Tauopathies Progressive Supranuclear Palsy And Corticobasal Degeneration
Formally described in 1964 by Steele, Richardson and Olszewski, PSP is a progressive neurodegenerative disease associated with axial rigidity, bradykinesia, postural instability, vertical supranuclear gaze palsy, speech and swallowing dysfunction, as well as fronto-executive cognitive and behavioural manifestations . Gait impairment typically progresses at an accelerated rate in PSP relative to PD, with early falls as a prominent feature. Several variants have been identified that challenge the classical clinicopathological characterization of the PSP syndrome. For example, unlike the classical syndrome , the PSP-parkinsonism variant exhibits more conspicuous limb rigidity with bradykinesia and/or tremor with moderate levodopa response in a proportion of patients, without early ocular or postural disturbances . Vertical gaze palsy is an important diagnostic feature of PSP, although it may not be evident at early disease stages . Histopathologically, evidence of neurofibrillary tangles composed of misfolded 4-repeat tau protein, neuropil threads and star-shaped tufted astrocytes are seen, mainly in the basal ganglia, brainstem and diencephalon .
Mri In Parkinson’s Testing
One of the more common tests done during a neurologic workup is an MRI scan and one may think that in the investigation of a disease that affects the brain such as Parkinsons, this imaging test would be a necessity. In the context of Parkinsons disease, however, an MRI is not particularly helpful. It looks at the structure of the brain which, for all intents and purposes, appears normal in this disease. An MRI may, however, be indicated when symptoms appear in younger people or if the clinical picture or the progression of symptoms is not typical for Parkinsons. In these situations, MRI can be used to rule out other disorders such as stroke, tumors, hydrocephalus , and Wilsons Disease .
Exclusion Of Symptomatic Parkinsonism
Structural brain imaging using cMRI with visual assessment of T2- and T1-weighted sequences including contrast-enhanced T1 imaging is usually normal in patients with early PD thus, its traditional role is the detection/exclusion of other underlying basal ganglia or brainstem pathologies . These include vascular, space-occupying or demyelinating lesions within the basal ganglia or brainstem, drug- or toxic-induced parkinsonism, e.g. due to manganism, or neurodegeneration with brain iron accumulation , normal pressure hydrocephalus, or infectious causes . Typical MR findings in patients with symptomatic parkinsonism are summarized in Table 2.
Table 2 MRI findings for differential diagnosis in symptomatic parkinsonism
Read Also: Parkinson’s Disease And Music Therapy
Living With Parkinson’s Disease
Coming to terms with a diagnosis of Parkinson’s and living with the disease is challenging and will take a lot of adjustment. There are still things you can do that can help you to feel more in control of your situation and to stay positive. Some things that might help could include:
- choosing to lead a healthy lifestyle
- making informed decisions related to your treatment
