Nursing Visits And Patient Characteristics
Correlations between monthly nursing visits and age, years with PD, HY stage, and the number of people in the patient’s household are listed in Table 3. A significant positive correlation was found between visits and HY stage , but only a weak positive correlation was found between visits and years with PD. A weak negative correlation was found between visits and the number of people in a household .
Clinical Stages Of Pd
Although clinical experts describe the symptoms and stages of PD differently, it is sometimes classified based on the daily-life disabilities with three stages as early, moderate, or advanced: Early represents the stage when a person has a mild tremor or stiffness but is able to continue work or other normal daily activities. This often refers to a person who has been newly diagnosed with PD Moderate refers to the stage when a person begins to experience limited movement. A person with moderate PD may have a mild to moderate tremor with slow movement Advanced refers to the stage when a person is significantly limited in his or her activity, despite treatment. Daily changes in symptoms, medicinal side effects that limit treatment, and loss of independence in the activities of daily living are common. A person with advanced PD may have significant and frequent changes in posture and movement with speech difficulties.
Tobias Warnecke MD, Rainer Dziewas MD, in, 2015
Parkinsons disease is a neurodegenerative disorder that causes difficulty with walking and coordination. It occurs when the brain can no longer produce enough dopamine, one type of chemical in the brain. A progressive disease, Parkinsonâs starts gradually and gets worse with time.
Levodopa And Rotigotine Exposure
Proportion of patients receiving concomitant levodopa increased with HY stage, from 2% at stage 1 to 100% at stage 4 . Baseline mean dose of concomitant levodopa also increased with HY stage . Mean±SD dose of rotigotine at EoM was 5.9±2.3mg/24h for HY stage 1 group , 7.1±3.7mg/24h for HY stage 2 , 7.5±3.9mg/24h for HY stage 3 , and 7.7±3.9mg/24h for HY stage 4 .
Recommended Reading: Sound Therapy For Parkinson’s Disease
Unilateral Involvement Only Usually With Minimal Or No Functional Impairment
The patient has tremor, rigidity, slowness and paucity of movement, or poor condition in the arm and/or legs on one side of the body. Occasionally one side of the face is involved, producing an asymmetry of expression that may look very like the effects of a mild stroke or Bells palsy. This stage of Parkinsons is often missed entirely. For example when the diagnosis is made at a more advanced Stage, the patient may remember having noticed an intermittent tremor of one hand many years before. Old home movies may show that the patient didnt swing one arm as much as the other did while walking. One hand or foot may have been clumsier than the other may have. Often these symptoms are so mild that no formal medical attention is sought. If sought it is not uncommon that the physician is unable to make a diagnosis, either by the most assiduous and astute physical examination or by the most advanced technology. Sometimes the disease must evolve over many years before a diagnosis can be made with certainty.
Usually was inserted into the original definition to modify minimal or no functional impairment: because, very rarely, a patient presents with very severe and disabling unilateral symptoms: extreme and violent tremor or rigidity and akinesia in one limb so severe that the limb is virtually paralyzed. Most doctors worry about a stroke or tumor which they should. When all necessary tests show nothing, one must wait and observe. Eventually Stage II may emerge.
Modified Hoehn And Yahr Scale
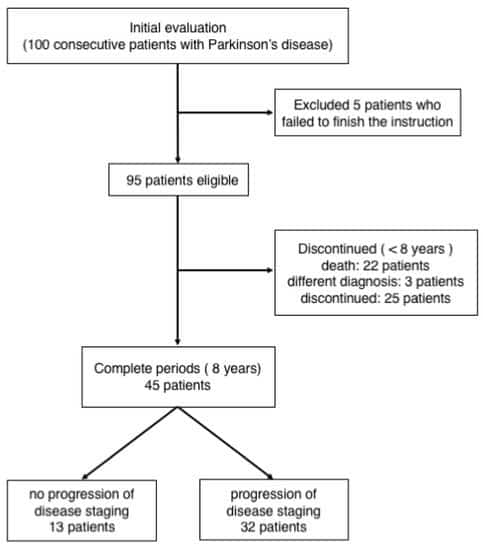
The Hoehn and Yahr scale is used to describe the symptom progression of Parkinson disease. The scale was originally described in 1967 and included stages 1 through 5. It has since been modified with the addition of stages 1.5 and 2.5 to account for the intermediate course of Parkinson disease. It was designed to be a descriptive staging scale to evaluate both disability and impairment related to clinical disease progression.
