Foot Stretches For Parkinsons
Seated Option: Rainbow Rollouts with Tennis Ball
*Try to keep your knee as still as possible, only moving at the ankle.
Standing Option: Rainbow Rollouts with Tennis Ball
BONUS: Arch Rollouts with Tennis Ball
Managing Pain In Parkinson’s
This article summarizes the incidence, types, and causes of reported pain in Parkinson’s Disease . A table of recommendations on how to involve patients with Parkinson’s in their own pain management is provided, along with approaches to pain assessment. Finally, there is a discussion of pain management principles in PD, including optimization of dopaminergic medications, use of analgesics, and innovative treatments for pain management .
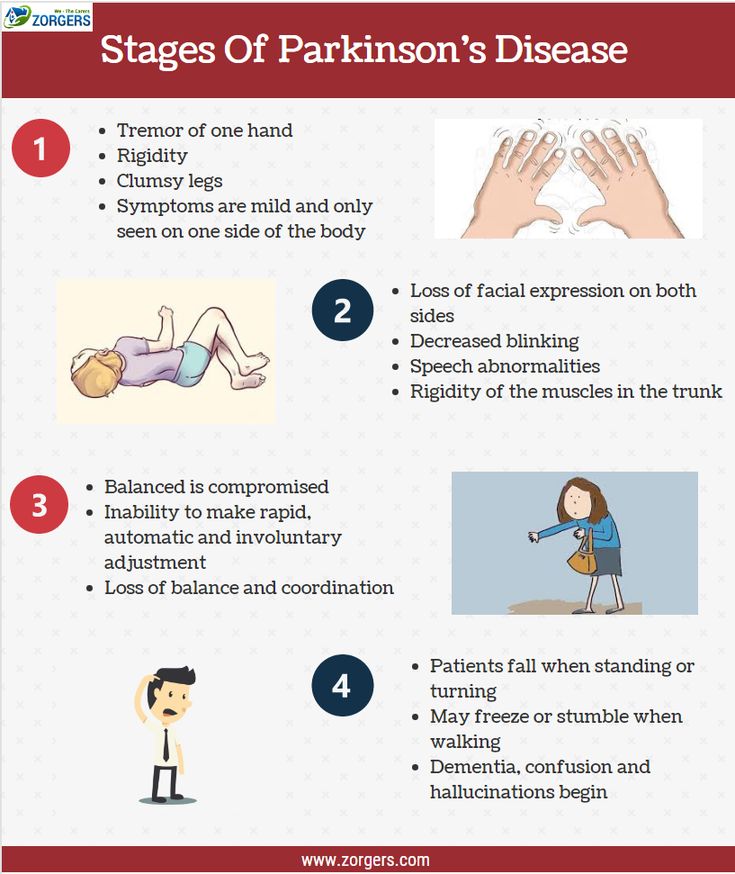
/4in Parkinson’s An Individual’s Movement Slows Down
Parkinson’s disease is a disorder of the nervous system that affects the movement of an individual. In this disorder the dopamine producing neurons of the brain are affected. When dopamine levels decrease in the brain, abnormal brain activity, leading to impaired movement is seen in an individual and this is one of the major symptoms of Parkinson’s disease.
Don’t Miss: Exercise For Freezing In Parkinson’s
Who Does It Affect
The risk of developing Parkinsons disease naturally increases with age, and the average age at which it starts is 60 years old. Its slightly more common in men or people designated male at birth than in women or people designated female at birth .
While Parkinsons disease is usually age-related, it can happen in adults as young as 20 .
How Can A Chiropodist Podiatrist Or Physiotherapist Help People With Parkinsons Look After Their Feet

If you have problems with your feet, you can visit a podiatrist or a chiropodist for advice there is no difference between them.
Podiatrists look at all areas of foot care, including how the foot should work during normal walking and the problems caused by not walking in a typical pattern.
Your podiatrist can train you to stretch and exercise your muscles to reduce the effects of stiffness or rigidity on your feet. They can also show you simple massage techniques to improve your movement and circulation.
Physiotherapists can also help you. They often work with podiatrists on foot-related mobility problems and to help prevent falls.