- keeping a diary of your symptoms in preparation for meetings with health and social care professionals
- attending a self-management course
Further Testing In Parkinsons
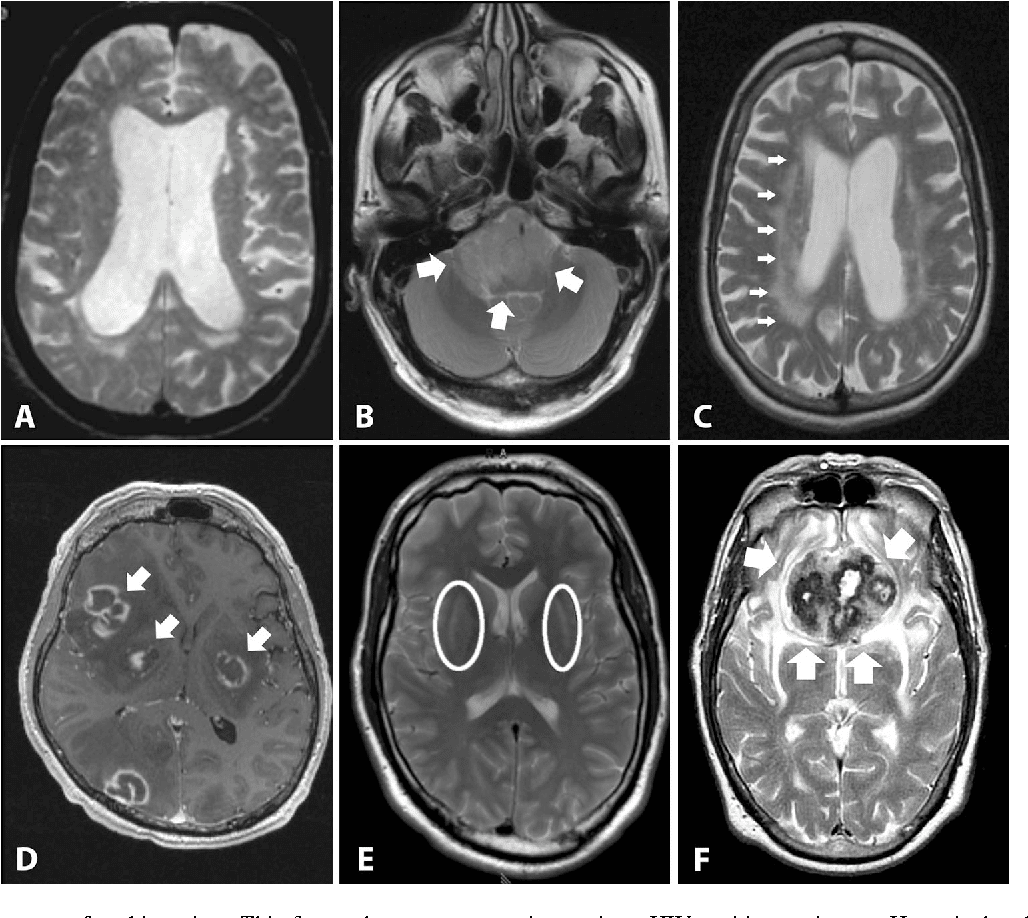
In other situations, where perhaps the diagnosis is not as clear, younger individuals are affected, or there are atypical symptoms such as tremor affecting both hands or perhaps no tremor at all, further testing may help. For example, imaging can play a role in differentiating between essential tremor and Parkinsons. It can also be important to confirm what is initially a clinical diagnosis of Parkinsons prior to an invasive treatment procedure such as surgical DBS
Recommended Reading: Cost Of Genetic Testing For Parkinson’s
Structural Magnetic Resonance Imaging With Conventional Mri Sequences
Due to its high spatial and contrast resolution, cMRI with assessment of T1-, T2-, proton density-weighted as well as T2 fluid-attenuated inversion recovery sequences offers in vivo visualization of regional, disease-specific tissue alterations and certain cMRI patterns that are typical for APDs. Atrophy patterns are better demonstrated by T1-weighted images, displaying anatomical details and providing an excellent grey and white matter contrast. More recently, advanced T1 sequences were developed to improve detection of nigral changes in PD patients. These include a variety of inversion recovery images and a recently developed neuromelanin-sensitive T1-weighted sequence . On NM-MRI, neuromelanin acts as a paramagnetic agent because of its iron-binding potential. On these images, neuromelanin-containing tissues appear as loci of high signal intensity allowing measurements of volume and concentration of neuromelanin in the substantia nigra and locus coeruleus . Moreover, it seems that visual inspection of NM-MRI sequences by experienced neuroradiologists provides results comparable to quantitative analyses in the detection of SN changes in early stage PD .
I Have Pd And Several Symptoms Should I Get A Datscan
Likely no. There is no need for DaTscan when your history and exam suggest Parkinsons disease and you meet the diagnostic criteria. Occasionally, if signs and symptoms are mild or you dont meet the diagnostic criteria, your doctor will refer you for a DaT scan. Keep in mind that ultimately the diagnosis is based on your history and physical exam. The DaT scan is most commonly used to complete the picture and is not a test for a diagnosis.
Read Also: Does Parkinson’s Affect Breathing
Qualitative Analysis Of Mri Scans
The MR scan session was well tolerated, but the data from five patients with PD were discarded because of degradation from involuntary movement. Therefore, measurements from 65 patients with PD and 10 healthy controls were used for statistical analysis.
At the time of neuroradiological review, it was noted that some cases had marked regional variations in signal intensity in their putamina. This was recorded in approximately 50% of cases and typically consisted of lower signal intensity on T2-weighted images in the caudal putamen when compared with the rostral putamen. All of the cases with a signal gradient were subsequently found to occur in patients with PD .