The modified Hoehn and Yahr scale is as follows :
- Stage 0: No signs of disease
- Stage 1.0: Symptoms are very mild unilateral involvement only
- Stage 1.5: Unilateral and axial involvement
- Stage 2: Bilateral involvement without impairment of balance
- Stage 2.5: Mild bilateral disease with recovery on pull test
- Stage 3: Mild to moderate bilateral disease some postural instability physically independent
- Stage 4: Severe disability still able to walk or stand unassisted
- Stage 5: Wheelchair bound or bedridden unless aided
Read Also: Is There A Genetic Test For Parkinson’s
How Are The Different Stages Of Parkinsons Treated
Treatment for Parkinsons depends on the severity of the symptoms. In the early stages, prescription medication may be enough to treat more mild symptoms. A 2019 review published in the journal Biomolecules listed some of the main pharmacological treatments for motor and non-motor symptoms for each stage of Parkinsons disease.
The main pharmacological treatments include medications such as l-dopa, a precursor to dopamine that crosses the blood-brain barrier to increase dopamine transmission, clonazepam or melatonin for REM sleep behavior disorder, and SSRIs or SNRIs for depression, which is a common non-motor symptom for Parkinsons. About 50% of people with Parkinsons experience depression.
L-dopa is the most effective and most prescribed medication for Parkinsons. Although it doesnt slow the progression of the disease or cure it, it can help control movement symptoms such as slow movement , rigidity, and tremors. However, one of the side effects of l-dopa is dyskinesia, strange, jerky movements that cant be controlled. You might decide to hold off on starting l-dopa if your symptoms are not getting in the way of your daily life.
Additional treatments for Parkinsons may include medications like dopamine agonists and monoamine oxidase inhibitors, and non-pharmacological treatment like physical therapy and speech therapy.
Subtypes Of Parkinsons Disease And Progression
What does seem to hold true for many people with PD is that a persons rate of progression is typically stable over time. Someone who has had a slow rate of progression in the past tends to have a slow rate of progression overall.
Although the progression of PD cant be determined exactly for any individual, researchers have tried to associate certain clinical features with rates of progression in the general PD population.
Tremor-predominant PD versus postural instability and gait disorder PD
In the past, several major types of Parkinsons disease were identified:
- Tremor-Predominant Subtype: tremor is the first and most characteristic feature
- Rigidity/Hypokinesia Subtype: slowness and stiffness are the most characteristic features. Those with the rigidity/hypokinesia subtype were shown to have a faster motor progression than those with the tremor-predominant subtype
- Postural Instability and Gait Disorder : balance and walking problems are the most prominent features. This subtype overlaps the rigidity/hypokinesia subtype. Studies also support the conclusion that those with the PIGD subtype experience more rapid motor decline than those with tremor-predominant PD
Diagnosis in middle age versus diagnosis in older age
Read more about How Parkinsons Disease Is Diagnosed
Low non-motor symptom burden at diagnosis versus high non-motor symptom burden at diagnosis
These individuals were then followed over time:
Don’t Miss: Michael J Fox Testimony For Parkinson’s Disease Research And Treatment
Tentative Protocol Of Clinical Trial
Once we confirm the safety and efficacy of the iPSC-derived DA progenitor cells manufactured by our protocol, we will make a formal request to the institutional and governmental committees about the clinical application of the cells. We, however, have not yet fixed the protocol of the clinical trial therefore, the tentative protocol below might be changed according to discussions with the committees.
Inclusion criteria: We will recruit PD patients with symptoms uncontrollable by medical treatment. The patients will be aged 5070 at the time of inclusion and be suffering from PD more than 5 years. The patients will be in the middle stage of their disease and show good response to l-dopa .
Exclusion criteria: Patients with significant cognitive impairment or severe disease histories including surgeries will be excluded.
Design: The study will be an open-labeled phase I or I/II study at a single institute . The number of the patients will be 510, with no control groups.
Fig. 3. A direct comparison of autologous and allogeneic transplantation of iPSC-derived neural cells in the brain of nonhuman primates. Autologous transplantation of iPSC-derived neurons elicited only a minimal immune response in the brain . In contrast, allografts caused an acquired immune response with the activation of microglia and the infiltration of leukocytes . Consequently, a higher number of DA neurons survived in the autografts.