Recommended Reading: Early Indications Of Parkinson’s Disease
What Is Parkinsons Disease
Parkinsons disease is a nervous system disease that affects your ability to control movement. The disease usually starts out slowly and worsens over time. If you have Parkinsons disease, you may shake, have muscle stiffness, and have trouble walking and maintaining your balance and coordination. As the disease worsens, you may have trouble talking, sleeping, have mental and memory problems, experience behavioral changes and have other symptoms.
Leg Pain And Parkinsons
Interestingly enough, one of my early symptoms of the disease was deep searing pain in my left leg, the type of pain my grandma had complained about many times. Initially this type of pain was worst in the morning as well as at night, making me think is was some sort of fasciitis. However not only did typical anti-inflammatories and muscle relaxants not alleviate my pain but pain worsened over time to a constant burning pain that felt as if someone was tearing the muscle and pouring hot oil on it. The pain was so excruciating it was permeating into all aspects of my life. I was constantly in need of deep tissue massage asking my husband to massage my legs just as my grandmother had asked of us time and time again. This helped only temporarily.
Which brings me to the four types of leg pain in PD.
You May Like: What Is The Prognosis For Parkinsons Disease
You May Like: Best Parkinson’s Doctors In Nj
The Peripheral Nervous System And Parkinsons Disease
It is well-established that the autonomic nervous system can be significantly affected in PD causing symptoms such as constipation, urinary dysfunction and orthostatic hypotension. The autonomic nerves that bring signals to the gut for example, can be directly affected by Lewy body-like accumulations and neurodegeneration.
What remains unclear is if motor and sensory nerves are also affected in PD.
Foot Cramps And Spasms
Foot cramps or spasms can occur suddenly and with no known cause. Some common theories as to why they occur include abnormal levels of minerals or electrolytes in the body, dehydration, kidney disease, thyroid disorders, certain medicines, and brain disorders such as Parkinsons disease, multiple sclerosis and dystonia. Muscle fatigue in the feet, numbness and tingling, twitching, rapid motions and tightening of the muscles are all common symptoms and can range in severity. Most cramps or spasms are temporary and will go away on their own with rest, stretching and hydrating. If these episodes continue to occur frequently, then a doctor should be contacted to test for a possible disorder or deficiency.
Dont Miss: Did Katherine Hepburn Have Parkinsons
You May Like: Does Parkinson Run In Families
What Are The Early Warning Signs Of Parkinson’s Disease
Parkinsons warning signs can be motor symptoms like slow movements, tremors or stiffness. However, they can also be non-motor symptoms. Many of the possible non-motor symptoms can appear years or even decades ahead of motor symptoms. However, non-motor symptoms can also be vague, making it difficult to connect them to Parkinson’s disease.
Non-motor symptoms that might be early warning signs include:
- Sleep problems such as periodic limb movement disorder , rapid eye movement behavior disorder and restless legs syndrome.
Not Your Usual Neck And Back Pain
There are many ways to get a backache. This is new for me lower back pain that leads to spasms and literally drives me to my knees.
It doesnt feel like the pain from overdoing it in the garden. Every gardener knows that exquisite twinge from too much lifting or shoveling. After all the years I have gardened, I know that pain well. This is not my usual lower back pain.
An article published in 2018 in the European Spine Journal found significantly more cases of low back pain, with longer durations, in patients with Parkinsons disease than in healthy controls. Parkinsons patients also experience more frequent and intense lumbar pain. Researchers concluded that Parkinsons progression can lead to degeneration of the lumbar spine, and this leads to low back pain for about 88% of this population.
Also Check: Parkinsons Bike Therapy
Recommended Reading: Parkinson’s Loss Of Appetite
Q What Is The Outlook For People With Parkinsons Disease
A. Most people can continue to work full time and lead relatively normal lives for many years after being diagnosed. The disease does not affect your life expectancy, and your age at diagnosis does not seem to have any effect on your long-term outlook. However, due to the progressive nature of the disease, many people do eventually become disabled.
Pain Presentation And Assessment In Pd
Most epidemiological data are based on questionnaires which were not specifically validated for PD patients so that results have to be interpreted with caution. The Kings Parkinsons disease pain scale is to date the only questionnaire that is specifically calibrated and validated for PD and is highly recommended to qualitatively and quantitatively assess pain and to ascribe the pain pathophysiologically. The scale contains seven different pain domains comprising musculoskeletal pain, chronic pain , fluctuation-related pain, nocturnal pain, oro-facial pain, discolouration or oedema/swelling and radicular pain as well as 14 sub-categories . This assessment tool is based on the pain classification according to Ford but also considers pain types of other classifications such as motor fluctuations or visceral pain .