Figure 1
- * Mean R2 relaxation rates in each ROI for patients with Parkinson’s disease and healthy controls . PD Measures are taken from patients’ most affected side. Healthy control values are an average of right and left sided measures.
- Levene’s test revealed unequal variances between groups, so the significance value reported assumes unequal variances. *Statistical significance, corrected for the three measures, was P< 0.016. FWM, frontal white matter SN, substantia nigra RP, rostral putamen MP, mid putamen CP, caudal putamen.
Hope In Progress: American Parkinson Disease Association Supports Researchers With $235 Million In New Funding
From genetic mutations to augmented reality, APDA-funded researchers delve into cutting-edge Parkinson’s research in pursuit of answers
NEW YORK, September 08, 2022 /PRNewswire-PRWeb/ — The American Parkinson Disease Association has just awarded $2.35 million to support cutting-edge Parkinson’s disease research for the 2022-2023 funding year an increase of more than 25 percent from the prior year. The funded research projects will explore a range of important and innovative topics including: understanding the molecular underpinnings of anxiety in PD, probing the role of DNA damage in genetic mutations in PD, testing of augmented reality in the treatment of freezing of gait, and more. APDA focuses on investing in the most promising clinicians and scientific projects focused on discovery of the cause and finding the cure for Parkinson’s disease and has been a funding partner in many major PD scientific breakthroughs since the organization began.
Grants for the year ahead have been awarded in the form of four Post-Doctoral Fellowships, thirteen Research Grants, one Diversity in Parkinson’s Disease Research grant, eight APDA Centers for Advanced Research, and one George C. Cotzias Memorial Fellowship, APDA’s most prestigious award.
The 2022-2023 APDA Research Grants
-
Gary Ho, MD, PhD — Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston MA
-
Erin Foster, PhD — Washington University, St, Louis, MO
# # #
Eloise Caggiano, American Parkinson Disease Association , 718-737-8151,
Don’t Miss: Shoes For People With Parkinsons
Dynamic Functional Connectivity Analysis
Dynamic connectivity matrices were derived using an overlapping sliding-window approach with windows of 44s duration in steps of 1 repetition size . A 232*232 weighted adjacency matrix representing the functional connectome for that time point was calculated for each window.
We then identified states of higher integration or segregation using a cartographic profile,,,. At each time point, the asymmetric algorithm of Rubinov and Sporns was used to identify network modules by applying the community Louvain algorithm, which iteratively evaluates different ways of assigning nodes to modules, in order to maximise the resulting modularity function Q:
where is the total weight of the graph , wij is the signed weight of the edge between nodes i and j, eij is the weight of an edge divided by the total weight of the graph , and MiMj is set to 1 when nodes i and j are in the same module and 0 otherwise. We performed 100 iterations for each time-resolved network with module size resolution parameter set at the default =1.
We calculated participation coefficient and within-degree Z-score for each node using the Brain Connectivity Toolbox. Participation coefficient was calculated as:
The within-module degree Z-score Zi was calculated as:
where is is the strength of connections between node i and other nodes in module s, and \is and is are, respectively, the average and the standard deviation of is over all nodes belonging to module s.
Further Testing In Parkinson’s
In other situations, where perhaps the diagnosis is not as clear, younger individuals are affected, or there are atypical symptoms such as tremor affecting both hands or perhaps no tremor at all, further testing may help. For example, imaging can play a role in differentiating between essential tremor and Parkinsons. It can also be important to confirm what is initially a clinical diagnosis of Parkinsons prior to an invasive treatment procedure such as surgical DBS
Read Also: How To Tell The Difference Between Essential Tremor And Parkinson’s
Regional Cerebral Glucose Metabolism And Pd
18F-FDG PET can be used to assess levels of resting regional cerebral glucose metabolism. Absolute levels in the lentiform nucleus lie within the reference range in PD however, covariance analysis reveals an abnormal profile of relatively raised resting lentiform nucleus and lowered frontal and parietotemporal metabolism . The degree of expression of this PD-related profile correlates with clinical disease severity, thus providing a potential biomarker of disease progression. Successful treatment with levodopa or deep brain stimulation reduces expression of the PD-related profile . Given this, changes in treatment could result in a potential confounding factor if 18F-FDG PET were to be used as a biomarker to follow PD progression.
