain that controls movement and coordination. As PD progresses, the amount of dopamine produced in the brain decreases, leaving a person unable to control movement normally.
There are five stages of Parkinsons disease:
Stage 1
Patients exhibit mild symptoms, such as tremoring and loss of balance. Typically this will occur in a single limb.
Stage 2
Inability to walk or stand including a noticeable slowing of physical movement.
Stage 4
Severe symptoms are noticeable however the patient can still walk. Rigidity and bradykinesia are often visible. Tremors or shakiness of the earlier stages may lessor become non-existent.
Stage 5
In the final stage of Parkinsons, patients are unable to take care of themselves and may not be able to stand or walk. These patients require constant nursing care.
Don’t Miss: Mortality Rate Of Parkinson’s Disease
What Are The Early Signs Of Parkinsons Disease
Early symptoms and possible warning signs of Parkinsons disease are: Writing becomes difficult and font is getting involuntarily smaller One sided tremor or shaking Involuntarily index finger and thumb rolling Dizziness or fainting Change of facial expression known as mask face Soft or lower voice then usual Sleep problems usually accompanied with sudden movements Walking and otherwise subconscious movements only seem possible when actively imitating them Hunching over or stooping
Dont Miss: Cleveland Clinic Parkinsons Bicycle Study 2017
Assessment Of The Efficacy Of Cell Transplants With Immunostaining Characterization
In the case of mDA progenitor neuron specifications, positive gene expression of common transcription factors FOXA2, LMX1A, and OTX2 and negative markers such as Afp, Gata4, and Brachyury have been quantitatively analyzed . More importantly, the upregulation and downregulation of these markers at a given stage in vitro governs the efficiency of cell fate determination. Unfortunately, these markers have been shown to coexpress in the diencephalic progenitor cells of the subthalamic nucleus . Furthermore, the expression of the positive genetic marker for DA neurons, tyrosine hydroxylase , a rate-limiting enzyme in dopamine synthesis , and the levels of GIRK2 have also been observed in many cell types in vitro . Moreover, common positive markers used to isolate high-quality DA progenitor cells include EN1 and SPRY1 Nurr1 FOXA2, LMX1B, and MSX1 , and the bicoid-related homeodomain factor Ptx3/Pitx3 . It is noteworthy that some discrepancies have been found with the requirement for the presence of floor plate-specific cell surface marker CORIN expression . A more recent study has identified a cell surface marker integrin-associated protein as a positive marker for FOXA2-positive DA progenitor cells .
Read Also: Words Of Encouragement For Someone With Parkinson’s
Disadvantages Of Stem Cell Approaches
While the stem cell approaches described potentially offer promising treatment approaches, a number of problems must be overcome in order for them to be used as a mainline treatment for PD.
Of course, any grafting therapy will require a neurosurgical procedure, and it must be demonstrated that this can be achieved safely, with minimal risk. Additionally, for allogenic grafts a period of immunosuppression will be required, with the associated risk of infection and malignancy. Having said this, there is postmortem evidence of FVM graft survival for over two decades, with only a transient period of immunosuppression, and taking into account the fact that the central nervous system is an immune-privileged site, it is unlikely that this will be a major problem .
It has been estimated that generating iPSCs from 150 human leukocyte antigen -typed individuals could allow for the development of haplobanks which would be able to provide HLA-matched cell products for over 90% of a population . This would mean that rather than an autologous grafting product being produced for each patient, that an iPSC line could be selected with which they were HLA compatible to generate a matched cell product. However, in order to achieve this, a degree of HLA mismatch would be necessary, and a period of immunosuppression would therefore probably be required. Additionally, this would still have significant economic costs .