Yunfeng Wu, Pinnan Chen, in, 2019
The Hoehn And Yahr Scale For Parkinson’s
Two doctors named Dr. Hoehn and Dr. Yahr developed a scale that puts Parkinsons disease into five stages.The first stage is the mildest stage of the disease and stage five is the worst stage.
The symptoms may be mild or severe or happen a lot, or not as much. Also, the time spent at each stage of the disease varies, and the skippingof stages, from Stage 1 to Stage 3, for example, is not uncommon.
Stage 1 The main symptoms- tremor, muscle stiffness, slowness of movement and problems with posture- are only onone side of the body. Problems with balance might also appear.
Stage 2 The disease will be on both sides of the body now and minor symptoms like problems with swallowing,talking and something called facial masking may be noticed.
Stage 3 The same symptoms of Stage 2 are still there but may be worse now. Problems with balance will now benoticed for the first time. At this stage, the person with Parkinson’s is still independent.
Stage 4 The person with Parkinson’s will now be getting more and more disabled and will need help with some orall activities of daily living.
Stage 5 At this stage the person is confined to a wheelchair or bed and needs total assistance.
Read Also: First Line Treatment For Parkinson’s
Fully Developed Severely Disabling Disease The Patient Is Still Able To Walk And Stand Unassisted But Is Markedly Incapacitated
The patient is unable to lead an independent life because of the need for help with some activities of daily living. It is this inability to live alone which marks the transition from Stage III to Stage IV. No matter how difficult it is for him/her, if the patient still is able to live alone, his/her disease is at Stage III not Stage IV. The patient at Stage IV however, does remain able to stand and walk unassisted.
Hoehn And Yahr Staging Scale Of Parkinsons Disease
Description
The Hoehn and Yahr Staging Scale of Parkinsons Disease by Hoehn and Yahr , is a standard clinical measure of the progression of Parkinsons disease designed to measure the signs and symptoms associated with functional impairment such as postural instability, rigidity, tremor, or bradykinesia, as well as other symptoms accompanying PD . The HY scale is a descriptive staging system, similar to the Functional Assessment Staging Scale for neurocognitive disorders, in which the clinician estimates the presence of functional deficits and objective signs seen in subjects with PD by employing a 5-point descriptive scale where increasing impairment is charted from unilateral disease , to bilateral disease without balance difficulties , to the presence of postural instability , loss of physical independence , and being wheelchair or bed bound . A modified version was developed in the 1990s that adds 0.5 point increments to the scoring scale to increase its descriptive value and sensitivity. Administration for each version requires the clinician to gather information against the inclusion/exclusion criteria of the 5 descriptive levels by observing the client as he or she performs activities. Both HY scales can be completed in less than 5 minutes.
| 5.0 | Wheelchair bound or bedridden unless aided |
Psychometrics
Advantages
You May Like: Keto Diet And Parkinson’s
Change From Baseline To Eom In Updrs Scores
Rotigotine improved mean UPDRS II+III total score vs placebo for each individual HY stage , with treatment differences increasing with increasing HY stage . The percentage change of the mean UPDRS II+III total score indicated a relative improvement with rotigotine between 18 and 25% across the different HY stages . Similar results were observed for UPDRS II subscore and UPDRS III subscore .
Are There Limitations To The Hoehn And Yahr Scale
One of the main limitations of the Hoehn and Yahr scale is that it focuses solely on motor symptoms. While Parkinsons primarily affects movement functions, it can have other symptoms such as sleep changes and restless leg syndrome, or cognitive changes such as mood changes, fatigue, loss of smell, and micrographia . Some patients with Parkinsons disease may also experience hallucinations or delusions.
To account for non-motor symptoms of Parkinsons disease, there is another rating scale known as the Unified Parkinsons Disease Rating Scale . Neurologists developed the UPDRS in 1987 as a gold standard for monitoring the response to medications used to decrease the signs and symptoms of Parkinsons disease. The scale contains four parts:
- Part I: Mentation, Behavior, MoodThe first part scores intellectual impairment, thought disorder, depression, and motivation/initiative.
- Part II: Activities of Daily LivingThe second part scores activities such as hygiene, dressing, walking, tremor, and sensory complaints.
- Part III: Motor ExaminationThe third part scores speech, facial expression, tremor at rest, hand movements, and other motor functions.