Eckert et al. performed 18F-FDG PET on 8 patients with suspected early parkinsonism but normal findings on 18F-dopa PET . None of these 8 patients expressed a PD-related profile of glucose metabolism, and over 3 y none of them showed any clinical progression of their disorder. This finding reinforces the viewpoint that normal dopaminergic imaging excludes the presence of a degenerative parkinsonian syndrome.
Mechanisms Underlying Dementia In Pd
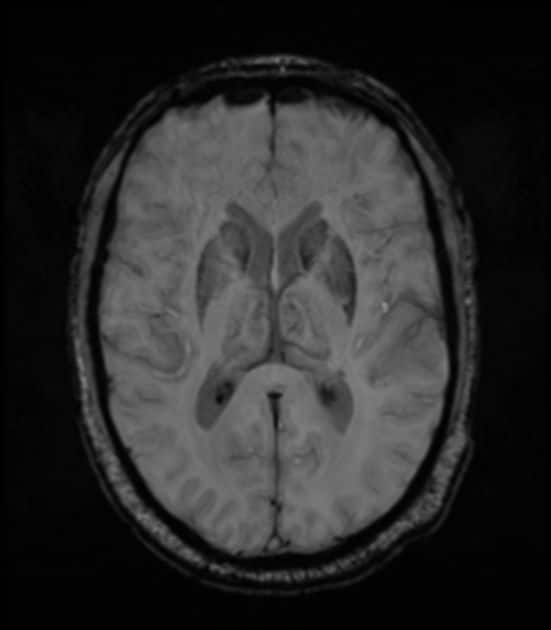
The overall prevalence of dementia is around 40% in patients with PD across different series, and the incidence is 6 times higher than that in age-matched healthy people, increasing with age . If PD patients live for 20 y, around 80% develop this complication . Factors contributing to the cognitive dysfunction include direct involvement of the cortex by Lewy body pathology, loss of cholinergic projections from the nucleus basalis of Meynert, degeneration of mesofrontal and mesolimbic dopaminergic projections, coexistent Alzheimer disease, and small-vessel pathology. The presence of these various contributors can be detected with a combination of structural and functional imaging.
Recommended Reading: Michael J Fox And Parkinson’s Disease
Brain Mri Advances For Parkinsons Disease
In Parkinsons disease, the damage to brain cells begins long before any symptoms develop. Therefore, at-risk patients can benefit from early diagnosis, and efforts to slow the progression of the disease can start early.
Researchers are working on newer MRI approaches to precisely detect Parkinsons disease-related structural and metabolic activity in the brain and correlate it to the function of the organ. For example, scientists from Oxford University used a technique called the resting-state functional MRI to assess the strength of nerve cells in the a region of the brain called the basal ganglia to send and receive information. Because the physical signs of brain cell damage in Parkinsons disease are not recognizable by conventional MRI, this approach may help visualize the impact of the damage on the activity of brain cells and aid in early diagnosis.
Similarly, MRI is used to identify Parkinsons disease-specific biomarkers. Tracking the biomarkers using high-field and ultra-high field MRI can identify Parkinsons disease patients and help follow the progression of the condition.
Although many of these advancements are yet to be implemented in the clinical setting, such adaptations may help better understand the disease and develop new treatments.
Postsynaptic Dopamine D2 Receptor Imaging
Using SPECT with 123I-IBZM and 123I–5-iodo-7-N– carboxamido-2,3-dihydrobenzofuran as ligands, binding potentials for postsynaptic D2 receptors were identified to be within the normal range in levodopa-treated PD as well as in patients with essential tremor and DLB . Conversely, reduced binding potentials were detected among MSA and PSP patients versus controls . Striatal D2 receptors were upregulated in drug-naïve PD patients, likely in response to nigrostriatal denervation with the greatest increase in the posterior putamen . Studies generally find the density of D2 receptors to be preserved among CBS patients, although this finding was not reliably shown on an individual case-to-case basis. Using 123I-IBZM as a tracer, Klaffke et al. , Pirker at al. and Plotkin at al. respectively reported 7 out of 8 , 8/9 and 7/9 clinically-diagnosed CBS patients with normal D2 bindings, suggesting preservation of dopamine D2 receptors. It is important to consider that a normal D2 SPECT scan may not exclusively confirm or discount an atypical PS. Further studies with pathologically-proven samples are warranted to determine the true sensitivity and specificity of D2 SPECT in distinguishing atypical PS.