In addition, there are some specific pain syndromes in PD which have to be kept in mind, including the so-called coat-hanger pain that occurs in cases of pronounced orthostatic dysregulation and although it is more frequent in multisystem atrophy it can occur also in PD and is often associated with strong headache and neck pain . Furthermore, pain due to constipation which is frequent in PD can cause abdominal pain.
Read Also: Beds For Parkinson’s Patients
How Is Parkinsons Disease Treated
There is no cure for Parkinsons disease. However, medications and other treatments can help relieve some of your symptoms. Exercise can help your Parkinsons symptoms significantly. In addition, physical therapy, occupational therapy and speech-language therapy can help with walking and balance problems, eating and swallowing challenges and speech problems. Surgery is an option for some patients.
Feet Exercises To Do At Home
Exercise 1
- Stand upright beside a chair or table, with your feet a few inches apart.
- Gently move your weight forwards, making sure your toes do not curl and your heels remain on the floor.
- Stay in this position for 5 seconds before moving back to upright. Again, keep your feet glued to the floor dont allow your toes to lift.
- Repeat this exercise a few times, forcing your feet to relax as your body is slowly moved over them in a controlled manner.
Exercise 2
- Sit on a chair and bring 1 foot up to rest on the other knee.
- Gently massage the soles of your feet in a long, steady stroke from the base of the heel to the end of each toe.
- Do this 5 times on each foot to stretch and loosen the skin, muscles and joints.
- If you have become stiff at the knees and hips, you may find getting into this position difficult.
- Its worth practising, but if its not possible, see if you can find a willing friend or family member to massage your feet for you!
Don’t Miss: Mitochondria And Parkinson’s Disease
Types Of Parkinson’s Pain
Most of the time, discomfort in muscles and joints is secondary to the motor features of Parkinsons lack of spontaneous movement, rigidity, and abnormalities of posture what is known as musculoskeletal pain. The most commonly painful sites are the back, legs, and shoulders and it is usually more predominant on the side more affected by parkinsonism.
But there are many other categories of pain associated with Parkinsons disease. Radicular or neuropathic pain is experienced as a sharp pain that can start in the neck or lower back with radiation to arm or leg respectively and is often associated with numbness or tingling, or a sensation of coolness in the affected limb. It is usually secondary to a pinched nerve due to something like a slipped disc.
Dystonia related pain occurs as its name suggests, at times of dystonia most often experienced in the foot, neck or face and arm at different points in the dosing schedule, particularly the off phase when there is not enough dopamine replacement but can uncommonly also occur at peak-dose times. It can be one of the most painful symptoms those with Parkinsons can face.
Akathisia pain is experienced as restlessness, a subjective inner urge to move, an inability to stay still and the inherent feelings of discomfort that it brings. It is primarily experienced in the lower limbs and can often be relieved by walking around.
Q Can Parkinsons Disease Affect My Sex Life
A. Reduced libido and impotence can result from physical and/or psychological factors of Parkinsons disease. In addition, some of the medicines used to treat the symptoms of Parkinsons disease can cause sexual dysfunction in men, and vaginal dryness in women. Fatigue can make matters worse.
It may help to try having sex in the morning after taking your medication. Medicines are available to help men with erectile difficulties, and vaginal lubricants may be of help to women.
Read Also: What Are The Initial Symptoms Of Parkinsons Disease
You May Like: Alan Alda Parkinson’s Diagnosis
What Are The Symptoms Of Parkinsons Disease
Symptoms of Parkinsons disease and the rate of decline vary widely from person to person. The most common symptoms include:
Other symptoms include:
- Speech/vocal changes: Speech may be quick, become slurred or be soft in tone. You may hesitate before speaking. The pitch of your voice may become unchanged .
- Handwriting changes: You handwriting may become smaller and more difficult to read.
- Depression and anxiety.
- Sleeping disturbances including disrupted sleep, acting out your dreams, and restless leg syndrome.