- Part IV: Complications of Therapy The final part scores whether and how often the patient experiences symptoms such as painful dyskinesias, dystonia , nausea, vomiting, or sleep disturbances.
Recommended Reading: Parkinson’s Final Stage Symptoms
Bme Application: Gait Analysis In Parkinsons Disease
Background
Parkinsons disease is a chronic hypokinetic disorder as a consequence of dopaminergic cell deterioration and basal ganglia dysfunction . The progressive apoptosis of dopaminergic cells in the substantia nigra would affect the neuromodulatory functions of the central nervous system and also cause the dyskinesia or other movement disorders. The primary symptoms of the PD motor dysfunction are resting tremor of 46 Hz, postural instability, rigidity, and bradykinesia . As a result of stiffness in lower limb muscles and slow locomotion, the gait cadence patterns are usually altered with higher degree of variability and fluctuations in PD patients with mild and moderate motor impairments . Recently, statistical methods have been effectively utilized to characterize the distinctive variability of gait patterns in PD patients .
Statistical Modeling
The histogram and kernel PDF estimator were used to establish the probability density models of stride time for healthy adults and PD patients, respectively . The optimal number of histogram bins was selected by following the minimization criterion of the global mean squared error between the reference of the Gaussian density function and the histogram estimated, which is also referred to as the Scotts choice .
The kernel probability density was established by the nonparametric Parzen-window approach. Let X = be a stride time series involving M samples in total. The probability density is estimated as
Implementation Of Nursing Care Items And Interstage Comparisons
Over the course of 24 nursing visits, the 21 patients with PD whom we observed received a total of 17 hours, 39 minutes, and 7 seconds of directly observed nursing time. The median length of a single nursing visit was 47 minutes, 2 seconds. After consulting with the participating nurses, a list of 29 care items was created. Figures Figures11 and and22 list the per-stage breakdown of the percentage of patients in that stage to whom a given care item was performed , as well as specific examples of care practices.
Comparisons of the percentage of nursing care provided at each HY stage. Fisher’s exact test indicates significantly different pairs after Bonferroni correction p < 0.1, p < 0.05, and p < 0.01 p values and percentages have been rounded off.
Comparisons of the percentage of nursing care provided at each HY stage. Fisher’s exact test indicates significantly different pairs after Bonferroni correction p< 0.1, p< 0.05, and p< 0.01 p values and percentages have been rounded off.
Recommended Reading: Meds For Parkinson’s Psychosis
Hoehn And Yahr Stage And Striatal Dat
- 1Roche Products Ltd., Welwyn Garden City, United Kingdom
- 2Department of Mathematics and Statistics, Lancaster University, Lancaster, United Kingdom
- 3Roche Pharma Research and Early Development , Neuroscience and Rare Diseases Discovery and Translational Area, Roche Innovation Center Basel, Basel, Switzerland
- 4Faculty of Psychology, University of Basel, Basel, Switzerland
- 5Department of Basic and Clinical Neuroscience, IoPPN, Kings College London, London, United Kingdom
Unified Parkinsons Disease Rating Scale
The Unified Parkinsons Disease Rating Scale has four parts. Each part has multiple points that are individually scored, using zero for normal or no problems, 1 for minimal problems, 2 for mild problems, 3 for moderate problems, and 4 for severe problems.
These scores are tallied to indicate the severity of the disease, with 199 points being the worst and total disability and 0 meaning no disability.3
In 2001, the Movement Disorder Society updated the rating scale with involvement from patients and caregivers. The updated scale is referred to as the UPDRS-MDS, and it was published in 2008. It now includes the following sections:3
Also Check: Parkinson’s Disease Symptoms And Treatment
Getting Care At Any Stage
Although the different scales are meant to measure the progression of Parkinsons disease and the response to medication and treatment, some patients may never progress to stage 5, and not everyone with Parkinsons will spend the same amount of time in each stage. Some people are diagnosed with Parkinsons when they are young and remain in the early stages for several years. Others may skip stages, or their progression to end-stage Parkinsons may be more rapid. It is also possible to experience symptoms like tremors but not have any balance issues.
No matter where you are in your Parkinsons journeywhether youre at stage 1 or stage 5know that youre alone. At PLM, there is a community of over 30,000 Parkinsons patients who know what youre going through. Join the conversation to connect with others who are like you and can support you through your illness.