You May Like: How To Take Care Of A Person With Parkinson Disease
Significance Of Mri In Diagnosis And Differential Diagnosis Of Parkinsons Disease
Log in to MyKarger to check if you already have access to this content.
Buy a Karger Article Bundle and profit from a discount!
If you would like to redeem your KAB credit, please log in.
Save over 20%
- Unlimited fulltext viewing Of this article
- Organize, annotate And mark up articles
- Printing And downloading restrictions apply
- Access to all articles of the subscribed year guaranteed for 5 years
- Unlimited re-access via Subscriber Login or MyKarger
- Unrestricted printing, no saving restrictions for personal use
The final prices may differ from the prices shown due to specifics of VAT rules.
Researchers Examine How Parkinsons Disease Alters Brain Activity Over Time
Tracking neural changes could help researchers test therapies that slow disease progression.
Neuroscientists peered into the brains of patients with Parkinsons disease and two similar conditions to see how their neural responses changed over time. The study, funded by the NIHs Parkinsons Disease Biomarkers Program and published in Neurology, may provide a new tool for testing experimental medications aimed at alleviating symptoms and slowing the rate at which the diseases damage the brain.
If you know that in Parkinsons disease the activity in a specific brain region is decreasing over the course of a year, it opens the door to evaluating a therapeutic to see if it can slow that reduction, said senior author David Vaillancourt, Ph.D., a professor in the University of Floridas Department of Applied Physiology and Kinesiology. It provides a marker for evaluating how treatments alter the chronic changes in brain physiology caused by Parkinsons.
For decades, the field has been searching for an effective biomarker for Parkinsons disease, said Debra Babcock, M.D., Ph.D., program director at the NIHs National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke . This study is an example of how brain imaging biomarkers can be used to monitor the progression of Parkinsons disease and other neurological disorders.
The study was supported by the NIH .
NIHTurning Discovery Into Health®
You May Like: How To Get Checked For Parkinsons Disease
Recommended Reading: Can You Still Drive With Parkinson’s Disease
T Mri Measures Changes In Brains Of Patients With Parkinsons Disease
Researchers at the University of Cambridge used a new ultra-high strength 7T MRI scanner at the Wolfson Brain Imaging Centre to measure changes in the brains of people with Parkinsons disease, progressive supranuclear palsy , or in good health. The study, published in Movement Disorders, suggests that 7T MRI scanners could be used to help identify those patients with Parkinsons disease and similar conditions most likely to benefit from new treatments for previously untreatable symptoms.
Patients with Parkinsons disease and PSP are often treated with drugs such as L-DOPA, which compensate for the severe loss of dopamine. But, dopamine treatment does little for many of the non-motor symptoms. That is why scientists have begun to turn their attention to noradrenaline, a chemical that plays a critical role in brain functions including attention and arousal, thinking and motivation.
Professor James Rowe from the Department of Clinical Neurosciences at the University of Cambridge, who led the study, said, Noradrenaline is very important for brain function. All of our brains supply comes from a tiny region at the back of the brain called the locus coeruleus which means the blue spot. Its a bit like two short sticks of spaghetti half an inch long: its thin, its small, and its tucked away at the very base of the brain in the brain stem.
-
New research indicates that blocking proteins with medications
Presynaptic And Postsynaptic Dopaminergic Imaging
11C-DTBZ tracer or labels the vesicular monoamine transporter type-2 , important for packaging and storing monoamines into synaptic vesicles. 11C-DTBZ PET have shown decreased striatal VMAT2 binding in PD reflecting nigrostriatal degeneration, accompanied by rather minimal compensatory changes . Conversely, the binding potential for 11C-methylphenidate was reduced to a much greater extent relative to 11C-DTBZ, suggesting marked compensatory down-regulation of striatal DAT activity . Using a novel 18F-tetrabenazine derivative , Okamura et al. detected the greatest regional decrease in VMAT2 binding in the posterior putamen, followed by anterior putamen and caudate nucleus in PD .
Also Check: Fitflop Shoes For Parkinsons
Recommended Reading: Va And Parkinson’s Disease