- Pain, lack of interest , fatigue, change in weight, vision changes.
- Low blood pressure.
These Treatments And Interventions May Help
Interventions tend to be most successful in the earlier stages, so you should bring your symptoms to your doctor’s attention “as you notice that you’re having trouble flexing the joints of your toes,” says the Cleveland Clinic.
Several treatment options may be available, which you can utilize in addition to pain management or anti-inflammatory medication, explains Scudday. “For more extreme or painful cases that do not respond to conservative treatment, surgery may be recommended as an option. Both hammertoe and claw toe can be surgically reconstructed and realigned into proper position or the entire toe joint can be replaced,” says the podiatrist. The patient may also consider wearing different shoes, padding their shoes, wearing arch support inserts, or practicing toe-strengthening exercises as a form of physical therapy.
And, of course, be sure to speak with your doctor about the underlying cause for the changes in your toes. If a neurological disease such as Parkinson’s is responsible, timely intervention for that condition may significantly improve your quality of life.
Also Check: Parkinson’s Age Of Onset
Calf Stretches For Parkinsons
Seated Option: Calf Stretch with Strap
Standing Option: Wall Push-offs x 20
*To increase the intensity of the stretch, back away from the wall until you reach a distance where you feel a strong stretch in your calves when youre leaning forward against the wall. Be sure to keep your heels down throughout the exercise.
Want More Practical Articles Like This
Much more can be found in ourEvery Victory Counts® manual. Its packed with up-to-date information about everything Parkinsons. It also includes a worksheet and resource section to help you put what youve learned into action. Request your copy of the Every Victory Counts manual by clicking the button below.
Don’t Miss: Does Parkinson’s Affect Breathing
The Use Of Levodopa And Peripheral Neuropathy
There are reports in the literature that levodopa use may increase the risk of peripheral neuropathy, although other studies suggest that this is not the case. There are studies that demonstrate for example, that cumulative Levodopa exposure correlates to prevalence of PN in people with PD. Other studies however, demonstrate no difference in the prevalence of PN whether the person was treated with Levodopa or not, suggesting that Levodopa treatment does not play a role in development of PN.
Another area of research that emerges from the literature is the potential role of Vitamin B12 deficiency in the development of PN in those with PD. Some studies suggest that Vitamin B12 deficiency is a more common cause of PN among those with PD than those with PN who do not have PD.
There is also research that suggests that levodopa treatment may contribute to PN through impairment of Vitamin B12 metabolism, leading to Vitamin B12 deficiency. Taking COMT inhibitors such as Entacapone may protect against this complication.
Regardless, if PN is diagnosed in anyone, whether they have PD or not, and whether they take Levodopa or not, Vitamin B12 and various other markers of Vitamin B12 metabolism should be tested. If Vitamin B12 levels are low or even low-normal, a person should take Vitamin B12 supplementation, which may help with the symptoms of PN. Other causes of PN, many of which can be checked with various blood tests, should be investigated as well.
Pain Due To Fluctuations Dyskinesia Or Dystonia
To reduce potentially pain provoking motor fluctuations and dyskinesias, the optimization of therapy aiming to smoothen dopaminergic plasma level is recommended. The use of prolonged acting dopamine agonists or substances reducing the dopamine degradation such as MAO-B or COMT inhibitors are thought to reduce painful motor fluctuations during day- and night-time as well as early-morning akinesia. PD patients with motor fluctuations, who received the finally not approved partial dopamine D2 agonist Pardoprunox as adjunct therapy to levodopa, showed in a post-hoc analysis of a RCT a greater decrease in VAS pain scores compared to placebo . Amantadine might be helpful for painful dyskinesia, but data is missing.
A second substance with a potential specific effect on pain might be safinamide. In a post-hoc analysis based on pooled data of two large RCTs, safinamide applied as add-on therapy to levodopa treatment was associated with less consumption of pain medication compared to placebo and a significant reduction of pain in two of three sub-items of the PDQ-39 scale reflecting musculoskeletal and neuropathic pain . Noteworthy, in the safinamide group a slightly higher percentage of patients had additional pain medication at study baseline. In summary, this limited benefit needs to be confirmed by dedicated future studies.
Read Also: Parkinsons And Immune System
You May Like: What Is Drug Induced Parkinson’s Disease